
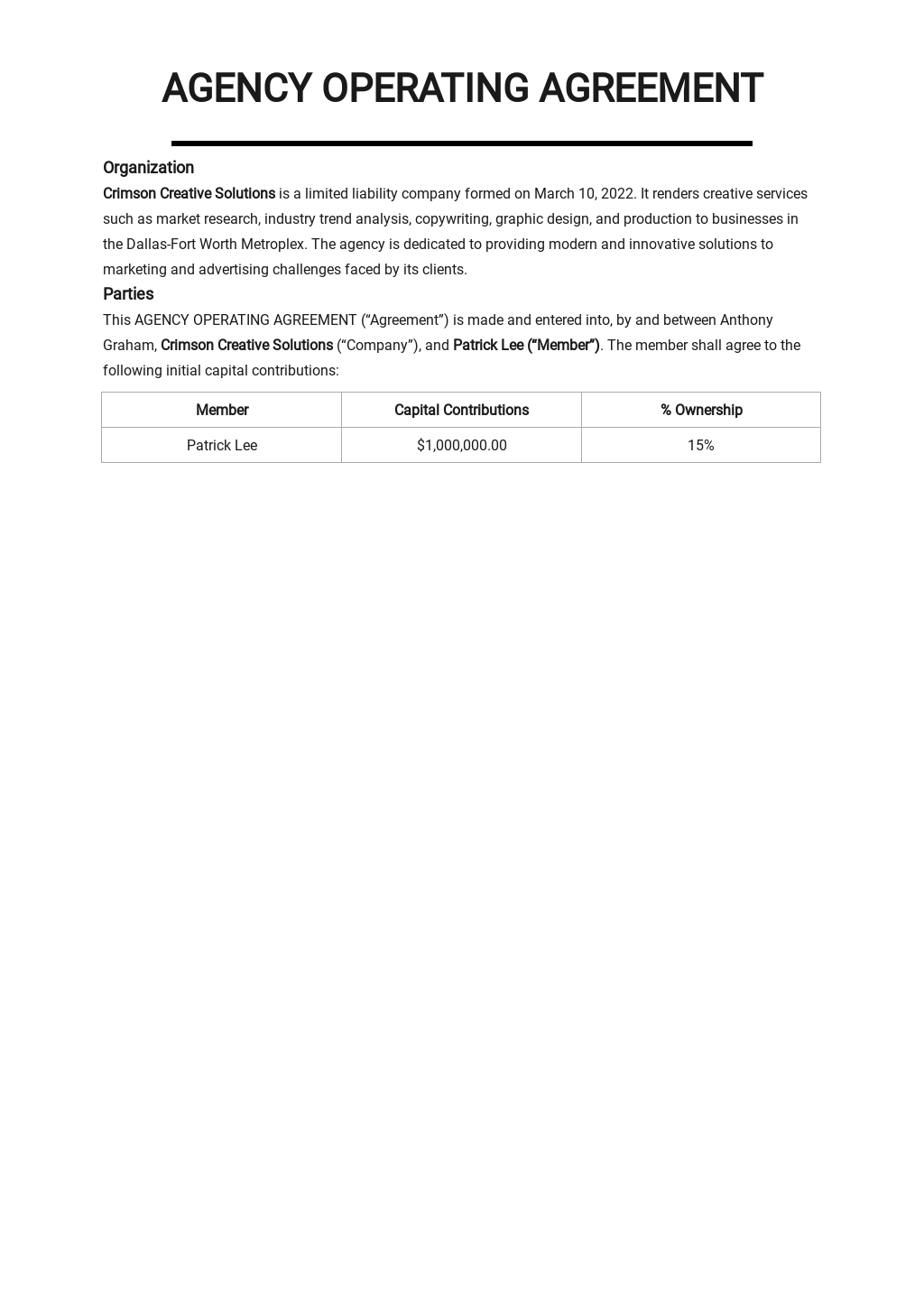
Master Settlement Agreement
- Master Settlement Agreement Fact Sheet. The Master Settlement Agreement (MSA) imposes major restrictions on tobacco company marketing practices and prohibits advertising aimed at youth.
- Settlement Payments to Counties and Cities
- Smokeless Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement. ...
Full Answer
What was the Master Settlement Agreement of 1998?
The 1998 Master Settlement Agreement between the major tobacco companies, 46 U.S. states, the District of Columbia and five U.S. territories transformed tobacco control.
What is the tobacco Master Settlement Agreement?
The Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement ( MSA) was entered on November 23, 1998, originally between the four largest United States tobacco companies ( Philip Morris Inc., R. J. Reynolds, Brown & Williamson and Lorillard – the "original participating manufacturers", referred to as the "Majors") and the attorneys general of 46 states.
What happens after the Master Settlement Agreement execution date?
After Master Settlement Agreement Execution Date, free samples cannot be distributed except in a facility or enclosed area where the operator ensures no underage person is present. Bans gifts without proof of age (legible driver’s license certified to be valid by the gift recipient).
Can a settling company benefit from a state’s settlement?
If a settling state enters into an agreement with a company not participating in this settlement and the terms are more favorable to the industry, settling companies can benefit, but only within that state.
What was the 1998 Master Settlement Agreement?
The 1998 Master Settlement Agreement between the major tobacco companies, 46 U.S. states, the District of Columbia and five U.S. territories transformed tobacco control. In the largest civil litigation settlement in U.S. history, the states and territories scored a victory that resulted in the tobacco companies paying the states ...
When did the MSA start?
The Attorneys General of the 46 states, the District of Columbia and five U.S. territories signed the MSA with the four largest U.S. tobacco companies in 1998.
Who was sued by the MSA?
territories in the mid-1990s against major U.S. cigarette manufacturers Philip Morris, R.J. Reynolds, Brown & Williamson and Lorillard, plus the tobacco industry's trade associations.
Does MSA include individual claims?
This did not include individual claims their citizens may have.
What is the purpose of entering into agreements with major retail chains?
Entering into agreements with major retail chains to ensure that retailers comply with state laws setting the minimum age at which tobacco products may be purchased and limiting the quantity and content of tobacco advertising at retail locations.
How many tobacco companies have settled under the MSA?
Eventually, more than 45 tobacco companies settled with the Settling States under the MSA. Although Florida, Minnesota, Mississippi, and Texas are not signatories to the MSA, they have their own individual tobacco settlements, which occurred prior to the MSA.
How does MSA work?
The MSA’s purpose is to reduce smoking in the U.S., especially in youth, which is achieved through: 1 Raising the cost of cigarettes by imposing payment obligations on the tobacco companies party to the MSA. 2 Restricting tobacco advertising, marketing, and promotions, including:#N#Prohibiting tobacco companies from taking any action to target youth in the advertising, promotion or marketing of tobacco products.#N#Banning the use of cartoons in advertising, promotions, packaging, or labeling of tobacco products.#N#Prohibiting tobacco companies from distributing merchandise bearing the brand name of tobacco products.#N#Banning payments to promote tobacco products in media, such as movies, televisions shows, theater, music, and video games.#N#Prohibiting tobacco brand name sponsorship of events with a significant youth audience or team sports. 3 Eliminating tobacco company practices that obscure tobacco’s health risks. 4 Providing money for the Settling States that states may choose to use to fund smoking prevention programs. 5 Establishing and funding the Truth Initiative, an organization “dedicated to achieving a culture where all youth and young adults reject tobacco.”
What is the purpose of the MSA?
The MSA’s purpose is to reduce smoking in the U.S., especially in youth , which is achieved through: Raising the cost of cigarettes by imposing payment obligations on the tobacco companies party to the MSA.
Is the MSA subject to constitutional defenses?
Also, because the contractual requirements of the MSA are in some ways broader than the authority granted to the FDA and are not subject to constitutional defenses, state attorneys general continue to step in where the FDA may be unable to act.
Do tobacco companies have to pay settlements?
Under the MSA, tobacco manufacturers are obligated to make annual payments to the Settling States in perpetuity, so long as cigarettes are sold in the United States by companies that have settled with the States. The NAAG Center for Tobacco and Public Health makes certain such payments are made.
Examples of Master Settlement Agreement in a sentence
A longitudinal study of externally visible cigarette advertising on retail storefronts in Massachusetts before andafter the Master Settlement Agreement.
More Definitions of Master Settlement Agreement
Master Settlement Agreement means the master settlement agreement, the smokeless tobacco master settlement agreement, and the consent decree approved and entered by the court in the case denominated State of Colorado, ex rel. Gale A. Norton, Attorney General v. R.J.
When was the MSA signed?
Since the MSA was signed in November 1998, about 50 other tobacco companies have signed onto the agreement and are also bound by its terms.
What is the MSA?
In 1998, the Attorney General's Office reached a settlement (the Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement or “MSA”) with the major U.S. tobacco manufacturers that imposes major restrictions on the industry's advertising and marketing machine, curtails its ability to fight anti-tobacco legislation in our political arena, and provides states quick mechanisms to enforce the agreement.
What was the MSA's mission?
The MSA also called for the creation of a nonprofit organization, the Legacy Foundation, funded by the settling states. This foundation was charged with educating the nation about the social costs, addictive nature and negative health effects associated with tobacco consumption.
When was the Master Settlement Agreement signed?
Adoption of the "Master Settlement Agreement". In November 1998 , the Attorneys General of the remaining 46 states, as well as of the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands, entered into the Master Settlement Agreement with the four largest manufacturers of cigarettes in the United States.
What is the tobacco master settlement agreement?
The Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement ( MSA) was entered in November 1998, originally between the four largest United States tobacco companies ( Philip Morris Inc., R. J. Reynolds, Brown & Williamson and Lorillard – the "original participating manufacturers", referred to as the "Majors") and the attorneys general of 46 states. The states settled their Medicaid lawsuits against the tobacco industry for recovery of their tobacco-related health-care costs. In exchange, the companies agreed to curtail or cease certain tobacco marketing practices, as well as to pay, in perpetuity, various annual payments to the states to compensate them for some of the medical costs of caring for persons with smoking-related illnesses. The money also funds a new anti-smoking advocacy group, called the Truth Initiative, that is responsible for such campaigns as Truth and maintains a public archive of documents resulting from the cases.
Why did the OPMs and the settling states not join the MSA?
The OPMs worried that the NPMs, both because they would not be bound by the advertising and other restrictions in the MSA and because they would not be required to make payments to the settling states, would be able to charge lower prices for their cigarettes and thus increase their market share.
How long does it take for a SPM to join the Master Settlement Agreement?
As an incentive to join the Master Settlement Agreement, the agreement provides that, if an SPM joined within ninety days following the Master Settlement Agreement's "Execution Date," that SPM is exempt ("exempt SPM") from making annual payments to the settling states unless the SPM increases its share of the national cigarette market beyond its 1998 market share, or beyond 125% of that SPM's 1997 market share. If the exempt SPM's market share in a given year increases beyond those relevant historic limits, the MSA requires that the exempt SPM make annual payments to the settling states, similar to those made by the OPMs, but based only upon the SPM's sales representing the exempt SPM's market share increase.
What was the 1997 National Settlement Proposal?
This proposed congressional remedy (1997 National Settlement Proposal (NSP), a.k.a. the "June 20, 1997 Proposal") for the cigarette tobacco problem resembled the eventual Multistate Settlement Agreement (MSA), but with important differences. For example, although the congressional proposal would have earmarked one-third of all funds to combat teenage smoking, no such restrictions appear in the MSA. In addition, the congressional proposal would have mandated Food and Drug Administration oversight and imposed federal advertising restrictions. It also would have granted immunity from state prosecutions; eliminated punitive damages in individual tort suits; and prohibited the use of class actions, or other joinder or aggregation devices without the defendant's consent, assuring that only individual actions could be brought. The congressional proposal called for payments to the states of $368.5 billion over 25 years. By contrast, assuming that the Majors would maintain their market share, the MSA provides baseline payments of about $200 billion over 25 years. This baseline payment is subject to
Who are the original participating manufacturers in the MSA?
The four manufacturers— Philip Morris USA, R. J. Reynolds Tobacco Company, Brown & Williamson Tobacco Corp., and Lorillard Tobacco Company —are referred to in the MSA as the Original Participating Manufacturers (OPMs). This settlement process yielded two other national agreements:
Who carried the Global Settlement Agreement?
The attorneys general did not have the authority to grant all this by themselves: the Global Settlement Agreement would require an act of Congress. Senator John McCain of Arizona carried the bill, which was much more aggressive than even the global settlement.
How long after master settlement agreement is it required to stop smoking?
Beginning 180 days after the Master Settlement Agreement Execution Date, companies must: Develop and regularly communicate corporate principles that commit to complying with the Master Settlement Agreement and reducing youth smoking.
When did tobacco companies enter into settlement agreements?
If tobacco companies, before October 1, 2000, enter into an agreement with better overall terms, settlement states will get the benefit of that agreement. (This does not apply to any agreement reached after the seating of a jury or commencement of trial.)
What happens after state specific finality?
After state specific finality, tobacco companies will be prohibited from opposing proposed state or local laws or administrative rules which are intended to limit youth access to and consumption of tobacco products.
Can you distribute free samples after master settlement?
After Master Settlement Agreement Execution Date, free samples cannot be distributed except in a facility or enclosed area where the operator ensures no underage person is present.
How long after MSA execution date can you make a payment?
Manufacturer may, beginning 30 days after the MSA Execution Date, make, orcause to be made, any payment or other consideration to any other person or entityto use, display, make reference to or use as a prop any Tobacco Product, TobaccoProduct package, advertisement for a Tobacco Product, or any other item bearing
What happens after the MSA execution date?
After the MSA Execution Date, the Original Participating Manufacturers and theTobacco-Related Organizations will support an application for the dissolution of anyprotective orders entered in each Settling State's lawsuit identified in Exhibit D withrespect only to those documents, indices and privilege logs that have been produced as ofthe MSA Execution Date to such Settling State and (1) as to which defendants have madeno claim, or have withdrawn any claim, of attorney-client privilege, attorney work-product protection, common interest/joint defense privilege (collectively, "privilege"),trade-secret protection, or confidential or proprietary business information; and (2) thatare not inappropriate for public disclosure because of personal privacy interests orcontractual rights of third parties that may not be abrogated by the Original ParticipatingManufacturers or the Tobacco-Related Organizations.
Can a manufacturer enter into a contract with a baseball team?
Manufacturer may enter into any agreement pursuant to which payment is made (or other consideration is provided) by such Participating Manufacturer to anyfootball, basketball, baseball, soccer or hockey league (or any team involved inany such league) in exchange for use of a Brand Name.
Can a participant manufacturer provide a coupon after the MSA execution date?
after the MSA Execution Date, no Participating Manufacturer may provide orcause to be provided to any person without sufficient proof that such person is anAdult any item in exchange for the purchase of Tobacco Products, or thefurnishing of credits, proofs-of-purchase, or coupons with respect to such apurchase. For purposes of the preceding sentence only, (1) a driver's license orother government-issued identification (or legible photocopy thereof), the validityof which is certified by the person to whom the item is provided, shall by itself bedeemed to be a sufficient form of proof of age; and (2) in the case of itemsprovided (or to be redeemed) at retail establishments, a Participating Manufacturershall be entitled to rely on verification of proof of age by the retailer, where suchretailer is required to obtain verification under applicable federal, state or locallaw.
What is the Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement?
The Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement simultaneously represents one of the most egregious examples of a government shakedown of private industry and offers a case study of the problems that stem from big government and big business scratching each other’s backs. It has turned the largest tobacco companies into an indispensable cash cow for politicians and bureaucrats, enabled irresponsible state spending, and, amazingly, has resulted in less money for public health and tobacco control while propping up a declining industry. As is the case with discriminatory tobacco taxes, the incentives of the MSA are perverse: the more people smoke, the more money the government gets to spend on whatever it wants. The biggest losers are those with tobacco-related diseases and smokers trying to quit.
What was the master settlement agreement between the tobacco companies and the states?
In November 1998, forty-six US states, along with the District of Columbia and five US territories, and the major tobacco companies entered into a contract of an extraordinary nature. (The other four states, Florida, Minnesota, Mississippi, and Texas, had entered similar agreements on their own beginning the year before.) The agreement, known as the Master Settlement Agreement (MSA), represented the culmination of a decades-long argument between the tobacco companies and state governments. After the dangers of smoking became known, the tobacco industry had engaged in extensive efforts to somehow stay in business, deflect and defeat lawsuits, and minimize negative attention. Public healthcare systems—and most of the healthcare in this country is taxpayer-funded or subsidized—had seen an influx of patients with smoking-related diseases, and state governments began filing lawsuits against the tobacco companies, claiming they wanted money to help cover smoking-related healthcare costs. The tobacco companies had lots of money but were nervous about the states’ potential to sue them out of business. So, they decided to talk. The result was the MSA.
What was the result of the MSA?
So, they decided to talk. The result was the MSA. Under the agreement, the tobacco companies would make payments, forever, to state governments. These would cover the costs of smoking-related illnesses.
What are the incentives of the MSA?
As is the case with discriminatory tobacco taxes, the incentives of the MSA are perverse: the more people smoke, the more money the government gets to spend on whatever it wants. The biggest losers are those with tobacco-related diseases and smokers trying to quit.
