
These settlements were among mountains for safety, but also along the seas so the people would have a mean of transportation. They settled too where the farm soil was fertile. Around 3 000 BCE
Common Era
Common Era or Current Era, abbreviated CE, is a calendar era that is often used as an alternative naming of the Anno Domini system ("in the year of the Lord"), abbreviated AD. The system uses BCE as an abbreviation for "before the Common (or Current) Era" and CE as an abbreviation for "Common Era".
Full Answer
What was the relationship between the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire?
Before this, the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire, centered in what is now modern-day Iran, had maintained an uneasy coexistence, but this expansion by the Persians would eventually lead to war.
Did the Persians enslave the Greeks?
Many people look at the Persians as some evil empire that wanted to enslave the Greeks. The Greeks are looked upon as the bastion of freedom, yet the majority of Greek cities practiced slavery of some sort. The Birthplace of Democracy, Athens, had slaves.
What are the characteristics of Ancient Greek settlements?
Settlements in ancient Greece G.P. Lavas In its general structure the ancient Greek settlement was fulfilling defensive, residential, sociopolitical and economic needs. The walls, the sacred edifices, the agora with its public buildings and open spaces were the architectural expression of communal functions, while the dwellings represented the
How did the Greeks defend themselves against the Persian Empire?
Although the Persian empire was at the peak of its strength, the collective defense mounted by the Greeks overcame seemingly impossible odds and even succeeded in liberating Greek city-states on the fringe of Persia itself. The Greek triumph ensured the survival of Greek culture and political structures long after the demise of the Persian empire.

What were the Greek settlements called?
Important colonies were Maroneia, and Abdera. The Milesians also founded Abydos and Cardia on the Hellespont and Rhaedestus in Propontis. The Samians colonised the island of Samothrace, becoming the source of its name.
Where is Persia in ancient Greece?
The heart of ancient Persia is in what is now southwest Iran, in the region called the Fars. In the second half of the 6th century B.C.E., the Persians (also called the Achaemenids) created an enormous empire reaching from the Indus Valley to Northern Greece and from Central Asia to Egypt.
Where did Greek colonists settle during the first wave of Greek colonization?
Greeks created settlements along the Aegean coast of Ionia (or Asia Minor) from the 8th century BCE. Important colonies included Miletos, Ephesos, Smyrna, and Halikarnassos. Athens traditionally claimed to be the first colonizer in the region which was also of great interest to the Lydians and Persians.
When did Greece take over Persia?
Greco-Persian Wars, also called Persian Wars, (492–449 bce), series of wars fought by Greek states and Persia over a period of almost half a century. The fighting was most intense during two invasions that Persia launched against mainland Greece between 490 and 479.
Did Sparta beat Persia?
Although the Greeks finally beat the Persians in the Battle of Platea in 479 B.C., thus ending the Greco-Persian Wars, many scholars attribute the eventual Greek success over the Persians to the Spartans' defense at Thermopylae.
Why did Persia lose to Greece?
The Greeks simply wouldn't accept the idea of being invaded by another country and they fought until they won. Another factor was that by uniting the city-states, particularly the Spartans and Athenians, it created a skilled, well balanced army that was able to defeat the Persians despite their numbers.
Who were the first settlers in Greece?
the MinoansThe First Greeks. Two major groups of people, the Minoans and the Mycenaeans, were the first to populate the Greek peninsula. Not much is known about either of these groups because they did not leave an abundance of written or physical evidence to provide clues about their civilization.
Who migrated to Greece?
The large majority of immigrants to Greece come from Albania; Albanians constitute 63.7% of the total documented migrant population in Greece, followed by Bulgarians, Georgians, Romanians, Russians, and Ukrainians. Immigrants are employed in construction, industrial manufacturing, and agriculture.
When did Greece ban slavery?
After the lawgiver Solon abolished citizen slavery about 594 bce, wealthy Athenians came to rely on enslaved peoples from outside Attica. The prolonged wars with the Persians and other peoples provided many slaves, but the majority of slaves were acquired through regular trade with non-Greek peoples around the Aegean.
Was Athens burned by Persia?
In 480 BC, Persian forces led by King Xerxes I burned down the city of Athens, as well as the Acropolis, in what is called “the Persian Destruction of Athens.” The destruction of the great city took place during the Persian Wars, a series of conflicts which began in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC.
Who won Persia or Greece?
Who won the Persian Wars? The alliance of Greek city-states, which included Athens and Sparta, won the Persian Wars against Persia from 490 to 480 BCE.
Who defeated Persia?
Alexander the GreatPersia was eventually conquered by Alexander the Great in 334 B.C.E. (356-323 BCE) Greek ruler, explorer, and conqueror.
Where is Persia located today?
country of IranPersia is today the country of Iran. By the 5th century B.C.E., it was the largest empire the world had ever seen, surpassing the size of their Assyrian predecessors.
Which nation was formerly known as Persia?
Iran (pronounced ee-RAHN), formerly known as Persia, is situated at the crossroads of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Arab states of the Middle East.
Why is Iran called Persia?
Generally, “Persia” today refers to Iran because the country formed over the center of the ancient Persian empire and the majority of its original citizens inhabited that land.
What nationality is a Persian?
IranThe Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
What was the first battle between the Persian Empire and the Greeks?
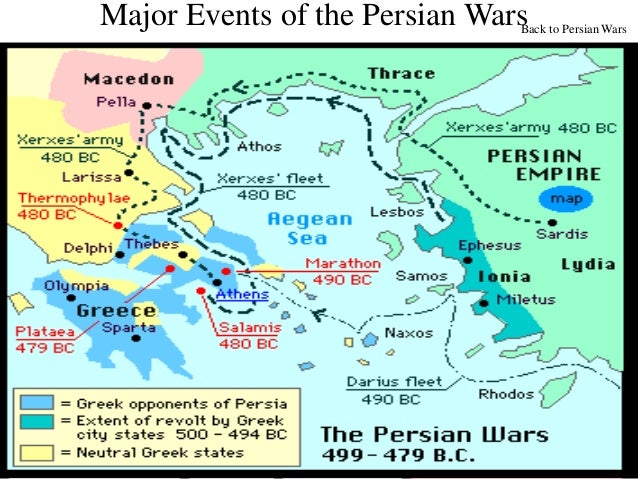
The first major battle between the Greek City-States and the Persian Empire was the Battle of Marathon with the Greek City-States led by either Callimachus or Miltiades and the Persians led by Datis and Artephernes. Before the next major battles Thermopylae and Artemision, Darius the Great died and his son Xerxes succeeded him as the new ruler of the Persians. The next major battle was the Battle of Salamis (a naval battle) after the Persians beat the Greeks in the Battle of Thermopylae. After the Persians were defeated by the Greek City-States at Salamis, their final major battle of the Persian Wars was in 479 BCE at the land Battle of Plataea, in which the Greek City-States emerged victoriously.
When did the Persian Wars start?
The Persian Wars, also known as the Greco Persian Wars, were a series of battles fought between Ancient Greece and the Achaemenid Persian Empire in the 5th century BCE.
Who were the Persian kings in the Greco-Persian Wars?
For full treatment, see ancient Greek civilization: The Persian Wars. In the generation before 522, the Persian kings Cyrus II and Cambyses II extended their rule from the Indus River valley to the Aegean Sea.
How many days did the Persians fight the Greeks?
The Persians met the Greeks in battle over a period of three days in August 480. At sea a detachment of 200 Persian ships attempted to surprise the Greek fleet, but the Greeks, forewarned, engaged the main Persian navy. That night a tremendous storm destroyed the Persian squadron while the Greeks were safely in port.
How long did the Persian invasion last?
Although the Persian invasion was ended by the battles at Plataea and Mycale, fighting between Greece and Persia continued for another 30 years. Led by the Athenians, the newly formed Delian League went on the offensive to free the Ionian city-states on the Anatolian coast.
What happened to the Persian fleet in September?
In September the Persians burned Athens, which, however, by that time had been evacuated. In the meantime, the Greeks decided to station their fleet in the Strait of Salamis. Themistocles devised a clever stratagem: feigning retreat, he lured the Persian fleet into the narrow strait.
What was the significance of the Battle of Salamis?
Battle of Salamis. The Battle of Salamis, 480 bce, in which Greece gained an uncontested victory over the Persian fleet. Classic Vision/age fotostock.
What was the Persian war?
Greco-Persian Wars, also called Persian Wars, (492–449 bce ), a series of wars fought by Greek states and Persia over a period of almost half a century. The fighting was most intense during two invasions that Persia launched against mainland Greece between 490 and 479. Although the Persian empire was ...
How many ships did the Greek fleet have?
A general Greek league against Persia was formed in 481. Command of the army was given to Sparta, that of the navy to Athens. The Greek fleet numbered about 350 vessels and was thus only about one-third the size of the Persian fleet.
What countries did the Greeks invade?
The Greeks under the Athenian-led Delian League invaded Turkey, Cyprus, and Egypt. In southern Turkey, the Greeks won an amazing victory at the battle of Eurymedon. The second Persian invasion of Greece lasted about two years. The Greek counterattacks continued from 478 until 449 BCE.
Where did the Persians leave their army?
After Salamis, the Persian navy sailed to Ionia in southwest Turkey while the Persians left an army of around 100,000 in Greece under Xerxes’ best general. At the battle of Mycale, the Greek navy sailed to the beached Persian navy and launched an amphibious battle on the slopes of Mount Mycale. The aggressive assault pushed into the Persian camp and effectively destroyed the remnants of the Persian navy.
Why did the Greeks lengthen their center?
The Greeks lengthened their center to match the width of the Persians and during the battle, the stronger Greek wings pushed through in a perfect pincer move. What might have happened is the Athenian center simply broke, causing the Persian center to pursue them while the Greek wings simply held.
What religion did the Persians follow?
Contrarily, the Persians mainly followed the religion of Zoroastrianism, which specifically outlaws slavery. Though their central government had massive power under a central ruler, which made some conquered nations feel like slave nations for the king.
What happened after Byzantium?
After Byzantium was taken the Spartans declared that they had had enough, but the Athenians kept going, gaining monetary and troop support from many of the other Greeks.
Which island was the moral stand of the Persians?
So Thermopylae was the moral stand and after Salamis, Plataea and Mycale the Persians were ousted and the war was over, right? Not for the Athenians. The naval force quickly went on to the island of Cyprus and then back to the then relatively minor city of Byzantium and conquered it.
Did the Greeks take Ionia?
The Greeks were unable to come close to bringing down the Persian Empire, but they took much of Ionia and incited some revolts in Egypt. Peace only came after a failed invasion of Cyprus and the rising tensions within Greece that would lead to the Peloponnesian Wars.
Summary
This chapter concerns the general situation in Greece during the last quarter of the sixth century and the start of the fifth: the years when Persia's defeat and annexation of the non-Greek kingdoms which bordered the Aegean to east and south brought the power of her empire significantly near to the Greeks of the Aegean and the mainland itself.
Keywords
Email your librarian or administrator to recommend adding this book to your organisation's collection.
What was the ideal size of the ancient Greek community?
considered to be between five and ten thousand. inhabitants within an area of not more than 180. hectares. The criterion for determining whether a. group of buildings constituted a settlement was the.
Is symbiosis mirrored in the town plan?
symbiosis was clearly mirrored in the town plan, with
Which Greek city fell to the Persians?
Athens soon falls, and the Persians overrun most of Greece. However, at the Battle of Salamis, a large island west of Athens, the combined Greek navy decisively beat the Persians. Xerxes retreated to Asia.
Where did the Persians retreat from?
479 BCE, Plataea: Persians retreating from their loss at Salamis encamped at Plataea, a small town northwest of Athens, where combined Greek forces badly defeated the Persian army, led by Mardonius. This defeat effectively ended the second Persian invasion. Later that year, combined Greek forces went on the offensive to expel Persian forces from Ionian settlements in Sestos and Byzantium.
What was the name of the island that the Persians attacked in 502 BCE?
502 BCE, Naxos: An unsuccessful attack by the Persians on the large island of Naxos, midway between Crete and the current Greek mainland, paved the way to revolts by Ionian settlements occupied by the Persians in Asia Minor. The Persian Empire had gradually expanded to occupy Greek settlements in Asia Minor, and the success ...
When did the Persians leave Asia?
Systematic expulsion of the Persians from settlements in Asia now began, continuing for 20 years. 476 to 475 BCE, Eion: Athenian general Cimon captured this important Persian stronghold, where Persian armies stored huge stores of supplies.
When did the Persian Wars start?
The Persian Wars (sometimes known as the Greco-Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between Greek city-states and the Persian Empire, beginning in 502 BCE and running some 50 years, until 449 BCE. The seeds for the wars was planted in 547 BCE when the Persian emperor, Cyrus the Great, conquered Greek Ionia.
Who led the Persian invasion of Greece?
The Persians burned settlements, but the nearby island of Delos was spared. This marked the first invasion of Greece by the Persians, led by Mardonius. 490 BCE, Marathon: The first Persian invasion of Greece ended with Athens decisive victory over the Persians at Marathon, in the Attica region, north of Athens.
Who conquered Ionia?
The seeds for the wars was planted in 547 BCE when the Persian emperor, Cyrus the Great, conquered Greek Ionia. Before this, the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire, centered in what is now modern-day Iran, had maintained an uneasy coexistence, but this expansion by the Persians would eventually lead to war.
What is the settlement pattern of Greece?
Settlement Patterns. The location of Greece has made it the crossroads of migrating Slavs, invading Turks, and other colonizing powers from Europe. Thanks to this, there are many ethnicities in the country. (Encyclopaedia Britannica) Greece was heavily populated in the prehistoric times.
What was the land of Greece?
Instead of an empire, the land of Greece was comprised of many city states. Trading centers like Corinth and Athens developed. Sparta became a city developed to the military. We can still see evidence of the Mycenaean and the Classical Greek era. The Parthenon in Athens is an example.
What was the prehistoric Greek civilization?
Greece was heavily populated in the prehistoric times. These settlements were among mountains for safety, but also along the seas so the people would have a mean of transportation. They settled too where the farm soil was fertile. Around 3 000 BCE, a civilization began to develop on the island of Crete. The people of Crete colonized mainland Greece. Instead of an empire, the land of Greece was comprised of many city states. Trading centers like Corinth and Athens developed. Sparta became a city developed to the military. We can still see evidence of the Mycenaean and the Classical Greek era. The Parthenon in Athens is an example. There are many temples and buildings remaining.
What happened to the population of Greece in the 20th century?
There was a drop in population growth in the 20th century. During the wars, many people left for Australia, the United States, Canada, and other places in Europe.
What is the largest city in Greece?
Larger towns like Athens, the capital, began to grow in size and commercially from the 1970s. It remains the largest city in Greece. (Encyclopaedia Britannica) Since then, immigration has picked up again but the fertility rate remains relatively low.
The Greeks Had Slaves, and The Persians Outlawed Slavery
Marathon Might Have Been An Accidental Victory
- One of the greatest Greek victories in their collective history might have been a lucky accident, for lack of a better word. The Greeks adopted aggressive tactics against the large Persian force. They wanted to get past the initial deadly range of the Persian archers, get a decisive battle in before the Persian cavalry could unload from the ships and to hopefully surprise and unnerve the Persia…
Two of The Most Important Battles of The War Often Get Forgotten
- The Persians entered Greece with the largest army the world had yet seen, right? They drank rivers dry, yet people think they were destroyed in the battles of Thermopylae and Salamis. While these battles were certainly epic and morally huge for the Greeks, the fact remained that the Persians still had an army and a navy that outnumbered the Greeks and could have still conquered them. …
The Greeks Went on The Attack Against Persia
- So Thermopylae was the moral stand and after Salamis, Plataea and Mycale the Persians were ousted and the war was over, right? Not for the Athenians. The naval force quickly went on to the island of Cyprus and then back to the then relatively minor city of Byzantium and conquered it. After Byzantium was taken the Spartans declared that they had had enough, but the Athenians k…