Full Answer
How did the development of agriculture lead to the rise of civilizations?
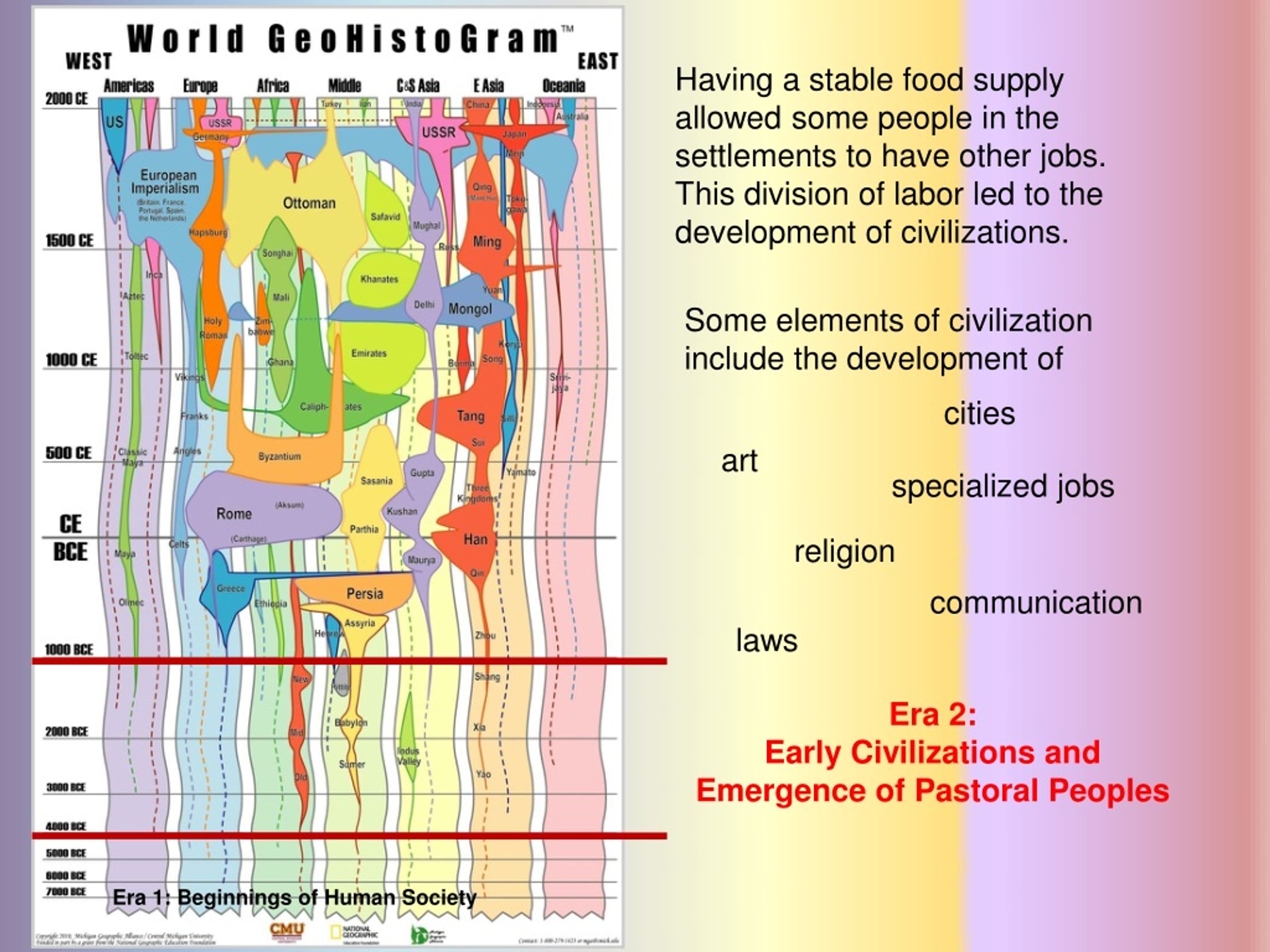
The development of agriculture led to the rise of civilizations. People had to stay in one place in order to grow and harvest crops. They also needed buildings in order to store crops. Many civilizations in the Middle East invested in irrigation structures in order to provide for stable water....
What was the impact of Agriculture on early humans?
Much debate, however, is centered on the impact of agriculture on early humans. Advances in agriculture and the domestication of animals in such places as Mesopotamia allowed people to form semi-sedentary and sedentary settlements, which led to the development of complex societies and civilizations.
How did the domestication of animals lead to the development of civilization?
Advances in agriculture and the domestication of animals in such places as Mesopotamia allowed people to form semi-sedentary and sedentary settlements, which led to the development of complex societies and civilizations.
How did agrarian reform lead to the development of cities?
Agriculture also led to an increase in cities; this also necessitated more governance. Scribes kept records of how much of each crop was harvested. Many civilizations in the Middle East kept crop records as part of their written histories.
How did agriculture develop civilization?
Agricultural communities developed approximately 10,000 years ago when humans began to domesticate plants and animals. By establishing domesticity, families and larger groups were able to build communities and transition from a nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle dependent on foraging and hunting for survival.
How does agriculture impact the development of civilizations?
When early humans began farming, they were able to produce enough food that they no longer had to migrate to their food source. This meant they could build permanent structures, and develop villages, towns, and eventually even cities. Closely connected to the rise of settled societies was an increase in population.
How did the development of agriculture affect human settlement?
Agriculture allowed people to stay in one place, and increased food production caused the population density to expand far beyond levels that could be sustained by hunting and gathering alone. This growth in population density provided a critical mass of people to sustain and spread contagious infectious diseases.
What civilizations were for agriculture?
The first agrarian civilizations developed at about 3200 BCE in Mesopotamia, in Egypt and Nubia (now northern Sudan), and in the Indus Valley. More appeared in China a bit later and in Central America and along the Andes Mountains of South America at about 2000–1000 BCE.
Why was the development of agriculture important?
Agriculture kept formerly nomadic people near their fields and led to the development of permanent villages. These became linked through trade. New economies were so successful in some areas that cities grew and civilizations developed.
What is agricultural civilization?
agrarian civilization — A large, organized human society that relies on a large number of its members producing food through agriculture. May incorporate hundreds of thousands or even millions of people, and include cities together with their surrounding farmed countryside.
How did the agricultural Revolution lead to the development of civilizations?
As food supplies increased and stabilized and industrialized centers moved into place, cities began to support larger populations, sparking the beginning of rural flight on a massive scale. In England, the proportion of the population living in cities jumped from 17% in 1801 to 72% in 1891.
How did the development of agriculture most influence the emergence of early civilizations?
The advent of civilization depended on the ability of some agricultural settlements to consistently produce surplus food, which allowed some people to specialize in non-agricultural work, which in turn allowed for increased production, trade, population, and social stratification.
What is agricultural development?
Agricultural development is defined as the process that creates the conditions for the fulfilment of agricultural potential. Those conditions include the accumulation of knowledge and availability of technology as well as the allocation of inputs and output.
Where did agriculture first develop?
the Fertile CrescentAgriculture originated in a few small hubs around the world, but probably first in the Fertile Crescent, a region of the Near East including parts of modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan.
What is history of agriculture?
The origin of agriculture was around ten thousand years ago or approximately four hundred human generations back in time and prehistory, before written records were kept. What is known is based on evidence gathered from archaeological sites.
When did agriculture start?
Agriculture was developed at least 10,000 years ago, and it has undergone significant developments since the time of the earliest cultivation. Independent development of agriculture occurred in northern and southern China, Africa's Sahel, New Guinea and several regions of the Americas.
Why was agriculture important to the development of civilization quizlet?
Agriculture was important to the development of civilization because it allowed people to have more time to specialize in things and spend more time to do other things than getting food.
How did the agricultural Revolution impact early humans?
The agricultural revolution had a variety of consequences for humans. It has been linked to everything from societal inequality—a result of humans' increased dependence on the land and fears of scarcity—to a decline in nutrition and a rise in infectious diseases contracted from domesticated animals.
How did agricultural revolution change and affect the structure of the society?
The increase in agricultural production and technological advancements during the Agricultural Revolution contributed to unprecedented population growth and new agricultural practices, triggering such phenomena as rural-to-urban migration, development of a coherent and loosely regulated agricultural market, and ...
What role does agriculture play in the economy?
Agriculture and its related industries (things like food sales and other industries that wouldn't exist or would be much smaller without agriculture) contribute $1.05 trillion to U.S. GDP, according to the latest data. That puts agriculture's contribution to the overall economy at about 6 percent.
Where did agriculture originate?
From its origins in China, agriculture moved south, eventually spreading across the Polynesian islands. In contrast, agriculture passed either slowly or not at all through the tropical and desert climates surrounding early agricultural sites in Egypt, sub-Saharan Africa, Central America, and the Andes.
How did agriculture spread?
From its origins in China, agriculture moved south, eventually spreading across the Polynesian islands. In contrast, agriculture passed either slowly or not at all through the tropical and desert climates surrounding early agricultural sites in Egypt, sub-Saharan Africa, Central America, and the Andes. Domesticated animals did not reach South Africa until around a.d. 200, the same time corn reached the eastern United States. It was therefore the plants, animals, and farm-related technologies of the Fertile Crescent and China that had the greatest impact on future civilizations.
What were the first crops in the world?
Their first crops were emmer wheat and barley, which were high in protein and easy to domesticate compared to plants native to other parts of the world. Cultivated emmer wheat, for example, is very similar to its wild ancestor, while it took thousands of years for modern corn to evolve from its half-inch-long ancestor.
Why did people settle in the fertile crescent?
For the thousands of years before plants and animals were domesticated, people roved in small bands, foraging for enough food to stay alive. Because of the abundance of wild foods in the Fertile Crescent, hunter-gatherers settled there permanently.
What were the first crops that were domesticated in the eastern United States?
The only crops domesticated in the eastern United States were squash and a few seed plants.
Why did animals evolve?
Animals also evolved in response to their new environments, some becoming larger and others smaller. The first domesticated animal was the dog, which was bred for hunting and food in several places around the world.
How did domestication affect the spread of diseases?
The domestication of animals also influenced the rise of epidemic diseases like smallpox, influenza, and measles. Using manure and human waste as fertilizer infected people with harmful bacteria. Once people started to live in close contact with animals, they were exposed to animal viruses that over time mutated into new ones causing human epidemics. When carriers of these diseases invaded unexposed populations—again, as the Spanish did in Central and South America—the result was devastating. For example, the natives of Hispaniola were entirely wiped out by germs carried by Christopher Columbus (1451-1506) and his sailors. The same process of virus mutations in farm animals is believed to occur today in southern China, where certain influenza viruses periodically shift to new forms that require new vaccines.
How did agriculture affect the early civilizations?
This led to civilizations developing their own material cultures. Agriculture also led to an increased population, as famine happened less often. Hunger still struck the early civilizations due to blights and drought; however, life was easier than it was during the nomadic period. Increasing populations also competed for decreasing resources as well as power over trade routes. This would lead to major wars between early civilizations that used professional soldiers.
How did agriculture change society?
One change was that people began to live in permanent settlements. Society moved from one being based on hunting and gathering, to one being based on farming. People no longer had to live a nomadic lifestyle.
How did the agricultural revolution affect humans?
The Agricultural Revolution, which coincided with the climate change at the conclusion of the last ice age, had a dramatic impact on humanity. Farming allowed humans to form permanent settlements and abandon their nomadic ways. Humans shifted from hunting and gathering models to fixed farming villages. As populations increased due to the increased surplus of food, urban areas surfaced. The surplus of food also led to developments that spawned civilization. As an example, the increased populations and surplus of food required governments to organize the surplus and protect property. It is also thought that religions became more sophisticated. The surplus of food also led to the development of social classes. Trade and a merchant class were born due to farming. Since all people were not needed for food acquisition in farming civilizations, specialized and artistic jobs or professions were developed. Two negative results of the Agricultural Revolution were warfare and increase in disease.
How did farming affect society?
As more people farmed, there was a surplus of food. This allowed various changes to occur. Cities and villages began to develop as people settled in one place. Since everybody didn’t have to farm, people began to do different jobs and worked in different professions such as trading, engineering, medicine, legal, accounting, law enforcement, and the military. This also led to the development of social classes. New tools were invented to help with the farming. For example, these tools helped to till the soil and plow the fields. People also no longer needed to kill animals just for getting food. They could develop products from the hides of the animals. These products included bedding, clothes, and tents. People no longer needed to consume food immediately. They were able to store and to save food for future use.
Why did people use draft animals in the Middle East?
People also turned to using draft animals in order to pull plows more efficiently. Agriculture also led to people taking on different jobs as... (The entire section contains 5 answers and 955 words.)
Why did people stay in one place?
People had to stay in one place in order to grow and harvest crops. They also needed buildings in order to store crops. Many civilizations in the Middle East invested in irrigation structures in order to provide for stable water. Over time, people selected the best strains of their crops in order to ensure the highest yields.
How did agriculture affect the Neolithic civilization?
Although it has been to be known pretty common these days, the development of agriculture had a huge impact on civilization. Known as the “Neolithic Revolution” which started about nine thousand BCE had a great affect of the way people lived. Since farming started it had a positive impact that cities and civilizations grew, not only that but the population grew as well. From roughly six to ten million people to what we know of today which is seven billion and still growing. There is really no saying as to what lead humanity to farming. Many have thought the climate change after the last ice age in the Near East brought along different seasonal conditions that helped with the growth of plants like wild cereals. In places like East Asia, there was pressure to use natural food resources.
How did agriculture affect the human race?
Agriculture had a positive impact on humanity in terms of population. This is due to the fact that over time we were able to replace things that weren’t consumable by humans with items that were. With techniques like irrigation we were also able to make plants where they normally wouldn’t have. Humans have been estimated to have existed for about two hundred thousand to three hundred thousand years ago. Yet, we have no evidence of our ancestors having discovered agriculture before fifteen to t thousand years ago.
What would happen if it weren't for the agricultural revolution?
If it weren’t for the agricultural revolution who knows where we would be today. Due to the fact that before agriculture humans were known to hunt for their food with a limited supply. All in all, with the upbringing of agriculture had a huge impact on the world we see today. Many of these practices are still done today with some changes.
How did farmers help the economy?
Farmers were able to produce more food than they needed leading them to be able to trade with others for other goods. What this meant is people who were not farmers were able to focus on other goods and were able to trade their good for food or any other goods available. People being able to focus on solely one thing took off the worry about finding food to survive. They were able to focus on one thing which lead to increased productivity which lead to better creations such as tools, weapons and buildings. This also had an impact on government to oversee their work and had military protect people and their resources.
How did pastoralism affect the environment?
This technique is done by removing a ring of bark from trees. This would dry out the trees making them easier to burn. The ash that was left over from the trees was used as a fertilizer for the soil. Although pastoralism was great it did bring up some challenges to not only the environment but to the people as well. There was always the fear of too many animals being heavily concentrated in one are due to “overgrazing” to the land. Overgrazing is when animals are concentrated in one area which can damage the vegetation and the ground would become liable to erosion. Which would mean they would no longer be able to use that part of land. Not only was overgrazing a concern but also the fear of animals transferring diseases to humans.
How did agriculture help humans?
The emergence of agriculture allowed humans to create permanent settlements with the hope of a stable food supply. This supporting question asks how changes and innovations unfolded, keeping a specific focus on warming temperatures and creation of hand tools for working with crops. These changes and technical innovations occurred over a long period of time, but together they represented a remarkable leap forward. Increasing temperatures opened the door for humans to learn how to cultivate wild plants, while new tools allowed humans to better manage crops and increase crop yields.
What was the challenge of Sumerians?
Another challenge people overcame was how to represent large numbers. Instead of making numerous inscriptions for large numbers, Sumerians developed a numbering system. Doing so allowed them to represent multiple instances of the same symbol. Like many people today, Sumerians used a base-10 system. Unlike people today, Sumerians also used a counting system in which the number 60 was a base.
How did Sumerians write?
The development of writing was a slow and gradual process. Sumerians began using tokens as counting stones to keep track of payments , taxes, and trade around 8000 BCE. Soon, however, this process became too difficult to manage. After about 4,000 years, people realized that the tokens were not really needed. Instead, they could make symbols that represented the tokens in clay. By about 3000 BCE, Sumerian images of tokens on clay tablets began to change. This new style of writing came to be known as “cuneiform,” which means wedge-shaped. The strokes were made by pressing a reed stylus into clay. The direction of writing also changed: Instead of writing top to bottom, people began to write from left to right in horizontal rows.
How did humans create the first system of writing?
The first writing systems date as far back as 8000 BCE when Neolithic humans started using counting tokens with simple markings on small stones to represent and communicate ideas. The tokens were used to represent the quantity of a commodity. For example, a cone-shaped token might represent a small amount of grain. Sumerian priests and royalty used tokens to record whether people had paid what they owed the temple or had received goods from the temple stores (like seed grain) in return for their labor. Archaeologist Denise Schmandt-Besserat describes this initial system of writing in her 1996 book How Writing Came About. She argues that humans developed this simple system of recording ideas as a precursor to more complex symbolic writing. Sometime around 3000 BCE Sumerians and Egyptians developed more complex systems of writing. These systems made use of cuneiform and symbolic representations.
