
The political development of the colony began with the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut (1638), a civil covenant by the settlers establishing the system by which the river towns of Windsor, Hartford, and Wethersfield agreed to govern themselves. The orders created an annual assembly of legislators and provided for the election of a governor.
Full Answer
What is the Connecticut Colony?
The Connecticut Colony or Colony of Connecticut, originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which became the state of Connecticut.
When was the first settlement in Connecticut?
Updated October 11, 2018. The founding of the Connecticut colony began in 1636 when the Dutch established the first trading post on the Connecticut River Valley in what is now the town of Hartford. The move into the valley was part of a general movement out of the Massachusetts colony.
What was the form of government in Connecticut before the Fundamental Orders?
For two years before the adoption of the Fundamental Orders, Windsor, Hartford and Wethersfield cooperated under a simple form of government composed of magistrates and representatives from each town, but the towns had no formal instrument of government.
Why did people settle along the Connecticut River?
The settlements that developed along the Connecticut River in the 1630s were the result of a search for fertile farmland more than a search for religious freedom. Thomas Hooker, a prominent minister in Newtown (Cambridge), Massachusetts, harbored clear democratic leanings, but was not an outspoken dissident.
See more

How was the Colony of Connecticut formed?
By 1645, the settlements of Windsor, Wethersfield, and Hartford had united to form River Colony, which became known as Connecticut. New Haven was separate, with its own government. Concerns about attacks by Indians and the Dutch led both colonies to become part of the New England Confederation in 1643.
What plan of government did the Connecticut settlers create?
Adopted in January 1639, the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut stated the powers and limits of government. The preamble of the Fundamental Orders officially formed a confederation under the guidance of God—standing in stark contrast to today's ideas about the separation of church and state.
What was the government in the Connecticut colony?
Connecticut ColonyGovernmentConstitutional monarchyLegislatureGeneral Court of the Colony of ConnecticutHistory• EstablishedMarch 3 163613 more rows
How did Connecticut govern themselves?
…the colony began with the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut (1638), a civil covenant by the settlers establishing the system by which the river towns of Windsor, Hartford, and Wethersfield agreed to govern themselves. The orders created an annual assembly of legislators and provided for the election of a governor.
Who founded the Connecticut Colony and why?
Thomas Hooker, a Puritan minister, left the Massachusetts Bay Colony and founded Hartford, Connecticut. Although a devout Puritan, he advocated the separation of religion from politics.
What was the first settlement in Connecticut?
While Connecticut was first explored by the Dutch, who founded trading posts, the first permanent settlements were made by English Puritans from Massachusetts, starting in 1633.
What is unique about the Connecticut Colony?
Interesting Connecticut Colony Facts: The Connecticut Colony was founded by Puritans and there was no tolerance for other religions. In 1614 a Dutchman named Adriaen Block became the first explorer of the Connecticut Valley.
Who settled in CT?
Though the Dutch began exploring Connecticut as early as 1614, the English were the first Europeans to put down roots in 1636. Under the leadership of Thomas Hooker, a prominent Puritan minister, 100 colonists established a settlement—modern-day Hartford—called the River Colony.
Why did they settle in Connecticut?
In 1636, the English arrived when a large group of Puritans from Massachusetts led by Thomas Hooker founded the Colony of Connecticut at the city of Hartford. They came looking for freedom of religion.
Why did the Connecticut River towns want this as their government?
January 14] 1639. The fundamental orders describe the government set up by the Connecticut River towns, setting its structure and powers. They wanted the government to have access to the open ocean for trading.
What country founded Connecticut Colony?
January 9, 1788Connecticut / Founded
Did the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut establish self government?
On May 29, 1638, Ludlow wrote to Massachusetts Governor Winthrop that the colonists wanted to "unite ourselves to walk and lie peaceably and lovingly together." Ludlow and other principals drafted the Fundamental Orders, which were adopted on January 14, 1639 O.S. (January 24, 1639 N.S.) and established Connecticut as ...
Why was Connecticut called the Constitution State?
The “Constitution State” “Connecticut was designated the Constitution State by the General Assembly in 1959. As early as the 19th Century, John Fiske, a popular historian from Connecticut made the claim that the Fundamental Orders of 1638/1639 were the first written constitution in history.
Was Connecticut a theocracy?
Perhaps not surprisingly, Connecticut was the last state to abolish its theocratic state.
What is Connecticut historically known for?
One of the original 13 colonies and one of the six New England states, Connecticut is located in the northeastern corner of the country. Initially an agricultural community, by the mid-19th century textile and machine manufacturing had become the dominant industries.
Who founded the Connecticut colony?
The Connecticut Colony formally declares war on the Pequot. The New Haven Colony is established by John Davenport, Theophilus Eaton, and a group of fellow Puritans.
Who established the first English settlement in Connecticut?
William Holmes, of the Plymouth Colony, establishes a trading post where the Farmington River meets the Connecticut River. It is arguably the first English settlement in Connecticut and ultimately becomes the town of Windsor. Captain John Oldham establishes a settlement south of the Dutch in Hartford that eventually becomes the town of Wethersfield.
What towns were established in Connecticut?
Settlers establish the towns of Fairfield, Guilford, Milford, and Stratford. John Haynes is chosen as Connecticut’s first governor. Connecticut becomes a founding member of the New England Confederation.
What is the Earl of Warwick's patent?
The Earl of Warwick signs the “Warwick Patent,” a deed of conveyance granting land rights in what is now southeastern Connecticut. The Dutch establish a fort, the House of (Good) Hope, at the modern-day location of Hartford.
Who established the Saybrook colony?
Captain John Oldham establishes a settlement south of the Dutch in Hartford that eventually becomes the town of Wethersfield. Engineer and soldier Lion Gardiner is hired to erect a fort at Saybrook, establishing the Saybrook Colony at the mouth of the Connecticut River.
Who was the Dutch explorer who settled the colony of Connecticut?
Timeline: Settlement of the Colony of Connecticut. Dutch explorer Adriaen Block sails along the Connecticut coastline and up the Connecticut River. The Earl of Warwick signs the “Warwick Patent,” a deed of conveyance granting land rights in what is now southeastern Connecticut.
What was the first state to be executed for witchcraft?
Connecticut becomes a founding member of the New England Confederation. The Saybrook and Connecticut colonies unite. The New London area, originally founded by John Winthrop Jr. , is established. In Hartford, authorities hang Alse Young, the first person in Connecticut to be executed for witchcraft.
When did the Connecticut colony start self-government?
On May 1, 1637 , leaders of Connecticut Colony's river towns each sent delegates to the first General Court held at the meeting house in Hartford. This was the start of self-government in Connecticut. They pooled their militia under the command of John Mason of Windsor, and declared war on the Pequots.
What is the history of Connecticut?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. The U.S. state of Connecticut began as three distinct settlements of Puritans from Massachusetts and England; they combined under a single royal charter in 1663.
Why did Andros ignore Connecticut?
Since Andros viewed New York and Massachusetts as the important parts of his Dominion, he mostly ignored Connecticut. Aside from some taxes demanded and sent to Boston, Connecticut also mostly ignored the new government. When word arrived that the Glorious Revolution had placed William and Mary on the throne, the citizens of Boston arrested Andros and sent him back to England in chains. The Connecticut court met and voted on May 9, 1689 to restore the old charter. They also reelected Robert Treat as governor each year until 1698.
How many Connecticut troops were in Bunker Hill?
In 1775, in the wake of the clashes between British regulars and Massachusetts militia at Lexington and Concord, Connecticut's legislature authorized the outfitting of six new regiments, with some 1,200 Connecticut troops on hand at the Battle of Bunker Hill in June 1775.
Where was the Saybrook colony?
They funded the establishment of the Saybrook Colony (named for the two lords) at the mouth of the Connecticut River, where Fort Saybrook, was erected in 1636. Another Puritan group left Massachusetts and started the New Haven Colony farther west on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in 1637.
What tribes lived in Connecticut?
The Connecticut region was inhabited by multiple Indian tribes which can be grouped into the Nipmuc, the Sequin or "River Indians" (which included the Tunxis, Schaghticoke, Podunk, Wangunk, Hammonassett, and Quinnipiac ), the Mattabesec or "Wappinger Confederacy" and the Pequot-Mohegan.
How long ago did people live in Connecticut?
Evidence of human presence in the Connecticut region dates to as much as 10,000 years ago. Stone tools were used for hunting, fishing, and woodworking. Semi-nomadic in lifestyle, these peoples moved seasonally to take advantage of various resources in the area. They shared languages based on Algonquian.
What was the role of the Connecticut colony in the establishment of self-government in the New World?
Connecticut Colony played a significant role in the establishment of self-government in the New World with its refusal to surrender local authority to the Dominion of New England, an event known as the Charter Oak incident which occurred at Jeremy Adams ' inn and tavern. Two other English settlements in the State of Connecticut were merged into ...
What was the name of the colony in Connecticut?
The Connecticut Colony or Colony of Connecticut, originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which became the state of Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settlement for a Puritan congregation, and the English permanently gained control ...
What was the economy of the British colonies?
The economy began with subsistence farming in the 17th century and developed with greater diversity and an increased focus on production for distant markets, especially the British colonies in the Caribbean . The American Revolution cut off imports from Britain and stimulated a manufacturing sector that made heavy use of the entrepreneurship and mechanical skills of the people. In the second half of the 18th century, difficulties arose from the shortage of good farmland, periodic money problems, and downward price pressures in the export market. In agriculture, there was a shift from grain to animal products. The colonial government attempted to promote various commodities as export items from time to time, such as hemp, potash, and lumber, in order to bolster its economy and improve its balance of trade with Great Britain.
What were the main commodities that the colonial government tried to promote?
The colonial government attempted to promote various commodities as export items from time to time, such as hemp, potash, and lumber, in order to bolster its economy and improve its balance of trade with Great Britain. Connecticut's domestic architecture included a wide variety of house forms.
What was the church in the colony during the American Revolutionary War?
In the middle of the 17th century, the government restricted voting rights with a property qualification and a church membership requirement. Congregationalism was the established church in the colony by the time of the American Revolutionary War.
Which two colonies were merged into one?
Two other English settlements in the State of Connecticut were merged into the Colony of Connecticut: Saybrook Colony in 1644 and New Haven Colony in 1662.
Who was the governor of Connecticut in 1751?
Roger Wolcott was a weaver, statesman, and politician from Windsor, and he served as governor from 1751 to 1754. Oliver Wolcot t was a signer of the Declaration of Independence and also of the Articles of Confederation, as a representative of Connecticut and the nineteenth governor.
The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut were based on a sermon from Thomas Hooker, and were the first written form of government in Connecticut. They mandated how the colonies of Windsor, Hartford, and Wethersfield would govern themselves.
The Royal Charter of 1662
This document did three main things: it consolidated the settlements of Connecticut into one large colony, it declared Connecticut as a royal colony of England (as opposed to a settlement owned by a private company), and it set up a government that will last for over 150 years.
The Dominion of New England
Around 1686, King Charles II became uncomfortable with how independent the colonies were becoming. He issued a charter that combined all of the colonies of New England into one group so that they were easier to control and protect from the growing threat of the French and their Indian allies.
When was Connecticut first settled?
While Connecticut was first explored by the Dutch, who founded trading posts, the first permanent settlements were made by English Puritans from Massachusetts, starting in 1633.
Why was Connecticut called the Provision State?
To George Washington, Connecticut was "The Provision State" because of supplies contributed to his army by Gov. Jonathan Trumbull - the only Colonial governor, incidentally, to support the cause of America’s independence from Great Britain.
What were the main activities of the 17th century colonists?
Agriculture and trade were primary activities of 17th century colonists, but because of limited land Connecticut people quickly turned to manufacturing.
When were the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut adopted?
The Connecticut General Court adopted the Fundamental Orders on January 14, 1639. (The colonists did not follow current conventions for marking a year and, thus, the date on the document itself is listed as 1638.)
When was Connecticut declared the Constitution State?
They are also the reason why, in 1959, the General Assembly officially designated Connecticut as “the Constitution State.”. By Bruce P. Stark; excerpted from Connecticut History and Culture: an Historical Overview and Resource Guide for Teachers (1985), edited by David Roth.
What is the role of the General Court?
The General Court was authorized to adopt and repeal laws, impose taxes, distribute land, apprehend and punish people for misdemeanors, and enact legislation to promote the general good. The General Court was granted, then, all legislative, executive, judicial, and administrative authority.
Who wrote the Fundamental Orders of the Massachusetts Bay Colony?
Roger Ludlow of Windsor, the only trained lawyer in the colony, probably drafted the Fundamental Orders, although he may have been assisted by Hartford residents John Haynes (a former Governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony), Edward Hopkins, and John Steel. The document consisted of a preamble and 11 orders or laws.
Who inspired the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut?
Detail from a facsimile printed in The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, 1934 - Connecticut State Library. The Fundamental Orders, inspired by Thomas Hooker’s sermon of May 31, 1638, provided the framework for the government of the Connecticut colony from 1639 to 1662.
Is Connecticut a constitution?
The matter of whether the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut should be considered a constitution in the modern sense, let alone honored as the first written constitution (as was once claimed), remains a matter of debate. Nevertheless, they served as the basis for government in Connecticut until 1662. They are also the reason why, in 1959, the General Assembly officially designated Connecticut as “the Constitution State.”
How long did the Connecticut colony exist?
The Connecticut Colony and New Haven existed as separate political entities until 1662 , when a charter was granted to the Connecticut Colony. It included a 73-mile-wide swath from Rhode Island to the Atlantic Ocean.
What colonies were in New Haven?
Security was a major concern of the four major New England colonies — Massachusetts, Plymouth, Connecticut and New Haven, all of whom refused to deal with independent-minded Rhode Island.
What colony was founded in the 17th century?
The Connecticut Colony grew over the years and by the middle of the 17th century incorporated Fairfield, Farmington, Middletown, New London, Norwalk, Saybrook and Stratford.
What river did the Dutch claim?
In that year, a small party from Plymouth also entered the Connecticut River. The Dutch asserted their claim to the lands, but the Massachusetts group, instead of retreating down river, sailed farther north and established a trading post at Windsor.
What was the first constitution written in America?
They drafted the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, sometimes cited as the first constitution written in America.
How many people moved from Massachusetts Bay to the West?
In 1635 and 1636, nearly 1,000 people moved from the Massachusetts Bay area into lands claimed by the Dutch in the Connecticut Valley.
Where did the Bay Colony settle?
In 1638, they founded a settlement at New Haven on Long Island Sound, a community intended to be both a trading post and a Bible Commonwealth.
How many towns were there in Connecticut?
Historian Bruce Daniels’s The Connecticut Town: Growth and Development 1635 – 1790 (Wesleyan University Press, 1979) is a terrific resource for understanding how Connecticut came to consist of 169 independent towns. The geographic pattern of settlement by the English (greatly simplified by necessity here) begins, perhaps not surprisingly, along the coast and major rivers. Water was an important resource and means of transportation, after all.
What was the class system in Connecticut?
There was a kind of class system in early Connecticut that stands in stark contrast to the ideals of equality and inclusion that later took hold in the American imagination. In early Connecticut towns—where there was little ethnic or racial diversity—there were three levels of recognized inhabitants, plus an invisible group. The most select level was the proprietors—the original settlers of the town. They (not the town) controlled the division of and management of land—much of which was held in common. New Haven initially required proprietors to be members of the congregational church, though that rule was not widespread in other towns.
What was the role of congregational churches in the early Connecticut towns?
Congregational churches also played a considerable role in the governance of early Connecticut towns. There was no separation of church and state as there is today. In fact, under English law that remained in force until the revolution, a town couldn’t exist without a church. Congregationalism was the established church of Connecticut through the whole colonial period and then retained this privileged status after Connecticut became a state. Until 1818, when congregationalism was finally disestablished, a portion of public taxes supported ministers’ salaries, local church expenses, and the common schools that churches in each town had the primary responsibility to provide.
How many towns were settled in the first century?
During the first period of settlement, from 1635 to 1675, 25 towns from Greenwich to Stonington on the coast and up the major river valleys were settled by family groups. “Farming, trading, and religious purity,” Daniels notes, were motivating factors in these towns’ settlement.
How many towns were there in the third colonial period?
During the third period of settlement, between 1737 and 1766, 14 towns formed in the only remaining unsettled lands: those in Litchfield County. In addition, four Massachusetts towns were annexed by Connecticut. The towns in Litchfield County were distinct in that they were formed by companies of proprietors who planned the new towns with a business-like precision—and then offered the lots to settlers or groups of settlers. By the end of the colonial period the area we know as Connecticut had taken its final shape (except for minor boundary changes) and there were settlers in every corner.
What was the role of the town clerk in the colony?
The town clerk was charged with maintaining town records. Among the lesser elected town offices were surveyors of highways (responsible for maintaining roads) and the fence viewers (responsible for maintaining fences along common lands and for corralling and returning stray livestock). A town might elect four to six fence viewers. Other positions included packers to inspect barrels of pork and beef to certify that they conformed to colony standards. Sealers did the same for tanned leather hides; there was a sealer of weights and measures who certified that scales used in business transactions were accurate. Finally, the ratesman recorded and assessed all the goods of any male older than 16 based on a schedule revised every few years by the general court.
What were the freemen's rights?
There was also a class called freemen who, once admitted by the general court (before 1729) or the town selectmen (thereafter), had voting rights that entitled them to vote for town and colony-wide offices, including the town’s representatives to the general court and the governor. There was an age and property requirement to qualify, and sometimes a term of residency in town. The property requirement decreased as time went on, and the trend was to expand white male suffrage.
Why was the Connecticut colony founded?
The Connecticut colony was founded in 1636 when the Dutch established the first trading post on the Connecticut River, part of a movement of people who left the Massachusetts Bay Colony to find better land. Thomas Hooker organized the colony to have a means of defense against the local Pequots.
How was the colonial government created?
The colonial government was created through the Fundamental Constitution of Carolina. It favored large land ownership, eventually leading to the plantation system. The colony was known for having religious freedom.
Why was the Pennsylvania colony founded?
Penn set up the colony to allow for religious freedom.
What was the role of the colony in the 1700s?
Each colony was set up in a way such that by the mid-1700s, they had a strong capacity for self-government and held local elections. Some early colonial governments foreshadowed elements that would be found in the U.S. government after independence.
What was the British government's system of control in the 1700s?
By the 1700s, the British government controlled its colonies under mercantilism, a system that regulated the balance of trade in favor of Britain. Over time, colonists became frustrated with this unfair economic system and with Britain's administration of taxation of the colonies without any accompanying representation in Britain.
Which colony was the first to be settled?
Virginia was the first permanently settled English colony, with the 1607 founding of Jamestown. The Virginia Company, a joint stock company which had been given the charter by King James I to found the colony, set up a General Assembly.
When was the Massachusetts Bay Company founded?
Massachusetts Bay Colony was created in 1629 by a charter from King Charles I, and the first settlers arrived in 1630. While the Massachusetts Bay Company was intended to transfer the colonial wealth to Britain, the settlers themselves transferred the charter to Massachusetts, turning a commercial venture into a political one. John Winthrop became the governor of the colony. However, according to the charter, the freemen, who included any of the charter's shareholders, could have drawn up a council, but Winthrop initially tried to keep that secret from them.
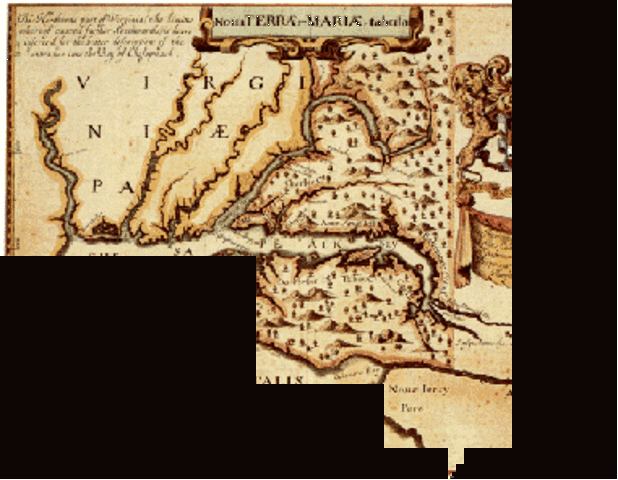
Overview
Colonies in Connecticut
Various Algonquian tribes long inhabited the area prior to European settlement. The Dutch were the first Europeans in Connecticut. In 1614 Adriaen Block explored the coast of Long Island Sound, and sailed up the Connecticut River at least as far as the confluence of the Park River, site of modern Hartford. By 1623, the new Dutch West India Company regularly traded for furs there and ten year…
First People
The name Connecticut is derived from the Mohegan-Pequot word that has been translated as "long tidal river" and "upon the long river", referring to the Connecticut River. Evidence of human presence in the Connecticut region dates to as much as 10,000 years ago. Stone tools were used for hunting, fishing, and woodworking. Semi-nomadic in lifestyle, these peoples moved seasonally to take advantage of various resources in the area. They shared languages based on Algonquian…
Territorial disputes
According to the 1650 Treaty of Hartford with the Dutch, the western boundary of Connecticut ran north from the west side of Greenwich Bay "provided the said line come not within 10 miles (16 km) of Hudson River." On the other hand, Connecticut's original charter in 1662 granted it all the land to the "South Sea" (i.e. the Pacific Ocean).
Conservatism
Connecticut was the land of steady habits, with a conservative elite that dominated colonial affairs. The forces of liberalism and democracy emerged slowly, encouraged by the entrepreneurship of the business community, and the new religious freedom stimulated by the First Great Awakening.
Yale College was founded in 1701 to educate ministers and civil leaders. After …
The American Revolution (1775–1789)
The conservative elite strongly supported the American revolution, and the forces of Loyalism were weak. Connecticut designated four delegates to the Second Continental Congress who would sign the Declaration of Independence: Samuel Huntington, Roger Sherman, William Williams, and Oliver Wolcott.
In 1775, in the wake of the clashes between British regulars and Massachusett…
Early National Period (1789–1818)
New England was the stronghold of the Federalist party. One historian explains how well organized it was in Connecticut:
It was only necessary to perfect the working methods of the organized body of office-holders who made up the nucleus of the party. There were the state officers, the assistants, and a large majority of the Assembly. In every county there was a sheriff with his deputies. All of the state, c…
Modernization and industry
Up until this time, Connecticut had adhered to the 1662 Charter, and with the independence of the American colonies over forty years prior, much of what the Charter stood for was no longer relevant. In 1818, a new constitution was adopted that was the first piece of written legislation to separate church and state in Connecticut, and give equality all religions. Gubernatorial powers were also expanded as well as increased independence for courts by allowing their judges to ser…
Overview
The Connecticut Colony or Colony of Connecticut, originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settlement for a Puritan congregation, and the English permanently gained control of the region in 1637 after struggles with the Dutch. The colony …
Leaders
Governor John Haynes of the Massachusetts Bay Colony led 100 people to Hartford in 1636. He and Puritan minister Thomas Hooker are often considered the founders of the Connecticut colony. Hooker delivered a sermon to his congregation on May 31, 1638, on the principles of government, and it influenced those who wrote the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut later that year. The Fundamental Orders may have been drafted by Roger Ludlow of Windsor, the only trained lawyer l…
Religion
The original colonies along the Connecticut River and in New Haven were established by separatist Puritans who were connected with the Massachusetts and Plymouth colonies. They held Calvinist religious beliefs similar to the English Puritans, but they maintained that their congregations needed to be separated from the English state church. They had immigrated to New England during the Great Migration. In the middle of the 18th century, the government restri…
Economic and social history
The economy began with subsistence farming in the 17th century and developed with greater diversity and an increased focus on production for distant markets, especially the British colonies in the Caribbean. The American Revolution cut off imports from Britain and stimulated a manufacturing sector that made heavy use of the entrepreneurship and mechanical skills of the people. In the second half of the 18th century, difficulties arose from the shortage of good farml…
See also
• List of colonial governors of Connecticut
• History of the Connecticut Constitution
• Connecticut Western Reserve
• History of Springfield, Massachusetts
External links
• Published colonial records
Archival collections
• Guide to the Connecticut Colony Land Deeds. Special Collections and Archives, The UC Irvine Libraries, Irvine, California.
Other