As of 30 January 2020, there are about 130 government-approved settlements, and 100 unofficial ones, which are home to around 400,000 Israelis in the West Bank, with an additional 200,000 Israelis residing in 12 neighborhoods in East Jerusalem.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
As of 2022, there are 140 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem. [16] In addition, there are over 100 Israeli illegal outposts in the West Bank. In total, over 450,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank excluding East Jerusalem, with an additional 220,000 Jewish settlers residing in East Jerusalem.
What is considered a settlement in Israel?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War —the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
How many settlers does Israel really have?
According to Peace Now, based on figures given by the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics for the end of 2018, the number of settlers is 427,800, an increase of 14,400 over the prior year.
How many new settlement homes has Israel built?
^ Israel Approves Construction of 1,700 New Settlement Homes. Reuters, 3 November 2013 ^ Israel Plans 24,000 New Homes for Jewish Settlers. Reuters, 12 November 2013
.jpg)
How many settlements does Israel have?
Today they total around 400,000 and live in about 130 separate settlements (this doesn't include East Jerusalem, which we'll address in a moment). They have grown under every Israeli government over the past half-century despite consistent international opposition.
Where were Israel's settlements?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War—the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
Which Israeli settlements are illegal?
Numerous UN resolutions and prevailing international opinion hold that Israeli settlements in the West Bank, East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights are a violation of international law, including UN Security Council resolutions in 1979, 1980, and 2016.
How many settlements are in Gaza?
21 settlementsDescription of the planIn the Gaza Strip (21 settlements):Bedolah Bnei Atzmon (Atzmona) Dugit Elei Sinai Gadid Gan OrGanei Tal Katif Kfar Darom Kfar Yam Kerem Atzmona MoragNeve Dekalim Netzarim Netzer Hazani Nisanit Pe'at Sadeh Rafiah YamIn the West Bank (4 settlements):KadimGanimHomesh
Has Israel stolen land?
Israel has declared at least 26 percent of the West Bank as “state land”. Using a different interpretation of Ottoman, British and Jordanian laws, Israel stole public and private Palestinian land for settlements under the pretext of “state land”.
What is wrong with Israeli settlements?
The settlements have a lot of security measures including Jewish-only roads and restrictions that split up Palestinian territory, often making it difficult for people to get to work, visit family or even go to the hospital when they are sick.
Is Israel illegally taking land?
For the last 50 years, Israel has been forcing thousands of Palestinians off their land, occupying and illegally using it to create settlements that exclusively house Jewish Israeli settlers. Entire Palestinian communities have been displaced by these settlements.
Why is Israel entitled to the land?
Jewish religious belief defines the land as where Jewish religious law prevailed and excludes territory where it was not applied. It holds that the area is a God-given inheritance of the Jewish people based on the Torah, particularly the books of Genesis and Exodus, as well as on the later Prophets.
Does Israel Own Palestine?
Presently, most of the West Bank is administered by Israel though 42% of it is under varying degrees of autonomous rule by the Fatah-run Palestinian Authority. The Gaza Strip is currently under the control of Hamas.
Was Palestine a country before Israel?
Israel Becomes a State In May 1948, less than a year after the Partition Plan for Palestine was introduced, Britain withdrew from Palestine and Israel declared itself an independent state, implying a willingness to implement the Partition Plan.
Is Israel occupying Palestine land?
BACKGROUND: Palestinian territory – encompassing the Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East Jerusalem – has been illegally occupied by Israel since 1967.
What was Israel before 1948?
The region was ruled under the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948, when the Jewish State of Israel was proclaimed in part of the ancient land of Israel. This was made possible by the Zionist movement and its promotion of mass Jewish immigration.
Why does Israel have settlements?
Settlements are communities of Jews that have been moving to the West Bank since it came under Israeli occupation in 1967. Some of the settlers move there for religious reasons, some because they want to claim the West Bank territory as Israeli land, and some because the housing there tends to be cheap and subsidized.
Who were the first settlers in Israel?
3,000 to 2,500 B.C. — The city on the hills separating the fertile Mediterranean coastline of present-day Israel from the arid deserts of Arabia was first settled by pagan tribes in what was later known as the land of Canaan. The Bible says the last Canaanites to rule the city were the Jebusites.
Why does Israel have settlements in the West Bank?
Israel has cited several reasons for retaining the West Bank within its ambit: a claim based on the notion of historic rights to this as a homeland as affirmed in the Balfour Declaration of 1917; security grounds, both internal and external; and the deep symbolic value for Jews of the area occupied.
Why did Israel build settlements in the West Bank?
If it's so controversial, why does Israel want to do it? Israel claims historical and religious rights to the West Bank as the ancestral land of the Jewish people. It also says its presence there - especially in the Jordan Valley - is strategically vital for its self-defence.
Where are the Israeli settlements?
Israeli settlements currently exist in the Palestinian territory of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and in the Syrian territory of the Golan Heights. East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights have been annexed by Israel, so residents are treated equivalently to the rest of Israel under Israeli law.
What are the settlements in East Jerusalem?
East Jerusalem settlements (2006) Golan Heights settlements (1992) Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Jewish ethnicity, built in violation of international law on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Israeli settlements currently exist in ...
How many settlements were there in the Gaza Strip?
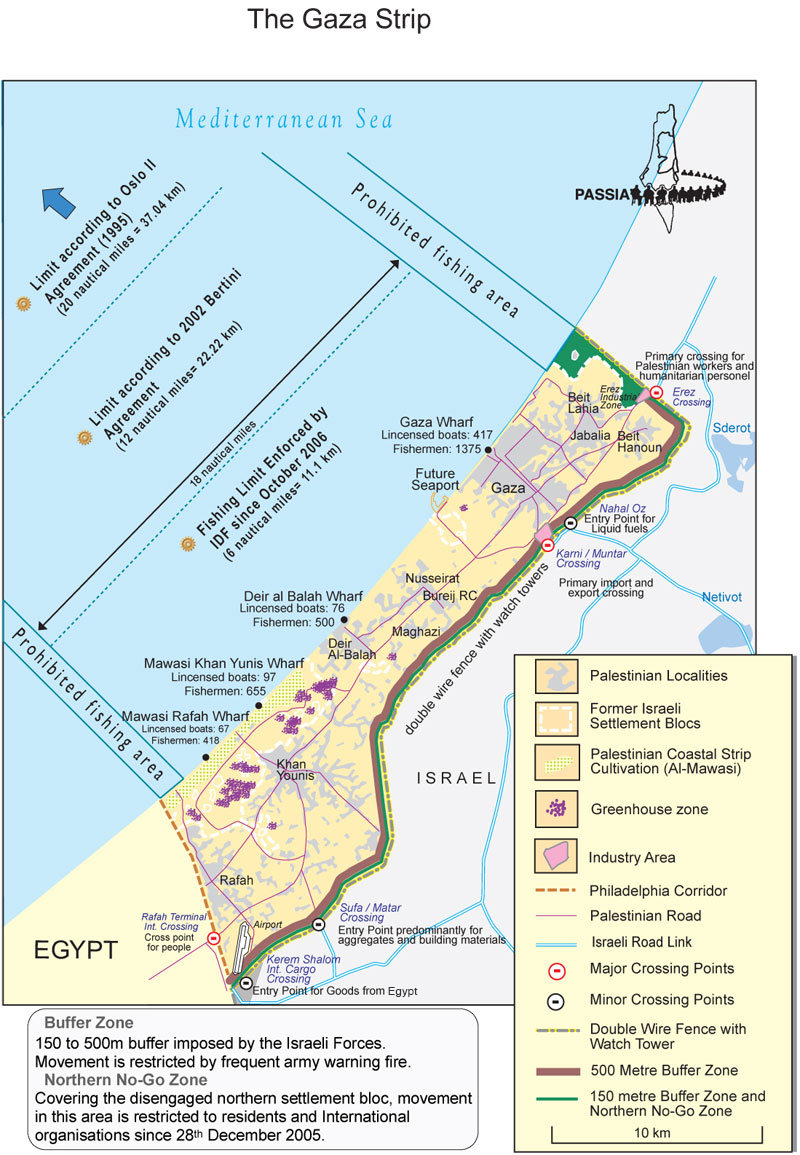
Before Israel's unilateral disengagement plan in which the Israeli settlements were evacuated, there were 21 settlements in the Gaza Strip under the administration of the Hof Aza Regional Council. The land was allocated in such a way that each Israeli settler disposed of 400 times the land available to the Palestinian refugees, and 20 times the volume of water allowed to the peasant farmers of the Strip.
How was Kiryat Arba established?
According to a secret document dating to 1970, obtained by Haaretz, the settlement of Kiryat Arba was established by confiscating land by military order and falsely representing the project as being strictly for military use while in reality, Kiryat Arba was planned for settler use.
What territories did Israel control?
It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and from Syria it captured most of the Golan Heights, which since 1981 has been administered under the Golan Heights Law .
How does settlement affect the economy?
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the security of the Israeli citizens living there.
When did the settlement division move to the PMO?
In 2009, the Netanyahu Government decided to subject all settlement activities to additional approval of the Prime Minister and the Defense Minister. In 2011, Netanyahu sought to move the Settlement Division again under the direct control of (his own) PMO, and to curtail Defense Minister Ehud Barak's authority.
What is an Israeli settlement?
Israeli settlement. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree.... Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the disputed territories captured by Israel in ...
How many people lived in settlements in 1993?
Settlements continued to expand in the decades that followed, and by 1993 there were more than 280,000 people living in settlements (130,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded).
What was the purpose of the settlements in the Jordan Valley?
Israel’s political and defense establishments, meanwhile—inspired in part by the peace plan of Yigal Allon, the deputy prime minister (1967–77)—spurred the development of settlements in strategic locations such as the Jordan Valley that would bolster Israel’s security and strengthen its hand in negotiations .
How many settlers were there in 2019?
Despite the agreement, settlement building proliferated, especially in the West Bank, and in 2019 the number of settlers reached nearly 630,000 (413,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded). Most of these newer settlers were motivated less by reasons of ideology or recovering lost property, however, than by cheaper housing and financial incentives ...
Where is Israel located?
Israel, country in the Middle East, located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bounded to the north by Lebanon, to the northeast by Syria, to the east and southeast by Jordan, to the southwest by Egypt,…
When were the settlements in the Sinai Peninsula evacuated?
Settlements in the Sinai Peninsula were either dismantled or evacuated in 1982, and settlements in the Gaza Strip were dismantled in 2005. It is disputed, moreover, whether communities in the formally annexed territories of East Jerusalem (part of the West Bank territory under Jordanian rule from 1949 to 1967) and the Golan Heights constitute ...
How many settlement outposts were there in the West Bank?
In addition, there were approximately 110 “settlement outposts” located throughout the West Bank. The outposts do not have official government recognition, although many of them were established with governmental assistance. Outposts are generally smaller than recognized settlements.
How many settlers are there in the West Bank?
There are an estimated 622,670 settlers in the West Bank.
How much did the settlement population increase in 2017?
According to the CBS, the annual growth rate of the settler population (excluding East Jerusalem) in 2017 was 1.75 times greater than that of the population in Israel: an annual increase of 3.5% in the settlements versus 2% in Israel.
What are outposts in Israel?
Outposts are generally smaller than recognized settlements. Eleven large Israeli neighborhoods were built in areas that Israel annexed to the Jerusalem Municipality after 1967. These neighborhoods are also considered settlements under international law.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are 126 Israeli settlements in the West Bank (excluding East Jerusalem), according to the September 2016 report from the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Geographically, these settlements are all across the West Bank. The West Bank is broken down into Areas A, B, and C, according to the Oslo Accords, ...
What are settlements?
Settlements are Israeli cities, towns and villages in the West Bank and the Golan Heights. (We will deal with East Jerusalem a bit later.) They tend to be gated communities with armed guards at the entrances. Why are they settlements and not simply Israeli residential areas? Because Israel is widely considered to be an occupying force in the territories. It is land that Palestinians, along with the international community, view as territory for a future Palestinian state.
Why are the West Bank and East Jerusalem considered occupied territory?
Israel began its occupation of the West Bank and East Jerusalem in 1967 during the Six-Day War. Seeing a military buildup in the surrounding Arab countries, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, after which Jordan, in turn, attacked Israel. Israel annexed East Jerusalem shortly thereafter, unifying the city under Israel’s authority. But Israel has never annexed the West Bank, part of which remains under military law.
Who are the settlers?
This is a very broad question, and requires a fair amount of generalization.
Why are the settlements controversial?
The settlements are built on land the Palestinians and the international community, along with some in the Israeli community, see as a future Palestinian state. Some of the settlements – especially the blocs – may be a part of Israel in a two-state solution through land swaps between Israelis and Palestinians. One concern, expressed by the European Union, and in the past by the US State Department, is that settlement expansion may make a contiguous, whole Palestinian state in the West Bank impossible.
What is the legal status of settlements?
The settlements are illegal under international law. The Fourth Geneva Convention, which concerns civilian populations during a time of war, states in Article 49 that, “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
What about East Jerusalem? And what is East Jerusalem anyway?
From 1948 to 1967, Jerusalem was divided by the Green Line, which is the cease-fire line of 1948 between Israel and Jordan. Although the city is now under Israeli governance, the distinction remains.
What are some examples of settlements in Israel?
But in practice, settlements look and operate much like any other small town in Israel — down to identical street signs and public transit. For example, Ariel in the northern West Bank is connected to Tel Aviv by a major highway and boasts Ariel University.
How many settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are approximately 130 West Bank settlements, ranging from small villages of 100 people near Arab towns, to the college town of Ariel with a population of 19,000, to the haredi Orthodox enclave of Modiin Illit, located just across the boundary from Israel proper, which has 70,000 inhabitants.
Why do Palestinians want to expand their settlements?
Palestinians, in addition to viewing the settlements as a violation of international law , see them as both physical and ideological obstacles to peace. Besides taking up the territory of a would-be Palestinian state, Palestinians see settlement expansion as a signal that Israelis are not sincere about withdrawing from the territory. Palestinians have also protested violence on the part of settlers.
How many people are in Tekoa?
Everything you need to know about Israeli settlements and the Trump administration’s announcement. Tekoa, an Israeli settlement of nearly 4,000 people in the West Bank's Gush Etzion bloc, is shown in 2019. (Laura Ben-David) ( JTA) — Secretary of State Mike Pompeo announced this week that the United States will no longer consider Israeli Jewish ...
What is the violation of the Fourth Geneva Convention?
Israeli settlements are also widely considered to be a violation of the Fourth Geneva Convention, which prohibits an occupier from “transfer [ring] parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”. Both Israel and the United States ratified this convention.
What countries did Israel capture in 1967?
In the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel captured large swaths of territory from neighboring countries. Israel took the Sinai Peninsula and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, the West Bank and eastern Jerusalem from Jordan, and the Golan Heights from Syria.
Which country was the first to recognize sovereignty over the Golan?
In March, President Donald Trump recognized Israeli sovereignty over the Golan, the first country to officially do so. Israelis had also previously settled in the Gaza Strip and Sinai Peninsula, but settlements there were evacuated when Israel withdrew from those territories.
How many people were in the last time Israel removed settlers?
The last time Israel forcibly removed settlers, it took about 8,000 people from two dozen small settlements in Gaza and it was a national trauma.
Why are Israeli settlements cheaper?
For some, it’s for ideological/religious reasons (which we’ll get into below); for others, it’s simply cheaper housing. Many settlement neighborhoods are within easy commuting distance of major Israeli cities and present a more affordable cost of living and a kind of pastoral quality of life — you know, the same reason some New Yorkers might move to Jersey. These settlers have left Israel’s crowded middle for airy communities in a beautiful landscape, often with government subsidies that make their homes cheaper than alternatives within Israel proper.
Why are settlements so controversial?
In short, because they are Jewish communities on a land that many want to become part of a future Palestinian state.
What do you mean by ideological settlers?
Ideological settlers are people who choose to live in the West Bank because they believe it is part of the land that God promised to Abraham and his descendants in the Bible. These settlers generally believe in the notion of “Greater Israel” — that is, that all of the land extending from the Mediterranean sea to the Jordan River, north to the borders with Lebanon and Syria, and south to the Red Sea, constitutes a Jewish inheritance.
How many Palestinians live in the West Bank?
As of writing this in 2019, over 3 million people live in the West Bank; 87% are Palestinians and 13% are settlers. Excluding Eastern Jerusalem, there are 132 “official” settlements — those recognized by the Israeli government — and 106 illegal outposts, or settlements established since the 1990s without government approval.
What is the name of the plateau that Israel captured in the 1967 war?
Golan Heights. Golan Heights. The Golan Heights is a plateau captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 war. It was effectively annexed by Israel in 1981. . Typically, when people talk about Israeli settlements, they’re talking about the West Bank.
What was the Jewish settlement in 1967?
Settlements are Jewish communities established in territories captured by Israel during the 1967. Six-Day War. Six-Day War. The Six-Day War was a war between Israel and multiple Arab states in 1967 that resulted in Israel vastly expanding the territory under its control, including the disputed territories of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. .

Overview
Number of settlements and inhabitants
As of 2022, there are 140 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem. In addition, there are over 100 Israeli illegal outposts in the West Bank. In total, over 450,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank excluding East Jerusalem, with an additional 220,000 Jewish settlers residing in East Jerusalem.
Additionally, over 20,000 Israeli citizens live in settlements in the Golan Heights.
Housing costs and state subventions
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the securit…
Character: rural and urban
Settlements range in character from farming communities and frontier villages to urban suburbs and neighborhoods. The four largest settlements, Modi'in Illit, Ma'ale Adumim, Beitar Illit and Ariel, have achieved city status. Ariel has 18,000 residents, while the rest have around 37,000 to 55,500 each.
History
Following the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel occupied a number of territories. It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt, it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and …
Geography and municipal status
Some settlements are self-contained cities with a stable population in the tens of thousands, infrastructure, and all other features of permanence. Examples are Beitar Illit (a city of close to 45,000 residents), Ma'ale Adumim, Modi'in Illit, and Ariel (almost 20,000 residents). Some are towns with a local council status with populations of 2,000–20,0000, such as Alfei Menashe, Eli, Elkana, Efrat and Kirya…
Types of settlement
• Cities/towns: Ariel, Betar Illit, Modi'in Illit and Ma'ale Adumim.
• Urban suburbs, such as Har Gilo.
• Block settlements, such as Gush Etzion and settlements in the Nablus area.
• Frontier villages, such as those along the Jordan River.
Resettlement of former Jewish communities
Some settlements were established on sites where Jewish communities had existed during the British Mandate of Palestine or even since the First Aliyah or ancient times.
• Golan Heights – Bnei Yehuda, founded in 1890, abandoned because of Arab attacks in 1920, rebuilt near the original site in 1972.
• Jerusalem – Jewish presence alongside other peoples since biblical times, various surrounding communities and neighborhoods, including Kfar Shiloah, als…