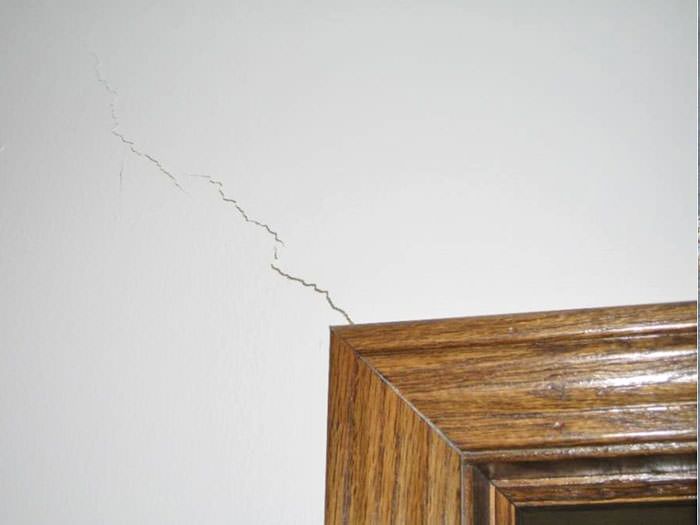

Causes of Settlement of Foundation
- Structural collapse of soil. Structural collapse of some soil, such as saline, non-cohesive soils, gypsum, silt and clay...
- Mining subsidence. Subsidence of ground may occur due to the removal of minerals and other materials from mines below.
- Underground erosion. Underground erosion may cause the formation of cavities in the subsoil...
What is the cause of foundation settlement?
The cause of foundation settlement is the reduction of volume air void ratio in the soil. Moreover, the magnitude of foundation settlement is controlled by many factors type of soil and foundation structure. Foundations on bedrock settle a negligible amount.
What causes structural settlement in clay soil?
This is the result of the decrease in the volume of loaded soil caused by the gradual expulsion of water from the voids. In clay soils, such Structural Settlement develops very slowly but may attain considerable magnitude in the course of the settlement.
How long does primary settlement of soil take place?
Take place over long period of time that ranges from 1 to 5 years or more. Primary settlement frequently occurs in saturated inorganic fine grain soil. Expulsion of water from pores of saturated fine grain soil is the cause of primary settlement.
What is primary settlement and secondary settlement?
Primary settlement frequently occurs in saturated inorganic fine grain soil. Expulsion of water from pores of saturated fine grain soil is the cause of primary settlement. Secondary settlement is the consolidation of soil under constant effective stress.

What are the causes of settlement of structure?
Foundation Settlement is due primarily to the expanding soil cycle (shrinkage and expansion) directly dependent on water content. This constant movement weakens and softens soils and can also create pockets/voids beneath your home's foundation, which your home will sink/settle into following the laws of gravity.
What is soil settlement?
In geotechnical engineering , settlement is defined as the vertical movement of the ground, generally caused be changes in stresses within the earth. Subsidence is a term often used to described 'caving in' or sinking of the ground, that may not be associated within changes in soil stresses.
What are the sources of settlement?
The following briefly describes a few of the more common causes of foundation settlement:1-Weak Bearing Soils.2-Poor Compaction.3-Changes in Moisture Content.4-Maturing Trees and Vegetation.5-Soil Consolidation.Foundation Underpinning and Piering.Foundation Push Piers.Push Pier Advantages:More items...
What are the three types of soil settlement?
There are three main types of soil settlement in geotechnical engineering: Uniform settlement. Differential settlement. Curvature settlement.
Which type of soils will cause soil settlement?
Immediate settlement take place mostly in coarse grained soils of high permeability and in unsaturated fine-grained soils of low permeability.
Why settlement of soil is important?
Settlement is an important criterion in the design of the foundations. Foundation settlement must be estimated carefully to ensure stability of buildings, towers, bridges, and any high cost structures. The main reason for the settlement occurrence is the compressive deformation of the soil.
What are the factors that influence the ground settlement?
Natural factors include: 1) Topography: the steep terrain, if drainage facilities undeserved or geologic conditions poor, it is easy to decrease the strength and stability of embankment; 2) Climate: seasonal climate makes moisture of the soil in the state of liquid or gas move from hot to cold and amass, which leads to ...
How can we prevent soil settlement?
Compacting the soil. Draining the soil, in case of cohesive types. Compacting the soil, in case of cohesion less soils. Confining the soil, increasing stiffness.
What are the effects of settlement?
The impact of human settlements on the environment increases with population growth, settlement expansion, economic growth and increased consumption. All indications are that the impact of human settlements on environmental resources is increasing.
What are the components of settlement of soil?
The total settlement of the ground consists of 3 components: immediate settlement (commonly referred to as elastic settlement, although this is a misnomer), consolidation settlement (or primary settlement) and creep settlement (or secondary settlement).
How do you determine soil settlement?
To find secondary consolidation settlement in the field (ΔHs), H = Thickness of the field consolidating stratum at the end of primary consolidation. Commonly initial thickness is used unless the primary consolidation is very large. Say more than 10% of initial thickness.
What are the types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed. Urban settlements are densely populated and are mostly non-agricultural. They are known as cities or metropolises and are the most populated type of settlement. These settlements take up the most land, resources, and services.
What are the types of soil settlement?
The total settlement of the ground consists of 3 components: immediate settlement (commonly referred to as elastic settlement, although this is a misnomer), consolidation settlement (or primary settlement) and creep settlement (or secondary settlement).
How do you determine soil settlement?
To find secondary consolidation settlement in the field (ΔHs), H = Thickness of the field consolidating stratum at the end of primary consolidation. Commonly initial thickness is used unless the primary consolidation is very large. Say more than 10% of initial thickness.
What are the types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed. Urban settlements are densely populated and are mostly non-agricultural. They are known as cities or metropolises and are the most populated type of settlement. These settlements take up the most land, resources, and services.
How long is soil settlement?
If left dry, clay and silt will settle rather quickly, i.e., 1-2 years. If they come in contact with water, they can settle in just a few months. However, we don't recommend using these soils around your foundation for structures or your lawn.
Causes For Structural Settlement?
Static loads are those imposed by the weight of a structure or an embankment.
What Is Soil Settlement?
Define Settlement: is the downward movement of the ground (soil) when a load is applied to it. The load increases the vertical effective stress exerted onto the soil. This stress, in turn, increases the vertical strain in the soil. This increase in vertical strain causes the ground to move downward.
What Is Foundation Structural Settlement?
The vertical downward displacements at the ground surface or the vertical downward displacement of a structure are often called Structural Settlement.
Types of Foundation Structural Settlement
This type caused by the compressive loading of the foundation based on the supporting soil may be divided into two kinds described as follows:
What is the difference between creep and immediate settlement?
Since soil particles are practically incompressible, consolidation settlements is caused by a reduction in voids due to gradual squeezing out of water. Finally, creep settlement occurs under a constant load and is depended on the stress history, the type of soil and the anisotropy of the soil.
What is the term for the movement of soil in the vertical direction?
Settlements refer to the soil’s movement in the vertical direction typically induced by stress changes. The total settlement of the ground consists of 3 components: immediate settlement (commonly referred to as elastic settlement, although this is a misnomer), consolidation settlement (or primary settlement) and creep settlement (or secondary settlement).
Which soil has higher permeability?
In particular, cohesionless soils have higher permeability than cohesive soils that have small voids blocking the water movement. In geotechnical design, the total settlement of the soil has to be properly predicted and must meet the requirements of the project. If the soil’s characteristics are not adequate to meet the aforementioned requirements ...
How long does creep settlement last?
The settlement process may be completed almost immediately or may last for a significant amount of time (even decades) depending on the soil’s permeability and water drainage paths.
Why does my foundation settle?
In some cases, homes can experience settlement as the soils underneath the foundation have a reduction in volume. This can be caused by the weight of the building over the years. Some foundation settlement is perfectly normal over time. Your home is heavy, and soils can compact more over time under the weight of your home. The amount of settlement typically varies based on the types of soils under your home. Soils such as saline, non-cohesive soils, gypsum, silt, and clay can create more settlement. In contrast, bedrock will settle much less.
Why does soil dry out?
These soils can dry out due to lowering water tables and, when the water is not replenished, it can cause the soil to compact ( subsidence ). In other cases, soils can breakdown and vertically compress due to the weight of the structure on the soil combined with other factors ( settlement ).
Why are trees bad for foundations?
Big trees, especially, are guilty of taking moisture away from the supporting soil under your foundation if planted too close to the foundation. Plants need water to survive and roots naturally seek out moisture. When the soils are shrinkable cohesive soils, plants can take away too much water from the foundation. This causes soils to shrink and foundations to sink. As you might expect, different species absorb different amounts of water. As a general guideline to planting distances from a property, root length and tree height are around the same.
What causes subsidence of the ground?
Some causes are man-made while others are natural geological changes. Natural causes such as fault movement or sediment compaction can cause subsidence. More commonly, however, the cause is man-made. Groundwater pumping, mining, oil and gas extraction, river channelization, and other manipulation of the ground can cause soil disruption that leads to subsidence.
What is foundation settlement?
Inevitably, soils deform under the load of foundation structures. The total vertical displacement that occur at foundation level is termed as settlement. The cause of foundation settlement is the reduction of volume air void ratio in the soil. Moreover, the magnitude of foundation settlement is controlled by many factors type of soil and foundation structure. Foundations on bedrock settle a negligible amount. In contrary, Foundations in other types of soil such as clay may settle much more. An example of this is Mexico City palace of fine arts has settled more than 15 feet (4.5m) into the clay soil on which it is founded since it was constructed in the early 1930s. However, building foundation settlement is normally limited to amounts measured in millimeter or fractions of an inch. Structures will suffer damages due to settlement of its foundation specifically when the settlement occur in quick manner. In this article, different types of foundation settlement along with their cases and expected effects on the structure will be discussed.
What is the most probable type of settlement?
If all parts of a building rest on the same kind of soil, then uniform settlement the most probable type to take place.
Where does immediate settlement take place?
Immediate settlement take place mostly in coarse grained soils of high permeability and in unsaturated fine-grained soils of low permeability.
How long does primary settlement take?
It also termed as primary consolidation. Take place over long period of time that ranges from 1 to 5 years or more. Primary settlement frequently occurs in saturated inorganic fine grain soil. Expulsion of water from pores of saturated fine grain soil is the cause of primary settlement.
What is differential settlement?
Differential settlement occurs if there is difference in soils, loads, or structural systems between parts of a building. in this case, different parts of the building structure could settle by substantially different amounts. Consequently, the frame of the building may become distorted, floors may slope, walls and glass may crack, ...
How many feet of soil did the Mexico City Palace of Fine Arts settle into?
An example of this is Mexico City palace of fine arts has settled more than 15 feet (4.5m) into the clay soil on which it is founded since it was constructed in the early 1930s. However, building foundation settlement is normally limited to amounts measured in millimeter or fractions of an inch.
What happens when a building is distorted?
Consequently, the frame of the building may become distorted, floors may slope, walls and glass may crack, and doors and windows may not work properly.
Why are settlements of granular soils more difficult to predict?
Settlements of granular soils, both elastic and creep movements, are more difficult to predict with any accuracy, largely because of the difficulty of obtaining and testing undisturbed soil samples, and settlements are usually estimated by indirect methods.
Which soil type has time dependent settlement?
Time-dependent settlements occur in both cohesive and granular soils, although the response time for granular soils is usually short.
What Is Foundation Structural Settlement?
The vertical downward displacements at the ground surface or the vertical downward displacement of a structure are often called Structural Settlement.
How does primary consolidation occur?
Primary consolidation results from the squeezing out of the water from the soil voids under the influence of excess pore-water pressures generated by the applied loading. This can take place over many months or years in clays but is usually quick in sands and gravels due to their greater permeability.
Why does lowering water level cause structural settlement?
Prolonged lowering of water level in fine-grained soils may introduce Structural Settlement due to consolidation. Repeated lowering also rising of water level in loose granular soils tend to compact the soil and cause Structural Settlement.
Why is structural settlement rarely uniform?
A Structural Settlement is seldom uniform over the area occupied by the foundation of a large building because of the non-uniformity of pressure distribution in the soil as well as variations in the compressibility at different parts of the area occupied by the foundations.
What is structural foundation?
A structural foundation is the part of a building that fixes it into the soil. These structures provide support for the main structures that appear above the soil level, much like the roots of a tree support the stem. One of its functions is to transfer loads from the structure to the ground.
Why do settlements occur on clay slopes?
The settlement may also occur due to creep on clay slopes.
What causes foundations to settle?
This sinking is called settlement of the structure. Following are the causes of foundation settlement: Structural collapse of soil. Mining subsidence.
Why does soil collapse?
Structural collapse of some soil, such as saline, non-cohesive soils, gypsum, silt and clay and loess, may occur due to the dissolution of the material responsible for the intergranular bond of grains.
What causes shrinkage in expansive soil?
Temperature change cause shrinkage in expansive soil due to which settlement occurs.
What causes cavities in the subsoil?
Underground erosion may cause the formation of cavities in the subsoil which when collapse cause settlement.
What is the final settlement of a foundation?
Generally, the final settlement of a foundation is of interest and U is considered equal to 1 (i.e. 100% consolidation) 1. Immediate Settlement. Immediate settlement takes place as the load is applied or within a time period of about 7 days. Predominates in cohesion less soils and unsaturated clay.
What is the difference between total settlement and differential settlement?
Total settlement is the magnitude of downward movement. Differential settlement is non-uniform settlement. It is "the difference of settlement between various locations of the structure. Angular distortion between two points under a structure is equal, to the differential settlement between the points divided by the distance between them.
Why is the leaning tower of Pisa undergoing consolidation settlement?
The lean is caused by consolidation settlement being greater on one side. This, however, is an extreme case. The principal settlements for most projects occur in 3 to 10 years.
How much settlement is acceptable for a road embankment?
A fixed-end arch would suffer greatly if the abutments settle or rotate. For road embankments, storage silos and tanks a settlement of 300mm - 600mm may be acceptable, but for machine foundations the settlement may be limited to 5mm 30mm. Different types of construction materials can withstand different degrees of distortion. For example, sheet metal wall panels do not show distress as readily as brick masonry.
What happens if soil shears fail?
A soil shear failure can result in excessive building distortion and even collapse. Excessive settlements can result in structural damage to a building frame nuisances such as sticking doors and windows, cracks in tile and plaster, and excessive wear or equipment failure from misalignment resulting from foundation settlements.
What is secondary consolidation?
Secondary consolidation may be the larger component if settlement in some soils, particularly in soils with a large organic component. Secondary consolidation is associated with both immediate & consolidation type settlements, although it is usually not of much significance with immediate settlements.
What happens after primary consolidation?
After primary consolidation the soil structure continues to adjust to the load for some additional time. This settlement is termed secondary consolidation/secondary compression. At the end of secondary consolidation the soil has reached a new K o -state (at-rest state).
What causes soil to shift unevenly?
The vibration of the soil from seismic activity, trains, structural work nearby, or even from traffic can cause soils to settle or shift unevenly, leading to structural damage to the building.
Why does my house settle?
The reasons behind your home’s settlement are rarely due to the foundation design itself, but because of changes happening in the soil.
What is Foundation Settlement?
The reasons behind your home’s settlement are rarely due to the foundation design itself, but because of changes happening in the soil.
What happens to foundations in summer?
During dry summer months, the soil around your foundation may begin to dry. Clay soils in particular shrink when they dry, creating a void between the structure and the soil. When this happens, your foundation settles, frequently resulting in structural damage.
Why is proper drainage important?
This is why proper site drainage is essential to ensure the subsoils maintain as close to uniform moisture content as possible throughout the year.
What is differential settlement?
Foundation settlement or differential settlement happens when builders don’t pay attention to the location’s soil composition, so they won't accommodate the foundation to the type of soil underneath it.
Why do tree roots grow in the ground?
Growing tree roots will catch moisture from the soil because they’re always searching for water, causing the soil to dry and shrink. It can take several decades before this type of problem becomes visible, and settlement is more likely to happen with shallow foundations than basement-level or deeper piers extending down many feet.
Causes of Settlement of Soil
How Do I Find My Soil Settlement?
- You can find soil settlement in your own house, when the soil settles, it goes down in a vertical direction. When the soil moves in the vertical direction, the foundationof the structure also goes down which produced cracks in walls and columns. These cracks indicate the settlement of soil.
What Are The Components of Settlement?
- The total settlement of filled soil or compacted soil has three-components, Immediate or elastic settlement, Primary settlement, andSecondary settlement 1. Elastic settlement:- Immediate settlement is denoted bySM. The immediate settlement of soil occurs at the beginning when the load of structure comes on soil through the footing and soil compressed, then air from the soil i…
Causes For Structural Settlement?
- May be caused due to the following facts: 1. Static loads are those imposed by the weight of a structure or an embankment. 2. Moving loads such as heavy traffic vehicles are transmitted through a road or airfield pavement. 3. Changes in moisture content may arise from natural causes such as seasonal fluctuation in the water table or the abstraction of water by roots of lar…
What Is Soil Settlement?
- Define Settlement:is the downward movement of the ground (soil) when a load is applied to it. The load increases the vertical effective stress exerted onto the soil. This stress, in turn, increases the vertical strain in the soil. This increase in vertical strain causes the ground to move downward. The settlement of soils in response to loading may...
What Is Foundation Structural Settlement?
- The vertical downward displacements at the ground surface or the vertical downward displacement of a structure are often called Structural Settlement. It is usually caused by the direct application of structural loads on the foundation, which in turn causes compression of the supporting material (soil or rock). However, in addition to the Structural Settlement under loads, …
Types of Foundation Structural Settlement
- This type caused by the compressive loading of the foundation based on the supporting soil may be divided into two kinds described as follows:
Methods of Predicting Structural Settlement
- 1. For the immediate structures:
The elastic theory may be used. Loading tests to provide useful information regarding an immediate Structural Settlement. - 2. For long-term consolidation Structural Settlement:
On clay soils, the most reliable method is that based on compressive tests on undisturbed samples and application of the theory of consolidation. If you liked this article, then please find us on Twitter and Facebook.