
Full Answer
What is a settlement tank on a septic tank?
A settlement or settling tank is a component you can add before a pump pushes water through a mechanical filtration system or to supplement a biological filtration system. As water goes through the settlement tank, waste, debris, and heavy particles will fall to the bottom of the tank.
What is the settling time of a settling tank?
A settling tank is to settle out a slurry that has particles with a settling velocity of 0.01 m/min. An engineer decides that a tank of 5 m wide, 15 m long, and 2 m deep is adequate. What is the maximum allowable water flow rate into the tank if 100% removal of particles is to be achieved? A settling tank has a residence time of two hours.
Where to place the settlement of a tank?
The settlement is more at the centre of tank, and typically 50% at the edge of tank. Since our nozzles and tank roof are connected / supported on shell, that is on outer edge of tank, we need to consider the settlement at outer edge of tank.
What is progressive settlement in a tank?
IN CASE OF CLAY: Progressive settlement. The settlement is more at the centre of tank, and typically 50% at the edge of tank. Since our nozzles and tank roof are connected / supported on shell, that is on outer edge of tank, we need to consider the settlement at outer edge of tank.
What Does Settlement Tank Mean?
How is drilling fluid circulated?
Can barite settle in tank?
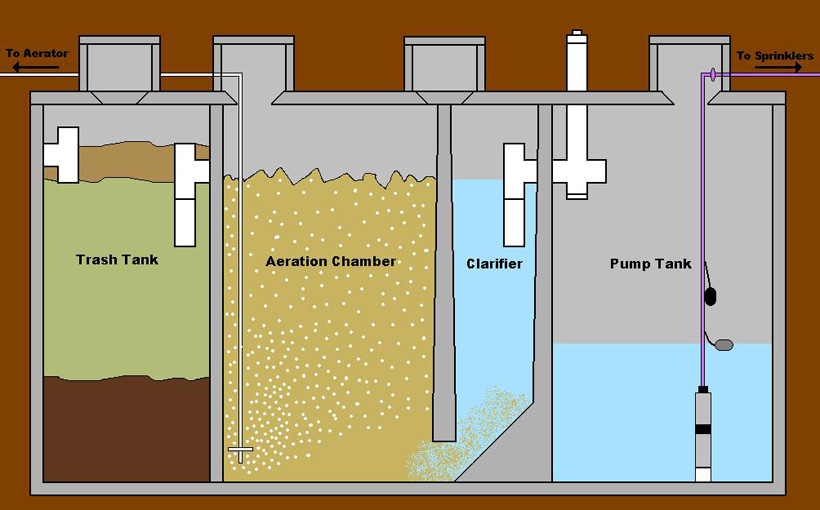
How do Settlement tanks work?
sedimentation tank, also called settling tank or clarifier, component of a modern system of water supply or wastewater treatment. A sedimentation tank allows suspended particles to settle out of water or wastewater as it flows slowly through the tank, thereby providing some degree of purification.
What is a primary settlement tank?
The Primary Settlement or sedimentation tanks are designed to reduce the velocity of the wastewater flow, allowing heavier organic solids (called raw sludge) to settle. They are the first stage of treatment after the removal of rags and grit in the inlet works.
What is the purpose of settling tank in ship?
The purpose of settling tank is to separate heavy solids particles and liquid (water ) from fuel mixture by a gravity separations. Or, The function of settling tank is to separate the sludge and water contained in the fuel oil,to act as a buffer tank and to provide a suitable constant fuel temperature of 50-70℃ .
What do settling tanks remove?
Usually, a primary settling tank (sedimentation or an Imhoff tank) is used to remove the greater portion of solids before the wastewater introduction to the VFCW bed.
What is the difference between primary settling tank and secondary tank?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What happens in the final settling tanks?
As the air and water mix, solid particles are lifted to the surface by rising air bubbles in the tank. The floating solids are then collected by a series of tank skimmers while the water is recycled back to the raw sewer to be processed through the plant.
What is the purpose of settling?
Settling is an important operation in many applications, such as mining, wastewater and drinking water treatment, biological science, space propellant reignition, and scooping.
What is sludge tank in ship?
Sludge tank – A tank provided to receive oily residues coming from the oily water filtering or separating equipment and from the purification of fuel and lubricating oils.
Why settling tank is used in engine fuel oil system?
Settling tanks are used to permit gross water and solids to settle on the bottom. Fuel tank overflow system : All tanks overflow to an overflow tank via a line w ith an observation glass. This line also incorporates a flow alarm.
What are the types of settling tank?
Types of Sedimentation TanksBased on methods of operation.Based on shape.Based on location.Fill and Draw Type Sedimentation Tank.Continuous Flow Type Sedimentation Tank.Horizontal flow type sedimentation tank.Vertical flow type sedimentation tank.Circular Tank.More items...•
How do you size a settling tank?
Dimensions of Sedimentation Tank The breadth of sedimentation tank should be provided is 10 to 12 meters while the length of sedimentation tank should be at least 4 times the breadth of sedimentation tank. The depth of tank should be 3 to 4.5 meters.
What are the different types of settling?
Different Types Of SettlingDiscrete settling.Flocculent settling.Hindered or zone settling.Compression settling.
What is secondary settling tank?
Secondary settling is the final step of the activated sludge-based biological waste water treatment. Secondary settling tanks (SSTs) are therefore an essential unit of producing a clear effluent.
What is secondary sedimentation tank?
The Secondary Sedimentation Tanks are circular tanks equipped with rotating mechanical sludge and scum collectors. Appurtenant systems include spray systems for moving scum and for odor control, and pumps for draining tanks.
How do you size a settling tank?
Area (A) = Volume of water/ over flow velocity The breadth of sedimentation tank should be provided is 10 to 12 meters while the length of sedimentation tank should be at least 4 times the breadth of sedimentation tank. The depth of tank should be 3 to 4.5 meters.
What is secondary treatment in wastewater?
Secondary treatment involves the removal of biodegradable organic matter (BOD) and suspended solids (TSS) through the processes of aeration and filtration. Secondary treatment is typically characterized as producing a treated wastewater effluent with a BOD of 25 mg/L or less and TSS of 30 mg/L or less.
What causes solid loss in a final settlement tank?
As discussed previously, solids loss from a final settlement tank, caused by plant failure, can easily be mistaken for a bulking or foaming incident. The effects of a pump failure or blockage can look very similar to that caused by a bulking or foaming sludge (i.e. rising sludge blanket or floating solids on the final tank). Filamentous microorganisms are present in most activated sludges in varying amounts and their presence does not necessarily mean that they are the cause of the solid loss. Correctly identifying the dominant filaments and getting a measure of their abundance is the first step in establishing this. Furthermore, an understanding of the mechanisms and drivers behind the predominance of filamentous microorganisms in the biomass will lead to control strategies for their eventual elimination.
Where is flow introduced in a gravity settlement tank?
After the coagulation and flocculation stages, flow is introduced upward through a “sludge blanket” in the lower part of a gravity settlement tank. Though provision of a delay time between coagulant and polymer addition is essential, this is sometimes omitted in error. Good flow distribution across the tank bottom is key. The tank may be rectangular or circular, inclined or hopper bottomed.
What are the advantages of a circular water tank?
The advantages of these tanks are: greater tolerance to hydraulic and quality changes, ideal for stop/start operation; infinite turn down; simplicity of operation; suitable for water containing high silt loads; and performance is not appreciably affected by diurnal temperature change. The primary drawback is their low surface loading rate and hence the large footprint and associated capital costs. Compared to rectangular tanks, circular tanks do not lend themselves to a compact layout. One such circular tank design known as Centrifloc ® is used for the treatment of R. Tigris water at the 1365 Ml/day Al Karkh water treatment works in Baghdad and is shown in Figure 7.2.
How many tanks can a pump serve?
Pumps related to storage can be grouped or located individually to serve one or two tanks. Groups of pumps will facilitate centralized operation but may require long suction piperuns. Lines carrying hot, cold, or flammable materials should be as short as possible, consistent with accommodating thermal stresses.
Why should tanks not be elevated?
Tanks containing flammable substances should not be elevated to provide gravity discharge because of the difficulties of stopping flows under fire conditions. Overhead piperacks should be kept to a minimum in bunded areas and pipes should be run in banks at grade on sleepers ( Figs. 10.2 and 34.2 ).
What is the second example of evaluating circumferential differential settlement?
11.15. The curves are shown in Fig. 11.18.
What is an interceptor tank?
Interceptors are settlement tanks which remove light, nonaqueous phase liquids (such as oil and gasoline) and, to a lesser extent, solids from wastewater. In the United Kingdom, there is an Environment Agency Guidance Note (PPG3—withdrawn in 2015 but still useful as a reference tool), as well as European standards (BS EN 858) ...
What is a settling tank?
Settling tanks are designed to minimize turbulence and allow the particles to fall to the bottom.
How long does a settling tank last?
A settling tank has a residence time of two hours. It is 4 m wide, 4 m deep, and 10 m long. What is the critical settling velocity of the particles to be settled out?
How does reactor volume affect the SST?
Basically, the reactor volume depends on organic load ( FSti) and the SST surface area on hydraulic load (PWWF). This is the reason why in Figure 17 the cost of the SST for the raw and settled wastewaters is the same but the cost of the reactor for the raw wastewater is higher than for the settled wastewater. From cost minimization analyses such as that above, generally it will be found that the range of reactor concentration for minimum construction cost (1) is higher for higher influent WW strengths (BOD 5, COD), (2) is higher for longer sludge ages, and (3) is higher for raw WW than settled WW at the same strength, because these three changes all increase the size of the biological reactor relative to that of the settling tank, (4) is lower for higher peak flow factors (fq ), and (5) is lower for poorer settling sludges because these two changes all increase the size of the settling tank relative to that of the biological reactor. A universal optimum therefore cannot be specified. In countries with low WW strengths and short sludge age plants (e.g., North America), the reactor concentration tends to be low (2000–3000 mgTSS l −1) and in countries with high WW strengths and long sludge age plants (e.g., South Africa), the reactor concentration tends to be high (4000–6000 mgTSS l −1) as the example WWs demonstrate.
What is the angle of the influent plate in Figure 7-97?
Figure 7-97 shows a tank that contains a stack of flat plates that nearly fills the tank. The plates are inclined at an angle of 60°. The influent end of the tank is equipped with a device to distribute incoming flow uniformly across the tank so that, to the extent possible, equal amounts of raw wastewater are caused to proceed through the spaces between each of the plates.
What is Figure 7-96?
Figure 7-96. Illustration of conceptual increase in removal efficiency by adding a series of false bottoms to an open, ideal settling tank.
What figure shows the removal of solids having a slow settling velocities?
Looking again at Figure 7-80, it can be seen that, no matter what the depth of the ideal settling tank, removal (by virtue of having reached the “bottom”) of solids having settling velocities much slower than v s could theoretically be achieved if a series of false bottoms were placed within the tank, similar to a stack of trays. Figure 7-96 illustrates such a concept.
What are the two critical elements of a settling tank?
Settling tanks are designed to approximate uniform flow and to minimize turbulence. Hence, the two critical elements of a settling tank are the entrance and exit configurations. Figure 7-5 shows one type of entrance and exit configuration used for distributing the flow entering and leaving the water treatment settling tank.
Where is settlement in a tank?
The settlement is more at the centre of tank, and typically 50% at the edge of tank.
What percentage of total settlement is piping stress analysis?
Then out of total settlement at Edge, 40% of total settlement is what we consider in piping stress analysis.
How big is a tank?
Whereas tank diameters are generally large, of the order of 10 m to 60 m. Due to this it is impractical to design its foundation with raft, which would be much bigger than this. Many times it has ring foundation with soil compacted within this concrete ring.
How Do Settlement Tanks Work?
A settlement tank replicates a natural process that happens in all bodies of water. Waste , debris, and other particles sink to the bottom since they’re heavier than water. In a natural environment, these particles settle and become part of the substrate.
Do You Need a Settlement Tank?
Installing a settlement tank for koi pond is usually something you have to plan for when building a new pond since you’ll need to set up a bottom drain. While there are some benefits to using a setting tank, not every koi pond setup needs one.
What Does Settlement Tank Mean?
A settlement tank is a compartment that allows solid content such as sand and cuttings to precipitate and sink to the bottom.
How is drilling fluid circulated?
The circulated drilling fluid is first passed through the shale shaker before entering the settlement tank. The received fluid is not stirred and allowed to rest.
Can barite settle in tank?
Since there is a possibility of the weighting agent barite also settling in the tank, a provision for bypass ing the undersize screen discharge slurry directly to the next processing compartment is advisable.
