
When you settle a debt with a creditor, you pay less than what you owe. The remaining amount is forgiven debt — also called canceled debt — which is often counted as taxable income. Debt settlement can make your tax returns more complicated or increase the taxes you owe.
Is there a tax impact with debt settlement?
When you do a debt settlement, the amount of your debt that's written off is generally reported to the IRS. And it's generally considered taxable income. If you do a debt settlement this year, you may end up owing the IRS money next year when you file your 2022 tax return.
Does settling debt affect your taxes?
Yes, the amount of debt you didn’t pay is generally reported to the IRS as income. While settling your debt may be a huge relief, you need to be prepared to pay taxes on the amount settled. Depending on the type of debt, your creditor may send you a 1099-C cancellation of debt tax notice.
Do I have to pay taxes on a debt settlement?
You only pay taxes on the difference. (Even if you don't get a 1099c for less than $600, you still owe taxes). And...debt "reduction" usually means they remove the penalty and interest from the balance, and you pay the rest. Debt "settlement" means they reduce the amount you borrowed. You pay taxes on settlement.
Will debt settlement affect my taxes?
When considering debt settlement, take into account the effect on your taxes. Work with a debt settlement attorney to determine if the consequences of paying off your debt through a settlement will have a negative impact to your tax filing. In most cases, you will still benefit from a debt settlement.
Do you have to pay taxes on a debt settlement?
Yes, you do have to pay taxes on a debt settlement. The IRS views the portion of your debt forgiven after debt settlement as income and therefore taxes you on it. Forgiven debt (also known as canceled debt) is taxed at the same rate as your federal income tax bracket.
How can I avoid paying taxes on credit card settlement?
If your creditor has settled your credit card debt for $30,000 less than what you owed, you are excluded from being taxed on the $20,000, since you're insolvent. However, you must pay taxes on the remaining $10,000 that was forgiven. Bankruptcy: If your credit card debt is forgiven in bankruptcy, it cannot be taxed.
How much taxes do you pay on Cancelled debt?
If a creditor discharged a debt of $600 or more, you should receive a Form 1099-C from the IRS showing the amount of debt forgiven for that tax year. In most cases, this is the amount you'll need to include in your gross income – the sum of your earnings before taxes – when filing your tax return.
Do Settlements get reported to IRS?
If the settlement agreement is silent as to whether the damages are taxable, the IRS will look to the intent of the payor to characterize the payments and determine the Form 1099 reporting requirements.
Does a 1099-C hurt you?
A copy of the 1099-C is not supplied to credit reporting agencies, though, so in that respect, the fact that you received the form has no impact on credit reports or scores whatsoever.
What happens if you don't report a 1099-C?
The creditor that sent you the 1099-C also sent a copy to the IRS. If you don't acknowledge the form and income on your own tax filing, it could raise a red flag. Red flags could result in an audit or having to prove to the IRS later that you didn't owe taxes on that money.
What to do if you get a 1099-C for an old debt?
If you receive a 1099-C on an old debt, your best option is to contact a CPA or tax professional. They'll help you determine how to settle the outstanding tax issue.
Do I have to report 1099-C on my taxes?
In most situations, if you receive a Form 1099-C from a lender, you'll have to report the amount on that form to the Internal Revenue Service as taxable income.
What type of settlement is not taxable?
personal injury settlementsSettlement money and damages collected from a lawsuit are considered income, which means the IRS will generally tax that money. However, personal injury settlements are an exception (most notably: car accident settlements and slip and fall settlements are nontaxable).
Do I get a 1099 for a lawsuit settlement?
If you receive a taxable court settlement, you might receive Form 1099-MISC. This form is used to report all kinds of miscellaneous income: royalty payments, fishing boat proceeds, and, of course, legal settlements. Your settlement income would be reported in box 3, for "other income."
Do settlement payments require a 1099?
One important exception to the rules for Forms 1099 applies to payments for personal physical injuries or physical sickness. Think legal settlements for auto accidents and slip-and-fall injuries. Given that such payments for compensatory damages are generally tax-free to the injured person, no Form 1099 is required.
What type of legal settlements are not taxable?
Settlement money and damages collected from a lawsuit are considered income, which means the IRS will generally tax that money. However, personal injury settlements are an exception (most notably: car accident settlements and slip and fall settlements are nontaxable).
Will I get a 1099 for a class action lawsuit settlement?
You won't receive a 1099 for a legal settlement that represents tax-free proceeds, such as for physical injury. A few exceptions apply for taxed settlements as well. If your settlement included back wages from a W-2 job, you wouldn't get a 1099-MISC for that portion.
Do you pay taxes on class action settlements?
Oftentimes, the nature of a class action suit determines if the lawsuit settlement can be taxable. Lawsuit settlement proceeds are taxable in situations where the lawsuit is not involved with physical harm, discrimination of any kind, loss of income, or devaluation of an investment.
Is Forgiven Credit Card Debt taxable?
In general, if you have cancellation of debt income because your debt is canceled, forgiven, or discharged for less than the amount you must pay, the amount of the canceled debt is taxable and you must report the canceled debt on your tax return for the year the cancellation occurs.
What Are The Implications of Debt Settlement?
Debt settlement sounds good at first glance, but what the creditor may not tell you is how settling your debt could affect your taxes and your credit report. Read on to better understand the tax implications of settling your debt.
Why Even Do A Debt Settlement?
Debt settlement may seem like a hassle when you consider (1) You or a debt settlement company have to negotiate (it may take several attempts) with creditors; (2) You have to save money to have the lump sum available; (3) The default history that’s already on your credit report, and the fact that (4) You’ll have to pay taxes on forgiven debt. You may wonder why you should even do a debt settlement.
What happens to the IRS after a debt settlement?
Following a debt settlement, the creditor will report to the IRS the amount that the debtor did not pay (the forgiven debt) as lost income. The IRS recognizes any forgiven debt over the amount of $600 as taxable income, so any amount of savings that a debtor achieves in debt settlement over this amount will be reduced by a tax liability.
What is debt settlement?
Debt settlement occurs when a debtor successfully negotiates a payoff amount for less than the total balance owed on a debt. This lower negotiated amount is agreed to by the creditor or collection agency and must be fully documented in writing. The settlement is often paid off in one lump sum, although it can also be paid off over time.
What happens if you don't receive a 1099-C?
Unfortunately, it can be the case that when a debtor has no knowledge of having received a 1099-C, the financial institution has reported the settlement to the IRS, exposing the debtor to further liability that may now also include IRS interest expense and penalties.
How to contact United Debt Settlement?
Contact United Debt Settlement to learn more about how debt settlement affects taxes. Give us a call at ( 888-574-5454) or fill out our online contact form and get a free savings estimate.
Can creditors accept debt settlements?
Although creditors are under no legal obligation to accept debt settlement offers, negotiating and paying lower amounts to settle debts is far more common than many people realize. A successful debt settlement can result in savings of thousands of dollars while relieving chronic aggravation and stress by putting an end to a seemingly endless cycle of monthly payments.
Is $10,000 insolvency taxable?
Any settled debt for up to $10,000, therefore, will not be subject to taxation. However, once the $10,000 threshold is met, any excess settlement amount above that becomes taxable. A $12,000 settlement savings, for example, would result in $2,000 of taxable income in this scenario.
Do you owe taxes after a debt settlement?
However, following a debt settlement, you may owe additional taxes to the IRS. Learn more from the experts at United Settlement about how debt settlement affects taxes.
What happens when you settle a debt?
When you settle a debt with a creditor, you pay less than what you owe. The remaining amount is forgiven debt — also called canceled debt — which is often counted as taxable income. Debt settlement can make your tax returns more complicated or increase the taxes you owe. This article will discuss debt settlement and how forgiven debt affects your taxes. Understanding the tax implications of canceled debt will help you be better prepared to negotiate debt forgiveness with your creditors. It’ll also help you understand how to prepare your tax returns correctly.
How long does it take to pay IRS debt?
The installment agreement — the IRS’s first choice in payment plan options — usually requires that you pay your tax debt in full within six years. With this agreement, you don’t have to demonstrate hardship or lack of financial ability. The partial payment installment agreement is a little more restrictive than the installment agreement. It requires more financial documentation so the IRS can assess if you can pay your tax debt. Other tax debt relief options with the IRS are more restrictive and have more difficult requirements. A tax professional may be able to provide more insight into tax relief options with the IRS.
What happens if you file Chapter 13?
If you file Chapter 13 bankruptcy, you’ll have a payment plan that can help you address your secured debts, like your home. This can stop the foreclosure process. Consulting with a bankruptcy attorney can help you understand your legal rights. If you’re facing foreclosure and tax ramifications, consider getting legal assistance to decide the best path forward for you. Also, can check out Upsolve’s free bankruptcy screener tool to get a better idea of what bankruptcy is and if it’s right for you and your family.
What to do if you can't pay your taxes in one year?
If you’re unable to pay off your tax bill in one year, don’t panic. The IRS offers payment plans. These options include an installment agreement, a partial payment installment agreement, an offer in compromise, and a currently not collectible status.
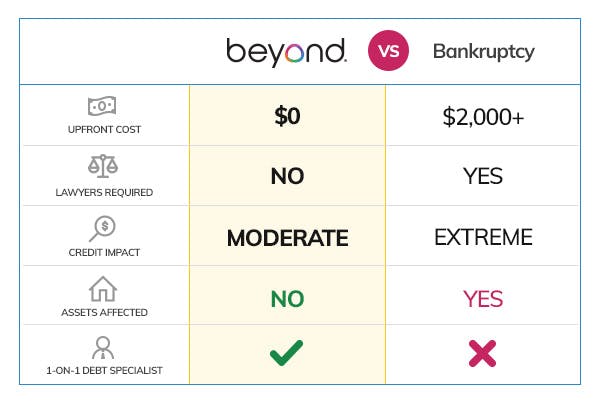
Why do you have to declare bankruptcy?
Declaring bankruptcy can be a useful tool to prevent or at least slow down a home foreclosure. Once you file bankruptcy, the court will issue an automatic stay. This protects you from your creditors and any collections activities while the bankruptcy is in process.
Is bankruptcy taxable if you file Chapter 7?
If you file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, many of your debts will be discharged. Debts discharged, or wiped away, during bankruptcy are not taxable. People who file Chapter 7 bankruptcy are typically insolvent anyway — meaning their liabilities exceed their assets. If the IRS considered the debt discharged in bankruptcy to be taxable, this could end up creating a tax debt for bankruptcy filers, which defeats the purpose of filing bankruptcy in the first place.
Can you settle debt with a creditor?
You might think that once you’ve successfully negotiated a debt settlement on an outstanding debt that you are done and you can kick up your feet and relax. Not so fast. When you settle a debt with a creditor, you pay less than what you owe. The remaining amount is forgiven debt — also called canceled debt — which is often counted as taxable income. Debt settlement can make your tax returns more complicated or increase the taxes you owe.
Why is settled debt considered taxable income?
Usually, getting a loan doesn’t count as income, so what makes debt settlement different? Well, you borrowed money, and debt settlement means you don’t pay it all back. So you received additional money that needs to be accounted for.
What is debt settlement?
Debt settlement, also known as debt forgiveness, is when a borrower and lender agree to settle a debt for less than what’s owed. This process is typically done when a borrower is behind on payments.
What happens if you don't receive a 1099-C?
Even if you don’t receive a 1099-C form, you should still report the debt forgiveness as income (if it exceeds $600). The creditor might have submitted a 1099-C form to the IRS and you just didn’t receive a copy. If this happens and you don’t report the income, you can be subject to IRS penalties or an audit.
What happens if you can't afford a 1099?
If you can’t afford this payment, you might find yourself in tax debt. After agreeing to debt forgiveness, your creditor will provide you with a 1099-C form so you can claim the income on your next tax return. The form will include the specific amount of debt that was forgiven.
How much credit card debt is forgiven?
If more than $600 of debt is forgiven, it’s considered income by the IRS and is therefore taxable. If you have $22,000 in credit card debt and settle for a payment of $12,000, then you can be taxed on the difference of $10,000. How much you pay in taxes will depend on what income tax bracket you’re in. The IRS has seven tax brackets.
How long do you have to stop paying debt?
Most debt settlement companies that help you through the debt forgiveness process advise you to stop making payments on your debt for a few months. This serves two functions: First, it puts your debt into delinquency, making the creditor more willing to engage in debt settlement conversations.
Why do lenders close out debt?
The lender will want to close out the debt to reduce their risk of further missed payments, so they agree to “settle.” The borrower makes a lump sum payment on a reduced balance that both parties have agreed to.
What is debt settlement and how does it work?
Let’s back up a bit. A debt settlement is when you pay less than what you actually owe and the creditor charges off the rest, releasing you from the obligation to pay that portion. This arrangement is often done with credit cards that are seriously overdue.
Do you have to pay taxes on charged-off debt?
Put this in the same category as that self-employed income you make on the side. If someone sends you a 1099 for the money they paid you, file it with your taxes and pay your share. Failure to do so could lead to penalties, interest, or even incarceration in extreme cases.
Debt canceled due to Insolvency
Last year was tough for a lot of people, so some debt settlements aren’t going to be the small variety you typically see on credit cards. In cases of mortgage cancellation and bankruptcy, that charged-off amount could leave you liable for several thousand dollars in taxes. Yikes.
What happens if you don't pay a debt collection agency?
Once your creditor (or debt collection agency) stops attempting to collect from you, the sum of $4,000 effectively has been given to you. At that point, it is considered income, you will receive a 1099-C form and will be taxed as such.
Why is a credit card debt considered insolvent?
You are considered insolvent because your debts exceed your assets, in this case by $20,000. Now assume $30,000 of credit card debt is forgiven. This is greater than the amount by which you were insolvent. Only the first $20,000 — the amount of insolvency — is exempt from taxation.
How much debt do you have to have to be insolvent?
You are considered insolvent because your debts exceed your assets, in this case by $20,000.
What happens if a student loan is forgiven?
If a student loan was forgiven under other circumstances, such as an inability to pay, then normal income tax regulations apply.
Can you put a credit card debt on your taxes?
Yes, that $10,000 in credit card debt you had forgiven, or the $50,000 of debt you thought you avoided after a short sale could end up on Line 21 of your next tax return as “Other Income” and on Line 43 as part of your “Taxable Income.”
Is a cancelled student loan subject to tax?
Canceled student loans are subject to a separate set of taxation rules.
Does the federal tax exemption apply to private education loans?
It does not apply to private education loans.
