Because you applied a force on the soil, which makes it compress and displaced it, making a dent. The same applies to buildings. A vertical displacement that happens on the structure when the load occurs is called settlement of the foundation.
Full Answer
What are the causes of structural settlement?
The Structural Settlement may be caused due to the following facts: Static loads such as those imposed by the weight of a structure or an embankment. Moving loads such as heavy traffic vehicles are transmitted through a road or airfield pavement.
How does reinforcement affect the settlement of load plate?
The results in these figures are consistent, that is, the settlement of load plate decreases with the increase of reinforcement layers. Compared with the unreinforced cushion, the continuity of cushion materials is enhanced with geogrid reinforcement, and the regulation ability of the cushion has been changed as well.
Can a support settlement cause internal forces in a structure?
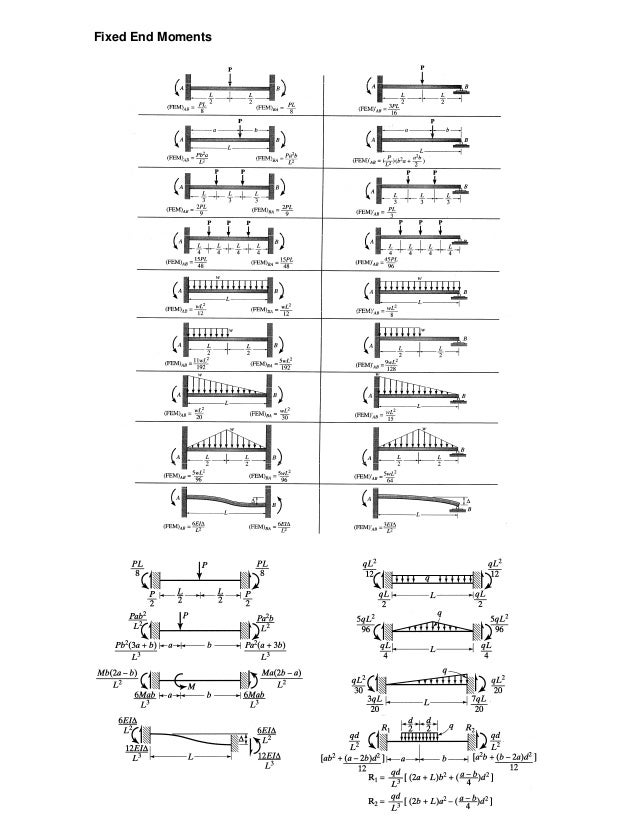
For externally determinate structures, support settlements will simply cause a rigid body rotation of the structure. Although this movement may be undesirable, the settlement cannot cause any internal forces in the structure itself. This situation is shown at the top of Figure 8.23.
What are the load settlement curves obtained during pile load tests?
Ruwan Rajapakse, in Pile Design and Construction Rules of Thumb (Second Edition), 2016 Load settlement curves obtained during pile load tests were similar in nature and one standard curve is shown in Fig. 8.27. Figure 8.27. Load versus settlement.

What is settlement load?
When the soil beneath a structure settles unevenly, it is called settlement load. Structures will sink and change shape when they experience settlement load. Settlement Failure.
What are the 3 types of loads?
The loads in buildings and structures can be classified as vertical loads, horizontal loads and longitudinal loads.
What are 4 types of loads?
Types of loads acting on a structure are: Wind loads. Snow loads. Earthquake loads. Special loads.
What are the 2 types of loads on a structure?
Loads are usually classified into two broad groups: dead loads and live loads. Dead loads (DL) are essentially constant during the life of the structure and normally consist of the weight of the structural elements. On the other hand, live loads (LL) usually vary greatly.
How do you classify loads?
The loads may be classified as: Dead loads. Live or fluctuating loads. Inertia loads or forces.
What is considered a live load?
Live loads are those loads produced by the use and occupancy of a building or structure and do not include construction loads, environmental loads (such as wind loads, snow loads, rain loads, earthquake loads and flood loads) or dead loads (see the definition of “Live Load” in IBC 202).
What are special loads?
“Special load” is the collective term for those items of cargo which, due to there nature or value will require special treatment by all personnel during the stages of acceptance, storage, stowage and transportation.
What is live load vs dead load?
The dead loads are permanent loads which result from the weight of the structure itself or from other permanent attachments, for example, drywall, roof sheathing and weight of the truss. Live loads are temporary loads; they are applied to the structure on and off over the life of the structure.
What are examples of live loads?
Live loads (also known as applied or imposed loads, or variable actions) may vary over time and often result from the occupancy of a structure. Typical live loads may include; people, the action of wind on an elevation, furniture, vehicles, the weight of the books in a library and so on.
What are the 5 types of loads on a static structure?
1 Loads on Structures• Static loads.• Dynamic loads.• Impact loads.Combinations of loads.Dead load.Live load.Wind load.Snow load.More items...
What is load explain its types?
Loads can be defined as the forces that cause stresses, deformations, or accelerations. These loads are applied to a structure or its components that cause stress or displacement. There are different types of structural loads such as dead load, live load, etc we need to consider during the design process.
What are the 5 forces that act on a structure?
The five types of loads that can act on a structure are tension, compression, shear, bending and torsion.
What are the 5 types of electrical loads?
The Different Types of Electrical LoadResistive Load. Any load that consists of a heating element is generally referred to as a resistive load. ... Inductive Load. ... Capacitive Load. ... Domestic (Residential) Load. ... Commercial Load. ... Industrial Load. ... Municipal Load.
Which is an example of load?
An example of load is furniture stacked into a moving van. Load is defined as to fill something up or to provide with an excess. An example of load is to pile a truck with furniture.
What are live loads and dead loads?
The dead loads are permanent loads which result from the weight of the structure itself or from other permanent attachments, for example, drywall, roof sheathing and weight of the truss. Live loads are temporary loads; they are applied to the structure on and off over the life of the structure.
What is load define its types?
Loads can be defined as the forces that cause stresses, deformations, or accelerations. These loads are applied to a structure or its components that cause stress or displacement. There are different types of structural loads such as dead load, live load, etc we need to consider during the design process.
Live Load
Live loads (also known as applied or imposed loads, or variable actions) may vary over time and often result from the occupancy of a structure. Typ...
Dead Load
A constant load in a structure (such as a bridge, building, or machine) that is due to the weight of the members, the supported structure, and perm...
Wind Loads
The term 'Wind Load' is used to refer to any pressures or forces that the wind exerts on a building or structure. There are actually three types of...
Dead Load Calculation
The total dead weight of a member would then be determined by multiplying that value times the length. The dead load of a floor or of a roof is gen...
Dead Load Examples
Dead loads, also known as permanent or static loads, are those that remain relatively constant over time and comprise, for example, the weight of a...
What Is Live Load?
Refers to loads that do, or can, change over time, such as people walking around a building (occupancy) or movable objects such as furniture. Live...
What Are Structural Loads?
Loads are generally the forces that can cause stresses, deformations, or accelerations. There are an ample range of distinct kinds of structural loads that can act upon a structure. It’s nature will be discrete according to the design, utilization, location, and materials.
What happens when horizontal load is applied on a structure?
Usually, when a horizontal load is applied on the structure, the structure will tend to fail or develop some significant cracks.
How are snow loads enumerated?
Snow loads are enumerated by the projections made by snow at distinct parts of the structure,
What direction does an earthquake load go?
Earthquake load is exerted on a structure in 2 directions i.e., vertical and horizontal direction. Of late, every building is designed to bear the seismic loads safely. The design of the earthquake load is in complete contrast from wind loads and gravity.
What are the forces that cause stresses, deformations, or accelerations?
Loads are generally the forces that can cause stresses, deformations, or accelerations. There are an ample range of distinct kinds of structural loads that can act upon a structure. It’s nature will be discrete according to the design, utilization, location, and materials.
What is the difference between a stiff and pliable structure?
A pliable structure can accommodate bijou stresses, whereas a stiff structure will significantly require careful designs.
What happens if the impact load is high?
If the value of the impact load is extremely high, it will directly fail & it won’t even provide a chance for the structure to crack.
What is the most widely considered type of load applied to structures?
In addition to the dead and live loads, the wind is the most widely considered type of loads applied load on structures is wind loads. With the increase of the height of the structure, wind pressure on the structure increase.
What are the different types of loads?
Different types of loads act on structures that shall be considered for the structural design based on their applicability. They can be classified as vertical loads and horizontal loads. Further, they can be separated as static and variable loads.
How to calculate earthquake force?
The easiest method is to calculate the earthquake forces as static loads and apply them to the structure to get the forces on the building. In this method, the base shear force is calculated based on the considered acceleration coefficients. Then this force is dived to the structure bases on the height and the mass of each floor. In this method, we assume the mass of the structure is lumped to find the responses.
What type of energy is released by blasting?
The Buring of blasting materials releases huge energy. This energy converted into thermal and kinematic energy.
Why is wind action not considered a critical load?
Wind action on smaller buildings is not considered usually because the notional loads become critical when wind pressure is smaller. However, when the building getting taller, wind pressure becomes critical.
What is the magnitude of a blast?
The magnitude of the blast pressure generated in a blast is a function of the scale distance. Scale distance depends on standoff distance (distance between the structure and blasting location) and the weight of the blasting materials.
Why is blast pressure variation simplified?
Blast pressure variation is simplified during the design due to the difficulty in using the pressure variation shown in the above figure. The relevant parameters can be calculated form the UFC 3- 340-2 for positive and negative phases.
What causes support settlements?
Support Settlements. Support settlements may be caused by soil erosion, dynamic soil effects during earthquakes, or by partial failure or settlement of supporting structural elements. Supports could also potentially heave due to frost effects (this could be considered a negative settlement).
What is the force method used for?
The force method may also be used to determine the effect of support settlement, temperature changes and fabrication errors on indeterminate structures. The latter two will only be discussed in terms of their effect on indeterminate structures; we previously discussed and analysed their effect on determinate structures in Section 5.7.
How to analyze an indeterminate truss?
To analyse an indeterminate truss with a temperature change or fabrication error , we must simply conduct the force method analysis as usual , except that the external 'loadings' on the primary system may derive from the temperature change or fabrication error. We previously studied the effect of temperature changes and fabrication errors on determinate trusses using virtual work. This was discussed in Section 5.6. Since the primary system in a force method analysis is determinate, the same analysis methods apply here.
Can a settlement cause internal forces?
Although this movement may be undesirable, the settlement cannot cause any internal forces in the structure itself. This situation is shown at the top of Figure 8.23. On the other hand, for indeterminate structures, settlement of structural supports can induce internal shears and moments as shown in the middle of Figure 8.23. This is because an indeterminate structure is effectively over-constrained, i.e. there are more restraints than the minimum required for stability.
Is BC a known force?
Going back to the full system now, with the redundant force in member BC included in the truss as a known force, the rest of the truss member axial forces may be found. This complete truss solution is shown in Figure 8.31.
What Is Foundation Structural Settlement?
The vertical downward displacements at the ground surface or the vertical downward displacement of a structure are often called Structural Settlement.
What happens when the weight of a structure causes differential structural settlement?
On the other hand, if the weight of structure causes differential Structural Settlement, the entire structural framework is subjected to an unacceptable increase in stresses distorting the framing system, eventually resulting in the collapse of the structure.
Why are settlements of granular soils more difficult to predict?
Settlements of granular soils, both elastic and creep movements, are more difficult to predict with any accuracy, largely because of the difficulty of obtaining and testing undisturbed soil samples, and settlements are usually estimated by indirect methods.
How does primary consolidation occur?
Primary consolidation results from the squeezing out of the water from the soil voids under the influence of excess pore-water pressures generated by the applied loading. This can take place over many months or years in clays but is usually quick in sands and gravels due to their greater permeability.
Why does lowering water level cause structural settlement?
Prolonged lowering of water level in fine-grained soils may introduce Structural Settlement due to consolidation. Repeated lowering also rising of water level in loose granular soils tend to compact the soil and cause Structural Settlement.
Why is structural settlement rarely uniform?
A Structural Settlement is seldom uniform over the area occupied by the foundation of a large building because of the non-uniformity of pressure distribution in the soil as well as variations in the compressibility at different parts of the area occupied by the foundations.
What is structural foundation?
A structural foundation is the part of a building that fixes it into the soil. These structures provide support for the main structures that appear above the soil level, much like the roots of a tree support the stem. One of its functions is to transfer loads from the structure to the ground.
What is load case 25 to 32?
Load cases from 25 to 32 will be used for checking occasional stresses with respect to code ASME B 31.3 allowable (=1.33 times Sh value from code). Use scalar combination for load cases 25 to 32 above and algebraic combination for others as shown in Fig. 2 attached below:
What is the sagging pressure for hydrotest?
Sustained and Hydrotest sagging below 10 mm for process lines and below 3 mm for steam, two-phase, flare lines and free-draining lines.
What is piping stress analysis?
Piping Stress Analysis is simply creating the load cases required for analysis and study the impact of the same on the behavior of the critical piping systems. A load case can be defined as a set of loads (Weight, Pressure, Temperature, External Forces, Displacements, etc) and boundary conditions for defining a particular loading condition. So Stress Analysis can not be thought without proper load case creation. Sometimes these load cases are mentioned in the piping stress analysis design basis. In this article, we will learn the basic load cases that are required for stress analysis activity.
How to find occasional stresses?
To find occasional stresses we need to add pure occasional cases with sustained load and then compare with code allowable values. The following sets of load cases are built for that purpose.
Can stress analysis be thought without load case?
So Stress Analysis can not be thought without proper load case creation. Sometimes these load cases are mentioned in the piping stress analysis design basis. In this article, we will learn the basic load cases that are required for stress analysis activity.
Is piping subject to seismic forces?
Piping may be subjected to occasional wind and seismic forces. So to check stresses in those situations we have to build the following load cases:
What is secondary load in piping?
What is a Secondary Load in a Piping System? Secondary loads are usually displacement driven loads. These loads are generated due to some kind of displacements imposed in the piping system, for example, thermal expansion, settlement, anchor movement, vibration, etc. Most of the time (not always, for example, tank settlement) these are cyclic in ...
What is a Primary Load in a Piping System?
Normally Force driven loads are called Primary loads. These loads are generated due to gravitational forces, internal or external fluid pressure, spring forces, relief valve discharge, pressure waves during water hammer or surge effects, etc. Hence, Primary loads are originated due to some kind of force acting on the piping system. A large value of Primary loads creates plastic deformation leading to catastrophic failure. In a catastrophic failure, each individual crystals are subjected to stresses which the body can not withstand and causes rupture.
What is the stress of piping?
From the mathematical definition of the stress, we all know that Stress is the Reaction Force per unit area. So, this clarifies that piping stresses are generated because of some kind of loads or forces in the piping system. The forces the piping system faces are categorized into two distinct groups. Secondary loads.
Is plastic deformation self limiting?
Self-Limiting Nature. Primary loads are not self-limiting. Once plastic deformation begins it continues until force equilibrium is achieved through changes in boundary condition or by material strain hardening or untill the element fails catastrophically.