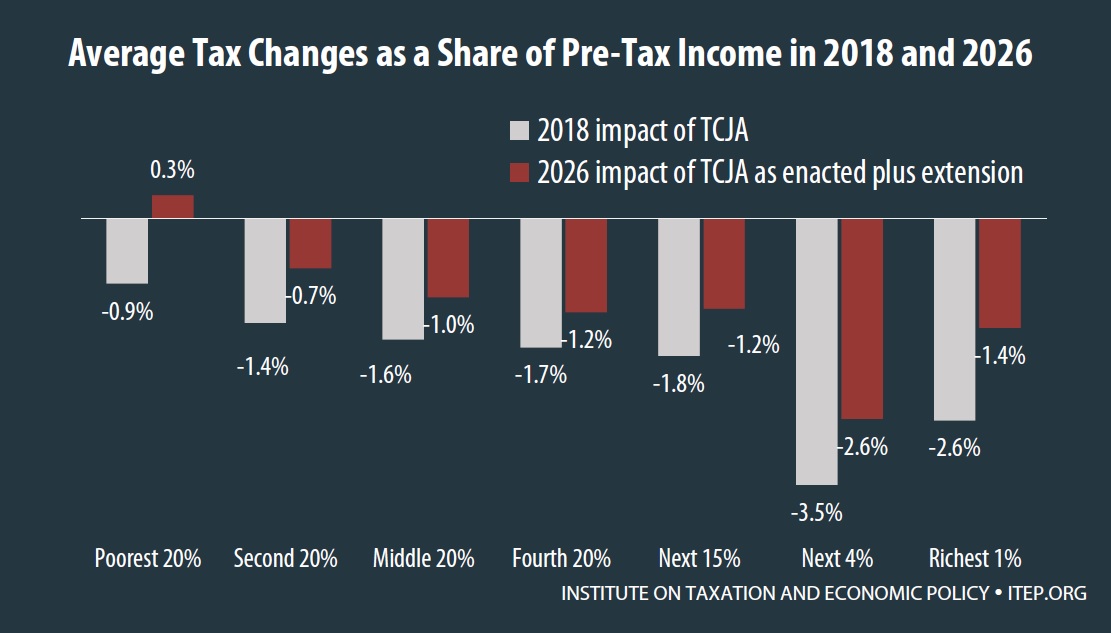
Full Answer
Are personal injury settlements taxable?
Generally, personal injury settlements are not taxable. Federal tax law specifically states that compensation for personal physical injuries or sickness will not be included in your gross income – the income you pay taxes on.
Do I have to pay taxes on a lawsuit settlement?
Your lawyer will need to take your time to explain your settlement to the IRS, and they will want to make sure you understand how to file your tax returns. If your attorney is your sole source of income, then you might have to pay taxes on your settlement. If you receive a settlement, it is essential to talk to a tax attorney and accountant.
How does a lump-sum settlement affect my taxes?
Receiving a large, lump-sum taxable settlement can push your income into a higher tax bracket. If you spread your settlement payments over a number of years, you will reduce the amount of income subject to the highest tax rates.
What happens to taxes on a settlement for back wages?
Let's say you filed a lawsuit for back wages from a W-2 job. This would be considered ordinary income. This means that you'll receive a W-2 for it, and income taxes and FICA taxes will both be withheld. Tax-wise, your settlement is pretty similar to a regular paycheck.
Do you have to pay federal taxes on a settlement?
Settlement money and damages collected from a lawsuit are considered income, which means the IRS will generally tax that money. However, personal injury settlements are an exception (most notably: car accident settlements and slip and fall settlements are nontaxable).
Are injury settlements taxable by the IRS?
Neither the federal government (the IRS), nor your state, can tax you on the settlement or verdict proceeds in most personal injury claims. Federal tax law, for one, excludes damages received as a result of personal physical injuries or physical sickness from a taxpayer's gross income.
What part of a settlement is taxable?
You might receive a tax-free settlement or judgment, but pre-judgment or post-judgment interest is always taxable (and can produce attorney fee problems).
How is money from a settlement taxed?
Settlements for automobile and property damages are not taxable, but there are exceptions. Like medical expenses, the IRS and the State of California consider these damages as reimbursement for a car or home previously paid.
How can I avoid paying taxes on a settlement?
How to Avoid Paying Taxes on a Lawsuit SettlementPhysical injury or sickness. ... Emotional distress may be taxable. ... Medical expenses. ... Punitive damages are taxable. ... Contingency fees may be taxable. ... Negotiate the amount of the 1099 income before you finalize the settlement. ... Allocate damages to reduce taxes.More items...•
Will I get a 1099 for a lawsuit settlement?
Most lawyers receiving a joint settlement check to resolve a client lawsuit are not considered payors. In fact, the settling defendant is considered the payor, not the law firm. Thus, the defendant generally has the obligation to issue the Forms 1099, not the lawyer.
Do you pay tax on a settlement agreement?
Settlement agreements (or compromise agreements as they used to be called), usually involve a payment from the employer to the employee. Such payments can attract income tax or national insurance contributions – but they can also sometimes rightly be paid tax free.
Are settlements tax deductible?
Generally, if a claim arises from acts performed by a taxpayer in the ordinary course of its business operations, settlement payments and payments made pursuant to court judgments related to the claim are deductible under section 162.
Why is a W 9 required for settlement?
The Form W-9 is a means to ensure that the payee of the settlement is reporting its full income. Attorneys are frequently asked to supply their own Taxpayer Identification Numbers and other information to the liability carrier paying a settlement.
How can you avoid paying taxes on a large sum of money?
Research the taxes you might owe to the IRS on any sum you receive as a windfall. You can lower a sizeable amount of your taxable income in a number of different ways. Fund an IRA or an HSA to help lower your annual tax bill. Consider selling your stocks at a loss to lower your tax liability.
Can the IRS take my personal injury settlement?
If you have back taxes, yes—the IRS MIGHT take a portion of your personal injury settlement. If the IRS already has a lien on your personal property, it could potentially take your settlement as payment for your unpaid taxes behind that federal tax lien if you deposit the compensation into your bank account.
Do I have to report insurance settlement to IRS?
Short- and long-term disability insurance proceeds, which are both designed to provide you with income if you're unable to work, are taxed the same way income is. You'll need to report these payments as earnings when you're filing.
Do you pay tax on a settlement agreement?
Settlement agreements (or compromise agreements as they used to be called), usually involve a payment from the employer to the employee. Such payments can attract income tax or national insurance contributions – but they can also sometimes rightly be paid tax free.
How Are Lawsuit Settlements Paid?
There are several steps you will need to follow in order to get your money. Read all the paperwork carefully.
What Types of Lawsuits are Taxed?
In general, lawsuits that deal with wages are treated as wages. A lawsuit that deals with injuries or damages are not. However, this is not cut and dried, so always speak with a professional to determine how your lawsuit is laid out and how the damages are allocated.
Why would a tax liability impact negotiations with insurance companies?
In addition, this would impact negotiations with the insurance company, because a tax liability may require that they negotiate more in their injury settlements.
Who should advise you before signing a settlement agreement?
Your attorney would be familiar with IRS guidance and should advise you before you sign the settlement agreement.
What is the purpose of settlement agreement?
Parties may try to structure their settlement agreement to maximize line items that are not treated as taxable income to keep as much money in their pocket as possible.
What are non-economic damages?
Then, you are also entitled to non-economic damages for your accident injuries. These are damages that relate to your physical injury or sickness.
What is the first form of personal injury compensation?
Personal injury compensation takes on two primary forms. The first is economic damages.
Is lost wages taxable income?
As a result, the IRS will use the “origin of the claim” test. If you file for lost wages because of employment discrimination, that would be considered taxable income.
Is lost wages considered gross income?
26 USC 104 excludes from the definition of “gross income” any payment that was awarded on the basis of a physical injury.
How much is L&I?
The benefit amount is 60 to 75% of the wage you were earning, depending on how many dependents you have. The minimum and maximum L&I can pay is set by the state legislature.
What is the waiting period for L&I?
However, the first 3 days immediately following your injury are considered a waiting period.
How long does it take to get a check from L&I?
Your first check will be mailed within 14 days from the date L&I or your self-insured employer receives notice from your doctor that you are unable to work if you are eligible and no further information is needed.
What are the criteria for loss of earnings?
Criteria: The worker’s loss of earnings must be greater than 5 percent of wages at the time of injury. Some examples include: Returning to work at a lower rate of pay. If you had more than one job at the time of injury and are restricted from performing on of the jobs. Return to work at regular wage but fewer hours.
Is time loss compensation taxed?
No taxes will be withheld. The IRS considers time-loss compensation to be a disability benefit, not earned income, so income tax laws do not apply.
What to do if your settlement is complex?
If your settlement was complex or included punitive damages, it’s best to consult a CPA or personally contact a lawyer. Whether your settlement came from out-of-court negotiations or the verdict of a lawsuit, it’s all the same when it comes to taxes.
What happens if a court awards punitive damages?
If a court did award punitive damages, your lawyer would request that those be calculated separately from compensatory damages. You would then be responsible for paying taxes only on the money received for punitive damages.
Is punitive damages taxable?
Punitive Damages and other Exceptions. If you receive money for punitive damages, however, that money is always taxable. Punitive damages are awarded only when a defendant has acted “willfully or recklessly;” in other words, if the defendant intentionally caused damage to the plaintiff.
Do you have to pay taxes on personal injury settlements?
As long as you have a physical injury (and, let’s face it, it’s unlikely you’ll be getting a settlement for those things unless you were physically injured), you don’t have to pay taxes on that money.
Is personal injury settlement taxable?
Generally, personal injury settlements are not taxable. Federal tax law specifically states that compensation for personal physical injuries or sickness will not be included in your gross income – the income you pay taxes on.
Is a car accident settlement taxable?
If, for example, you made a claim based on employment discrimination at work, or emotional distress from a car accident, but didn’t have the slightest physical injury, then your settlement or verdict would be taxable.
Can you get punitive damages for a personal injury settlement?
Bottom Line: You probably didn’t receive punitive damages for your personal injury settlement, but you can consult your injury lawyer if you’re not sure.
What happens if you get a settlement from a lawsuit?
You could receive damages in recognition of a physical injury, damages from a non-physical injury or punitive damages stemming from the defendant’s conduct. In the tax year that you receive your settlement it might be a good idea to hire a tax accountant, even if you usually do your taxes yourself online. The IRS rules around which parts of a lawsuit settlement are taxable can get complicated.
What to do if you have already spent your settlement?
If you’ve already spent your settlement by the time tax season comes along, you’ll have to dip into your savings or borrow money to pay your tax bill. To avoid that situation, it may be a good idea to consult a financial advisor. SmartAsset’s free toolmatches you with financial advisors in your area in 5 minutes.
What can a financial advisor do for a lawsuit?
A financial advisor can help you optimize a tax strategy for your lawsuit settlement. Speak with a financial advisor today.
Can you get damages for a non-physical injury?
You could receive damages in recognition of a physical injury, damages from a non-physical injury or punitive damages stemming from the defendant’s conduct. In the tax year that you receive your settlement it might be a good idea to hire a tax accountant, even if you usually do your taxes yourself online.
Is a lawsuit settlement taxable?
The tax liability for recipients of lawsuit settlements depends on the type of settlement. In general, damages from a physical injury are not considered taxable income. However, if you’ve already deducted, say, your medical expenses from your injury, your damages will be taxable. You can’t get the same tax break twice.
Is representation in a civil lawsuit taxable?
Representation in civil lawsuits doesn’t come cheap. In the best-case scenario, you’ll be awarded money at the end of either a trial or a settlement process. But before you blow your settlement, keep in mind that it may be taxable income in the eyes of the IRS. Here’s what you should know about taxes on lawsuit settlements.
Is emotional distress taxable?
Although emotional distress damages are generally taxable, an exception arises if the emotional distress stems from a physical injury or manifests in physical symptoms for which you seek treatment. In most cases, punitive damages are taxable, as are back pay and interest on unpaid money.
Why is debt taxed as if it were your regular income?
It’s essentially treated as if it were your regular income because it’s money you borrowed that you’re no longer obligated to pay back. If you settle large amounts of debt, the tax bill can easily run to thousands or tens of thousands of dollars in additional tax.
How much is the IRS exclusion for canceled mortgages?
Until 2016, the IRS allowed an exclusion of up to $2,000,000 in canceled mortgage debt. This exclusion allowed the vast majority of taxpayers forced into foreclosure or short sales to escape the “double penalty” of a tax bill for any unpaid mortgage debt. However, beginning in 2017 the IRS dialed back the exclusion.
Can you pay extra taxes on forgiven debt?
So, an extra tax bill on any forgiven debt as part of your gross income adds a financial burden to someone already experiencing hardship. But there is some good news — IRS allows taxpayers to exclude canceled debt income (i.e. no extra tax due on canceled debt) under certain conditions.
Is canceled debt taxable income?
Under IRS guidelines, canceled debt counts as taxable income. In ordinary circumstances, receiving a loan is not considered income, and paying it back is not a deduction. But when a lender cancels the debt, the IRS treats the amount of canceled debt as if it is indeed income. Most taxpayers know they pay income tax on their wages, ...
Do you pay taxes on canceled debt?
Most taxpayers know they pay income tax on their wages, or if they sell stock, or sell a house. However, many are unaware that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) also levies income tax on canceled debts. The IRS treats canceled debt as part of your gross income, which increases your tax liability. Unless you take action, you could be paying taxes ...
Can you lose your tax refund?
You could lose your refund, or worse, you could end up owing the IRS and facing new challenges with tax debt. Income tax on settled debts often operates as a “double penalty.”. Financial difficulties are typically the root cause of credit card debt, repossession and foreclosure.
Does the IRS have a settlement program?
The IRS also has resolution programs specifically designed for those with financial difficulties — such as a payment plan, “ Currently Not Collectible ” hardship status, or a settlement if you qualify. If you would like more information, we have tax professionals on staff to conduct an investigation into your tax situation. They can determine if you might qualify for some relief.
