Full Answer
How did the Vikings build their houses?
The Viking houses in their newly conquered lands were built with the ancient Viking way with stone foundations. The walls were often made with a mixture of materials. The farmstead of the Vikings stood on flat and well-drain land and next to it was the gazing area for the animals.
What was the settlement pattern of the Vikings?
The Vikings who established homes in the lands they conquered during the 9th-11th centuries AD used a settlement pattern that was based primarily on their own Scandinavian cultural heritage. That pattern, contrary to the image of the Viking raider, was to live on isolated, regularly spaced farmsteads surrounded by grain fields.
Where did the Vikings settle in Europe?
Other Viking Settlements 1 Hofstaðir, Iceland 2 Garðar, Greenland 3 Beginish Island, Ireland 4 Áth Cliath, Ireland 5 Eastern Settlement, Greenland
What impact did the Vikings have on the world?
These explorations and settlements have had a decisive impact upon these places that persists even today. The Vikings’ motivations for faring so far across the globe and founding new settlements in the lands they reached were as varied as the individuals who undertook these tremendous projects.

What were Viking settlements made of?
Viking Settlement Characteristics Structures in Viking settlements—dwellings, storage facilities, and barns—were built with stone foundations and had walls made of stone, peat, sod turfs, wood, or a combination of these materials. Religious structures were also present in Viking settlements.
Where did the Vikings build their settlements?
Longer lasting and more established Norse settlements were formed in Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Russia, Great Britain, Ireland and Normandy.
How did the Vikings build their buildings?
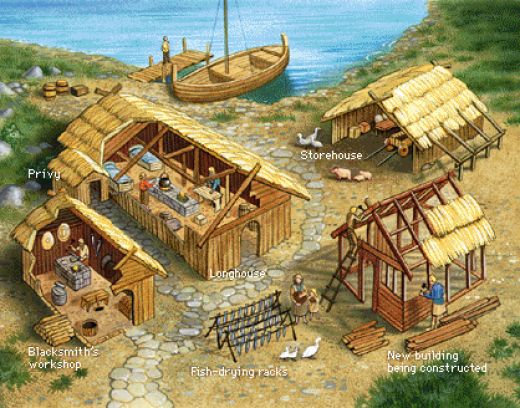
Viking houses were built of wood. The longhouses had bowed walls in plan, forming a ship-like outline. The walls were lined with clay or consisted of wooden planks placed vertically into the ground, which supported the roof, along with two rows of internal posts. Outside the house was often supported by sloping posts.
What were the Vikings settlements like?
They lived in long rectangular houses made with upright timbers (wood). The walls were made of wattle (woven sticks, covered with mud to keep out the wind and rain). Viking houses were often one room homes with a cooking fire in the middle. The smoke escaped through a hole in the roof.
What was the biggest Viking settlement?
Hedeby/Haithabu Located just south of the modern border with Germany, Hedeby was said to be one of the largest Viking settlements. During the 10th century, one traveller described it as: “a very large city at the very end of the world's ocean.”
Do Viking villages still exist?
For almost 20 years, he worked to establish the permanent Viking village Njardarheimr, which finally opened in 2017. The village is built to scale at a stunning location in the innermost part of beautiful Nærøyfjord. “It's authentic in style and built by traditional methods.
How long did it take Vikings to build a house?
It depends on what resources and materials were available. A possible estimate is one to two years (the reconstruction took one year to build), but we must also consider that the house seems to have been continually added to and maintained.
What did the Vikings do in their settlements?
The Vikings and their families mostly lived in small villages that were near the coast. Despite their reputation as brave warriors and terrifying raiders, the Vikings spent most of their time farming and fishing. The Vikings grew wheat to make bread and beer, and raised animals such as sheep, pigs and cattle.
Did Vikings use stone walls?
They were usually built slightly back from the waterline. They were dug into the ground as well as built up. They had to be extremely long because the Viking Ships could be 25 meters long or longer. The walls were made of wood with stones piled up at the base.
Did Vikings sleep sitting up?
Beds were most likely lined with straw and animal skin. However, some historians believe that the Vikings actually slept sitting up with their backs against the wall given the limited and confined space that was available on the benches.
How do Vikings say hello?
Etymology. Originally a Norse greeting, “heil og sæl” had the form “heill ok sæll” when addressed to a man and “heil ok sæl” when addressed to a woman. Other versions were “ver heill ok sæll” (lit. be healthy and happy) and simply “heill” (lit.
Did the Vikings have blue eyes?
Blue eyes were very common among Northern Vikings, while brown eyes were more common in the Viking settlements of England, Ireland, and mainland Europe. In modern times, most people who claim to be of Viking descent have blonde hair and blue eyes, but that doesn't mean that all Vikings shared this appearance.
What did the Vikings do in their settlements?
The Vikings and their families mostly lived in small villages that were near the coast. Despite their reputation as brave warriors and terrifying raiders, the Vikings spent most of their time farming and fishing. The Vikings grew wheat to make bread and beer, and raised animals such as sheep, pigs and cattle.
What were Viking towns called?
The areas the Viking settled in were known as Danelaw. It covered an area roughly east of a line on a map joining London and Chester. The Saxons lived south of the line.
Where did Norwegian Vikings settle?
Voyaging by sea from their homelands in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, the Norse people settled in the British Isles, Ireland, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, Normandy, and the Baltic coast and along the Dnieper and Volga trade routes in eastern Europe, where they were also known as Varangians.
What was a Viking village called?
Thwaite comes from the Norse thveit, meaning a clearing or meadow. By far the most common is -by which means farmstead or village. Like most conquerors, when Vikings moved to a new area they settled into communities alongside the previous inhabitants, then changed the names they found difficult to pronounce.
How were Viking houses built?
The Viking houses in their newly conquered lands were built with the ancient Viking way with stone foundations. The walls were often made with a mixture of materials. The farmstead of the Vikings stood on flat and well-drain land and next to it was the gazing area for the animals.
What did the Vikings do?
The Vikings had a traditional farming economy. They focused on the barley and raising the cattle like sheep, horses, pigs, etc. The Vikings still carried on fishing. Their main marine supply included the seaweed, fish, and shellfish. They caught the seabirds for eggs as well.
How did the Vikings start their raiding tradition?
The Vikings started their raiding tradition with small raids with a group of seafarers. Such small raids gradually turned into conquests by the large army. Generally, the Vikings once applied the run-and-hit tactics on the plundered site. They used to pay no attention to control the territory. But as time progressed, the ancestral land could not fulfil their ambition, they conquered new land and started settling down in these new land. But how did the Vikings settle down in the newly conquered land?
Did the Vikings live like their fathers?
Farewell to the ancestral land did not mean farewell to the traditional living pattern. The Vikings still chose to live like their fathers once did. They chose the coastline region to settle down. Living in the coastline regions meant they could work with their great ships not only for raiding but also for fishing.
Why did the Vikings move?
Another theory is that there was a population boom and there was not enough arable land around, so these new young adults had been looking for places to call their own. Trade routes were expanding and the wealth now moved further into Europe, enticing the Vikings into Western Europe and beyond. Also, this time of warm temperatures was a good time to move, as the Little Ice Age didn’t start till about 1250. No matter the reason, the population of the Vikings moved and grew as they raided, explored, and eventually colonized new areas .
Where did the Vikings expand?
The theories behind Vikings’ expansion of settlements in Eastern and Western Europe. From the 8 th to the 11 th century, there was an expansion of Viking influence from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden into eastern and western Europe. Travel by sea was the easiest way for these Scandinavian people to explore.
What were the animals that were farmed in Viking times?
The cattle from the Viking age were actually smaller than today’s animals, being only about 120 cm high. Sheep were also farmed and kept for their milk, wool, and meat. Neutered Sheep (wethers) could graze where they wished, but the ewes were penned.
Why did the Franks push into the southern end of Scandinavia?
The Franks were also already pushing into the southern end of Scandinavia and attacking Viking villages so that the people could have been pushed out due to this. Map of England in 878, depicting the Danelaw territory.
How big was the Viking longhouse?
There, an old Viking farm had a longhouse made from wood, stone, and earth; it was about 20 meters long and five meters wide . There was a building alongside the longhouse that would have been used as a cattle barn, with stalls and a drainage trench down the center.
What was the easiest way to travel in the Viking Age?
Travel by sea was the easiest way for these Scandinavian people to explore. It was in the 8 th century that shipbuilding expanded, which in turn started the raids that marked the beginning of the Viking Age.
What were the crops of the Vikings?
The crops that the Vikings favored were grains; the three most predominantly raised were barley, rye, and oats. Wheat was grown as a luxury item and only in the southern areas. If the climate and soil were right, they also grew cabbage, beans, onions, and peas. Flax was grown as a utility crop for linen production. Large fields were worked by oxen pulling an arðr; the arðr cut grooves or channels into the soil, unlike the plow that turns the soil over. Smaller areas were turned over with hand tools. Vikings used manure on their fields to enable growing crops that were planted year after year. Crop rotation wasn’t used until later. They used sickles to harvest the grain, and once it was dry, they threshed it. They used the grain to make ale, porridge, and flour for bread. For heating, the Vikings would burn peat and wood; any iron smelting done in the community used wood in great quantities, About Education reported.
Why were the Vikings the first to settle?
In places that the Vikings were the first sizable group to explore and/or settle, these were the quest for fame, prestige, and honor; the desire for the level of personal freedom that one can only find in a sparsely-populated area with no pre-established government; and the ability to take advantage of virgin natural resources.
Why did the Vikings settle in the lands they explored?
In places that the Vikings were the first sizable group to explore and/or settle, these were the quest for fame, prestige, and honor; the desire for the level of personal freedom that one can only find in a sparsely-populated area with no pre-established government; and the ability to take advantage of virgin natural resources.
What did the Norse call the sheep islands?
The Norse named the islands the Færeyjar , “Sheep Islands.” The islands were treeless, so the settlers built their homes out of turf and rock. The islands’ economy was heavily dependent on livestock and harvesting the products of the sea, particularly fish, whales, and birds. [2]
What were the Vikings driven by?
In places where the Vikings conquered existing populations, they were driven by political ambitions, the desire for wealth through tribute and the control of trade, and, as in newly-inhabited lands, the ability to make a name for oneself. [1]
What were the Vikings' accomplishments?
As impressive as the Vikings’ accomplishments as raiders and warriors were, their accomplishments as explorers and settlers were equally magnificent. The Vikings ventured far from their homelands in Scandinavia and became the first Europeans to discover Greenland and even North America (which they called “Vinland”) – roughly 500 years before Christopher Columbus. Along the way, they became the first people to establish sizable settlements in Iceland and other North Atlantic islands, and also colonized the territories their warriors conquered throughout northern Europe. These explorations and settlements have had a decisive impact upon these places that persists even today.
How many ships set sail for Greenland in 985?
[15] Erik’s persuasion was successful, and in the summer of 985, twenty-five ships set sail for Greenland.
Which conquest had the deepest impact on the British Isles?
The Viking conquest with the deepest and longest impact was that of the British Isles. [29] The Scandinavians who migrated to England, Scotland, and Ireland forever changed the character of those countries. Perhaps this should be unsurprising given the sheer extent of Viking rule in these places. By the late ninth century, the Norse controlled virtually all of England besides Wessex, and large swaths of Scotland and Ireland as well. [30]
What did the Vikings do in Ireland?
When the Vikings came to Ireland they mostly performed hit & run raids. There were no large towns or cities so their raids focused on settlements around costal areas. Ireland did start gaining a reputation as a place of Christian monastic settlements which brought more invading Vikings.
What was the name of the river that the Vikings sailed into?
When the Viking longboats sailed into the River Liffey during the 9th century they built a longphort (ship harbour). It was also built on south bank of the River Liffey and would be used as a winter camp. When the Vikings began to settle in the area their settlement became known as Dyflinn.
Why was Dublin important to the Vikings?
As the Norsemen continued life in Dublin the area became an important trading post. With links all over the world the Vikings would use Dublin to continue raids on Ireland and Britain, build ships, and even became known for its barrel making. Excavations of Dublin city in the 20th century discovered Duiblinn was a thriving Viking community, ...
What was the name of the Viking town in Dublin?
Excavations of Dublin city in the 20th century discovered Duiblinn was a thriving Viking community, an important town and hub. Viking leadership of Dublin would finally come to an end by 902. As described in the Annals of Ulster:
What happened to the Norse Kingdom of Dublin?
The end of the Norse Kingdom of Dublin. Ímar died in 873, the same year the king of Lochlainn died and a year later Olaf died during a campaign against the King of Picts in Scotland. The death of the 3 Viking leaders brought uncertainty for the Norse Kingdom of Dublin. As the Norsemen continued life in Dublin the area became an important trading ...
Where were wooden hurdles placed?
Wooden hurdles were placed on the mud bed of the river to make a crossing bridge during low tide. During the Christianisation of Ireland, a large monastic settlement was founded and located southeast of Átha Cliath. The Christian settlement was located beside a tidal pool in the River Poddle, Duiblinn (Blackpool).
When the Dublin Vikings started concentrating more on Britain, the native Irish saw this as an oppurt?
When the Dublin Vikings started concentrating more on Britain the native Irish seen this as an oppurtunity by attacking the Viking settlements. In 867 a Norse settlement near Dublin was attacked with a further attacks on Dublin, although this did little to stop further attacks from the Vikings.
What was the main building of the Vikings?
The farm. Most Vikings lived on a farm, which was often bounded by a fence. The farm was centred around a dwelling house – the longhouse – which was the main building. Apart from the dwelling house, the farm often consisted of various areas of activity and other buildings, including outbuildings, barns, stables and workshops.
Where did the Vikings live?
Photo: Anne Pedersen. Viking homes have been found in nearly all parts of Denmark. Only a small proportion of the Vikings lived in towns. Most of them were farmers, who lived in small villages consisting of 6-7 farms. For them the farm, domestic animals and agriculture were all pivotal to the daily routine.
What was the role of banquets in Viking society?
Banqueting plays an important role in the Viking societies described in the saga literature and eddic poems.
What were Viking houses made of?
Viking houses were built of wood. The longhouses had bowed walls in plan, forming a ship-like outline. The walls were lined with clay or consisted of wooden planks placed vertically into the ground, which supported the roof, along with two rows of internal posts. Outside the house was often supported by sloping posts.
What was in the middle of the Viking house?
In the middle of the house was an oblong fireplace – the long fireplace. Here the food was made. Along the walls there were plank beds, on which the Vikings could sit or sleep. At one end of the house the animals were housed in stalls, if there were no stables at the farm. The Vikings constantly repaired their houses.
What is the reception scene in Gotlandic?
A door is shown. In front of the door stands a woman with a drinking horn in her hand, ready to receive guests. The scene is often interpreted as the arrival of dead warriors at Valhalla, and the woman as a valkyrie, who is receiving them. However, the scene may also show how the reception to an ordinary banquet was performed.
Where did the Vikings bury their dead?
The Vikings buried their dead a short distance from the settlement, typically 300 - 600 m away. Many farms and burial places were separated by a watercourse. This has been identified at significant Danish sites, such as Gammel Lejre and Tissø on Zealand and Mammen, near Viborg, in Jutland.
What did the Vikings bring to Europe?
So, in fact, you could argue that the Vikings brought a huge amount of economic dynamism and trade through this informal empire, this network, that by that stage stretched across western Europe.
Why have we forgotten rivers?
We’ve forgotten now, because our rivers are shallow and encroached on, we’ve built embankments and dykes, but rivers in the past were mighty highways that ran through this country .
Who destroyed the Church of Mercia?
It was then effectively wiped from the history books having been totally destroyed by the Vikings, who then stayed there.
Why did the Vikings travel?
And because the environment could be very different than it is in Scandinavia, they would often adapt their houses to the surrounding area.
Why are Viking longhouses curved?
The truss framework also gave the walls the curved shape that we all know, because some of the weight from the roof was pushed out on some of the posts that supported the roof. Inside a Viking longhouse. The longhouses were not easy to build, it was very time-consuming and demanded a lot of manpower.
How many people could live in a Viking longhouse?
In fact, these longhouses had so much room that 30-50 people could live here, including their slaves (A slave is called ”Træl” in Danish) and animals. Viking longhouse at Trelleborg, Denmark Photo: by Schorle. A longhouse was on average 30 meters long and 8 meters wide in the middle.
What animals did the Vikings have?
The Vikings had many different kinds of animals such as sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle, but they also had pets such as cats to help kill the rodents such as mice. In the early Viking age, we start to see that the houses become bigger and wider than it was in the iron age, and the Viking longhouse is a good example of that.
Why was hospitality important in the Viking Age?
In the Viking age, hospitality was very important to the people because you never really knew who the wanderer who knocked on your door really was. The God Odin was known to travel around Midgard, but merchants and other travelers could also turn up at your doorstep.
What was the main building on a farm?
On a farm like this the main building was typically the longhouse, here, the family sat and enjoyed their meals, rested, and slept. Next, to the longhouse, there could be other buildings such as barns, stables, or workshops.
Where are pit houses used?
However, we do have one from Denmark in the Municipality of Stevns, in the town of Strøby at the farm called Toftegård.
