What factors contributed to the settlement of the Great Plains
Great Plains
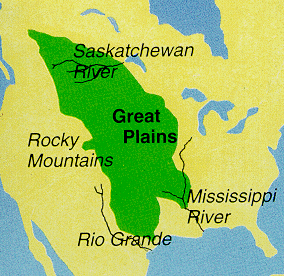
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland, located in North America. It lies west of the Mississippi River tallgrass prairie in the United States and east of the Rocky Mountains in the U.S. and Canada.
Full Answer
What was the first settlement in the Great Plains?
European Settlement of the Great Plains. The main settlement of the Great Plains occurred after the 1840 migrations to Oregon and the 1849 Gold Rush to California. Environmental historian William Cronon has interpreted the history of the Great Plains in terms of narrative.
What happened to the Great Plains after European settlement?
European Settlement of the Great Plains. The overgrazed Plains were depleted of the perennial grasses that had supported one steer on every two acres and were seeded with less nutritious annuals that supported one steer per 5 to 10 acres. As perennials declined, wind and water erosion increased and topsoils were lost.
Why did farmers leave the Great Plains in the 1930s?
Settlement came in years of good rains, so the Great Plains were overpopulated in the first rush. A heavy emigration followed the twin blows of drought and economic depression in the 1930s. Many grain farmers left because their farms were too small and more vulnerable to drought than the cattle ranches.
Why did people move to the Great Plains?
Younger sons from the eastern seaboard - where the population was growing and land was becoming more expensive - went because it was a chance to own their own land. They were followed by other Americans - such as tradesmen and government officials - who hoped to make their living from the farmers who had moved onto the Plains.

Why did settlement increase in the Great Plains?
In 1862, at the height of the US Civil War, Abraham Lincoln took advantage of the absence of the slave-owning southern states to sign into law the Homestead Act of 1862. This revolutionary act opened up huge amounts land in the American Great Plains to private settlement.
What promoted settlement of the Great Plains?
The railroads promoted settlement by providing land along their tracks and by mounting vigorous advertising campaigns. Attracting immigrants to the Plains was economically important for land companies, as well as for the already settled residents of the territories and many newly organized states.
What was the settlement of Great Plains?
The Great Plains were sparsely populated until about 1600. Spanish colonists from Mexico had begun occupying the southern plains in the 16th century and had brought with them horses and cattle. The introduction of the horse subsequently gave rise to a flourishing Plains Indian culture.
How did settlers change the Great Plains?
Settlement from the East transformed the Great Plains. The huge herds of American bison that roamed the plains were almost wiped out, and farmers plowed the natural grasses to plant wheat and other crops. The cattle industry rose in importance as the railroad provided a practical means for getting the cattle to market.
Why did people settle in the Great Plains in the 1800s?
1) Manifest Destiny: The US Government wanted settlers to move onto the Plains as they needed the land to be settled and farmed and for communities and towns to grow up and expand. This was needed if the USA was to be a rich and successful country. The government therefore promoted the idea of Manifest Destiny.
What were the 5 reasons for westward expansion?
What were 5 reasons for westward expansion?free land railroad gold and silver adventure and opportunity cattleWhat were some challenges the cowboys faced on the long drive?Violent storms, wind, rain, moving rivers, stampedes, rustlers, hot sun, discrimination, and 15 hours on the saddle38 more rows
What are the Great Plains known for?
Eight of the leading U.S. wheat states (Kansas, North Dakota, Texas, Montana, Nebraska, Colorado, Oklahoma, and South Dakota) lie within the Great Plains, and the Prairie Provinces are the leading wheat producers in Canada. Of increasing importance are crops of such oilseeds as sunflower and canola.
What encouraged settlers to move west to Great Plains?
The Homestead Act encouraged settlers to move to the Great Plains. Life was hard, but settlers discovered that they could grow wheat using new technologies. By 1890 the land had been settled and farmed, and there was no longer a true frontier in the United States.
What factor caused the greatest increase in settlement of the Great Plains after the Civil War?
Encouraged by the Homestead Act of 1862 which gave willing farmers land on the Great Plains, and new technologies which allowed people to live in more challenging environments, farmers and immigrants flocked to the Great Plains during the decades after the Civil War.
What were the factors that contributed to the development of the Great Plains?
Students' answers will vary but they should mention some of the following factors: the free land provided to people willing to work the land; the decade of unusually frequent rain; the global demand for wheat; the Great Plains' suitability for bonanza wheat farming; and the new farming technologies developed in the ...
What encouraged settlers to move west to Great Plains?
The Homestead Act encouraged settlers to move to the Great Plains. Life was hard, but settlers discovered that they could grow wheat using new technologies. By 1890 the land had been settled and farmed, and there was no longer a true frontier in the United States.
How did the Homestead Act encourage settlement of the Great Plains?
The Homestead Act encouraged western migration by providing settlers with 160 acres of land in exchange for a nominal filing fee. Among its provisions was a five-year requirement of continuous residence before receiving the title to the land and the settlers had to be, or in the process of becoming, U.S. citizens.
What factors pushed people to move to the Great Plains to farm?
European immigrants flooded onto the Great Plains, seeking political or religious freedom, or simply to escape poverty in their own country. Younger sons from the eastern seaboard - where the population was growing and land was becoming more expensive - went because it was a chance to own their own land.
What factor caused the greatest increase in settlement of the Great Plains after the Civil War?
Encouraged by the Homestead Act of 1862 which gave willing farmers land on the Great Plains, and new technologies which allowed people to live in more challenging environments, farmers and immigrants flocked to the Great Plains during the decades after the Civil War.
What was the main settlement of the Great Plains?
European Settlement of the Great Plains. The main settlement of the Great Plains occurred after the 1840 migrations to Oregon and the 1849 Gold Rush to California. Environmental historian William Cronon has interpreted the history of the Great Plains in terms of narrative. The grand narrative of America, Cronon argues, is a story of progress.
What were the two factors that led to the development of the Great Plains?
Historian Walter Prescott Webb's The Great Plains (1931) builds on Turner's progressive narrative, describing the rancher's and farmer's fron tiers on the Plains in terms of two formative factors — environment and technology . Webb states: "New inventions and discoveries had to be made before the pioneer farmer could go into the Great Plains and establish himself."12 Technologies allowed settlers to subdue a forbidding environment that had three main characteristics not found in the eastern United States. First, as pioneers moved west of the 100th meridian, the environment of the Plains became increasingly arid, lacking the minimum twenty inches of rainfall per year that would support agriculture reliably. Second, the Plains were treeless, and therefore did not provide the timber for fuel and building materials readily available in the East. Third, the Trans-Mississippi Plains were level, rising only gradually westward, which meant that rivers were shallow and lacked the power to operate mills or float ships.
What was the fourth technology that subdued the Plains?
The fourth technology that subdued the Plains was the John Deere plow. Like the mill, the plow was one of the important pieces of technology that changed Western history. The earliest plows of southern Europe, pulled by oxen, successfully scratched the dry shallow soils of the Mediterranean region.
What are the two formsative accounts of the Great Plains?
Two formative accounts reveal the environmental history of the Great Plains as a progressive narrative: Frederick Jackson Turner's "Significance of the Frontier in American History" (1893); and Walter Prescott Webb's The Great Plains (1931) . The opposite, or declensionist narrative, according to Cronon, relates history as environmental decline.
What technology did Webb use to control the Plains?
Following the Colt six-shooter (1835), which had subdued the Plains Indians, the second piece of technology that, from Webb's perspective, transformed the Plains was barbed wire.
What is the grand narrative of the Great Plains?
The grand narrative of America, Cronon argues, is a story of progress. The frontier narrative depicts that formative story and, as such, is the master narrative of American culture. A hostile environment, initially conceptualized as ...
What was the Great Plains?
A hostile environment, initially conceptualized as a Great American desert, was gradually brought under control and transformed into a garden, making the Great Plains a Garden of the World. That transition in perception occurred as people increasingly settled the Plains and gained control over nature.
When did the settlers move to the Plains?
After 1865, thousands of settlers moved onto the Plains.
Who hoped to make their living from the farmers who had moved onto the Plains?
They were followed by other Americans - such as tradesmen and government officials - who hoped to make their living from the farmers who had moved onto the Plains.
Why did grain farmers leave the Great Plains?
Many grain farmers left because their farms were too small and more vulnerable to drought than the cattle ranches.
Who settled the prairies?
The Prairie Provinces were settled by British, German Russians (many of them Mennonites ), Ukrainians, and Scandinavians. Buffalo Hunt, Chase, painting by George Catlin, 1844. Many of the immigrants were religious, thrifty, hardworking people who developed a strong attachment to the land.
What are the crops grown in the Great Plains?
Thus, the Great Plains have remained basically an agricultural area producing wheat, cotton, corn (maize), sorghum, and hay and raising cattle and sheep.
What did the Spanish bring to the Plains?
Spanish colonists from Mexico had begun occupying the southern plains in the 16th century and had brought with them horses and cattle. The introduction of the horse subsequently gave rise to a flourishing Plains Indian culture. In the mid-19th century, settlers from the eastern United States began to supplant the Indians, ...
When did cattle replace buffalo?
Indians on horseback exploited the buffalo herds for some two and a half centuries; but in the 1870s cattle replaced the buffalo, and cowboys replaced the Indians. In the 1880s and ’90s farmers began to crowd the ranchers, and wheat began to replace cattle. Settlement came in years of good rains, so the Great Plains were overpopulated in ...
Which states have potash?
The Great Plains states also produce much mineral wealth, with Texas leading the nation in mineral production and four other plains states (Oklahoma, New Mexico, Wyoming, and Kansas) ranking high.