
John Lupala 3 has seven recommendations for neighborhood design in informal African cities: (1) contain city sprawl; (2) create tenure systems through land pooling and replotting; (3) effect participatory and incremental regularizing of “informal urban types” and properties; (4) implement localized planning and improved information management systems; (5) identify appropriate housing forms for the city’s future; (6) reduce plot sizes; and (7) regularize and improve exterior public spaces.
Full Answer
What is an informal settlement?
Informal settlements are residential areas where (UN-Habitat, 2015b; Brown, 2015): inhabitants often have no security of tenure for the land or dwellings they inhabit ‒ for example, they may squat or rent informally; neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure;
How to ameliorate informal settlements in LMICs?
As a consequence, to ameliorate informal settlements, local governments in LMICs have commissioned remediation plans from architectural and urban planning firms, many of which are from high resource countries.
What challenges do home-based workers in informal settlements face?
Home- based workers also face challenges to entrepreneurial activity. Women in informal settlements spend more time and energy accessing basic services than other urban counterparts, limiting their ability and time to earn through paid employment.
What can we learn from Kigali about improving informal settlement design?
For example, in Kigali, some 42.4% of the population is under 15 years of age, which means improved informal settlement designs should anticipate multi-child households and include public recreational spaces, day care venues, schools, and footpath safety.
How many people will live in slums by 2050?
What is Molokaone's community organization?
About this website
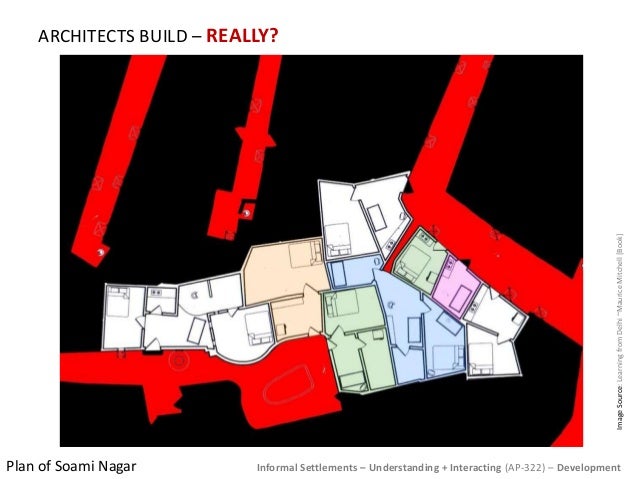
How do you develop an informal settlement?
Additionally, Janice Perlman4 sets forth eight recommendations for the improvement of informal settlements: (1) provide a variety of housing options in regards to tenure and payment, such as short-term rental, long-term lease, cohousing, and financed purchase; (2) invest in education, healthcare, and social services ...
What materials are used to make informal settlements?
Building materials commonly used were timber, bricks, tiled, bamboo, timber board and ceramic. However, since the settlement areas are surrounded by the river, the houses and the dwellers regularly hit by the floods.
What are the 3 biggest problems of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management.
What are examples of informal settlements?
Common categories or terms associated with informal housing include: slums, shanty towns, squats, homelessness, backyard housing and pavement dwellers.
What are the causes of informal settlement PDF?
According to UN-Habitat (2015:2), informal settlements are caused by a range of interrelated factors, including population growth and rural-urban migration, lack of affordable housing for the urban poor, weak governance (particularly in the areas of policy, planning, land and urban management resulting in land ...
What is the hypothesis of informal settlement?
The hypothesis is novel as it suggests that enforcement of the law through evictions of informal settlements and curtailment of informal urban development leads to compromised livelihood for low-income groups. Consequently, the study argues that modes of informal urban development should be accepted.
What are the characteristics of informal settlements?
Characteristics include inadequate access to safe water and sanitation, poor quality of housing, overcrowding, and insecure residential status.
What is another word for informal settlement?
Shanty town Sometimes called a squatter, informal or spontaneous settlement, shanty towns often lack proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity, hygienic streets, or other basic human necessities.
What is the biggest informal settlement in South Africa?
SowetoThose living in informal dwellings – defined as a wood and iron structure – have decreased slightly from 16.2% in 1996 to 13.0% in 2016....These are the 20 biggest townships in the country (Stats SA, 2011)#1TownshipSoweto2011 Population1 271 628Neighbouring townJohannesburg19 more columns•Aug 14, 2016
What are the conditions and problems in informal settlements?
Moreover, informal settlements are space where the neighborhood effects related to poor sanitation, overcrowding, poor housing, physical hazard, pollution, and poverty exposed the dwellers to everyday health risks and keep them in a “risk trap”.
What are the advantages of informal settlement?
It offers choice, it gives people what they want, it enables individual creativity and it is affordable. It is also simple to build and easy to use. So, a powerful brand — the informal settlement — is in town. And it's reshaping the city.
What is the problem of informal settlers?
Informal Settlements have been associated with many social problems such as high levels of poverty, illiteracy and crime. Not forgetting the inadequate local services, especially healthcare, education and youth facilities.
What are characteristics of informal settlement?
Characteristics include inadequate access to safe water and sanitation, poor quality of housing, overcrowding, and insecure residential status.
What is the main reason for the development of informal settlements?
A number of interrelated factors have driven the emergence of informal settlements: population growth; rural-urban migration; lack of affordable housing; weak governance (particularly in policy, planning and urban management); economic vulnerability and low-paid work; marginalisation; and displacement caused by ...
What causes informal housing?
1 Poverty. According to the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), poverty and social ostracism are the primary causes of informal settlements in most nations. Governments around the world grapple with fiscal deficits and therefore promote and subsidize industrial sectors that can revitalize the economy ...
How does informal settlements affect the environment?
A lack of basic needs and services leads to informal settlements having impacts on the environment. This includes inadequate sanitation which leads occupants to pollution, the use of coal and biomass fuel for lighting, causing air pollution and in turn contributing to the emission of greenhouse gases.
A QUICK GUIDE TO DEALING WITH COMMON INFORMAL SETTLEMENT PROBLEMS
settlement in particular. Propose the creation of a joint committee to research further and to identify options. 3.3 - 3.5 Agree on goals and guiding principles.
Smart Solutions for Slums - Cordaid International
Slums are areas full of potential. They provide a wealth of creativity, talent and entrepreneurship. Slum dwellers are consumers that demand decent and affordable basic services like housing and sanitation. Women and young people strive for a job or business which generates income for their families. Cordaid Urban Matters develops and provides smart solutions to improve the living conditions ...
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR SLUMS - Cordaid
Sanitation The Smart Solution Sanitation improves the hygienic conditions in slums and creates busi-ness opportunities. Cordaid supports the setting up of a local business that
What is informal settlement?
Informal settlements are residential areas where ( UN-Habitat, 2015b; Brown, 2015 ): inhabitants often have no security of tenure for the land or dwellings they inhabit ‒ for example, they may squat or rent informally; neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure; housing may not comply with planning and building regulations, ...
What are the factors that contribute to the emergence of informal settlements?
A number of interrelated factors have driven the emergence of informal settlements: population growth; rural-urban migration; lack of affordable housing; weak governance (particularly in policy, planning and urban management); economic vulnerability and low-paid work; marginalisation; and displacement caused by conflict, natural disasters and climate change ( UN-Habitat, 2015b ).
How does informal settlement affect women?
For women, for example, this can heighten barriers they face in accessing livelihood opportunities. Home-based workers also face challenges to entrepreneurial activity ( Chant, 2014 ). Women in informal settlements spend more time and energy accessing basic services than other urban counterparts, limiting their ability and time to earn through paid employment ( UNFPA, 2007 ). In addition, the prevalence of male-biased land tenure policies and restrictions on women’s rights to own property decreases the likelihood of alternative housing options. Poor quality housing, or eviction and homelessness, can also increase the risk of insecurity and sexual violence ( Chant, 2013; McIlwaine, 2013 ).
What are neighbourhoods lacking?
neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure; housing may not comply with planning and building regulations, and is often situated in geographically and environmentally sensitive areas (see Topic Guide on Provision and Improvement of Housing for the Poor, Patel, 2013). A number of interrelated factors have driven ...
What is informal settlement?
Informal settlements, housing that has been created in an urban or peri-urban location without official approval, make up a large portion of Johannesburg’s urban poor. They are repeatedly displaced by formal development projects, only to re-emerge elsewhere.
How does informal urban development manifest itself in your day-to-day work?
On the one hand we have become less precious about architecture as a highly refined object as well as more strategic, even opportunist, in how we apply our energies.
What made you decide to found 26’10 south Architects? Was there a particular moment that sealed the decision for you?
We met in 2003 while working on an exhibition about Johannesburg for the Bienal de São Paulo. We clicked as a couple and as like-minded professionals with working and studying experiences outside South Africa. Thorsten spent his internship at OMA in Rotterdam and Anne studied at the Academy of Applied Arts in Vienna where she completed her diploma under Zaha Hadid.
Can informal settlements be solved?
While the structural problems at the root of informal settlements cannot easily be solved they can be unpacked and made visible – as cities in the making which, despite severe deprivations, outperform environments created for the urban poor by educated professionals.
Is 26'10 South Architects formal or informal?
The word informal is often seen as the opposite of what is formal and correct. That is reason enough for many to avoid the concept in their businesses. Yet 26’10 south Architects don’t work against informality but with it. The company has produced works stretching from housing projects in townships to development plans for large parts ...
Could you tell us about the Weltstadt Project in which you were involved?
Partaking in the Weltstadt project alongside a range or students, academics and young professionals was very interesting for our practice in that we were recognized as working experts (as opposed to theorists) in the field of urban informality. As a knowledge management project it exposed us to less of the typical risks associated with construction and the insights gained could be plowed back into our practice.
How many people will live in slums by 2050?
It is estimated that the 1 billion who live in slums and informal settlements will grow to 3 billion by 2050 without more action. Rose Molokoane, the coordinator of Slum Dwellers International in South Africa brought home her country’s experience in dealing with huge inequality twenty-five years after apartheid was abolished.
What is Molokaone's community organization?
Molokaone and her community organization is pushing for inclusion, integration and for those living in informal settlements to be able to own their own homes. “Our government is talking about integration and everybody moving from the settlements to the city.
What did Fiori and Brandao argue about urbanism?
Fiori and Brandao (2007, p.3) argue that attempts of spatial designers in this period such as mass housing, slum eradication and modernist urban planning were driven by the belief that architecture and urbanism could ‘promote development and shape social relations’.
What is the overlay of inappropriate urban typologies that cannot deal with the scale of the housing problem?
In South Africa, the overlay of inappropriate urban typologies that cannot deal with the scale of the housing problem has resulted in a constant weaving of formal and informal as people try to survive in the divided cities. 1.THE UNITED NATIONS MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS AND DEFINING AN INFORMAL SETTLEMENT.
What is urban design?
Urban design, like capacity development also seeks to work at different physical project scales and societal levels at one time and through one process. Without a macro, mesa and micro understanding there will be limits to any truly sustainable lift in capacity, or any successful urban design scheme.
What is design exploration?
The design exploration makes proposals for interventions that can become part of an open discussion and design process involving community, government and internal and external experts in Johannesburg in mid 2008. In this phase, the urban design vision will be challenged and reworked by government and community.
What is the appendix of a design vision?
The appendix also sets out the steps that will be taken to move the design vision back into community and government ownership. The appendix also proposes evaluation methods for this project based on those used by the United Nations, World Bank and NGOs for capacity development projects.
What is informal settlement?
Hence, settlements can range from small camps to towns to villages to large developed cities. Therefore informal settlements can be defined as unplanned, un-owned, piece of land on which people of the deprived class occupy illegally and carryout construction there. The occupants of the accommodating areas neither have any legal claim nor do they follow any building or construction rules and regulations. Whereas UN defines these informal settlements or slums as the area having “five Deprivations” which are as follows: “Clean water, improved sanitation, sufficient living area so as not to be over-crowded, durable housing, and secure tenure.”1
How did informal settlements affect Pakistan's economy?
For the purpose to keep it brief the city of Karachi has been taken under study. Main variables which are considered includes; population living in slums, total labor force of slums, labor force employed, labor force unemployed and the nature of Pakistan’s economy. Moreover through the research it has been deduced that due to the ever increasing urbanization and urban sprawl the delivery of provision of adequate housing facility is not being hampered due to which lower income class is bound to live in the informal settlements. The research methodology adopted for this paper is secondary data. Most of the data has been taken from World Bank while the remaining has been taken from Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Descriptive analysis has been applied in order to investigate the statistics. The results show that 55 % of the population of Karachi lives in slum areas, with 40% people without jobs and 28% have been dismissed from their occupations, not only this the GDP of the country has been falling since last 10-15 year and has shrunk to 5.4. The paper provides certain recommendations with which the problem can be eradicated. Certain policy options, political steps and government intervention can help solve the problem.
What are the negative effects of the Karachi slums?
He has mentioned various negative effects of the slums which mainly include the increased terrorist activities, thefts, and extremist fragmentation. According to the author the fueling of the terrorists grown in the slum areas cause serious consequences and does not only effect the people living their but also have some sort of socio-economic, environmental, and political costs.
Why are there slums in cities?
These settlements are imposing threats to the sustainable development of every city and have serious implications on the political, economic, social, and cultural facets of the society. These slums have increased due to a number of reasons which mainly include population growth, intensive rural urban migration, lack of proper housing facilities along with adequate provisions of houses to every citizen of the country, economic weakness, lack of proper policy making, poor urban management and planning, low wages of the blue-collar workers (due to which they are unable to afford the basic necessities), refugees due to natural disaster and wars (e.g. afghan refugees in Pakistan), and last but not the least the class differences created by the society. It can also be seen the government does not acknowledge any sort of these under-developed areas within the developed cities and neither has it worked to improve the situation. On the other hand local governments either oppose these settlements or they dislodge them; it shows rigidity and reluctance towards it and does not take the case of housing requirements up to the top level concerned authorities. Incarnating in the slums has adverse effect on the people living there. This hypothesis can be evident from the example being followed as stated by UNFPA: “For women, this can heighten barriers they face in accessing livelihood opportunities. Home- based workers also face challenges to entrepreneurial activity. Women in informal settlements spend more time and energy accessing basic services than other urban counterparts, limiting their ability and time to earn through paid employment. In addition, the prevalence of male-biased land tenure policies and restrictions on women’s rights to own property decreases the likelihood of alternative housing options. Poor quality housing, or eviction and homelessness, can also increase the risk of insecurity and sexual violence.”
Why is poverty increasing in slums?
From the above mentioned data it can be devised that the population as well as the number of households in the slum areas are increasing day by day and it is expected that the urban poverty will also increase due to rapid urbanization and no proper planning and development mechanism adopted by the local government as well as the national/ federal government.
How does illegal settlement affect economic development?
Gerald Myoro in his article, The Impact of Illegal Settlement on Economic Development, writes that the informal settlements are a problem for the society that inhibits the economic development of any country, region or city. He says that it is also the result of state and local government’s lack of planning and improper policies. Economic development of a country is followed by increased living standards, along with provision of basic facilities to the people. But it can also be seen that both the things are relatively interchangeable, living standards also affect the economic development and vice versa. He argues that economic development is a process
Why is urbanization without growth called urbanization?
This can be named as “Urbanization without growth” because people are continuously moving from internal Sindh to Karachi in order to have access to basic amenities and better living conditions along with job opportunities but they end up living in
How many people will live in slums by 2050?
It is estimated that the 1 billion who live in slums and informal settlements will grow to 3 billion by 2050 without more action. Rose Molokoane, the coordinator of Slum Dwellers International in South Africa brought home her country’s experience in dealing with huge inequality twenty-five years after apartheid was abolished.
What is Molokaone's community organization?
Molokaone and her community organization is pushing for inclusion, integration and for those living in informal settlements to be able to own their own homes. “Our government is talking about integration and everybody moving from the settlements to the city.
