Why did the Dutch colonized South Africa?
Why did the Dutch colonized South Africa? The initial purpose of the settlement was to provide a rest stop and supply station for trading vessels making the long journey from Europe, around the cape of southern Africa, and on to India and other points eastward .
Who were the first Dutch settlers?
the first dutch settlers in america Following English explorer Henry Hudson's 1609 exploration of the Hudson River, a new joint stock company, the Dutch West India Company (1621), gained colonization rights in the Hudson River area and founded New Netherland (New York).
Why did the Dutch come to America?
The Dutch word for farm Dutch west India company Was set up in 1627 to trade furs with Native Americans. Their main goal was to send settlers to North America to set up a colony Peter Minuit In 1626 arrived as first governor of New Amsterdam.
What did the Dutch colonists do in America?
The Dutch Republic started attempts to establish colonies in North America in early 16th century. The Dutch East India Company, also known as WIC, was established in 1602. Its primary task was to explore the Americas and claim suitable territories for the Republic.

What were the earliest settlements of the Dutch?
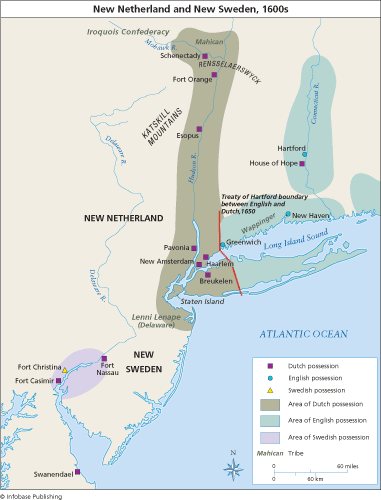
After some early trading expeditions, the first Dutch settlement in the Americas was founded in 1615: Fort Nassau, on Castle Island along the Hudson, near present-day Albany. The settlement served mostly as an outpost for trading in fur with the native Lenape tribespeople, but was later replaced by Fort Orange.
What were the names of the Dutch settlements?
Former Dutch colonial possessionsDutch East Indies with company rule (1603–1949), and Dutch New Guinea (until 1962)Dutch India (1605–1825)Dutch Gold Coast (1612–1872)New Netherlands (1614–1667, 1673–1674)Dutch Guianas (1616–1975)Dutch Formosa (1624–1662), and Keelung (Fort Noord-Holland; 1663–1668)More items...
Where did the Dutch establish a settlement?
The Dutch established a settlement at Masulipatnam in Andhra Pradesh.
Who were the first Dutch settlers in America?
Following English explorer Henry Hudson's 1609 exploration of the Hudson River, a new joint stock company, the Dutch West India Company (1621), gained colonization rights in the Hudson River area and founded New Netherland (New York).
What is Dutch settlement?
Definition of Dutch settle : a wooden bench whose back may be tipped forward to form a table.
Where were the earliest settlements of the Dutch French and English?
Where were the earliest settlements of the Dutch, French, and English in the Americas? New France, Virginia and the Masscheussets Bay Colony, and most of the eastern seaboard of North America.
Who came first Dutch or English?
European Powers That Came To IndiaEuropeansCame to IndiaYearPortuguese14981500Dutch16021605English16001613French16641668Apr 18, 2017
Which was the earliest settlement of Dutch in India?
PulicatThe earliest settlement of the Dutch was at Pulicat. Pulicat, now known as Pazhaverkadu, is a historic seashore town in Thiruvallur District, of Tamil Nadu state, India.
Which country were the Dutch belong to?
the NetherlandsOver time, English-speaking people used the word Dutch to describe people from both the Netherlands and Germany, and now just the Netherlands today.
How do I find my Dutch ancestors?
Top 10 Dutch genealogy websitesOpen Archives. This website publishes genealogical records from the archives in the Netherlands, often with scans or links to the original records.Archieven.nl. ... WieWasWie. ... FamilySearch. ... Digital Resources Netherlands and Belgium. ... Nationaal Archief. ... Delpher. ... Family name database.More items...•
Are the Pennsylvania Dutch German?
The Pennsylvania Dutch are descendants of early German-speaking immigrants who arrived in Pennsylvania in the 1700s and 1800s to escape religious persecution in Europe. They were made of up German Reformed, Mennonite, Lutheran, Moravian and other religious groups and came from areas within the Holy Roman Empire.
Why did the Dutch treat native peoples differently?
Unlike the French and Spanish, the Dutch did not emphasize religious conversion in their relationships with Native Americans. Instead, they focused on trade with American Indians in present-day New York and New Jersey.
What was the name of the whole Dutch settlement in the New World?
New NetherlandNew Netherland was the first Dutch colony in North America. It extended from Albany, New York, in the north to Delaware in the south and encompassed parts of what are now the states of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Connecticut, and Delaware.
What were the Dutch settlers called in South Africa?
Boer, (Dutch: “husbandman,” or “farmer”), a South African of Dutch, German, or Huguenot descent, especially one of the early settlers of the Transvaal and the Orange Free State. Today, descendants of the Boers are commonly referred to as Afrikaners.
What were the Dutch colonies in Africa?
The two major countries in Africa that were colonized by the Dutch were South Africa and Ghana. The colonies that became Ghana were referred to as the Dutch Gold Coast.
Who were the Dutch settlers in South Africa?
The Cape Colony (Dutch: Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa.
OVERVIEW
Located in northwestern Europe, the Netherlands is bounded to the east by Germany, to the south by Belgium, and to the north and west by the North Sea. The Netherlands has about 16,000 square miles of landmass, making the country roughly equal in size to New Jersey and Maryland combined.
Acculturation and Assimilation
During the chief era of Dutch immigration, 1621-1970, religious and ideological viewpoints structured the character of public institutions in the Netherlands. In the Dutch Republic (1580-1795), Reformed Protestants controlled the government, schools, public charities, and most aspects of social behavior.
Language
In general, the Dutch language is no longer used by Dutch Americans. The vast majority of postwar immigrants have adopted English and the small number of immigrants who have arrived since the 1960s are bilingual because English is virtually a second language in the Netherlands.
Family and Community Dynamics
Colonial New Netherland (New York), like Jamestown and other trading post colonies, attracted single men, few women, and even fewer families.
Religion
Neither Dutch Catholics nor Jews have retained discernible ethnic practices in their religious exercises. Both groups are part of international organizations which, because they used either Latin or Hebrew in formal rituals, were not drawn into major controversies regarding vernacular language usage in worship.
Employment and Economic Traditions
Free enterprise capitalism was introduced to the United States by the joint stock companies that colonized the eastern seaboard. The New Netherland Colony (New York) exemplified that phenomenon just as obviously as Jamestown and the New England Company.
Politics and Government
The vast majority of Dutch Americans are Republicans but they are usually not political activists. During the Anglo-Boer War (1899-1902), Dutch Americans organized to influence U.S. foreign policy in favor of the South African Boers.
The Land of Lenape
The area of Manhattan first belonged to the Native American tribe Lenape. This tribe is known also as the Delaware Indians, and they created the First Nations band government. Their territory included the area of New Jersey, the Lower Hudson Valley, the Delaware River, and western Long Island.
A Dutch Englishman
In 1609, an Englishman who worked for the Dutch East India Company, Henry Hudson, reached Manhattan Island. Before his feet touched this area, he traveled through many lands and oceans. He wanted to find a prospective North-West Passage to Cathay, in modern China, and traveled to the Arctic Circle.
When the Dutch Bought Manhattan
Manhattan became a part of the land known as the New Netherlands - a colonial province located on the East Coast of North America which covered the territory from the Delmarca Peninsula to Cape Cod, and included the territory of modern New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Connecticut, parts of Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island.
The Heritage of Manhattan
Nowadays, the history of the first people in Manhattan is covered by monumental buildings. Nobody there speaks in the native language of the Lenape and relatively few in Dutch.
Forts and Factorijen
The first of two Forts Nassau was built in Mahican territory during the first decade, where commerce could be conducted with Indians, and factorijen (small trading posts) went up at Schenectady, Schoharie, Esopus, Quinnipiac, Communipaw, Ninigret, Totoket, Schuykill, and elsewhere.
Nut Island
The States General of the Dutch Republic awarded the newly formed Dutch West India Company a trade monopoly for the region in 1621, and New Netherland became a province of the Dutch Republic in 1624. The South River was initially chosen as the site of the capital because the colonists felt that it had the best climate.
Patroonships
In 1629, the Dutch West India Company introduced the Charter of Freedoms and Exemptions, a series of inducements commonly known as the patroon system.
South River
Another patroon patent was Zwaanendael Colony later named by the British, Lewes, Delaware (the town is still known as such), the first Dutch colonial settlement on the Zuyd Rivier ( Delaware Bay ), but it was plundered soon after its founding in 1631.
Fresh River (Connecticut)
The Dutch established a short-lived factorij trading post at Kievits Hoek (or Plover's Corner) in present-day Old Saybrook, Connecticut shortly after constructing their first settlement on the island of Manhattan.
North River
The port called the Manhattans grew up at the mouth of the North River (Hudson River). New Amsterdam was the capital of the province and received its municipal charter in 1652; this included the isle of Manhattan, Staaten Eylandt, Pavonia, and the Lange Eylandt towns, including Gravesend, Breuckelen, and Nieuw Amersfoort .
The Dutch Belt
Colonial settlers spread throughout the region after the final transfer of power to the English with the Treaty of Westminster (1674), establishing many of the towns and cities that exist today. The Dutch Reformed Church played an important role in this expansion.