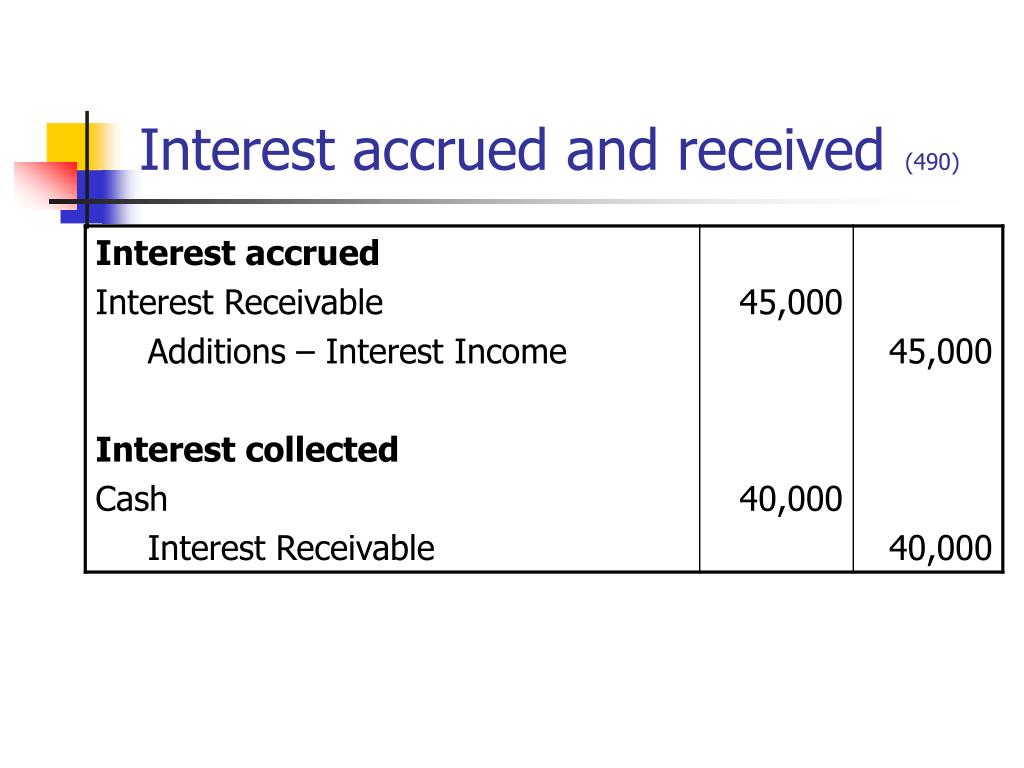
Settlement Interest means, with respect to any payment required to be made pursuant to Section 3.2 (c) (a “ Settlement Payment ”), the sum of accrued interest on the amount of such Settlement Payment, calculated at the Settlement Rate as from time to time in effect, for the period from the Closing Date to and including the date upon which such Settlement Payment is made (calculated on the basis of the actual number of days elapsed in a year of 365 or 366 days, as the case may be).
What is'accrued interest'?
What is 'Accrued Interest'. Accrued interest is the amount of interest earned on a debt but not yet collected. Interest accumulates from the date a loan is issued or when a bond's coupon is made. BREAKING DOWN 'Accrued Interest'. Accrued interest is calculated based on the last day of the accounting period.
What is accrued interest on bonds?
Accrued interest occurs when a bond is not traded on its coupon payment date. It is the part of the interest that a bond buyer gives up from the last coupon payment date to the date the bond is bought. The amount of accrued interest can be calculated by the formula below:
What does settled without accrued interest mean?
Under the “settled without accrued interest” convention, seller generally keeps (if and when paid by borrower) all interest accruing through the earlier of the actual closing date or the “Commencement Date” 1 for “delayed compensation” 2, but buyer has no obligation to front such interest to seller at closing 3 .
Which amount of accrued interest should be recorded?
The amount of accrued interest to be recorded is the accumulated interest that has yet to be paid as of the end date of an accounting period. Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period.
What is the meaning of accrued interest?
In accounting, accrued interest refers to the amount of interest that has been incurred, as of a specific date, on a loan or other financial obligation but has not yet been paid out. Accrued interest can either be in the form of accrued interest revenue, for the lender, or accrued interest expense, for the borrower.
What is settlement interest?
Settlement Interest means the amount obtained by accruing interest on the Settlement Payment at the Settlement Rate, in effect from time to time, for the period from (but excluding) the date on which the Effective Time occurs to (but excluding) the date upon which the Settlement Payment is made.
What happens when you buy a bond with accrued interest?
If you're selling, you're entitled to the price of the bond, plus the accrued interest that the bond has earned up to the sale date. The buyer compensates you for this portion of the coupon interest, which is generally handled by adding the amount to the contract price of the bond.
How do you clear accrued interest?
To record the accrued interest over an accounting period, debit your Interest Expense account and credit your Accrued Interest Payable account. This increases your expense and payable accounts.
How is interest calculated on a settlement?
the amount payable at settlement multiplied by the default interest rate, divided by the number of days in the calendar year, multiplied by the number of days between the original settlement date and the new settlement date (to account for the daily interest rate accrued).
What is the purpose of a settlement option?
The primary objective of settlement option is to generate regular streams of income for the insured. Description: Under settlement option, the insured receives a regular flow of income from the insurer post the maturity of the policy.
Does accrued interest include settlement date?
Definition of Accrued Interest The purchaser must pay this amount of accrued interest to the seller at the time of the transaction's settlement. Interest accrues from the date of the last interest payment date up to, but not including, the transaction's settlement date.
What is the difference between interest and accrued interest?
Accrued interest is the accumulated interest that has been recognized and recorded but has not been paid as of a specific date. Regular interest is the payment made in exchange for borrowing money from a lender.
Who pays accrued interest?
The accrued interest is paid by the buyer of a bond to the seller; the issuer is not involved in the process. The accrued interest payment is added to the market price, so bonds will always cost more than the quoted price.
What will be the treatment of accrued interest if appearing in the trial balance?
Accrued Income is treated as an asset for the company , hence it will be shown in Asset Side in the Balance Sheet.
What does accrued mean in accounting?
An accrual is an accounting adjustment used to track and record revenues that have been earned but not received, or expenses that have been incurred but not paid.
What does settlement mean in banking?
Settlement involves the delivery of securities or cash from one party to another following a trade. Payments are final and irrevocable once the settlement process is complete. Physically settled derivatives, such as some equity derivatives, require securities to be delivered to central securities depositories.
What is the interest on a pre settlement loan?
The interest rates on lawsuit loans run between 27% and 60% a year—rates that are comparable to payday loans. On a $25,000 loan, the interest can cost you $12,500 or more in just one year.
Does accrued interest include settlement date?
Definition of Accrued Interest The purchaser must pay this amount of accrued interest to the seller at the time of the transaction's settlement. Interest accrues from the date of the last interest payment date up to, but not including, the transaction's settlement date.
What is Treasury settlement?
Settlement involves the finalization of a payment, so that a new party takes possession of transferred funds. The treasurer should be aware of these processes in order to understand the timing of payment transfers.
What is accrued interest?
Accrued interest refers to interest generated on an outstanding debt during a period of time, but the payment has not yet been made or received by the borrower or lender.
What is an adjusting entry for accrued interest?
The adjusting entry for accrued interest consists of an interest income and a receivable account from the lender’s side, or an interest expense and a payable account from the borrower’s side.
What is the borrower's entry?
The borrower’s entry includes a debit in the interest expense account and a credit in the accrued interest payable account. The lender’s entry includes a debit in accrued interest receivable and a credit in the interest revenue.
What is accrual interest in accounting?
Accrual-based accounting requires revenues and expenses to be recorded in the accounting period when they are incurred, regardless of when the cash payments are made.
What is a T account?
T Accounts Guide If you want a career in accounting, T Accounts may be your new best friend. The T Account is a visual representation of individual accounts
Is interest income a current asset?
Since the payment of accrued interest is generally made within one year, it is classified as a current asset ...
Does the clean price include accrued interest?
The amount of accrued interest should be earned by the bond seller. The quoted price in the bond market, known as the clean price or flat price, does not include any accrued interest. When a bond is traded between two coupon payment dates, its full price (also known as dirty price), which is the present value of its future cash flows, ...
What is the interest paid on a bond?
The interest paid on a bond is compensation for the money lent to the borrower, or issuer, this borrowed money is referred to as the principal. The principal amount is paid back to the bondholder at maturity. Similar to the case of the coupon, or interest payment, whoever is the rightful owner of the bond at the time of maturity will receive ...
How often do bonds pay interest?
These interest payments, known as coupons, are typically paid every six months. During this period the ownership of the bonds can be freely transferred between investors. A problem then arises over the issue of the ownership ...
What happens after a bond is converted to shares?
After the bond has been converted to shares of the issuer, the bondholder stops receiving interest payments. At the time an investor converts a convertible bond, there will usually be one last partial payment made to the bondholder to cover the amount that has accrued since the last payment date of record. For example, assume interest on ...
What happens when you buy bonds in the secondary market?
When buying bonds in the secondary market, the buyer will have to pay accrued interest to the seller as part of the total purchase price. An investor that purchases a bond sometime between the last coupon payment and the next coupon payment will receive the full interest on the scheduled coupon payment date ...
What happens to the bond when it is sold before maturity?
If the bond is sold before maturity in the market the seller will receive the bond's market value. The accrued interest adjustment is thus the extra amount of interest that is paid to the owner of a bond or other fixed-income security. The amount paid is equal to the balance of interest that has accrued since the last payment date of the bond.
When buying bonds in the secondary market, do you have to pay the seller?
When buying bonds in the secondary market, the buyer will have to pay accrued interest to the seller as part of the total purchase price. An investor that purchases a bond sometime between the last coupon payment and the next coupon payment will receive the full interest on the scheduled coupon payment date given that they will be the bondholder of record. However, since the buyer did not earn all of the interest accrued over this period, they must pay the bond seller the portion of the interest that the seller earned before selling the bond.
How often do you pay coupon payments on a bond?
Interest accumulates from the date a loan is issued or when a bond's coupon is made, but coupon payments are only paid twice a year. The accrued interest adjustment on a bond is the amount paid, which is equal to the balance of interest that has accrued since the last payment date of the bond.
Examples of Settlement Interest in a sentence
Any amounts paid under Section 8.3 or Section 8.5, shall bear interest for the period from and including the day following Bank Closing to and including the day preceding the payment at the Settlement Interest Rate.
More Definitions of Settlement Interest
Settlement Interest means the amount obtained by accruing interest on the Settlement Payment at the Settlement Rate, in effect from time to time, for the period from ( but excluding) the date on which the Effective Time occurs to (but excluding) the date upon which the Settlement Payment is made.
Related to Settlement Interest
Settlement Interest Rate means, for the first calendar quarter or portion thereof during which interest accrues, the rate determined by the Receiver to be equal to the equivalent coupon issue yield on twenty-six (26)-week United States Treasury Bills in effect as of Bank Closing as published in The Wall Street Journal; provided, that if no such equivalent coupon issue yield is available as of Bank Closing, the equivalent coupon issue yield for such Treasury Bills most recently published in The Wall Street Journal prior to Bank Closing shall be used.
What Does Accrued Interest Mean?
The accrual basis of accounting requires that expenses must be recognized when incurred regardless of when they are actually paid. Thus, interest that is due on a certain date but goes unpaid is still recorded to reflect the expense.
What happens when a bondholder sells a bond?
At the time of sale, the buyer pays the bondholder the net value of the bond plus the accrued interest, which is the product of the coupon rate multiplied by the number of days that have elapsed since the last payment.

Understanding Accrued Interest
- Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period. For example, assume interest is payable on the 20th of each month, and the accounting period is the end of each calendar month. The month of April will require an accrual of 10 days of interest, from the 21st t…
Accrued Interest Example - Accounting
- Consider the following example. Let us assume there is a $20,000 loan receivable with an interest rate of 7.5%, on which payment has been received for the period through the 20th day of the month. In this scenario, to record the extra amount of interest revenue that was earned from the 21st to the 30th of the month, the calculation would be as follows: 1. (7.5% x (10 / 365)) x $20,00…
Accrued Interest Example - Bonds
- Accrued interest is an important consideration when purchasing or selling a bond. Bonds offer the owner compensation for the money they have lent, in the form of regular interest payments. These interest payments, also referred to as coupons, are generally paid semiannually.1 If a bond is bought or sold at a time other than those two dates each year, the purchaser will have to tack on…
Accrual Interest in Accounting
Accrual Interest in Accounting – Example
- For example, on March 21, a company borrows $100,000 from a bank at an annual interest rate of 6%, and its first interest payment is due in 30 days on April 20. The annual interest is $6,000 ($100,000 * 4%), and the monthly payment is $500 ($6,000 / 12). Assuming the accounting period ends on March 31 for both the lender and the borrower, the interest payment incurred within the …
Accrued Interest in Bonds
- Under the bond perspective, accrued interest refers to the part of the interest that has been incurred but not paid since the last payment day of the bond interest. Bonds can be traded in the market every day, while their interests are usually paid annually or semi-annually. Accrued interest occurs when a bond is not traded on its coupon payment da...
Accrued Interest in Bonds – Example
- For example, a Treasury bond with a $1,000 par value has a coupon rate of 6% paid semi-annually. The bond matures in two years, and the market interest rate is 4%. The last coupon payment was made on March 31, and the next payment will be on September 30, which gives a period of 183 days. The coupon payment for each period is $30 ([6%/2] * $1,000). If a trader buys the bond on …
Additional Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Accrued Interest. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: 1. Accounting Transactions 2. Coupon Rate 3. Net Present Value (NPV) 4. T Accounts Guide