Spain was driven by three main motivations. Columbus, in his voyage, sought fame and fortune, as did his Spanish sponsors. To this end, Spain built a fort in 1565 at what is now St. Augustine, Florida; today, this is the oldest permanent European settlement
European colonization of the Americas
The European colonization of the Americas describes the history of the settlement and establishment of control of the continents of the Americas by most of the naval powers of Western Europe. Systematic European colonization began in 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by the Italian explorer Christopher Columbus sailed west to find a new trade route to the Far East but inadvertently landed in wh…
Full Answer
What was the first European settlement in North America?
European Colonization of North America. The invasion of the North American continent and its peoples began with the Spanish in 1565 at St. Augustine, Florida, then British in 1587 when the Plymouth Company established a settlement that they dubbed Roanoke in present-day Virginia. This first settlement failed mysteriously and in 1606, the London ...
Why did European countries colonize the Americas?
Colonization, or the desire to establish permanent settlements, soon followed. Some of these European countries fought one another for control over trade and the riches of the New World. While they all shared a desire for wealth and power, their motivations for colonization differed somewhat, and thus the pattern and success ...
How did Native Americans resist European colonization?
While Native Americans resisted European efforts to amass land and power during this period, they struggled to do so while also fighting new diseases introduced by the Europeans and the slave trade. Learn more about the colonization of North America and the plight of Native Americans with these classroom resources.
How did the European age of exploration affect the Americas?
European settlement and diseases devastated indigenous populations and led to a scramble for lands on a continental scale that resulted in a checkerboard of Euro-American societies from the Hudson Bay in northern Canada to Tierra del Fuego, an island group off the southern tip of South America.
What was the name of the area where the Native Americans lived before the arrival of the Europeans?
Which countries established colonies in North America?
What was the area before John Smith's voyage?
What did Native Americans call their home?
Where did the Spanish invade?
When did the French and Dutch start colonizing New York?
Who was the first person to map the Chesapeake Bay?
See 4 more
About this website

What were the reasons for European settlement in North America?
The opportunity to make money was one of the primary motivators for the colonization of the New World. The Virginia Company of London established the Jamestown colony to make a profit for its investors. Europe's period of exploration and colonization was fueled largely by necessity.
How did European nations first gain the land they colonized in North America?
The invasion of the North American continent and its peoples began with the Spanish in 1565 at St. Augustine, Florida, then British in 1587 when the Plymouth Company established a settlement that they dubbed Roanoke in present-day North Carolina.
How did European settlements impact North America?
Colonization ruptured many ecosystems, bringing in new organisms while eliminating others. The Europeans brought many diseases with them that decimated Native American populations. Colonists and Native Americans alike looked to new plants as possible medicinal resources.
What 3 main factors attracted European colonization to the Americas?
Historians generally recognize three motives for European exploration and colonization in the New World: God, gold, and glory.
When was the first European settlement in North America?
Even before Jamestown or the Plymouth Colony, the oldest permanent European settlement in what is now the United States was founded in September 1565 by a Spanish soldier named Pedro Menéndez de Avilés in St.
Why did the settlers come to America?
Colonists came to America because they wanted political liberty. They wanted religious freedom and economic opportunity. The United States is a country where individual rights and self-government are important.
Who colonized North America?
In the late 16th century, England (British Empire), Kingdom of France, Spanish Empire, and the Dutch Republic launched major colonization programs in North America.
Who was the first European to land in North America?
Five hundred years before Columbus, a daring band of Vikings led by Leif Eriksson set foot in North America and established a settlement.
Who was the first European to land in North America?
Five hundred years before Columbus, a daring band of Vikings led by Leif Eriksson set foot in North America and established a settlement.
Who were the first Europeans to colonize America quizlet?
The Spanish were the first Europeans to reach North America. You just studied 80 terms!
How the exploration and colonization of the Americas by Europe changed the world?
The Europeans brought technologies, ideas, plants, and animals that were new to America and would transform peoples' lives: guns, iron tools, and weapons; Christianity and Roman law; sugarcane and wheat; horses and cattle. They also carried diseases against which the Indian peoples had no defenses.
What are the causes of European exploration and colonization?
Reasons for Exploration: All of the European nations ( Spain, France, England, and the Netherlands) came to America for the same 4 major reasons: wealth & power, religion, nationalism, and the Renaissance spirit of curiosity and adventure.
Timeline of the European colonization of North America
Before Columbus. 986: Norsemen settle Greenland and Bjarni Herjólfsson sights coast of North America, but doesn't land (see also Norse colonization of the Americas). c. 1000: Norse settle briefly in L'Anse aux Meadows in Newfoundland. c. 1450: Norse colony in Greenland dies out. 1473: João Vaz Corte-Real perhaps reaches Newfoundland; writes about the "Land of Cod fish" in his journal.
European Colonization of the Americas Timeline
Plymouth Colony established in modern-day Massachusetts, North America; foundational colony of the later United States.
European Colonization of the Americas - World History Encyclopedia
The wealth Spain acquired from their colonies and the enslavement and sale of indigenous people encouraged England to establish their own presence in the New World. The first two colonies – Popham and Roanoke Colony – failed but the third, Jamestown, founded in Virginia in 1607, succeeded.The Plymouth colony followed, founded in 1620 in Massachusetts and, afterwards, the basic regions of ...
Home | Library of Congress
Home | Library of Congress
What was the impact of the migration of Europeans to the Americas?
The migration of several million Europeans to the Americas during this period was fundamental to the formation of New World society. European settlement and diseases devastated indigenous populations and led to a scramble for lands on a continental scale that resulted in a checkerboard of Euro-American societies from the Hudson Bay in northern Canada to Tierra del Fuego, an island group off the southern tip of South America. From the Atlantic ports of Europe—principally of Britain, Spain, and Portugal—wave after wave of settlers, rich and poor, took ship seeking their fortune "beyond the seas."
What was the result of European settlement and diseases?
European settlement and diseases devastated indigenous populations and led to a scramble for lands on a continental scale that resulted in a checkerboard of Euro-American societies from the Hudson Bay in northern Canada to Tierra del Fuego, an island group off the southern tip of South America.
How many emigrants were there in the first century?
Annual rates of emigration climbed steadily across the three centuries, from 2,000 annually before 1580, to 8,000 per year in the second half of the seventeenth century, and between 13,000 and 14,000 per year in the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. Three principal phases of movement can be identified. The first century and a half was dominated by Spanish and Portuguese emigrants, who made up 87 percent of the 446,000 settlers leaving Europe between 1492 and 1640.
What is servant emigration?
Servant emigration was generally a two-stage process shaped by the same social and economic forces that influenced broader patterns of lower-class movement. Indentured servants were a subset of a much larger group of young, single, and poor men and women who moved from village to village and town to city in search of greater opportunities than were to be had at home. Cities and ports throughout Europe attracted the surplus labor of the surrounding countryside and market towns, as well as from further afield. London, for example, was a magnet for the poor, who poured into the capital and took up residence in the burgeoning slums outside the ancient city walls. According to a contemporary, they included "soldiers wanting wars to employ them,… serving-men whose lords and masters are dead,… masterless men whose masters have cast them off, [and] idle people, as lusty rogues and common beggars." They came, he observed, "hearing of the great liberality of London," (Beier 1985, pp. 40-41).
Where did the Spanish emigrate from?
Whether free or unfree, emigration from Europe to America was intensely regional. During the sixteenth and first half of the seventeenth centuries, the origins of Spanish emigrants were heavily skewed toward the southwest. Andalusia alone contributed between one-third and one-half of all migrants from Spain. In the late seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the character of Spanish emigration changed dramatically, with far higher numbers of people moving from the poorer provinces of the north coast, the east, and from the Balearic and Canary Islands.
How many settlers made their way to the American Middle Colonies?
Only about 23,000 settlers made their way to the American Middle Colonies and 21,000 to New England. English immigration represented the transfer of a massive labor force to America, which was essential for the development of staple agriculture—sugar and tobacco—in the West Indies and Chesapeake.
What was the dominant form of white migration during the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries?
As mentioned above, free migration was the dominant form of white movement during the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries and in the period after 1750. A key characteristic of the second half of the eighteenth century was the increasing numbers of skilled and independent migrants opting to leave Europe against a background of growing prosperity and trade. As American commerce flourished and channels of communication were strengthened, the cost of passage fell and colonies became increasingly attractive and accessible.
What countries were involved in the colonization of the Americas?
During this period of time, several European empires —primarily Spain, Portugal, Britain, and France —began to explore and claim the natural resources and human capital of the Americas, resulting in the displacement and disestablishment of some Indigenous Nations, and the establishment of several settler-colonial states.
How did the colonization of the Americas affect the Caribbean?
According to scientists from University College London, the colonization of the Americas by Europeans killed so much of the indigenous population that it resulted in climate change and global cooling. Some contemporary scholars also attribute significant indigenous population losses in the Caribbean to the widespread practice of slavery and deadly forced labor in gold and silver mines. Historian, Andrés Reséndez, supports this claim and argues that indigenous populations were smaller previous estimations and "a nexus of slavery, overwork and famine killed more Indians in the Caribbean than smallpox, influenza and malaria."
Why did the population of the Americas drop?
After European contact, the native population of the Americas plummeted by an estimated 80% (from around 50 million in 1492 to eight million in 1650), mostly as the result of outbreaks of Old World disease.
Why did the Dutch want independence?
The Netherlands had been part of the Spanish Empire, due to the inheritance of Charles V of Spain. Many Dutch people converted to Protestantism and sought their political independence from Spain. They were a seafaring nation and built a global empire in regions where the Portuguese had originally explored. In the Dutch Golden Age, it sought colonies. In the Americas, the Dutch conquered the northeast of Brazil in 1630, where the Portuguese had built sugar cane plantations worked by black slave labor from Africa. Prince Johan Maurits van Nassau-Siegen became the administrator of the colony (1637–43), building a capital city and royal palace, fully expecting the Dutch to retain control of this rich area. As the Dutch had in Europe, it tolerated the presence of Jews and other religious groups in the colony. After Maurits departed in 1643, the Dutch West India Company took over the colony, until it was lost to the Portuguese in 1654. The Dutch retained some territory in Dutch Guiana, now Suriname. The Dutch also seized islands in the Caribbean that Spain had originally claimed but had largely abandoned, including Sint Maarten in 1618, Bonaire in 1634, Curaçao in 1634, Sint Eustatius in 1636, Aruba in 1637, some of which remain in Dutch hands and retain Dutch cultural traditions.
What was Columbus' first island?
Columbus's first two voyages (1492–93) reached the Caribbean island of Hispaniola and various other Caribbean islands, including Puerto Rico and Cuba.
Why was the rapid rate at which Europe grew in wealth and power unforeseeable in the early 15th century?
The rapid rate at which Europe grew in wealth and power was unforeseeable in the early 15th century because it had been preoccupied with internal wars and it was slowly recovering from the loss of its population which was caused by the Black Death. The strength of the Turkish Ottoman Empire held on trade routes to Asia prompted Western European monarchs to search for alternatives, resulting in the voyages of Christopher Columbus and the accidental re-discovery of the " New World ".
Which two kingdoms were part of the non-European world?
In the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas ratified by the Pope, the two kingdoms of Castile (in a personal union with other kingdoms of Spain) and Portugal divided the entire non-European world into two spheres of exploration and colonization.
Which country gained all of France's important North American possessions?
By the Treaty of Paris England gained all France's important North American possessions; Spain was toô. .
Who was the first colonist to colonize the eastern seaboard of North America?
James I (1566–1625) granted charters to some merchants to colonize the eastern seaboard of North America. The London Virginia Company was allocated what is now Virginia and Maryland and the Plymouth Company the coast of New England as far as Maine. This company's charter was revoked and a royal colony, whose council's seal is shown, established in 1624.
How did the pattern of migration change over the years?
The pattern of migration changed over the years. From 1580 to 1619 England settled the eastern seaboard while France established settlements in Canada and down the Mississippi. The next 30 years saw the increase of African slave migration as well as the establishment of New England and the Scandinavian and Dutch colonies. Then England consolidated her hold and the Irish, Scots and Germans led the March westwards.
What was the purpose of the Jamestown settlement?
The next attempt to establish an English colony in the area, the Jamestown settlement – established by the Virginia Company in 1607 – was basically a commercial venture, although the aims of the company included helping to build a strong merchant fleet, training mariners for England's protection, spreading the gospel and planting a Protestant colony in a land still threatened by Catholic Spain.
How many people crossed the Atlantic to the New World?
Six and a half million people had crossed the Atlantic to the New World by the 1770s. One million whites came from Europe – mostly from England, France, Germany and Spain; the other five and a half million were black slaves from West Africa, who were transported in appallingly cramped conditions in the slave ships. Chained flat to the decks they could cause little trouble and needed less food, thereby maximising the profits of the traders.
What were the main reasons for the establishment of North American colonies?
Trade and religion were the two principal motives for the founding of North American settlements. Religious enthusiasts, hampered at home by the inquisition in Spain and the Court of High Commission in England, were sometimes willing to venture into the unknown, but without the prospect of trade with Europe they could survive only in subsistence conditions. During the 50 years following the foundation of Jamestown, further colonies were established, mostly by the English. Plymouth was established in 1620 by the Pilgrim Fathers, who sought religious and civil autonomy from the English Government, and Maryland by Lord Baltimore, for Roman Catholics, in 1632. In 1625 the Dutch founded New Amsterdam, later renamed New York, as a trading post, to be followed by the Swedes and Finns.
What were the Indian villages in Chesapeake Bay?
Fig 7. Indian villages, the home of semi-nomadic hunters, bordered the rivers that flow into Chesapeake Bay and the creeks and inlets of New England. The early settlers bartered beads and trinkets for large tracts of land, much of it already cleared for cultivation, thus beginning the relentless process of Indian dispossession. Ports such as Baltimore and Fredericksburg were established around Chesapeake Bay by the 18th century. .
Who was the first French explorer to settle in North America?
In 1534, navigator Jacques Cartier claimed northern North America for France; in 1608, fellow explorer Samuel de Champlain founded the first French settlement of Quebec on the cliffs over the St. Lawrence River.
Which European country established the firmest foothold in North America?
In 1664, Britain took over the colony of New Netherland and renamed it New York. Of all the European countries, England established the firmest foothold in North America. Like the other European countries, England was motivated in part by the lure of both riches and the Northwest Passage.
How did England benefit financially from the colonization of the New World?
The opportunity to make money was one of the primary motivators for the colonization of the New World.
What countries fought for control over trade and the riches of the New World?
Each of the major European powers—Spain, France, the Netherlands, and England —sent explorers to the New World. Colonization, or the desire to establish permanent settlements, soon followed. Some of these European countries fought one another for control over trade and the riches of the New World. While they all shared a desire for wealth ...
Why did Columbus want to build a fort in Florida?
Spain was driven by three main motivations. Columbus, in his voyage, sought fame and fortune, as did his Spanish sponsors. To this end, Spain built a fort in 1565 at what is now St. Augustine, Florida; today, this is the oldest permanent European settlement in the United States. A few fledgling Spanish settlements were established nearby, but clashes with Native Americans who lived there, and the lack of gold or other riches made many of them short-lived. Spanish conquistadors had better success in South America, where they conquered the Aztec and Inca Empires and claimed the land for Spain. Spain soon grew rich from ample deposits of gold and silver in Mexico, Central America, and South America.
What were the main motivations for colonizing Spain?
While they all shared a desire for wealth and power, their motivations for colonization differed somewhat, and thus the pattern and success of their colonies varied significantly. God, Gold, and Glory. Spain was driven by three main motivations. Columbus, in his voyage, sought fame and fortune, as did his Spanish sponsors.
Why did the Dutch settle in New Amsterdam?
The primary motivation for Dutch settlement of this area was financial—the country wanted to add to its treasury. To this end, Dutch traders formed powerful alliances with Native Americans based on the trade of beaver pelts and furs. Farmers and merchants followed. Success was short-lived, however. In 1664, Britain took over the colony of New Netherland and renamed it New York.
What was the first site of enslavement of Africans in North America?
1525: Estêvão Gomes enters Upper New York Bay. 1526: Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón briefly establishes the failed settlement of San Miguel de Gualdape in South Carolina, the first site of enslavement of Africans in North America and of the first slave rebellion.
Where did Columbus sail?
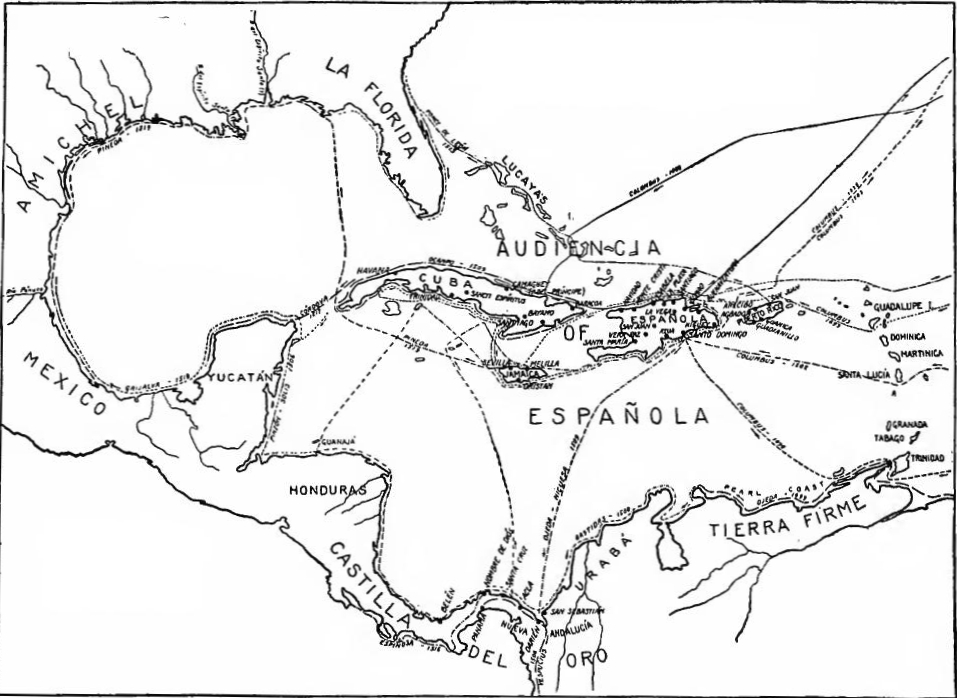
1502: Columbus sails along the mainland coast south of Yucatán, and reaches present-day Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama. 1503: Las Tortugas noted by Columbus in passage through the Western Caribbean present-day Cayman Islands.
What happened in the late fifteenth century?
Late fifteenth century. 1492: Columbus sets sail aboard the Niña, Pinta, and Santa Maria. 1492: Columbus reaches the Bahamas, Cuba and Hispaniola. 1492: La Naviad is established on the island of Hispaniola; it was destroyed by the following year. 1493: The colony of La Isabela is established on the island of Hispaniola.
When did the Spanish reach New Mexico?
1598: Spanish reach Northern New Mexico. 1600: By 1600 Spain and Portugal were still the only significant colonial powers. North of Mexico the only settlements were Saint Augustine and the isolated outpost in northern New Mexico. Exploration of the interior was largely abandoned after the 1540s.
What was the name of the island in 1615?
1615 – Fort Nassau – Dutch. 1615 – Renews, Newfoundland – English. 1618 – Bristol's Hope – English. Map of the northern part and parts of the southern parts of the Americas, from the mouth of the Saint Laurent River to the Island of Cayenne,with the new discoveries of the Mississippi (or Colbert) River.
What was the name of the area where the Native Americans lived before the arrival of the Europeans?
People lived in the area called New England long before the first Europeans arrived. The lives of these Native Americans—part of the Algonquian language group—would be forever changed by the arrival of English colonists.
Which countries established colonies in North America?
Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands established colonies in North America. Each country had different motivations for colonization and expectations about the potential benefits. Grades. 3 - 12+.
What was the area before John Smith's voyage?
This map was created by National Geographic, for the book Voices from Colonial America: Maryland , 1643-1776, to demonstrate what this area was like before John Smith’s voyages as well as the routes of his voyage. Until John Smith's exploratory voyages of the Chesapeake Bay in 1608 and 1609 opened the region to European settlement, the land belonged to the Piscataways, Choptanks, and other Algonquian peoples, as it had for thousands of years. Choice land on the eastern and western shores of the bay was snapped up by colonists and turned into large English farms.
What did Native Americans call their home?
Native Americans called the land of the southeast their home for thousands of years before European colonization. The settlement of the Carolinas brought about a drastic change to their lives.
Where did the Spanish invade?
The invasion of the North American continent and its peoples began with the Spanish in 1565 at St. Augustine, Florida, then British in 1587 when the Plymouth Company established a settlement that they dubbed Roanoke in present-day Virginia. This first settlement failed mysteriously and in 1606, the London Company established a presence in what would become Jamestown, Virginia. From there, the French founded Quebec in 1608, then the Dutch started a colony in 1609 in present-day New York. While Native Americans resisted European efforts to amass land and power during this period, they struggled to do so while also fighting new diseases introduced by the Europeans and the slave trade.
When did the French and Dutch start colonizing New York?
From there, the French founded Quebec in 1608, then the Dutch started a colony in 1609 in present-day New York. While Native Americans resisted European efforts to amass land and power during this period, they struggled to do so while also fighting new diseases introduced by the Europeans and the slave trade.
Who was the first person to map the Chesapeake Bay?
Starting in 1607, Captain John Smith set about exploring and describing the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. This map, published in 1612, would become the primary cartographic resource on the region for nearly seven decades.
