What are Anglo settlers?
The Anglo-Americans were people who moved from the United States to Texas. They spoke English. Their parents or ancestors had come from northern Europe to America. Most of the Anglo-Americans did not come to Texas in large groups. Often families came alone.
What was the purpose of the Anglo settlement?
Anglo-Americans were drawn by inexpensive land and believed annexation of Texas to the United States was likely and would improve the market for the land. Some settlers were fleeing debts and sought refuge in the Mexican colony, where they were safe from American creditors.
What are Mexican Anglos?
Answer. Anglo (meaning non-Hispanic white) migration to Texas began in earnest after Mexico secured its independence from Spain in 1821. In the new republic, Texas was just one part of the state of Coahuila-Texas, a region in Mexico's northern borderlands in which Native communities were powerful.
How did the Anglo settle in Texas?
In 1820, Moses Austin, a bankrupt fifty-nine-year-old Missourian, asked Spanish authorities for a large Texas land tract that he would promote and sell to Anglo-American pioneers. The following year, the Spanish government gave him permission to settle in Texas.
What means Anglo-American?
Definition of Anglo-American 1 : an inhabitant of the U.S. of English origin or descent. 2 : a North American whose native language is English and especially whose culture or ethnic background is of European origin.
Why did the Anglo-Saxons settle in Britain?
Many Anglo-Saxons came peacefully, to find land to farm. Their homelands in Scandinavia often flooded so it was tough to grow enough food back there.
Why is it called Anglo-American?
Anglo-America The expression Anglo has come to signify a white, English-speaking North American as distinct from one of Latin-American descent.
What were Mexican settlers in Texas called?
Texians were Anglo-American residents of Mexican Texas and, later, the Republic of Texas. Today, the term is used to identify early settlers of Texas, especially those who supported the Texas Revolution. Mexican settlers of that era are referred to as Tejanos, and residents of modern Texas are known as Texans.
Where did Anglo-Americans come from?
Anglo-America, cultural entity of North America whose common spoken language is English and whose folkways and customs historically have been those of northern Europe. It comprises most of the United States and Canada, with French-speaking Canada a notable exception.
Who brought the first Anglo settlers to Texas?
Moses AustinDiedJune 10, 1821 (aged 59) Missouri Territory, United StatesNationalityAmericanOccupationBusinessman, empresarioKnown forBeing awarded the first land grant to settle Anglo-Americans in Spanish Texas5 more rows
Who originally settled Texas?
Spanish missionariesSpanish missionaries were the first European settlers in Texas, founding San Antonio in 1718.
What were the three main settlements in Texas?
San Antonio, Nacogdoches, and La Bahía, the most important civil settlements in Texas during the Spanish period, developed in the vicinity of these mission-presidio complexes.
What did Mexico hope to gain from Anglo settlement?
What did Mexico hope to gain from Anglo settlement in Texas? They hoped to prevent border violations by horse thieves and to protect the territory from Native American attacks.
Where did the Anglo-Saxons settle?
EnglandThe Anglo-Saxons were migrants from northern Europe who settled in England in the fifth and sixth centuries.
What was the main purpose of the Mexican colonization law of 1824?
On August 18, 1824, the new Mexican government passed the General Colonization Law. This statute allowed foreigners to gain title to land that was not within 20 leagues of the border of another country or within 10 leagues of the coast. Settlers would be exempt from taxes for ten years.
Which of the following had the greatest impact on Anglo settlement in Hispanic Texas?
Which of the following had the greatest impact of Anglo settlement in Hispanic Texas? Mexican land grants provided inexpensive properties in Texas. (Mexican government approved land grants to encourage Anglos to move to Texas.
What were the Anglo-Saxons?
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain was a process by which Germanic invaders who arrived in Britain in the mid-5th century quickly pushed the Britons into fringes of the island and established a series of kingdoms, which by the 8th century became increasingly sophisticated with rulers who were among the most powerful in Europe. The Germanic invaders, the Angles , Saxons, and Jutes , were collectively known as the " Anglo-Saxons "; the Saxons established kingdoms in Wessex, Essex, Sussex, Kent, and Hwicce; the Angles established the kingdoms of East Anglia and Northumbria; and the Jutes settled in Hampshire and the Isle of Wight before being assimilated into the Saxons. The Brythonic tribes were defeated and scattered by the Saxons, establishing holdout kingdoms in Wales and Cornwall, while the Picts maintained their independence before ultimately founding the kingdom of Scotland in 843. Following the Anglo-Saxon conquests of the 5th and 6th centuries, the newly-established Germanic kingdoms began to feud amongst each other, setting the stage for two centuries of competitive warfare for hegemony over the other Anglo-Saxon states. By the 830s, Mercia had lost its hegemony due to invasions by Wessex and Vikings. The age of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms ended in 867 with the arrival of the Great Heathen Army of Vikings, which led to the destruction of all of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms except for Wessex, which would go on to lead the successful Anglo-Saxon resistance to the Viking invasions of England and unite England by the end of the 10th century.
What were the Anglo-Saxons' gains in the West?
The Anglo-Saxons made rapid territorial gains in the century after their arrival in England. There was a pause in around 500 AD when, according to the near-contemporary Gildas, the Britons won a great victory at Mons Badonicus, led by a war-leader whom later tradition identified with King Arthur. By 550, however, the Anglo-Saxon advance had resumed and a decisive victory at Dyrham in Gloucestershire in 577 opened most of the West Country to them. By around 600, the Britons had been reduced to control of the area known as Dumnonia ( Devon, Cornwall, and Somerset ), Wales, Cumbria, and Scotland .
What was the cause of the destruction of Mercia?
By the 830s, Mercia had lost its hegemony due to invasions by Wessex and Vikings. The age of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms ended in 867 with the arrival of the Great Heathen Army of Vikings, which led to the destruction of all of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms except for Wessex, which would go on to lead the successful Anglo-Saxon resistance to ...
What is the evidence for early Anglo-Saxon kingdoms?
The British king Vortigern is said to have invited their leaders Hengest and Horsa to bring a troop of mercenaries to protect his kingdom against other barbarian marauders. A Gallic chronicle dates a Saxon victory to 440 and it is probable that somewhere around this time the nucleus of the groups who would form the later Anglo-Saxon kingdoms began to settle in England.
When was the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle written?
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, compiled in the 9th century, names the founders of several other kingdoms, although there is little independent historical evidence for any of these figures.
Who was the king of Kent and Sussex?
Concerned at the rising power of Wessex, King Beornwulf of Mercia marched against Egbert in 825 but was defeated at the Battle of Ellendun. As a result Egbert was acknowledged as King in Kent, Surrey, Sussex, and Essex.
Who were the Germanic invaders?
The Germanic invaders, the Angles , Saxons, and Jutes, were collectively known as the " Anglo-Saxons "; the Saxons established kingdoms in Wessex, Essex, Sussex, Kent, and Hwicce; the Angles established the kingdoms of East Anglia and Northumbria; and the Jutes settled in Hampshire and the Isle of Wight before being assimilated into the Saxons.
When did the Anglo-Americans settle in Texas?
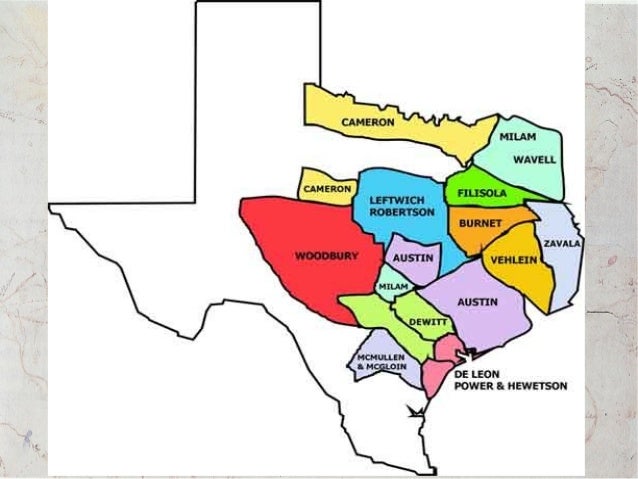
Anglo-American Colonization. Anglo-American colonization in Mexican Texas took place between 1821 and 1835. Spain had first opened Texas to Anglo-Americans in 1820, less than one year before Mexico achieved its independence. Its traditional policy forbade foreigners in its territory, but Spain was unable to persuade its own citizens to move to remote and sparsely populated Texas. There were only three settlements in the province of Texas in 1820: Nacogdoches, San Antonio de Béxar, and La Bahía del Espíritu Santo (later Goliad), small towns with outlying ranches. The missions near the latter two, once expected to be nucleus communities, had been or were being secularized (i.e., transferred to diocesan from Franciscan administration), while those near Nacogdoches had been closed since the 1770s. Recruiting foreigners to develop the Spanish frontier was not new. As early as the 1790s, Spain invited Anglo-Americans to settle in Upper Louisiana (Missouri) for the same reason. The foreigners were to be Catholic, industrious, and willing to become Spanish citizens in return for generous land grants. Spain expected the new settlers to increase economic development and help deter the aggressive and mobile Plains Indians such as the Comanches and Kiowas. Mexico continued the Spanish colonization plan after its independence in 1821 by granting contracts to empresarios who would settle and supervise selected, qualified immigrants.
Why were Anglo Americans attracted to Hispanic Texas?
Anglo-Americans were attracted to Hispanic Texas because of inexpensive land. Undeveloped land in the United States land offices cost $1.25 an acre for a minimum of 80 acres ($100) payable in specie at the time of purchase.
Who was the colonist who offered sanctuary to the colonists?
Robertson's colonists surreptitiously passed Nacogdoches and reached the Brazos in November. Amid a flurry of letters to officials, Austin offered the unlucky settlers sanctuary, a step approved officially in September 1831. Meanwhile Robertson asked Austin, who was leaving to take his seat in the state legislature at Saltillo, to intercede for an extension of the six-year contract. Austin agreed, although he believed the case dead-the six years was up, the Law of April 6, 1830, prevented Anglo settlement, and a French immigration company had already applied for the old Leftwich grant. In early February, however, Austin asked the state for a contract in his name and that of his associate, Samuel May Williams, to settle 800 European and Mexican families on the former Nashville grant, plus some additional land north and west. The application was approved on February 25, 1832.
Was the Anglo-American colonization of Texas a success?
Anglo-American colonization in Texas was obviously a success, although not what Mexican leaders envisioned. Neither side worked to understand, appreciate, nor resolve the cultural differences intrinsic to the union proposed by Mexico and accepted by Anglo-American immigrants.
What is the Anglo-Saxon name?
Bede the Venerable had called Antiqui Saxones (“Old Saxons”). The name formed part of a title, rex Angul-Saxonum (“king of the Anglo-Saxons”), which was sometimes used by King Alfred of Wessex (reigned 871–99) and some of his successors. By the time of the Norman Conquest, the kingdom that had developed from the realm of the Anglo-Saxon peoples had become known as England, and Anglo-Saxon as a collective term for the region’s people was eventually supplanted by “English.” For some time thereafter, Anglo-Saxon persisted as an informal synonym for English, but that use diminished as emigrants from Asia, Africa, the Caribbean, and other areas beyond northern Europe further reshaped Britain’s ethnic composition.
What is the name of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom?
The name formed part of a title, rex Angul-Saxonum (“king of the Anglo-Saxons”), which was sometimes used by King Alfred of Wessex (reigned 871–99) and some of his successors. By the time of the Norman Conquest, the kingdom that had developed from the realm of the Anglo-Saxon peoples had become known as England, ...
What did the Anglo-Saxons represent?
Ethnically, the Anglo-Saxons actually represented an admixture of Germanic peoples with Britain’s preexisting Celtic inhabitants and subsequent Viking and Danish invaders. Read More on This Topic. United Kingdom: Anglo-Saxon England.
When did the Germanic foederati settle in England?
Although Germanic foederati, allies of Roman and post-Roman authorities, had settled in England in the 4th century ce , tribal...
When did the Anglo-Saxons become unified?
During that period, though, the various peoples commonly grouped together as Anglo-Saxons were not politically unified until the 9th century, and their reign over England was interrupted by 26 years of Danish rule that began in 1016 with the accession of Canute.
When did the Germanic tribes arrive in England?
Although Germanic foederati, allies of Roman and post-Roman authorities, had settled in England in the 4th century ce, tribal migrations into Britain began about the middle of the 5th century. The first arrivals, according to the 6th-century…
What is an Anglo-Saxon?
Anglo-Saxon is a term that was rarely used by Anglo-Saxons themselves. It is likely they identified as ængli, Seaxe or, more probably, a local or tribal name such as Mierce, Cantie, Gewisse, Westseaxe, or Norþanhymbre. After the Viking Age, an Anglo-Scandinavian identity developed in the Danelaw.
What is the Anglo-Saxon language?
In scholarly use, it is more commonly called Old English. The history of the Anglo-Saxons is the history of a cultural identity.
How did the Mercian army succeed?
Mercian military success was the basis of their power; it succeeded against not only 106 kings and kingdoms by winning set-piece battles, but by ruthlessly ravaging any area foolish enough to withhold tribute. There are a number of casual references scattered throughout the Bede 's history to this aspect of Mercian military policy. Penda is found ravaging Northumbria as far north as Bamburgh and only a miraculous intervention from Aidan prevents the complete destruction of the settlement. In 676 Æthelred conducted a similar ravaging in Kent and caused such damage in the Rochester diocese that two successive bishops gave up their position because of lack of funds. In these accounts there is a rare glimpse of the realities of early Anglo-Saxon overlordship and how a widespread overlordship could be established in a relatively short period. By the middle of the 8th century, other kingdoms of southern Britain were also affected by Mercian expansionism. The East Saxons seem to have lost control of London, Middlesex and Hertfordshire to Æthelbald, although the East Saxon homelands do not seem to have been affected, and the East Saxon dynasty continued into the ninth century. The Mercian influence and reputation reached its peak when, in the late 8th century, the most powerful European ruler of the age, the Frankish king Charlemagne, recognised the Mercian King Offa 's power and accordingly treated him with respect, even if this could have been just flattery.
Where did the name "Angul-Seaxan" come from?
The Old English ethnonym "Angul-Seaxan" comes from the Latin Angli-Saxones and became the name of the peoples the English monk Bede called Angli around 730 and the British monk Gildas called Saxones around 530. Anglo-Saxon is a term that was rarely used by Anglo-Saxons themselves.
What were the Germanic tribes that migrated to Europe?
The migrants were Germanic tribes such as the Goths, Vandals, Angles, Saxons, Lombards, Suebi, Frisii, and Franks; they were later pushed westwards by the Huns, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars, and Alans.
Why was symbolism important to the Anglo-Saxons?
Richards suggests that in societies with strong oral traditions, material culture is used to store and pass on information and stand instead of literature in those cultures. This symbolism is less logical than literature and more difficult to read. Anglo-Saxons used symbolism to communicate as well as to aid their thinking about the world. Anglo-Saxons used symbols to differentiate between groups and people, status and role in society.
When did Germanic tribes start?
Germanic tribes who started to inhabit parts of Great Britain from the 5th century onwards. This article is about Anglo-Saxon culture and society. For historical events in Anglo-Saxon England, see Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain and History of Anglo-Saxon England. For other uses, see Anglo-Saxon (disambiguation).
