Dispute settlement process
- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
- Technical explanation of the DSU
- Rules of Conduct on rules and procedures for settling disputes
- Working Procedures for Appellate Review
Full Answer
What are the methods for settling disputes?
These relate to:
- The property or legality of an employer to pass an order under the standing orders.
- The application and interpretation of standing orders.
- Discharge or dismissal of workers including reinstatement or grant of relief to workmen wrongfully dismissed.
- Withdrawal of any statutory concession or privilege. ...
- Illegality or otherwise of a strike or lockout.
What is a settlement dispute?
What settlement means. Settlement means that the parties to a dispute have decided to put an end to that dispute. The parties can agree to settle their dispute at any time, including before proceedings are commenced and even after trial before the judgment is handed down.
Why is settling disputes important?
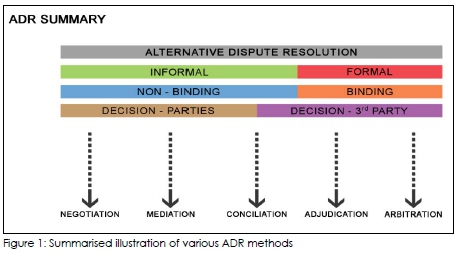
Settling disputes is necessary to attain peace and harmony among individuals or firms. Courts offer to settle disputes according to the law. However, parties can also solve their disputes without the services of a court and avoid costly litigations. This alternative method of settling disputes is called Alternative Dispute Resolution or ADR for ...
Is WTO Dispute Settlement effective?
To summarize the main findings, the WTO dispute settlement system has been most effective in "disarming" Section 301. Since the debacle of the auto talks in 1995, the United States has rarely resorted to Section 301 unilaterally, as it often had in the 1980s.

What do you mean by dispute settlement understanding?
The term “Dispute Settlement Understanding” means the Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes referred to in section 3511(d)(16) of this title .
What is the purpose of dispute settlement?
A central objective of the (WTO) dispute settlement system is to provide security and predictability to the multilateral trading system (Article 3.2 of the DSU).
How does the dispute settlement mechanism work?
There are three main stages to the WTO dispute settlement process: (i) consultations between the parties; (ii) adjudication by panels and, if applicable, by the Appellate Body; and (iii) the implementation of the ruling, which includes the possibility of countermeasures in the event of failure by the losing party to ...
What are the types of disputes?
Family Disputes.Commercial Disputes.Industrial Disputes.Property Disputes.
How are disputes resolved?
There are many types of dispute resolution processes, but arbitration; mediation; and negotiation are the three most common types of alternative dispute resolution. Negotiation is the least formal type of ADR.
What is the importance of dispute resolution?
➢In an ideal world, dispute resolution provides certainty in such a fashion that the issue in dispute is resolved and will not resurface again. Ideally, dispute resolution is complete, in that it covers the issue in dispute plus any directly related issues.
How do I settle a dispute without going to court?
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution that provides a final and binding outcome to litigation which does not require recourse to the Courts. It is a consensual process in the sense that it will only apply if the parties agree it should.
What are the ways of settling disputes in your locality?
Negotiation, mediation and arbitration, often called ADR or alternative dispute resolution, are the most well known. Whether you are involved in a family or neighborhood dispute or a lawsuit involving thousands of dollars, these processes should be considered.
What is the role of the WTO dispute settlement body?
The DSB has authority to establish dispute settlement panels, refer matters to arbitration, adopt panel, Appellate Body and arbitration reports, maintain surveillance over the implementation of recommendations and rulings contained in such reports, and authorize suspension of concessions in the event of non-compliance ...
How do I settle a dispute without going to court?
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution that provides a final and binding outcome to litigation which does not require recourse to the Courts. It is a consensual process in the sense that it will only apply if the parties agree it should.
Is WTO dispute settlement Effective?
If one compares the WTO dispute settlement system with the previous dispute settlement system of GATT 1947, the current system has been far more effective. Moreover, its quasi-judicial and quasi-automatic character enables it to handle more difficult cases.
What does a trade dispute mean?
A trade dispute is defined as 'a dispute between workers and their employer which relates wholly or mainly' to one or more of a number of specified matters (TULR(C)A s244(1)). In the following sections we consider the requirements that a dispute must meet to qualify for statutory immunity.
What is the WTO dispute settlement?
Dispute settlement. Resolving trade disputes is one of the core activities of the WTO. A dispute arises when a member government believes another member government is violating an agreement or a commitment that it has made in the WTO.
When did the WTO agree to clarify the DSU?
At the Doha Ministerial Conference, in 2001, WTO members agreed to negotiate to improve and clarify the DSU — the rules and procedures governing the settlement of WTO disputes.
What is a DSU?
The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
How many years of cooperation between the WTO and the European Law Students Association?
With August marking 20 years of collaboration, the WTO and the European Law Students Association (EL…
How does the WTO dispute settlement process work?
Here, in more detail, is how the WTO dispute settlement process works:
What is the WTO dispute settlement agreement?
The Dispute Settlement Understanding of the World Trade Organization (WTO) establishes a set of rules and procedures and provides a forum for resolving trade disputes between WTO member countries. When disputes cannot be resolved, the Understanding authorizes the use of trade sanctions against the member country that has been found in violation of a WTO agreement.
What happens if the losing party fails to comply with the panel's recommendations within the allotted time?
If the losing party fails to comply with the panel’s recommendations within the allotted time, it must enter into consultations with the winning party to seek agreement on compensation. Compensation may be granted in a variety of ways (e.g., tariff reductions or the lifting of quotas on certain products). If an agreement on compensation cannot be reached within 20 days of the expiration of the allotted time, then the DSB can authorize the winning party to apply equivalent trade sanctions (e.g., increased tariffs) against the losing party.
How long does it take to settle a dispute in the WTO?
Appeals are heard by a separate group of experts, who review issues of law covered in the panel report and then issue their own report with their own findings and recommendations. In all, it can take about 15 months to settle a dispute in the WTO.
How long does it take for a court panel to report?
After hearing arguments from both sides and after examining all the evidence, the panel makes its decision and prepares a draft report which is reviewed by both parties to the dispute, who are given an opportunity to comment on it. The panel then issues its final report, which includes its findings and recommendations. The final report should be issued, as a general rule, within six months of the start of the proceedings.
When did the reinsurance agreement go into effect?
This Agreement went into effect on January 1, 1995.
Can exporters complain directly to the World Trade Organization?
Individual exporters cannot take their trade complaints directly to the World Trade Organization. They must work through their own governments.
What is dispute settlement understanding?
The Dispute settlement understanding is the central pillar of the multilateral trading system of the World Trade Organisation framed as a legal text containing the rules for dispute settlement in the WTO. The current dispute settlement system of WTO was created during Uruguay Round. It is embodied in the Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes, commonly referred to as the Dispute Settlement Understanding and abbreviated “DSU”. It should be noted that the current dispute settlement system is the result of the evolution of rules, procedures and practices developed over almost half a century under the GATT 1947.
Who is involved in dispute settlement?
The participants in the dispute settlement system are the Member governments of the WTO), which can take part either as parties or as third parties. The WTO Secretariat, WTO observer countries, other international organizations, and regional or local governments are not entitled to initiate dispute settlement proceedings in the WTO.

Article 1
- Coverage and Application 1. The rules and procedures of this Understanding shall apply to disputes brought pursuant to the consultation and dispute settlement provisions of the agreements listed in Appendix 1 to this Understanding (referred to in this Understanding as the “…
Article 2
- Administration 1. The Dispute Settlement Body is hereby established to administer these rules and procedures and, except as otherwise provided in a covered agreement, the consultation and dispute settlement provisions of the covered agreements. Accordingly, the DSB shall have the authority to establish panels, adopt panel and Appellate Body reports, maintain surveillance of i…
Article 4
- Consultations 1. Members affirm their resolve to strengthen and improve the effectiveness of the consultation procedures employed by Members. 2. Each Member undertakes to accord sympathetic consideration to and afford adequate opportunity for consultation regarding any representations made by another Member concerning measures affecting the operation of any c…
Article 5
- Good Offices, Conciliation and Mediation 1. Good offices, conciliation and mediation are procedures that are undertaken voluntarily if the parties to the dispute so agree. 2. Proceedings involving good offices, conciliation and mediation, and in particular positions taken by the parties to the dispute during these proceedings, shall be confidential, and without prejudice to the right…
Article 6
- Establishment of Panels 1. If the complaining party so requests, a panel shall be established at the latest at the DSB meeting following that at which the request first appears as an item on the DSB's agenda, unless at that meeting the DSB decides by consensus not to establish a panel (5). 2. The request for the establishment of a panel shall be made in writing. It shall indicate whethe…
Article 7
- Terms of Reference of Panels 1. Panels shall have the following terms of reference unless the parties to the dispute agree otherwise within 20 days from the establishment of the panel: “To examine, in the light of the relevant provisions in (name of the covered agreement(s) cited by the parties to the dispute), the matter referred to the DSB by (name of party) in document ... and to …
Article 8
- Composition of Panels 1. Panels shall be composed of well-qualified governmental and/or non-governmental individuals, including persons who have served on or presented a case to a panel, served as a representative of a Member or of a contracting party to GATT 1947 or as a representative to the Council or Committee of any covered agreement or its predecessor agree…
Article 9
- Procedures for Multiple Complainants 1. Where more than one Member requests the establishment of a panel related to the same matter, a single panel may be established to examine these complaints taking into account the rights of all Members concerned. A single panel should be established to examine such complaints whenever feasible. 2. The single panel …
Article 10
- Third Parties 1. The interests of the parties to a dispute and those of other Members under a covered agreement at issue in the dispute shall be fully taken into account during the panel process. 2. Any Member having a substantial interest in a matter before a panel and having notified its interest to the DSB (referred to in this Understanding as a “third party”) shall have an …
Introduction to Dispute Settlement in The WTO
Dispute Settlement Process
- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU)is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
- Technical explanationof the DSU
- Rules of Conducton rules and procedures for settling disputes
- Working Procedures for Appellate Review
Dispute Settlement Body
- The General Council convenes as the Dispute Settlement Body (DSB)to deal with disputes between WTO members.
The Appellate Body
- Appeals are handled by the permanent seven-member Appellate Bodywhich is set up by the Dispute Settlement Body and broadly represents the range of WTO membership.
Dispute Settlement Activity — Some Figures
- As of end-2020, WTO members had submitted 598 requests for consultations, the first stage in the dispute settlement process.
Documents
Interpretation of WTO Agreements
- The WTO Analytical Indexis a comprehensive guide to the interpretation and application of the WTO agreements by the Appellate Body, dispute settlement panels and other WTO bodies. It contains extracts of key pronouncements and findings from tens of thousands of pages of WTO jurisprudence, including panel reports, Appellate Body reports, arbitral decisions and awards, an…
Negotiations to Improve Dispute Settlement Procedures
- At the Doha Ministerial Conference, in 2001, WTO members agreed to negotiate to improve and clarify the DSU— the rules and procedures governing the settlement of WTO disputes.
Secretariat's Informal Consultations Concerning The Panel Process
- At the request of the Director-General, the Secretariat initiated in 2010 a process of informal consultationswith a view to exploring whether it is possible to find efficiency gains in the panel process.