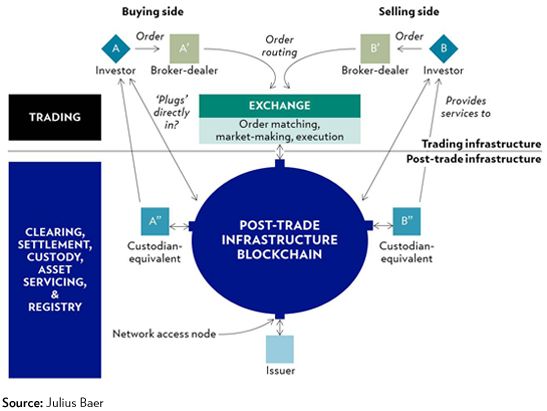
Is blockchain technology the future of clearing and settlement?
Clearing and settlement are the interest at the moment, but blockchain solutions are not evident in this space in the first wave. It’s more likely to be noticed in the preceding waves.
What is a blockchain and how does it work?
A blockchain allows a network of businesses to use a shared ledger upon which they can conduct their transactions. This shared ledger provides all parties with security, speed and transparency – while removing middlemen and reducing friction. Traditional methods of clearing and settlement rely on middlemen to facilitate trust & security.
Which firms are experimenting with blockchain technology?
Across the globe, big name firms and established players have been experimenting with blockchain and distributed ledger technology. The list extends from one end of the world to the other USA based Broadridge Financial Solutions will be using blockchain trade settlement in the repo market.
Is blockchain the future of the stock market in India?
Their “uClear” blockchain platform allows for real time clearing and settlement of securities. Fast forward to 2018, and we have the Security and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) have begun exploring blockchain technology for trading the stock market.

How long does it take for blockchain to settle transactions?
If you'd like to send or withdraw your funds, please wait 7 days for us to receive your funds and the holding period to be lifted. The holding period is designed to protect you from fraud and theft if your Blockchain.com account is compromised.
Does blockchain reduce settlement process?
One of the main benefits of blockchain is that it offers a more efficient and effective clearing and settlement process.
How does cryptocurrency settlement work?
Crypto settlement is relative Zero Hash, our cryptocurrency custodian, handles all cryptocurrency trades and positions. When establishing and holding a crypto position over multiple days, the cost of the position sweeps (transfers) from Apex Clearing to Zero Hash after opening the position.
What is faster settlement in blockchain?
When investors have a desire to settle early, slowing down block time and making blocks smaller creates congestion on the blockchain. Investors are then willing to pay larger transaction fees in order to get into blocks faster and, hence, settle their trades faster.
What is clearing and settlement process?
Settlement involves exchanging funds between the two banks, while clearing can end without any interbank money movement. In the clearing process, funds move between the recipient's or sender's bank account and their bank's reserves.
What are the risks of using blockchain?
Right now, there are three major new risks for enterprise blockchain and smart contract deployments: old software, software flaws and operational flaws. Hang on a minute. These are the same risks we've been dealing with in computing for 50 years.
Does crypto take 2 days to settle?
Instant Settlement For Robinhood Crypto, funds from stock, ETF, and options sales become available for buying within 3 business days. However, limited cash deposits and all proceeds from crypto sales are available to instant accounts immediately.
How do you get paid from cryptocurrency?
In order to receive payment in cryptocurrency, you'll have to open an account and a digital wallet on a special exchange. It's not hard to launch on a service like Coinbase Commerce, but it is unfamiliar to most.
How long does it take for funds to settle on Crypto com?
Every 1 hour (24 sessions per day at 00:00, 01:00, 02:00 … 23:00 UTC) daily is when settlement occurs, this is known as the Session End Time.
What is the main purpose of blockchain?
How Does a Blockchain Work? The goal of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In this way, a blockchain is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed.
What is a settlement network?
Interbank clearing and settlement networks allow banks to settle USD payments within a day and international payments within two days.
What is KYC blockchain?
KYC is a process by which banks obtain information about the identity and address of the purchasers. It's a regulator governed process of performing due diligence for verifying the identity of clients.
How does blockchain impact the process of settlements and KYC?
KYC Blockchain Implementation The blockchain architecture and the DLT allow us to collect information from various service providers into one cryptographically secure and unchanging database that does not need a third party to verify the authenticity of the knowledge.
Can blockchain be used for physical assets?
The use of blockchain technology to track physical assets is not new. However, the state of the art concepts are not applicable due to several limitations. One limitation is the scalability of blockchains with regard to the number of transactions that can be processed by the network.
What is DVP settlement?
Delivery versus payment (DVP) is a securities industry settlement method that guarantees the transfer of securities only happens after payment has been made. DVP stipulates that the buyer's cash payment for securities must be made prior to or at the same time as the delivery of the security.
What will blockchain replace?
Bank of America, JPMorgan, the New York Stock Exchange, Fidelity Investments, and Standard Chartered are testing blockchain technology as a replacement for paper-based and manual transaction processing in such areas as trade finance, foreign exchange, cross-border settlement, and securities settlement.
What is clearing trades and securities?
Businesses have to endure these unnecessary fees as well – but on a grander scale. They trade securities that have various risks managed by the clearinghouse. This leads to higher fees. Businesses are then forced to pass these costs down to their consumers.
Is the ASX blockchain?
The Australian Securities Exchanges (ASX) isn’t interested in falling behind either. ASX will be launching their blockchain based financial services by 2021. The goal is to allow stockbrokers & fund managers to use the blockchain for real-time settlement and tracking.
What Is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. The innovation with a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
Who Invented Blockchain?
Blockchain technology was first outlined in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two mathematicians who wanted to implement a system where document time stamps could not be tampered with. 1 In the late 1990s, cypherpunk Nick Szabo proposed using a blockchain to secure a digital payments system, known as bit gold (which was never implemented). 18
How Does a Blockchain Work?
The goal of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In this way, a blockchain is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed. This is why blockchains are also known as a distributed ledger technology (DLT) .
What Is a Blockchain Platform?
A blockchain platform allows users and developers to create novel uses of an existing blockchain infrastructure. One example is Ethereum, which has a native cryptocurrency known as ether ( ETH ). 16 But the Ethereum blockchain also allows the creation of smart contracts and programmable tokens used in initial coin offerings (ICOs), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These are all built up around the Ethereum infrastructure and secured by nodes on the Ethereum network.
How does blockchain technology work?
Blockchain technology achieves decentralized security and trust in several ways. First, new blocks are always stored linearly and chronologically. That is, they are always added to the “end” of the blockchain. After a block has been added to the end of the blockchain, it is extremely difficult to go back and alter the contents of the block unless a majority of the network has reached a consensus to do so. That’s because each block contains its own hash, along with the hash of the block before it, as well as the previously mentioned time stamp. Hash codes are created by a mathematical function that turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters. If that information is edited in any way, the hash code changes as well.
What is blockchain in computer?
A blockchain is a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. The innovation with a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
Why do miners need to be paid to mine bitcoin?
That’s because when miners add a block to the bitcoin blockchain, they are rewarded with enough bitcoin to make their time and energy worthwhile. When it comes to blockchains that do not use cryptocurrency, however, miners will need to be paid or otherwise incentivized to validate transactions.
Settlement Risk
In any capital markets transaction, the buyer pays the seller for the delivery of the securities or other asset type, on the settlement date of the trade. One party must pay the other party for the security, commodity, or currency they are purchasing. For example, assume Party A buys 100 shares of Apple stock from Party B.
Delivery Versus Payment (DvP)
This concept is fairly straightforward. In our first example (Figure 1), Party B would have to deliver the stock (security) first and then and only then would Party A release the cash.
Clearinghouses
A clearinghouse, sometimes referred to as a Central Counterparty (CCP), is an industry-wide centralized processing system established in financial markets. In some markets, a clearing house supports the clearing of securities, while another may support the clearing of derivatives, and in others they support both.
Payment versus payment (PvP)
In a foreign exchange transaction one currency is exchanged for another currency. CLS Group was created to reduce settlement risk. An FX transaction can either settle spot (which generally refers to trade date plus 1 or 2 business days, depending on the currency) or forward (which implies that it settles on some date after the spot date).
Enter Blockchain?
Blockchain 2 has promised to transform the financial markets from operations, trade finance, insurance, payment systems, rehypothecation and compliance, to creating world peace (not really, but sometimes it sure feels that way with everyone saying how great it is!!).
Footnotes
1 For a summary and interesting take on this event go to https://bankunderground.co.uk/2015/06/24/boe-archives-reveal-little-known-lesson-from-the-1974-failure-of-herstatt-bank/
About the Author: Kenneth Kapner
Ken Kapner, CEO and President, started Global Financial Markets Institute, Inc. (GFMI) a NASBA certified financial learning and consulting boutique, in 1998.
Who is the CEO of Chain?
Interestingly Adam Ludwin, CEO of Chain who developed the NASDAQ blockchain clearing system, disagrees: “When people say blockchain technology will change Clearing and Settlement, what that really means is that blockchain technology will make Clearing and Settlement redundant.
Is blockchain effective?
Today, what we see is that it may be effective and possible to apply blockchain technology to a ledger controlled by a centralised structure – RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement), TARGET2 for Securities (T2S), DTCC, ASX, NASDAQ and so on. However, many of these central structures then need to link across industries, regions and continents to connect all the players involved. Creating a blockchain that could be shared by all counterparties – every bank and intermediary worldwide – is still a long way away. As David Rutter, CEO and founder of R3CEV states:
Is clearing and settlement a centralised industry?
The interesting aspect of all of this stuff about Clearing and Settlement is that the current industry structure is dominated by centralising institutions: central banks, Central Counterparty Clearing structures, Central Securities Depositories (CSDs) and centralised collateral management systems, such as the ECB’s Correspondent Central Banking Model (CCBM). Yet blockchains are meant to be decentralised, so how can this work in a centralised operation? Well it can because most of the developments are being run as permissioned or double permissioned networks by these central operators, on behalf of their markets. Banks and stock exchanges globally are working with blockchain start-ups, led by people who have been immersed in these market spaces, to realise this dream of billions of dollars of savings.
Can blockchain be shared by all counterparties?
However, many of these central structures then need to link across industries, regions and continents to connect all the players involved. Creating a blockchain that could be shared by all counterparties – every bank and intermediary worldwide – is still a long way away.
Is blockchain the solution to clearing and settlement?
Nevertheless, even with all of this excitement when it comes down to it, blockchains are not the solution for Clearing and Settlement. The reason I say this is that the issue is not a technical one but an industry challenge. Over a decade ago, Europe tried to change the market structure and produced a report by Alberto Giovannini listing the 15 barriers to an integrated European market. Those challenges had little to do with technology, and were far more about legal and structural challenges. Those are still challenges that need to be resolved if we are to have an effective shared ledger in the Clearing and Settlement markets. It is for these reasons that even with distributed shared ledgers and smart contracts, the centralisation of clearing will not disappear.
