
What colonies were affected by the proclamation of 1763?
New colonies. Besides regulating colonial expansion, the Proclamation of 1763 dealt with the management of inherited French colonies from the French and Indian War. It established government for four areas: Quebec, West Florida, East Florida, and Grenada .
How did settlements develop beyond the proclamation line?
Many settlements already existed beyond the proclamation line, some of which had been temporarily evacuated during Pontiac's War, and there were many already granted land claims yet to be settled. For example, George Washington and his Virginia soldiers had been granted lands past the boundary.
Why did Washington revoke the proclamation of 1763?
The Proclamation of 1763 will soon be revoked, Washington explained, because—“this I say between ourselves”—it was only meant “as a temporary expedient to quiet the minds of the Indians.”
Why were land companies denied land grants by King George III?
Organized land companies asked for land grants, but were denied by King George III. British colonists and land speculators objected to the proclamation boundary since the British government had already assigned land grants to them.
See more

Which court was used to hold smuggling trials?
This reinforced the policy that smuggling trials were to be held at vice-admirality courts rather than colonial courts
Which group of people agreed to support Britain in the French and Indian War?
Under his leadership, the British army finally began winning battles in the French and Indian War, and the Iroquois agreed to support Britain
What was the purpose of the British search warrant?
this general search warrant allowed British customs officials to search any colonial ship or building they believed to be holding smuggled goods
Why did the British oppose the Proclamation Line?
British colonists and land speculators objected to the proclamation boundary since the British government had already assigned land grants to them. Including the wealthy owners of the Ohio company who protested the line to the governor of Virginia, as they had plans for settling the land to grow business. Many settlements already existed beyond the proclamation line, some of which had been temporarily evacuated during Pontiac's War, and there were many already granted land claims yet to be settled. For example, George Washington and his Virginia soldiers had been granted lands past the boundary. Prominent American colonials joined with the land speculators in Britain to lobby the government to move the line further west.
Who issued the Proclamation of 1763?
t. e. The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain.
How did the Royal Proclamation affect the American Revolution?
Others have argued that colonial resentment of the proclamation contributed to the growing divide between the colonies and the mother country. Some historians argue that even though the boundary was pushed west in subsequent treaties, the British government refused to permit new colonial settlements for fear of instigating a war with Native Americans, which angered colonial land speculators. Others argue that the Royal Proclamation imposed a fiduciary duty of care on the Crown.
What was the name of the British colony in 1763?
John River on the Labrador coast was reassigned to the Newfoundland Colony. The lands west of Quebec and west of a line running along the crest of the Allegheny Mountains became (British) Indian Territory, barred to settlement from colonies east of the line.
What were the first two treaties that were signed with the Native Americans?
The first two of these treaties were completed in 1768; the Treaty of Fort Stanwix adjusted the border with the Iroquois Confederacy in the Ohio Country and the Treaty of Hard Labour adjusted the border with the Cherokee in the Carolinas. The Treaty of Hard Labour was followed by the Treaty of Lochaber in 1770, adjusting the border between Virginia and the Cherokee. These agreements opened much of what is now Kentucky and West Virginia to British settlement. The land granted by the Virginian and North Carolinian government heavily favored the land companies, seeing as they had more wealthy backers than the poorer settlers who wanted to settle west to hopefully gain a fortune.
What was the French and Indian War?
Under the treaty, all French colonial territory west of the Mississippi River was ceded to Spain, while all French colonial territory east of the Mississippi River and south of Rupert's Land (save Saint Pierre and Miquelon, which France kept) was ceded to Great Britain. Both Spain and Britain received some French islands in the Caribbean, while France kept Haiti and Guadeloupe.
What is the difference between indigenous law and indigenous law?
Note: "Aboriginal law" refers to Canadian law dealing with indigenous peoples, whereas "indigenous law" refers to the customary law of individual indigenous groups.
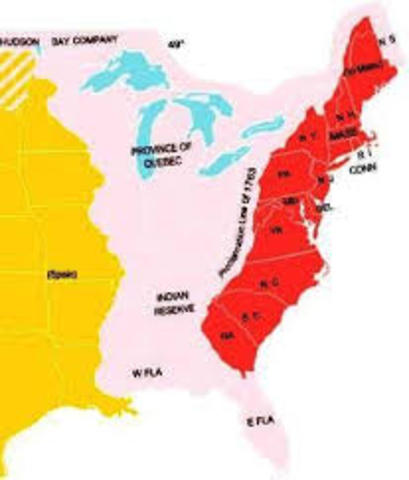
North America at The End of The Seven Years' War
The British Attempt to Enforce The Proclamation
- The British made a perfunctory effort to enforce the proclamation, periodically stopping settlers as they headed west and forcibly removing others. On one occasion, redcoats from Fort Pitt in present-day Pittsburgh even burned the huts of some nearby pioneers and escorted them back across the boundary. For the most part, though, colonists disregard...
The American Colonists Rebel
- Ultimately, the new acquisitions failed to quiet colonial discontent with the Proclamation of 1763. And though it would be later overshadowed by other complaints against the British, such as the Sugar Act, the Stamp Act, the Townshend Acts, the so-called Intolerable Acts and the Boston Massacre, it remained enough of a concern that the Declaration of Independencecriticized King …