
Full Answer
What are differential settlements?
What are differential settlements? Settlement of the foundation soil is a vertical displacement of the soil surface caused by the workload of the building. During and after the building construction, settlement of the foundation structure is considered normal and acceptable to a certain extent.
How does differential settlement cause cracks in a foundation?
This settlement causes cracking to the foundation since one side of the structure is sinking faster than the other. Differential settlement is the uneven or unequal settling of a building’s foundation. This occurs when the soil under your foundation contracts, expands, or shifts irregularly.
Does clay soil cause differential settlement?
If your foundation sits on clay soil, you are likely to experience differential settlement after some time. Your footing will settle downwards during the dry seasons as the clay shrinks. The bedrock is one of the strongest supports a foundation can have.
What are the signs of differential settlement?
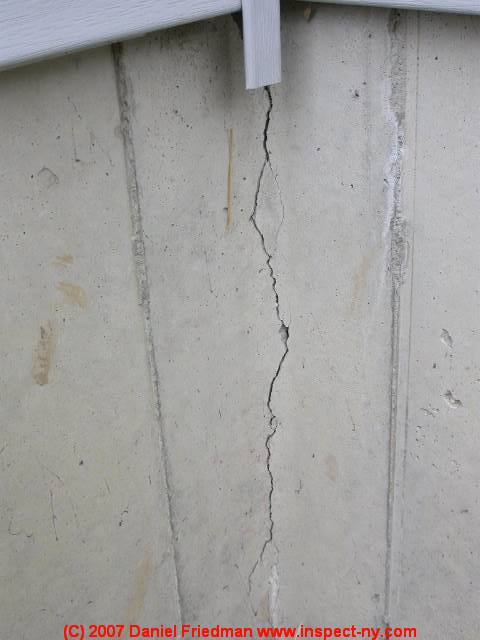
Leaving out extreme cases like the Leaning Tower of Pisa, the most common sign of differential settlements is the occurrence of cracks on the structure at an angle of 45˚, usually around the openings (doors, windows).
How much differential settlement is too much?
The industry standard is 1 inch of differential settlement in 20 feet. Anything greater than this can be considered too much.
What type of foundation is effective for overcoming differential settlement?
A floating foundation is an excellent option to choose to overcome excessive settlements. The compensating foundation reduces the net load on the soil and consequently reduces differential settlement.
How do you fix a settled foundation?
When a foundation is settling, it can be fixed by enlisting a company to lift the foundation and make it level again. To do this, the crew must excavate under the specific areas of your house that are sinking. Then they place piers (sometimes called pilings) directly under the foundation.
What is a differential settlement?
Differential settlement commonly occurs as a result of the non-uniform movement of the underlying soils (soil settlement at different rates). This type of settlement can result in cracking to the foundation, exterior cladding, and interior finishes.
What is the best foundation repair method?
1. Steel Piers. This is the foundation repair that most structural engineers will recommend for your home. This is a solid and proven method of stabilizing a foundation that has started to shift or sink into unstable ground.
Why differential settlement is considered harmful for a structure?
When properly compacted, this fill soil can provide a perfectly solid base for supporting foundations, but when not compacted, the soil may settle and compress unevenly under the foundation, leading to structural damage.
How much is a differential settlement?
Aesthetic and Serviceability RequirementsType of SettlementLimiting factorMaximum SettlementDifferential settlementOne-storey brick mill building, wall cracking0.001 – 0.002 LPlaster cracking0.001 LReinforced concrete building frame0.0025 – 0.004 LReinforced concrete building curtain walls0.003 L15 more rows•Dec 13, 2012
How serious is foundation settling?
The Difference Between Foundational Settling and Problems That said, standard settling is nothing to worry about and often won't have too much of an impact on the foundation and structure of a building. With soil expansion and contraction, it is normal for a part of a building to move a few inches.
When should you walk away from foundation issues?
The most glaring issue has to deal with the foundation. When to walk away from foundation issues? Horizontal or diagonal cracks measuring more than 1/4 of an inch is a good reason to walk away.
How do you calculate differential settlement?
Where this is the case the differential settlement can be estimated by calculating the total settlement for each part of the structure and comparing. This calculation can be done using other spreadsheets included in the Foundation Settlement Calculation Suite.
What is the difference between settlement and differential settlement?
Unlike uniform or “normal” settling, which basically means that the foundation settles at the same rate over its entire footprint area, differential settlement involves a non-uniform movement of the underlying soil, which causes the foundation along with the structure above to settle in an uneven fashion.
What causes the most damage to structural foundations?
Soil movement beneath a home's foundation is the leading cause of structural damages.
What is differential settlement of foundation?
1. Uneven settlement of the soil beneath the foundation of a structure that may lead to “sinking” of different parts of the structure which causes cracks and other structural problems.
What are the different types of foundation settlements?
What is Foundation Settlement? Its Types and CausesImmediate settlement.Primary settlement.Secondary settlement.
What are the methods of minimizing settlement?
Compacting the soil. Draining the soil, in case of cohesive types. Compacting the soil, in case of cohesion less soils. Confining the soil, increasing stiffness.
How many types of foundation settlements are there?
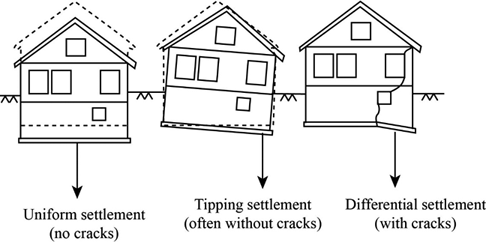
The settlement in the foundation can be classified into two types namely the uniform foundation settlement and the differential foundation settlement.
What Is Differential Settlement?
Namely, this process refers to the uneven or unequal settling of a structure. It happens due to many factors, one of which is the uneven weight distribution of a building. This in turn will make the foundation unable to bear the load of the building as it sinks into the soil, resulting in severe structural damage.
How to prevent differential foundation settlement?
When it comes to differential foundation settlement, the best tip we can offer is to keep an eye out on the soil during construction. Prevention is key here as it can save you from unpleasant situations and more importantly, costly repairs. However, if it’s too late for prevention now, you can look into underpinning the foundation by using foundation piers to improve its stability.
Why does my house settle unevenly?
The soil beneath a structure can also expand, contract, and shift, causing your home to settle uneven ly. The reasons for such soil behavior are many and include drought conditions, floods, tree roots, run-down water lines, and even poor drainage. The first clear signs of differential settlement are cracks in the concrete and the brick veneer as well as hard-to-open doors and windows .
What happens if you settle your foundation?
With time, the cracks will begin to grow, allowing both moisture and pests into the lower level of your home. On the other hand, the doors and windows will be unable to open and close properly. This will also lead to numerous problems such as drops in temperature and poor energy efficiency. However, these are just byproducts of a settling foundation, and the bigger picture is even worse.
Is differential settlement out of nowhere?
Like most problems, differential settlement doesn’t appear out of nowhere. It has its roots in the construction process on which you must keep an eye. Soil plays a major role in differential settlement, so we’re going to take a look at two polar-opposite soil types and explain how both can be behind differential settlement in Alabama and Tennessee.
Does clay expand or shrink?
This first type of soil is not a builder’s best friend. Depending on the weather, clay will either shrink or expand. You could say it’s somewhat similar to a sponge. Clay expands when in contact with water during a wet season while it reduces during a drought. This is the reason why experts call it highly expansive soil. Therefore, if your home is sitting on top of clay, it is more than likely to settle and sink.
What is differential settlement?
This type of settlement can result in cracking to the foundation, exterior cladding, and interior finishes. Additionally, with a pier and beam foundation system, each individual pier may settle at a different rate, which is different than the settlement that would occur to a slab foundation.
How does settlement occur?
Settlement occurs from soil consolidation due to a reduction in voids or spaces between soil particles due to applied loads or changes in moisture content. The loss of moisture in soils causes consolidation. As the moisture takes up volume in the soil, and when the moisture is expelled, the soil loses volume and consolidates.
What is Settlement?
Settlement is the downward movement of the ground (soil) when a load is applied to it. The load increases the vertical effective stress exerted onto the soil. This stress, in turn, increases the vertical strain in the soil. This increase in vertical strain causes the ground to move downward. In fact, most buildings settle over time. However, most building settlement occurs during the first few years after construction, unless there are changes in the drainage patterns around the building, severe changes in weather, or other external factors. Ongoing building settlement is uncommon.
What Causes Settlement of Soils?
Settlement occurs from soil consolidation due to a reduction in voids or spaces between soil particles due to applied loads or changes in moisture content. The loss of moisture in soils causes consolidation. As the moisture takes up volume in the soil, and when the moisture is expelled, the soil loses volume and consolidates. In the opposite circumstance, when there is a buildup of moisture in the soils, smaller clays and silts, which were previously used to fill the voids between larger soil types and provide additional structural support, will drain downwards in the ground when the moisture eventually subsides. This will cause the supporting soil to lose its load-bearing capabilities.
How to level a slab that has settled?
Slabs that have settled can be leveled by the use of mudjacking or polyurethane foam. Mudjacking is the use of flowable concrete or grout and polyurethane foam is a closed cell foam. In both uses, holes are drilled in the settled slab and the flowable fill is pumped through. The pressure exerted through the pumping process raises the slab as well as consolidating the soil to prevent future settlement. Polyurethane foam is typically more expensive than mudjacking; however, it is typically stronger, has a longer life span, will not retain moisture, and the slab can be utilized sooner.
Why do my floors sag?
Sagging Floors. Sagging floors generally occur when a house was built with a pier and beam foundation system. The individual piers will settle at different rates, resulting in the floors that sag at the location of the settled pier.
What is Vertex looking for?
VERTEX is looking for talented individuals to join a highly technical team of forensic consultants, design engineers, construction managers, and environmental scientists.
How much elevation loss can be recovered from a settling foundation?
At first, your foundation may dip a little, say, by 1/2”. But, over time, the sinking may reach severe levels. Usually, only 1/2” to 2/3” of elevation loss can be recovered, so catch it early.
What happens if you delay settling?
A worst-case scenario would be your home could become uninhabitable. Wall cracks could widen. This would create an entry point for insects and rodents. Larger cracks in your walls and foundations could also lead to increased moisture levels, leading to the growth of mold and mildew.
Why is foundation settling so bad?
Because of our moisture sensitive Texas clay soil, foundation settling is a serious problem for many homeowners. Basically, foundation settling occurs when the weight of your home sinks into the ground below. It is most common for settling to occur on the perimeter and then migrate inwards. This is because about 60% of a houses weight is on the perimeter walls.
What to do if your chimney is separating from your house?
If your chimney is separating from your home, have it checked out. It’s likely that your home is experiencing a foundation issue.
Why do houses settle on the perimeter?
It is most common for settling to occur on the perimeter and then migrate inwards. This is because about 60% of a houses weight is on the perimeter walls. If your house or other structures appear to be having settlement issues, have it examined immediately. That is because settling is a common cause of a foundation problem.
How to stop elevation loss?
About a third of the time the problem can be stopped by correcting drainage problems , such as; grading surface drains and french drains. Should the elevation loss be too great, there will be the need for underpinning, which is the installation of piers.
What is differential settlement?
Differential settlement is primary aspect of any building design. It is well known that settlement may occur in the area where soil having low bearing capacity. Foundation gets settled due to load acting on structure, calamity, consolidation, nature of soil ground water table fluctuation, forces.
What happens if all footings settle equally?
If all the footings settle equally, it will not hamper the structure's strength so much but differential settlement will cause serious issues. Differential settlement is basically different footings having different settlement. Differential settlement is primary aspect of any building design.
What happens if the load on two columns is different?
If the load on the two columns is different and if the proportion of the isolated footings doesn't take into consideration settlement issues then differential settlement is going to take place.
What is the solution under the case of isolated foptings?
So, the one of the solutions under the case of isolated foptings is to proportion two close columns in a way that makes the stress under the two footings nearly equal. If the stress is equal then the settlement would be equal ( given the soil property under both columns is the same).
Why does foundation get settled?
Foundation gets settled due to load acting on structure, calamity, consolidation, nature of soil ground water table fluctuation, forces. Even a small amount of differential settlement can cause redistribution of.
How to tell if a foundation is settling?
Over time soil beneath a home will be compromised by rain and changes in climate. The soil can freeze and compact and heat and expand. This will begin to cause sinking or settlement in a foundation. You will even begin to notice these signs in your home! Start looking for long cracks in walls, doors and windows not closing as easily, and brick separation. These could be the beginning signs of a more serious foundation problem.
How to make a building flat again?
You need to find a hard stable layer under neath then pile or micro pile new foundations thren jack the building so its flat again.. Basically put things like big car jacks between new foundation and building base.. The building may need strengthening or repairs internally either because of damage or make it so it can be jacked.. This not simple job.. Needs an experienced contractor and design professional to do..
What is differential settlement?
Differential settlement is the term used in structural engineering for a condition in which a building's support foundation settles in an uneven fashion, often leading to structural damage. All buildings settle somewhat in the years following construction, and this natural phenomenon generally causes no problems if ...
How to tell if a building has differential settlement?
Obvious signs include cracks in the concrete slab or foundation walls supporting the building, or doors and windows that are out of square or hard to open and close.
What is poorly compacted soil?
Poorly compacted soil. Building sites for commercial or residential structures often consist of land that has been artificially leveled and filled for ease of construction. When properly compacted, this fill soil can provide a perfectly solid base for supporting foundations, but when not compacted, the soil may settle and compress unevenly under the foundation, leading to structural damage.
Why does my foundation settle?
Soil that is either too dry or too wet can cause foundation settlement. When moisture builds up, soils saturate and lose their load-bearing capacity. Dry soils shrink in volume. Either situation can cause uneven settling of the foundation.
What is uneven foundation settling?
Uneven foundation settling—differential settlement —is best prevented by careful analysis of the soil before a building foundation is constructed. The best soils for building foundations are nonexpansive —meaning that they contain little clay or silt content. Ideally, the building site will be native soil rather than a site artificially filled with outside soil.
How to tell if a foundation is differentially settled?
Other signs of differential settlement include breaks in seams between drywall panels, tilting chimneys, bulging walls, and exterior stairs that begin to tilt or sink. Some cracking in foundation walls is normal and expected with the passage of time, but when these cracks are wider at the top and narrow or nonexistent at the bottom, the soil beneath the foundation is likely settling at an uneven rate. You may see signs of vertical movement in the building's foundation, such as changes in the relative position of the foundation in relation to patios or concrete slabs edging the building.
Why is there uneven settlement of a foundation?
Uneven settlement of a foundation is always caused by some form of shifting of the soil beneath the foundation, but this shifting can take place for several reasons.
What Causes Differential Settlement?
The main cause of differential settlement is the expansion and contraction of the soil beneath the foundation. The main reasons for this movement are:
How long does it take for a settlement to occur?
This can occur after 2 to 3 years from the completion of the building. Uniform settlement does not bring any severe issue to the building.
What does difference of elevation/settlement of two adjacent columns in a structure give?
The difference of elevation/settlement of two adjacent columns in a structure will give the value of the differential settlement. The difference of elevation across the boundary of the structure can also give a value for differential settlement if there exists any non-uniformity.
Is differential settlement necessary?
Prevention of Differential Settlement. Its not necessary that the differenti al settlement will leave behind a symptom. So its necessary to evaluate the site with utmost accuracy and care. If the site is made of clayey or expansive or contracting soils, a resistance or helical pier system will be the best choice.
Does differential settlement leave a symptom?
Its not necessary that the differential settlement will leave behind a symptom. So its necessary to evaluate the site with utmost accuracy and care. If the site is made of clayey or expansive or contracting soils, a resistance or helical pier system will be the best choice.

Signs of Differential Settlement
- Whether settlement happens in a few months or takes a couple of years, the problems that arise remain pretty much the same. You’re likely to experience multiple issues such as: 1. Wall and Floor Damage 2. Distortions or Warping on your Building’s Frame 3. Foundation Cracks and Deterioration of Slabs 4. Structural instability that makes your building unsafe 5. Sticking Doors …
Restoring A Settling Foundation
- Your sinking foundation needs to be underpinned using piers and there are a few ways to do this. What this does is transfer the heavy load to the stable bedrock and stabilize the foundation.
Differential Settlement Prevention
- When it comes to foundation issues, prevention is vital. Builders should start by assessing the soil to confirm that it is perfect for the type of structure they want to put up. Ideally, you should build a house on soil layers with minimal clay or silt. This way, you will not have to worry about the soil under your foundation shrinking and expandin...