
... settlement hierarchy is a way of grouping and arranging these settlements into a hierarchy, thereby reflecting their rank based on one of the following criteria: (1) area and population, i.e., size of the settlement; (2) range and number of facilities and services within each settlement; and (3) relative sphere of influence 2 of each settlement.
What is the result of a settlement hierarchy?
The result is a settlement hierarchy. A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services. As you move up the settlement hierarchy the size of the settlement increases, as does the population and the range of services available.
How can we categorise settlements according to their size?
We can categorise settlements according to their size and shape. The result is a settlement hierarchy. A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services.
Why is the term'settlement hierarchy'problematic?
This term, used primarily in the United Kingdom, is problematic for some people since a hierarchy can sometimes imply that the things on top are better than things on the bottom. Keep in mind that this isn't an actual goal of the settlement hierarchy.
What happens as you move up the settlement pyramid?
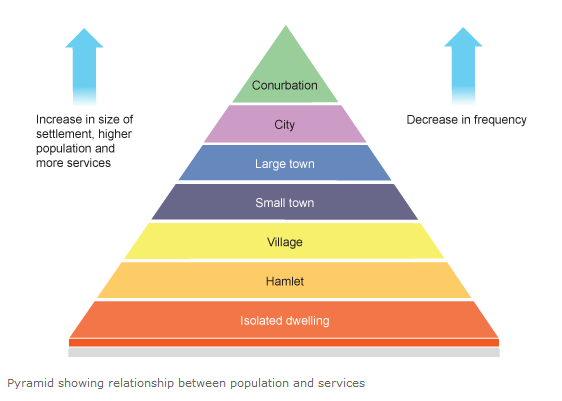
As you move up the pyramid, each layer represents a settlement that is larger in size and population, but which occurs less frequently. and finally, the conurbation, or a collection of cities and their associated suburbs with a population of over three million people.

What does a settlement hierarchy show?
A settlement hierarchy involves the classification of settlement types according to a number of factors; these include accessibility to services and the level of facilities provided by the settlement.
What is settlement pyramid?
settlement hierarchy is a way of grouping and arranging these settlements into a hierarchy, thereby reflecting their rank based on one of the following criteria: (1) area and population, i.e., size of the settlement; (2) range and number of facilities and services within each settlement; and (3) relative sphere of ...
What can be found at the base of the settlement hierarchy?
A settlement hierarchy ranks human population centers by size, population, and expected availability of services. Smaller settlements are at the bottom of the hierarchy, starting with the smallest dwellings with only a few people, and the world's largest cities and conurbations are at the top.
Why do we need settlement hierarchy?
The Settlement Hierarchy is an important component of the Local Plan because it provides the evidence base which will be used to inform the plans spatial option by underpinning the determination of the quantum and distribution of growth in the rural areas.
What is the order of settlement hierarchy?
A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services. As you move up the settlement hierarchy the size of the settlement increases, as does the population and the range of services available.
What are 4 types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed.
What are settlement hierarchies and how do they affect people?
A settlement hierarchy is when settlements are put in an order and classified based on their size and/or the range of services that they provide for people. The higher up the hierarchy you go, there are fewer settlements but they increase in their size in terms of population and the number of services provided.
Which of the following is at the highest level in hierarchy of settlements?
Conurbation occupies the highest position in the hierarchical human settlement. It comprises of large cities, towns and other urban areas that merge due to physical expansion caused by increased population, to form one continuous industrially developed area.
What are the 5 types of settlements?
There are 5 types of settlement classified according to their pattern, these are, isolated, dispersed, nucleated, and linear.
What makes a good settlement site?
a local water supply for drinking, washing, cooking and transport. dry land, so that people could build on areas that don't flood. a defendable site, eg a hilltop or river bend, to protect from attackers. good farm land with fertile soils, so people could grow crops.
What are the characteristics of settlements?
Characteristics that define human settlements are their site, location, size, function, form, and structure.Site refers to the exact location of where a settlement first started. ... Situation refers to the location of a settlement in relation to the surrounding area.More items...
What is a hierarchy in geography?
The Geography hierarchy contains attributes such as Country and Region, as well as Distribution Center, Call Center, and employee-specific attributes.
What are the 3 types of settlement patterns?
There are generally three types of settlements: compact, semi-compact, and dispersed.
What is settlement in foundation design?
Settlement is the downward movement of the ground caused by a load consolidating the soil below it or causing displacement of the soil. Settlement often refers to the downward movement of the ground around an excavated space, such as that for tunnels, shafts, or basements.
What is settlement in social studies?
A settlement is a colony or any small community of people. If a bunch of people build houses on the moon together, they'll have the first lunar settlement. A settlement is also the resolution of something such as a lawsuit. One kind of settlement is a place where people live.
What is settlement in geology?
In geotechnical engineering , settlement is defined as the vertical movement of the ground, generally caused be changes in stresses within the earth. Subsidence is a term often used to described 'caving in' or sinking of the ground, that may not be associated within changes in soil stresses.
What is the name of the pyramids that organize information about people?
As you may have noticed, we organize a lot of things into pyramids (the food pyramid, the exercise pyramid, etc). What if we need to organize information about places where people live by size and number of services? There's a pyramid for that too. It's called the settlement hierarchy.
What is a conurbation?
Finally, we get to the top of the pyramid. A conurbation is a collection of cities and their associated suburbs with a population of over three million people. You know how some cities seem to sort of melt together, creating one giant urban space? That's a conurbation. Conurbations have large and diverse populations, as well as a substantial amount of physical space, which lets them provide the greatest amount of services. Due to the high population numbers and the cost of maintaining these settlements, they are also less common than cities, towns, villages, hamlets, or isolated places. Even so, they're at the top of our hierarchy.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What is a settlement hierarchy?
A hierarchy is a ranking of items. So a settlement hierarchy is a ranking of settlements. This term, used primarily in the United Kingdom, is problematic for some people since a hierarchy can sometimes imply that the things on top are better than things on the bottom.
What does the bottom layer of the pyramid represent?
The bottom layers have fewer people and fewer services, but are more common. As you move up the pyramid, each layer represents a settlement that is larger in size and population, but which occurs less frequently. The layers, from bottom to top, are:
What is an isolated place?
isolated place, or a settlement with only a few households ; hamlet, or small places with populations of 100 people or less; village, or slightly bigger places that have a few hundred people; small town, or a slightly larger place that has a population of between 1,000 and 20,000 people;
How many people are in a conurbation?
and finally, the conurbation, or a collection of cities and their associated suburbs with a population of over three million people.
What is the German planning system?
The German planning system is based on the Central Place Theory developed by Walter Christaller in the 1930s and first applied in the Nazi Era, especially in Poland. Every settlement is categorized by function: highly central cities Oberzentrum [ de] (e.g. Hamburg, with speciality clinics for tropical diseases), middle central cities Mittelzentrum [ de] (for periodic functions e.g. Homburg (Saar) with major schools (starting at 5th grade)) and basic central towns Grundzentrum [ de] /Unterzentrum (e.g. Illingen with basic doctors and Supermarket). The number of inhabitants is less important: thus a city such as Kaiserslautern (100,000 people) can be a highly specialized city, because it is a centre for the surrounding rural area.
How many people live in Gigalopolis?
Gigalopolis or Gigacity - an incorporated of a group of megalopolis, containing over one hundred million residents.
What is the name of the city with a population of over one billion?
Eperopolis - incorporated gigacities in excess of one billion population, in which the entire continental region is an unbroken continuum of human settlements.
What is settlement hierarchy?
e. A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England.
What is the ecumenopolis?
Ecumenopolis - a theoretical construction in which the entire surface area of Earth is taken up by human settlements, or at least, that those are linked so that to create urban areas so big that they can shape an urban continuum through thousands of kilometers which cannot be considered as a gigalopolis. As of the year 2009, the United Nations estimated that for the first time more than 50% of the world's populations lived in cities, so if these were linked, the total population of this area would be about 3,400,000,000 people as of 2010.
How does a settlement affect its hierarchy?
A settlement's population size, its geographic area, its status and the availability of services can all affect this hierarchy. Position in a settlement hierarchy can also depend on the sphere of influence. This is how far people will travel to use the services in the settlement: if people travel further the town becomes more important and ranks higher in the settlement hierarchy.
What is a Regiopolis?
Regiopolis or City - a large city with a large population and many services. The population is less than one million but over 300,000 people.
How to categorize settlements?
We can categorise settlements according to their size and shape. The result is a settlement hierarchy. A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services.
What is the difference between a settlement hierarchy and a smaller settlement?
A settlement hierachy. As you move up the settlement hierarchy the size of the settlement increases, as does the population and the range of services available. Smaller settlements tend to provide only low order services such as a post office and newsagents. Whereas, larger settlements have more high order services such as leisure centres ...
What is high order settlement?
This is the market area that a settlement services (the distance people will travel to use services). High order services usually have a high threshold. This means they need a higher number of people to use the service in order to remain profitable.
The setltement hierarchy pyramid describes how change in population of a dweeling depends on the size and services of the dwelling
The setltement hierarchy pyramid describes how change in population of a dweeling depends on the size and services of the dwelling.
You then have a small town, like Haslemere. It has 100 houses, a few pubs, a small inn, a main road and a supermarket
You then have a small town, like Haslemere. It has 100 houses, a few pubs, a small inn, a main road and a supermarket.
details
Threshold - The boundary around a shop that it needs to get people from to stay in buisness
What are the services that settlements provide?
The number of services that a settlement provides increases with settlement size. Small settlements will only provide low-order services such as a post offices, doctors and newsagents. Large towns, cities and conurbations will provide low and high-order services such as leisure centres, chain stores and hospitals.
What is the result of grouping and classifying settlements according to their size and shape?
If we group and classify a number of settlements according to their size and shape, the result is settlement hierarchy.
What are the characteristics of a settlement?
Settlement characteristics. Settlements are varied in size, type and location. More can be learnt about a settlement by studying its size, placement in the landscape, and its situation in relation to surrounding features. Part of. Geography.
Which has a larger sphere of influence?
Larger settlements and conurbations have a much larger sphere of influence than smaller ones. This means they attract people from a wider area because of the facilities they offer. Cities such as London have a global sphere of influence, whereas a small hamlet or village may only have a sphere of influence of a couple of kilometres.
What is the range of a service?
The range of a service or product is the maximum distance people are prepared to travel to purchase it. The range of a newspaper is much lower than an item of furniture for example.
Summary
A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England. The term is also used in the planning system for the UK and for some other countries such as Ireland, India, and Switzerland. The term was used without comment by the geographer Bria…
Overview
In Europe, centuries-old settlements were surrounded by farmland and tended not to be wider than 30 minutes' walk from one end to the other, with wealthier people monopolizing the "town center", and poorer people living on the town's outskirts or nearby countryside (the "sphere of influence"). With the advent of decentralization technologies (e.g., bicycles, trains, cars, etc.), American settlements reversed this trend before reaching their saturation point, with vast farmla…
Example of a settlement hierarchy
In this example, a roadhouse is at the lowest level while the ecumenopolis is at the top with the greatest number of residents:
This is only an example, and in other contexts, the population criteria for each category of settlement might be different.
Note: This settlement hierarchy is adapted from the work of Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis fo…
Settlement hierarchy by country
The position of a settlement in the hierarchy is intended to inform decisions about new developments, such as housing. Rather than define the hierarchy by population, an alternative way to construct the hierarchy is based on the services that are available within each settlement. Settlements are described as "level 1", "level 2", etc. rather than using terms such as village or town. The Government planning statement (PPS3) does not specifically mention "settlement hie…
See also
• Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis
• Ekistics
• Green transport hierarchy
• Street hierarchy
External links
• Why Cities Are Where They Are?