
How much does the VA spend secretly settling cases?
In 2014 and 2015, the Department of Veterans Affairs spent nearly $6.7 million to secretly settle cases with hundreds of employees who were either fired or forced into retirement due to inadequate performance, according to a USA Today investigation.
Can I appeal a denied VA disability rating?
If you've been denied disability compensation from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) or believe your disability should have received a higher rating, you have the right to appeal the VA decision.
What are my options if I disagree with a VA decision?
The legacy VA appeals process has changed to the decision review process. If you disagree with a VA decision dated on or after February 19, 2019, you can choose from 3 decision review options (Supplemental Claim, Higher-Level Review, or Board Appeal) to continue your case.
What happens if the VA fails to follow the law?
Sometimes, at the Regional Office or at the Board of Veterans Appeals (BVA), the VA fails to adhere to the laws and regulations that govern its operations. When this is the case, the oversight of the U.S. Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims may be necessary to obtain a successful outcome in your case. Talk to a Lawyer.
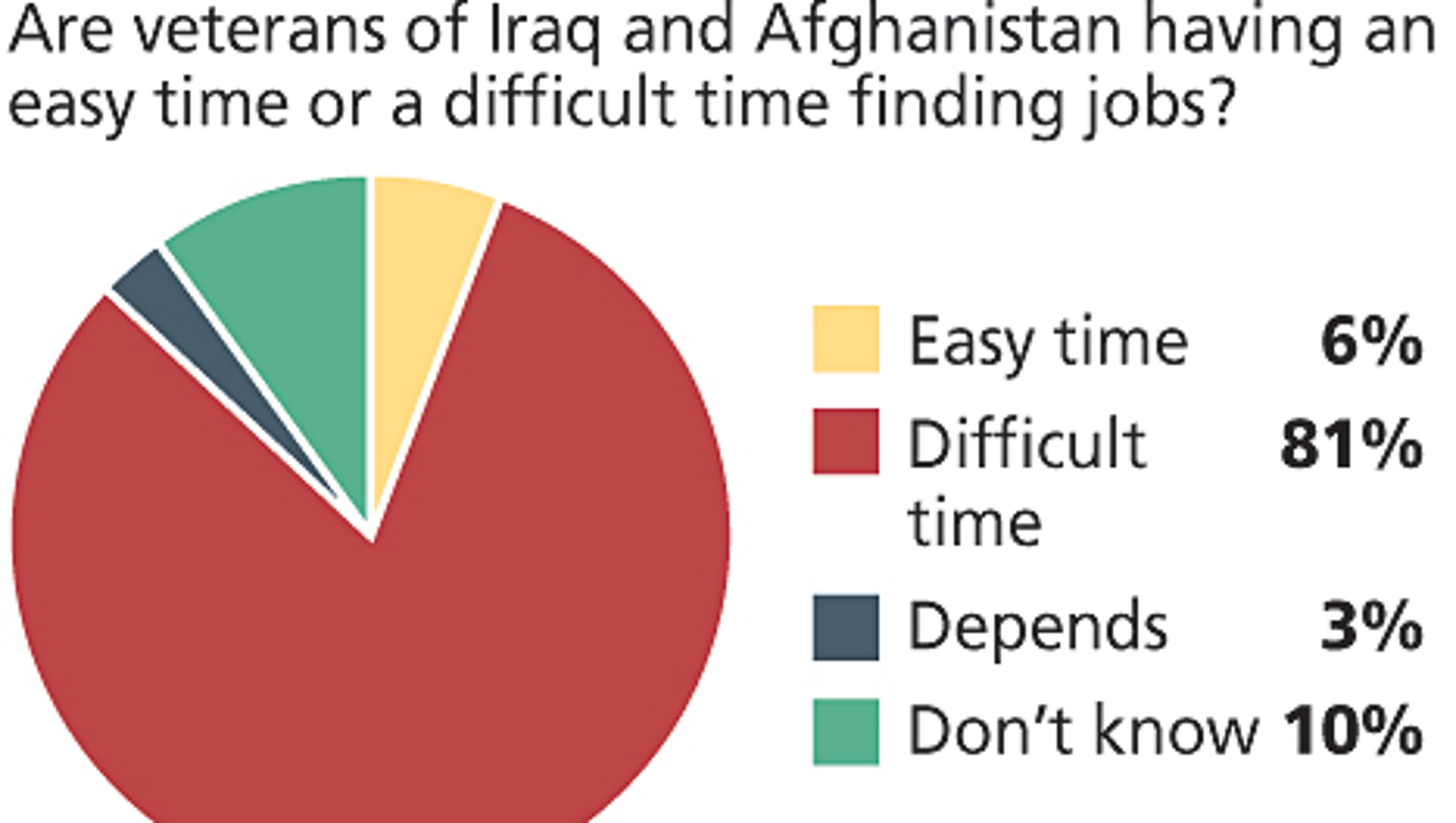
What are the chances of winning an appeal with the VA?
Historically, the VA disability appeal success rate for veterans has been considered relatively low. According to the Board of Veterans Appeals (BVA) Annual Report for Fiscal Year 2021 recorded a 32% acceptance rate for legacy decisions and 38.1% for AMA decisions.
What happens when a VA appeal is granted?
Set up direct deposit: When a Veteran wins an appeal, the VA will send an award packet. The Veteran can then sign up for a direct deposit for their benefits. If a Veteran does not set up direct deposit, the VA will send monthly paper checks to the Veteran's last known address.
How long does a VA appeal take 2022?
about 11-12 monthsHow long does a BVA direct review appeal take? In 2022, a direct review appeal to the VA Board of Appeals takes the board about 11-12 months to come to a decision from when you first file an appeal.
How long does a VA compensation appeal take?
Unless you are filing a fully developed claim, or your appeal is so simple that the Board of Veterans' Appeals (BVA) can issue an award within 30 days, your initial claim can take anywhere from 9-15 months to process. The VA appeals process timeline for an informal claim is typically within 9-12 months.
Do you get back pay for VA disability appeal?
If I win my VA disability appeal, do I still get back pay? If your VA disability appeal is approved, you should get back pay all the way back to your effective date. Most veterans will find their effective date is the date they filed the claim.
How does VA calculate back pay?
So if the veterans received $100/month for the 20% rating but should have received $150/month for the 30% rating, the VA Disability Back Pay will be $50/month (150 – 100 = 50) times the number of months the change applies.
How many times can you appeal a VA disability claim?
There is no limit to how many times you can appeal different applications. You should submit new evidence with each claim. The best way to win an appeal is to do it right the first time. The VA disability appeals process can take years.
Why do VA appeals take so long?
The politics of pending claims The problem with trying to close out disability claims quickly is that more mistakes are made on the initial Rating Decisions, and thus more veterans will want or need to file an appeal. Thus, the backlog of cases simply shifts from the initial claim level to the appellate level.
Whats the longest a VA claim can take?
The VA publishes its claims processing timelines, and in general, you can expect to receive a VA rating decision within 90 to 120 calendar days (3-4 months) from beginning to end. However, VA disability claim decision timelines can vary drastically—from just a few days to two years or more.
How long does it take to get a decision after BVA?
BVA Decision Issued: The average wait time for a Board decision is 248 days. Potential BVA Remanded Decision: Wait times will vary greatly. Appeal to Court of Appeals Veterans' Claims (CAVC): If you are denied at the BVA, you may be able to appeal to the CAVC.
How can I speed up my VA appeal?
How Do I Expedite My VA Claim? If you fall into one of the categories listed above, you can apply to have your case expedited. To do so, you will need to fill out a Priority Processing Request via VA Form 20-10207. The five-page form contains instructions for applying to have your claim expedited.
What happens when you appeal a VA disability claim?
If you asked for a DRO appeal, the VA will write to you and ask you for more information about what parts of the decision you would like the VA to review. If you didn't ask for a hearing, the DRO will make a decision based on the records on file for your claim.
How many times can you appeal a VA decision?
There is no limit to how many times you can appeal different applications. You should submit new evidence with each claim. The best way to win an appeal is to do it right the first time. The VA disability appeals process can take years.
What happens at VA disability appeal hearing?
To start, the Veterans Law Judge will ask you to take an oath that you'll tell the truth during the hearing. You'll then: Tell the judge why you think you qualify for the VA benefits in your claim. Answer any questions the judge may have about your appeal.
What percentage of VA remands are approved?
Fiscal Year 2018: Board of Veterans' Appeals Approval Rate Of this 35.75 percent, 19.61 percent (16,729) were allowed without any remanded issues, while 16.14 percent (13,763) were allowed with at least one remanded issue. Within the 85,288 decisions completed in FY 2018, VA decided on a total of 253,450 issues.
What is the VA decision review process?
VA decision reviews and appeals. The legacy VA appeals process has changed to the decision review process. If you disagree with a VA decision dated on or after February 19, 2019, you can choose from 3 decision review options (Supplemental Claim, Higher-Level Review, or Board Appeal) to continue your case.
How long do you have to file a decision review?
In most situations you have one year from the date on your decision letter to request a decision review. The deadline to file may be different if you have a fiduciary claim or a contested claim, or you’re filing a Supplemental Claim.
Who can help you request a decision review?
A Veterans Service Organization or VA-accredited attorney or agent can help you request a decision review.
Can you submit new evidence to a higher level review?
You can’t submit new evidence with a Higher-Level Review. Decision review option: Board Appeal. You can appeal to the Board of Veterans’ Appeals and have a Veterans Law Judge review your case. After you request a decision review. Find out what happens after you request a decision review. Contested claims.
Can you file a Supplemental Claim?
You can file a Supplemental Claim if you have new and relevant evidence that we didn't have when we reviewed your case before.
Why Hire a Lawyer to Help with Your Veterans Affairs Disability Claim Appeal?
The VA disability compensation system is supposed to be veteran-friendly. But, the reality is that the rules and regulations governing the claims process can be confusing and frustrating for everyone involved.
What to do before VA appeal?
Before a veteran goes through the VA appeals process, the veteran should understand why the VA denied his or her claim. The veteran’s appeal must directly address the VA’s reasons and consider the evidence and law that the VA cited in its decision. Our experienced VA disability lawyers can help by identifying why the VA denied your claim and what new arguments or evidence will help win an appeal.
What is the VA's disability rating?
The VA uses Diagnostic Codes for just about every imaginable injury or illness, one of which will be assigned to the service-connected disability. Each Diagnostic Code has an associated rating schedule that sets forth rules for rating a disability. In some cases, the VA uses additional rules, regulations and caselaw to rate disabilities. The VA will rate a veteran’s disability in 10 percent increments. If the VA determines that a veteran is not at least 10 percent disabled by a service-connected condition, it will assign a 0 percent rating, meaning the veteran will not receive any monthly compensation even though service connection was granted.
What does the VA look for in a medical opinion?
Poorly formed medical opinion. The VA will look for certain information when reviewing current medical records from a VA doctor or a private physician. When a doctor provides a medical opinion to the VA must rationally explain his or her opinion on the extent of the veteran’s disability and whether the disability is related to service. The VA looks for certain language and phrasing. If the doctor’s medical opinion lacks this language, the evaluator may deny the claim. Our experienced VA disability attorneys can help make sure that the medical evidence in your file contains the necessary legal language.
Can disabled veterans appeal VA decisions?
The VA provides multiple opportunities for disabled veterans to appeal its decisions. But an appeal must address the initial problem — what kept your claim from being approved in the first place.
Can a veteran be denied a disability claim?
The VA will likely deny a claim if a veteran fails to provide current medical records of examination, diagnosis and treatment for a specific condition or a group of specified conditions that constitute a disability. Sometimes a statement by the veteran about his or her current symptoms is enough, or will convince VA to provide an examination to develop your claim.
Can you appeal a VA decision?
You have the right to appeal any decision by the VA that you think is incorrect.
What is the BVA in VA appeals?
If you appealed to the Board of Veterans Appeals (BVA), the BVA is required to include in its decisions a discussion of the facts and law on which the decision is based. You will need an attorney's help to check whether the BVA failed to properly address medical or lay evidence that helped your claim. Consult with a VA disability attorney to determine if this is a basis for appeal in your case.
What to do if the VA denies your appeal?
If the BVA denies your appeal, your options are to bring an appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims, ask the BVA to reconsider its decision, or file a reopened claim at the VA Regional Office. At this stage, it's best to have the assistance of a VA disability attorney to help you determine the best course of action.
Why is the VA required to provide a medical exam?
The VA is required to provide this exam when there isn't sufficient medical evidence in the file and there is: evidence that you have a current disability.
Does the VA have to adhere to the laws?
Sometimes, at the Regional Office or at the Board of Veterans Appeals (BVA), the VA fails to adhere to the laws and regulations that govern its operations. When this is the case, the oversight of the U.S. Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims may be necessary to obtain a successful outcome in your case.
Can you win an appeal against a VA disability claim?
You may be able to win an appeal if you can show that the VA made a mistake on your claim; for instance, the VA evaluated your disability under the wrong code in the Schedule of Rating Disabilities, which gave you a lower rating. Sometimes veterans are denied benefits because of procedural mistakes made by the VA.
Who Can Represent Claimants in Cases Before the VA?
Lawyers or Agents must be accredited in order to represent claimants before the Department of Veterans Affairs. The accreditation process exists to ensure that veterans and their family members receive skilled and informed representation throughout the VA claims and appeals process.
How Can Veterans Find VA-Accredited Lawyers or Representatives?
VA hosts a searchable database where veterans can look for accredited representatives. The database includes accredited VA disability lawyers, claims agents, or VSO representatives. Additionally, those seeking representation may also visit their local Regional Office for assistance.
How Do Accredited Representatives Get Paid?
Typically, accredited veterans’ advocates charge a contingency fee based on retroactive benefits recovered. This means that if a claimant is awarded retroactive benefits, based on eligibility stemming from a previous date in time, then the veteran’s advocate would receive a percentage of those retroactive benefits, according to the agreement entered into between the claimant and the representative.
What Are Some Red Flags to Watch Out For When Hiring Lawyers or Representatives?
The individual is not accredited – Individuals may not legally represent claimants in cases before VA unless they are accredited.
Why are veterans organizations beneficial?
Organizations like these can be very beneficial to veterans because of their experience and their services are free of charge. VA-accredited attorneys and claims agents typically represent claimants once VA has issued a rating decision on the veteran’s initial claim.
What happens if a veteran outsources their legal work?
They outsource their legal work – If a representative outsources their legal work, they may not be giving the case the full amount of attention it requires. Veterans may also become frustrated when speaking with their representative if they are not knowledgeable about their case, since the legal work has been outsourced.
What are VA accredited individuals not allowed to do?
VA-accredited individuals shall NOT: Evade a rule of conduct “through the actions of another;”. Engage in deceitful, fraudulent, misrepresentative, or dishonest conduct; Violate any provisions included in Title 38 United States Code, or Title 38, Code of Federal Regulations; Charge, solicit, or enter an agreement for unreasonable or unlawful fees;
How much did the Department of Veterans Affairs spend on settling cases?
In 2014 and 2015, the Department of Veterans Affairs spent nearly $6.7 million to secretly settle cases with hundreds of employees who were either fired or forced into retirement due to inadequate performance, according to a USA Today investigation.
How many cases did the VA rescind firing orders?
In 126 cases, the VA agreed to “rescind firing orders and allowed employees to resign or retire instead.”. And in 82 cases, “the VA said it would purge negative records from employees’ personnel files.”.
How much did a VA radiologist get paid?
In another case, a VA radiologist was paid $42,000 of unused sick and leave pay and allowed to resign after the agency found that he had misread “dozens of CT scans” at a VA hospital in Spokane, Washington. That doctor left the VA with a clean reference.
Who was the podiatrist that resigned from the VA?
In one case, Dr. Thomas Franchini, a VA podiatrist, was allowed to “quietly resign” after it was concluded that in 88 cases he had made mistakes that harmed veterans at the VA hospital in Togus, Maine.
Who was paid money after being removed from the US government?
In an exhaustive report published on Oct. 11, USA Today cited numerous instances in which problem employees — including doctors, nurses, and other medical workers — were paid substantial sums of money upon their removal from the agency.
Does the VA report podiatrists?
The VA also said in response to the USA Today report that it will review its policy of reporting only some medical professionals to the national data bank. Currently, the VA does only reports certain types of medical providers, not including podiatrists.
Did the VA conceal the reasons for separation?
In many cases, the VA agreed to conceal the reasons for their separation, and even expunged records of poor performance. While USA Today was only able to pull data from 2014 and 2015, the report exposes how VA protocols for firing medical staff who have committed negligence and misconduct allows many to secure employment in ...
How to value damages in an employment discrimination case?
One reasonable way to value damages in an employment discrimination case is to see what amounts of damages have been awarded in other cases for emotional distress. This does not create a hard and fast rule, because damage awards for emotional distress very much depend on the circumstances of each case and how the individual employee has been ...
What was the award for emotional distress in Sebek v. Attorney General?
Sebek v. Attorney General, EEOC Appeal No. 07A00005 (March 8, 2001) ($200,000 award for emotional distress). The Administrative Judge's award of $200,000 was upheld by the Commission because the agency failed to provide the Commission the evidentiary record that was before the EEOC Administrative Judge.
What was the award for emotional distress in Linehan v Marion County?
Linehan v. Marion County Coroner's Office, EEOC Appeal No. 1120080001 (August 24, 2009) ($200,000 award for emotional distress). Award based on the emotional distress Complainant suffered from being demoted and fired, and from having his name besmirched in the press, all of which resulted "in months of treatment and counseling." Complainant did not submit medical records in support of the emotional distress claim.
What was Fonda Wall v. Department of Justice?
Fonda-Wall v. Department of Justice, EEOC Appeal No. 0720060035 (July 29, 2009) (The Commission increased an Administrative Judge's award for emotional distress from $150,000 to $200,000). Complainant was in constant fear of the supervisor's retaliatory acts. The rumors about her mental health were detrimental to her reputation. The Agency's actions caused her to be transferred and suffer in her family and financial life. Complainant's emotional harm manifested itself into physical harm over a period of 8 years. In addition to the $200,000 emotional distress award, EEOC awarded pecuniary damages for wear and tear on Complainant's vehicle in the amount of $ 8,859.16; trailer rental and storage costs in the amount of $ 3,484.19; moving expenses in the amount of $ 1,136.00; lodging costs in the amount of $ 244.08; lost profit on the sale of Complainant's home in the amount of $65,600.00; tutoring costs for Complainant's children due to readjustment after being involuntarily moved twice in the amount of $ 32,000.00; attorney's fees incurred for child custody issues arising from Complainant taking children out of state in the amount of $ 3,000.00; cell phone costs in the amount of $ 4,628.59; fees paid to a special advocate for Complainant's children in the amount of $ 5,000.00; plane fare for children to visit their father in her former work location in the amount of $1,289.00; office supply costs in connection with this complaint in the amount of $3,000.00; and past and future psychological care for Complainant's children's separation anxiety from their father and stepfather in the amount of $12,996.60.
What was the outcome of McCormick v. Department of Justice?
McCormick v. Department of Justice (Federal Bureau of Investigation), EEOC Appeal 0720100040 (November 23, 2011) ($200,000 award for emotional distress ). The Commission held the Agency's inept actions to accommodate complainant's disability were not in good faith. The Agency engaged in egregious, substantial discriminatory and retaliatory conduct that increased the physical pain and damage to complainant's neck and shoulder, and caused her to suffer severe depression. The Agency's negative memorandums circulated about complainant caused her emotional distress in that she feared the Agency was trying to fire her rather than accommodate and help her. The emotional distress led to permanent spasms that further damage to the discs in her back. Complainant suffered from migraines, lack of sleep, and severe and chronic pain. Her professional reputation was damaged by the portrayals as an insubordinate employee who refuses to do assignments. Complainant suffered a loss of enjoyment of life that is ongoing; changes in her demeanor, outlook, and physical and mental conditions that imperiled her marriage, hindered her ability to properly care for her young child; created a serious and potentially permanent rift with a child in college. She has withdrawn socially from friendships.
What was the award in Munno v. Department of Agriculture?
Munno v. Department of Agriculture, EEOC Appeal No. 01A01734 (February 8, 2001) (The Commission increased an award of $150,000 in emotional distress to $250,000). Complainant's serious psychological and emotional injuries required treatment for an indefinite period. The Complainant was a manager whose ongoing emotional injury was extreme, but who was capable of performing her duties and qualified for promotion to a senior management position.
Who is involved in settlement negotiations?
While these are statutory guidelines that courts will follow in issuing awards, and while they may serve as benchmarks or guidelines in settlement negotiations, ultimately, settlement negotiations are between the employee, the employer, and their respective attorneys. Consulting with your attorney regarding the details of your particular situation and the value your claim may have is therefore always an important step to take prior to filing any lawsuit.
How does the identity of an employer affect settlement?
The Employer: Certainly, the identity of the employer itself will also make a difference in the amount likely to be recovered in a particular case. Some employers, for example, tend to be more litigation-oriented and less inclined to settle a case, while others are more inclined to make settlement offers fairly quickly. Additionally, the larger an employer is in terms of size, the greater the chances are that a larger settlement is likely. On the other side of the coin, if the employer is very small or not very financially profitable, the chances of a significant settlement are much lower.
What is the goal of a discrimination lawsuit?
The goal of any lawsuit is, of course, to try to make the victim of the discrimination “whole” – at least to the extent that it is possible to do so. Nevertheless, there are certain factors that your attorney may consider in helping you to place an estimated value on your case. Some of these factors include:
Why is it impossible to get exact numbers of settlements?
Again, these are approximations. It is impossible to get an exact number, because many settlements are not revealed to the public.
What is settlement based on?
In most cases, the settlement you would receive is calculated based on your “damages”, the losses you incurred as a result of the wrongful termination. These damages need to be proven with documents for them to be taken seriously by a court or jury, and the employer.
How to resolve a dispute with an employer?
Dispute resolution usually runs through 3 phases: 1 Talking face to face: The first form of dispute resolution is a conversation. In fact, the prerequisite for many EEOC claims is first notifying the employer of a discriminatory behavior taking place. 2 Mediation: When face to face communications is unsuccessful, a mediator may be hired to help the parties arrive at a solution. The mediator offers an opinion on the case, but has no official say in it’s outcome. The mediator’s role is simply to bring the parties together and help them solve their differences.#N#Some courts require mediation, before a lawsuit is filed. 3 Arbitration: This method of resolving a dispute is similar to mediation, but also different. It is similar in the sense that the conflicting parties meet and strive to come to an agreement. However, it is different because the arbitrator will make a legally binding decision in the end.
How long does it take to get back to pre discharge pay?
Labor market studies have shown that it takes a person 3-5 years to catch up with pre-discharge salary levels, meaning that front pay may be awarded calculating for this difference.
What is the average fee of a lawyer?
The average fee of lawyers is around 30% of the settlement received. Even if you deduct this amount from the final settlement, you’ll still be left with more money than if you went at it alone.
Is an out of court settlement a good idea?
An out of court settlement is usually the best case scenario for both the employee and the employer . Providing an average out of court settlement for wrongful termination cases is not possible, simply because public disclosure of settlements is obligatory only in specific cases (EEOC, when the employer is a government body and ...
Do benefits have to be included in economic damages?
Benefits are a substantial part of most workers’ compensation packages, so they need to be included in the economic damages calculations.
