Settlements are Israeli cities, towns and villages in the West Bank and the Golan Heights The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant, spanning about 1,800 square kilometres. The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between disciplines: as a geological and biogeographical region, the Golan Heights is a basaltic plateau bordered by the Yar…Golan Heights
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem or Eastern Jerusalem is the sector of Jerusalem that was occupied by Jordan during the Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was occupied by Israel. Since the 1967 Arab-Israeli War, East Jerusalem has been, along with the res…
Full Answer
What is considered a settlement in Israel?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War —the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
Where are the Israeli settlements in the West Bank?
[12] [13] [14] [15] Israeli settlements currently exist in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), claimed by the State of Palestine as its sovereign territory, and in the Golan Heights, widely viewed as Syrian territory.
Why did Israel build settlements in the Old Testament?
Israeli settlements were erected for a variety of reasons. In some cases, Israelis sought to recover property lost in the 1948 war and the hostilities leading up to it, such as the core settlements of Gush Etzion between Jerusalem and Hebron.
Where are the remains of Jewish settlement in Jerusalem?
^ Israel Antiquities Authority (10 April 2007). "Remains of Jewish settlement revealed in the Shu'afat neighborhood of Jerusalem". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs website. Retrieved 28 July 2018. ^ "Jerusalem even older than thought: Archaeologists find 7,000-year-old houses".
See more
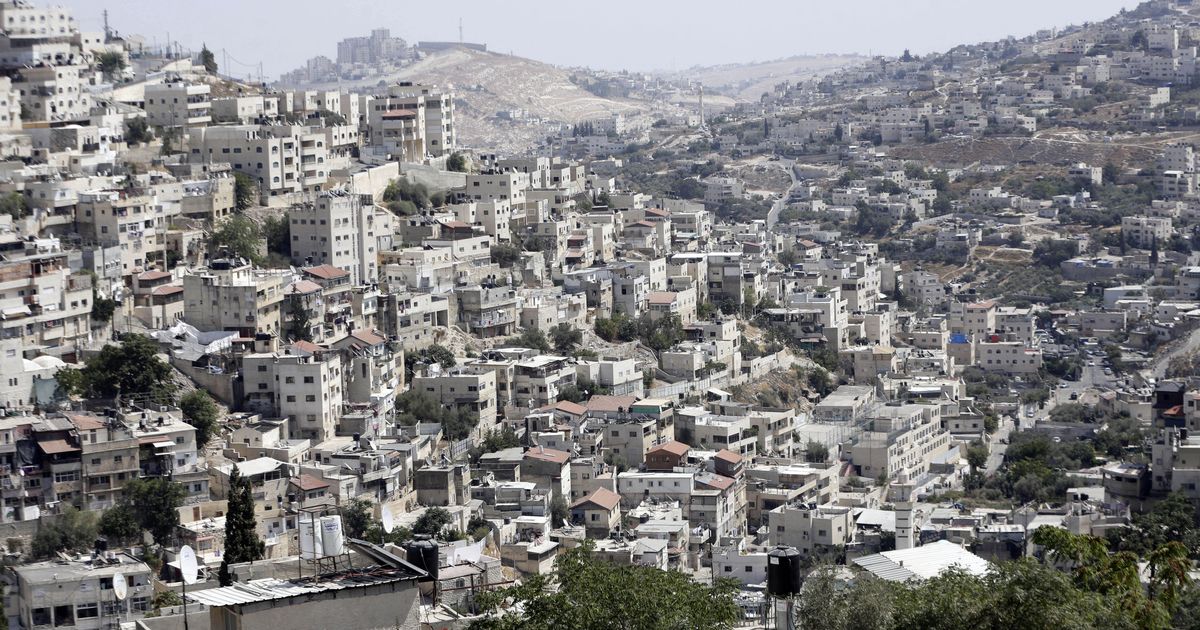

What does settlement mean in Israel?
Settlements are Jewish communities in historic Palestine built by the Zionist movement pre-1948 and thereafter by the state of Israel. These communities can range in size from single-person outposts to entire cities. One of the first settlements built by Zionists was Tel Aviv in the early 20th century.
What is a settlement in Palestine?
Settlements are communities of Jews that have been moving to the West Bank since it came under Israeli occupation in 1967. Some of the settlers move there for religious reasons, some because they want to claim the West Bank territory as Israeli land, and some because the housing there tends to be cheap and subsidized.
Are settlements in Israel illegal?
At present, based on the result of numerous UN resolutions that cite Article 49 of the Geneva Convention, the consensus view of the international community is that Israeli settlements are illegal and constitute a violation of international law.
How many settlements does Israel have?
Today they total around 400,000 and live in about 130 separate settlements (this doesn't include East Jerusalem, which we'll address in a moment). They have grown under every Israeli government over the past half-century despite consistent international opposition.
Why does Israel have settlements?
Ideological settlers, seeking to maximize Jewish possession of biblical lands, set up settlements such as Kiryat Arba near Hebron. Settlements continued to expand in the decades that followed, and by 1993 there were more than 280,000 people living in settlements (130,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded).
Why is Israel taking Palestinian homes?
Israel demolishes the homes of two people accused of carrying out a deadly attack in the occupied West Bank last year. Israeli troops have demolished the homes of two Palestinians accused of carrying out a deadly shooting attack in the occupied West Bank last year, the military said.
Where are the settlements in Israel?
Israeli settlements currently exist in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), claimed by the State of Palestine as its sovereign territory, and in the Golan Heights, widely viewed as Syrian territory.
What human rights has Israel violated?
Israel's continued policies and practices had resulted in flagrant human rights violations and abuses, including brutalisation of children, torture, forcible transfers, and colonisation of land.
What was Israel before it became Israel?
When World War I ended in 1918 with an Allied victory, the 400-year Ottoman Empire rule ended, and Great Britain took control over what became known as Palestine (modern-day Israel, Palestine and Jordan).
Who occupies Jerusalem now?
IsraelJerusalemJerusalem יְרוּשָׁלַיִם (Hebrew) القُدس (Arabic)Administered byIsraelClaimed byIsrael and PalestineIsraeli districtJerusalemPalestinian governorateQuds46 more rows
What is the current status of Jerusalem?
The status of Jerusalem is disputed in both international law and diplomatic practice, with both the Israelis and Palestinians claiming Jerusalem as their capital city.
What was Israel before 1948?
The region was ruled under the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948, when the Jewish State of Israel was proclaimed in part of the ancient land of Israel. This was made possible by the Zionist movement and its promotion of mass Jewish immigration.
What are settlements in history?
Settlements may include hamlets, villages, towns and cities. A settlement may have known historical properties such as the date or era in which it was first settled, or first settled by particular people.
Where are the settlements in Israel?
Israeli settlements currently exist in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), claimed by the State of Palestine as its sovereign territory, and in the Golan Heights, widely viewed as Syrian territory.
When did Israel settle in Palestine?
1967When the guns fell silent in 1967, the Israeli state began building colonies, or settlements, for its Jewish Israeli citizens on Palestinian land it had just occupied. Settlements have become the hallmark of the Israeli colonial project in Palestine.
How many settlements are in the West Bank?
As of 2022, there are 140 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem. In addition, there are over 100 Israeli illegal outposts in the West Bank.
Where are the settlements located?
Settlements are located in three places: the. West Bank. The West Bank is the territory captured from Jordan by Israel in 1967. It remains the core piece of disputed territory between Israelis and Palestinians. , parts of Eastern Jerusalem, and the. Golan Heights.
Why are Israeli settlements cheaper?
For some, it’s for ideological/religious reasons (which we’ll get into below); for others, it’s simply cheaper housing. Many settlement neighborhoods are within easy commuting distance of major Israeli cities and present a more affordable cost of living and a kind of pastoral quality of life — you know, the same reason some New Yorkers might move to Jersey. These settlers have left Israel’s crowded middle for airy communities in a beautiful landscape, often with government subsidies that make their homes cheaper than alternatives within Israel proper.
Why are settlements so controversial?
In short, because they are Jewish communities on a land that many want to become part of a future Palestinian state.
What do you mean by ideological settlers?
Ideological settlers are people who choose to live in the West Bank because they believe it is part of the land that God promised to Abraham and his descendants in the Bible. These settlers generally believe in the notion of “Greater Israel” — that is, that all of the land extending from the Mediterranean sea to the Jordan River, north to the borders with Lebanon and Syria, and south to the Red Sea, constitutes a Jewish inheritance.
Where did this belief come from?
The ideology of the religious settler movement draws significantly from the messianic beliefs of religious Zionism — specifically, the teachings of Rabbi Avraham Yitzhak Kook and his son Rabbi Zvi Yehuda Kook about active redemption.
How many Palestinians live in the West Bank?
As of writing this in 2019, over 3 million people live in the West Bank; 87% are Palestinians and 13% are settlers. Excluding Eastern Jerusalem, there are 132 “official” settlements — those recognized by the Israeli government — and 106 illegal outposts, or settlements established since the 1990s without government approval.
What is the name of the plateau that Israel captured in the 1967 war?
Golan Heights. Golan Heights. The Golan Heights is a plateau captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 war. It was effectively annexed by Israel in 1981. . Typically, when people talk about Israeli settlements, they’re talking about the West Bank.
What is an Israeli settlement?
Israeli settlement. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree.... Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the disputed territories captured by Israel in ...
What was the purpose of the settlements in the Jordan Valley?
Israel’s political and defense establishments, meanwhile—inspired in part by the peace plan of Yigal Allon, the deputy prime minister (1967–77)—spurred the development of settlements in strategic locations such as the Jordan Valley that would bolster Israel’s security and strengthen its hand in negotiations .
How many people lived in settlements in 1993?
Settlements continued to expand in the decades that followed, and by 1993 there were more than 280,000 people living in settlements (130,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded).
When were the settlements in the Sinai Peninsula evacuated?
Settlements in the Sinai Peninsula were either dismantled or evacuated in 1982, and settlements in the Gaza Strip were dismantled in 2005. It is disputed, moreover, whether communities in the formally annexed territories of East Jerusalem (part of the West Bank territory under Jordanian rule from 1949 to 1967) and the Golan Heights constitute ...
How many settlers were there in 2019?
Despite the agreement, settlement building proliferated, especially in the West Bank, and in 2019 the number of settlers reached nearly 630,000 (413,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded). Most of these newer settlers were motivated less by reasons of ideology or recovering lost property, however, than by cheaper housing and financial incentives ...
What is the West Bank?
West Bank, area of the former British-mandated (1920–47) territory of Palestine west of the Jordan River, claimed from 1949 to 1988 as part of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan but occupied from 1967 by Israel. The territory, excluding East Jerusalem, is also known within…
Where is Israel located?
Israel, country in the Middle East, located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bounded to the north by Lebanon, to the northeast by Syria, to the east and southeast by Jordan, to the southwest by Egypt,…
What are the settlements in East Jerusalem?
East Jerusalem settlements (2006) Golan Heights settlements (1992) Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Jewish ethnicity, built in violation of international law on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Israeli settlements currently exist in ...
Where are the Israeli settlements?
Israeli settlements currently exist in the Palestinian territory of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and in the Syrian territory of the Golan Heights. East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights have been annexed by Israel, so residents are treated equivalently to the rest of Israel under Israeli law.
How many settlements were there in the Gaza Strip?
Before Israel's unilateral disengagement plan in which the Israeli settlements were evacuated, there were 21 settlements in the Gaza Strip under the administration of the Hof Aza Regional Council. The land was allocated in such a way that each Israeli settler disposed of 400 times the land available to the Palestinian refugees, and 20 times the volume of water allowed to the peasant farmers of the Strip.
What was the Allon Plan?
It implied Israeli annexation of major parts of the Israeli-occupied territories, especially East Jerusalem, Gush Etzion and the Jordan Valley. The settlement policy of the government of Yitzhak Rabin was also derived from the Allon Plan.
How was Kiryat Arba established?
According to a secret document dating to 1970, obtained by Haaretz, the settlement of Kiryat Arba was established by confiscating land by military order and falsely representing the project as being strictly for military use while in reality, Kiryat Arba was planned for settler use.
What territories did Israel control?
It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and from Syria it captured most of the Golan Heights, which since 1981 has been administered under the Golan Heights Law .
How does settlement affect the economy?
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the security of the Israeli citizens living there.
When did the first settlements in Jerusalem occur?
Scholars believe the first human settlements in Jerusalem took place during the Early Bronze Age—somewhere around 3500 B.C.
Which country took over Jerusalem?
After World War I, Great Britain took over Jerusalem, which was part of Palestine at the time. The British controlled the city and surrounding region until Israel became an independent state in 1948. Jerusalem was divided during the first 20 years of Israel’s existence.
Why is the Western Wall considered the holiest place in the world?
Each year, millions of Jews from around the world visit the wall. Because Muslims control the Temple Mount (the true site of the ancient Temples), the Western Wall is considered the holiest place where Jews can pray.
When was the second Temple destroyed?
In 37 B.C., King Herod restructured the second Temple and added retaining walls to it. Jesus was crucified in the city of Jerusalem around 30 A.D. The Romans destroyed the second Temple in 70 A.D. In 632 A.D., Muhammad, the Islamic prophet, died and was said to have ascended to heaven from Jerusalem.
Why did Israel take over the Temple Mount?
Because it has religious and historical implications, occupation of the Temple Mount has been the cause of bitter conflict for centuries, especially between Jews and Muslims living nearby. During the Six-Day War, Israel gained control of the Temple Mount.
What was the name of the mosque that was built on the Dome of the Rock?
In 1187, Muslims recaptured the Dome of the Rock and re-designated it as a shrine. A silver-domed mosque, called al-Aqsa, sits adjacent to the Dome of the Rock on the Temple Mount. Both structures are considered holy to Muslims.
What religions are in Jerusalem?
Jerusalem is a site of major significance for the three largest monotheistic religions: Judaism , Islam and Christianity , and both Israel and Palestine have claimed Jerusalem as a capital city. Because of these strong, age-old associations, bloody conflicts to control the city and sites within it have been waged for thousands of years.
Who captured Jerusalem?
Jerusalem was captured in 1073 by the Seljuk Turkish commander Atsız. After Atsız was killed, the Seljuk prince Tutush I granted the city to Artuk Bey, another Seljuk commander. After Artuk's death in 1091 his sons Sökmen and Ilghazi governed in the city up to 1098 when the Fatimids recaptured the city.
What is the holy city of Jerusalem?
In Sunni Islam, Jerusalem is the third-holiest city, after Mecca and Medina. In Islamic tradition, in 610 CE it became the first qibla, the focal point for Muslim prayer ( salat ), and Muhammad made his Night Journey there ten years later, ascending to heaven where he speaks to God, according to the Quran.
Why is West Jerusalem not recognized internationally?
From 1949 until 1967, West Jerusalem served as Israel's capital, but was not recognized as such internationally because UN General Assembly Resolution 194 envisaged Jerusalem as an international city. As a result of the Six-Day War in 1967, the whole of Jerusalem came under Israeli control. On 27 June 1967, the government of Levi Eshkol extended Israeli law and jurisdiction to East Jerusalem, but agreed that administration of the Temple Mount compound would be maintained by the Jordanian waqf, under the Jordanian Ministry of Religious Endowments.
How many people left Jerusalem in 2005?
In terms of the local population, the number of outgoing residents exceeds the number of incoming residents. In 2005, 16,000 left Jerusalem and only 10,000 moved in. Nevertheless, the population of Jerusalem continues to rise due to the high birth rate, especially in the Haredi Jewish and Arab communities.
What is the kingdom of Melchizedek in the Dead Sea Scrolls?
The Aramaic Apocryphon of Genesis of the Dead Sea Scrolls (1QapGen 22:13) equates Jerusalem with the earlier "Salem" (שלם), said to be the kingdom of Melchizedek in Genesis 14.
How many members are on the Jerusalem City Council?
The Jerusalem City Council is a body of 31 elected members headed by the mayor, who serves a five-year term and appoints eight deputies. The former mayor of Jerusalem, Uri Lupolianski, was elected in 2003. In the November 2008 city elections, Nir Barkat was elected. In November 2018, Moshe Lion was elected mayor.
How many times has Jerusalem been destroyed?
Throughout its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th millennium BCE, in the shape of encampments of nomadic shepherds.
Where are the Israeli settlements?
This is a list of Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights. Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement ...
When did Israel start building settlements in the Golan Heights?
Golan Heights. Construction of Israeli settlements began in the portion of the Golan Heights held by Israel in 1967, which was under military administration until Israel passed the Golan Heights Law extending Israeli law and administration throughout the territory in 1981.
What happened to East Jerusalem?
Following the capture and occupation of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem in 1967, the Israeli government effectively annexed the formerly Jordanian occupied territory and extended the Jerusalem municipality borders by adding 70,500 dunams of land with the aim of establishing Jewish settlements and cementing the status of a united city under Israeli control. The Jerusalem Master Plan 1968 called for increasing the Israeli population of Arab East Jerusalem, encircling the city with Israeli settlements and excluding large Palestinian neighborhoods from the expanded municipality. Jerusalem was effectively annexed by Israel in 1980, an act that was internationally condemned and ruled "null and void" by the United Nations Security Council in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478. The international community continues to regard East Jerusalem as occupied territory and Israel's settlements there illegal under international law.
Is the Israeli settlement illegal?
The international community considers Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories illegal under international law, violating the Fourth Geneva Convention 's prohibition on the transfer of a civilian population to or from occupied territory, though Israel disputes this.
Did Israel have settlements in the Sinai Peninsula?
Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement from Gaza in 2005 and the Sinai settlements were evacuated with the Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty and the return of the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. This list does not include West Bank ...
Does Israel have a right to the Golan?
Israel maintains it has a right to retain the Golan, citing the text of UN Resolution 242, which calls for "safe and recognised boundaries free from threats or acts of force". However, the international community rejects Israeli claims to title to the territory and regards it as sovereign Syrian territory.
Is East Jerusalem annexed?
Israel in effect annexed East Jerusalem with the Jerusalem Law and considers settlements in the expanded boundaries of East Jerusalem to be neighborhoods of Jerusalem and not settlements. The United Nations Security Council ruled that act "null and void" in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, and the international community considers East Jerusalem to continue to be held under Israeli occupation .
Where did the Jewish community live in Jerusalem?
By partition in 1947, a thriving Jewish community was living in the eastern part of Jerusalem, an area that included the Jewish Quarter of the Old City. This area also contains many sites of religious importance, including the City of David, the Temple Mount and the Western Wall.
What was the city of Jerusalem before 1865?
Before 1865, the entire population of Jerusalem lived inside the Old City walls, what today would be considered East Jerusalem. Later, when the city expanded due to population growth, both Jews and Arabs began to build in new areas of the city.
Is East Jerusalem part of Israel?
East Jerusalem was formally recognized as part of Israel by Israel's Supreme Court in 1967; however, the international community considers Jewish communities beyond the 1949 armistice line as illegel settlements. Before 1865, the entire population of Jerusalem lived inside the Old City walls, what today would be considered East Jerusalem.

Overview
- Conflict Resolution — The main way to resolve such conflict in antiquit was to call a meeting of the ekklesia, the assembly of the people, and listen to and consider speeches following the conventions of deliberative rhetoric, the aim of which speeches was to overcome ‘stasis’ [standi…
Housing costs and state subventions
Number of settlements and inhabitants
Character: rural and urban
History
Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, overwhelmingly of Jewish ethnicity, built on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli settlements to be illegal under international law, though Israel disputes this.
Israeli settlements currently exist in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), …
Geography and municipal status
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the securit…
Types of settlement
As of 2022, there are 140 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem. In addition, there are over 100 Israeli illegal outposts in the West Bank. In total, over 450,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank excluding East Jerusalem, with an additional 220,000 Jewish settlers residing in East Jerusalem.
Additionally, over 20,000 Israeli citizens live in settlements in the Golan Heights.
Resettlement of former Jewish communities
Settlements range in character from farming communities and frontier villages to urban suburbs and neighborhoods. The four largest settlements, Modi'in Illit, Ma'ale Adumim, Beitar Illit and Ariel, have achieved city status. Ariel has 18,000 residents, while the rest have around 37,000 to 55,500 each.