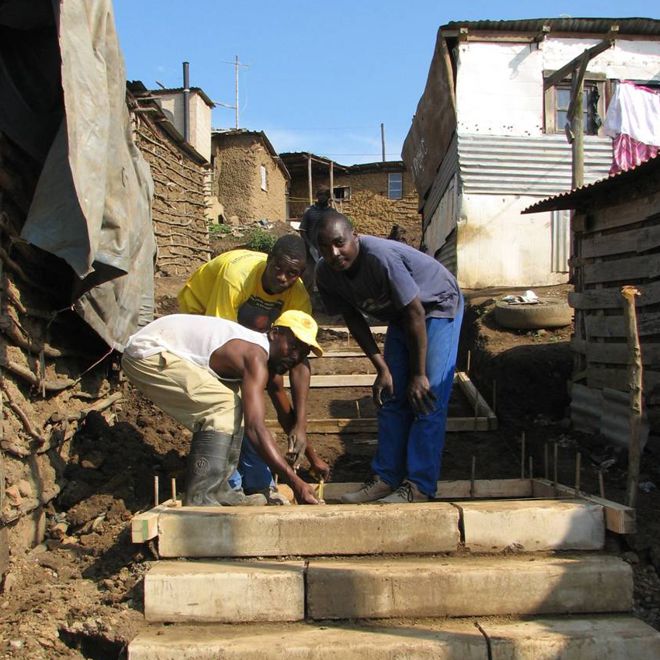
Upgrading is a term given to measures to improve housing conditions in the informal settlements or ‘slums’ that house a high proportion of urban dwellers in all low-income and most middle-income nations.
Can upgrading improve quality of life in informal settlements?
When done properly, upgrading can be transformative for residents and their communities. Rather than disrupting vital networks by uprooting and relocating residents, upgrading programmes are the best way to improve quality of life within informal settlements.
What is informal settlement growth?
The growth of informal settlements, slums and poor residential neighbourhoods is a global phenomenon accompanying the growth of urban populations.
How to improve informal settlements in South Africa?
The incremental, in-situ upgrading of informal settlements with the provision of basic services and functional tenure security is the only viable solution for informal settlements in S.A. PPT has played a leading role in pioneering and mainstreaming this approach and in enabling a range of prevailing barriers to be overcome.
What do city governments do about informal settlements?
City government attitudes to informal settlements range from opposition and eviction to reluctant tolerance and support for legalisation and upgrading.

What physical factors are to be considered in upgrading settlement?
This paper discloses that the basic concept for physical upgrading in a slum settlement consists of three elements: (1) arranging street networks as fundamental systems that structure the settlement, (2) constructing public utility systems that are essential for livelihoods, and (3) providing common space and amenities ...
Why are informal settlements increasing?
A number of interrelated factors have driven the emergence of informal settlements: population growth; rural-urban migration; lack of affordable housing; weak governance (particularly in policy, planning and urban management); economic vulnerability and low-paid work; marginalisation; and displacement caused by ...
What does informal settlement mean?
Informal settlements are residential areas that do not comply with local authority requirements for conventional (formal) townships. They are, typically, unauthorised and are invariably located upon land that has not been proclaimed for residential use.
What are examples of informal settlements?
Common categories or terms associated with informal housing include: slums, shanty towns, squats, homelessness, backyard housing and pavement dwellers.
What are the effect of informal settlement?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management. These characteristics impact negatively on the environment posing risk and susceptibility to health problems associated with informal settlements.
What are the advantages of informal settlement?
It offers choice, it gives people what they want, it enables individual creativity and it is affordable. It is also simple to build and easy to use. So, a powerful brand — the informal settlement — is in town. And it's reshaping the city.
What is another word for informal settlement?
Shanty town Sometimes called a squatter, informal or spontaneous settlement, shanty towns often lack proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity, hygienic streets, or other basic human necessities.
What are the 3 biggest problems of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management.
What are the types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed. Urban settlements are densely populated and are mostly non-agricultural. They are known as cities or metropolises and are the most populated type of settlement. These settlements take up the most land, resources, and services.
What are the main characteristics of an informal settlement?
Characteristics include inadequate access to safe water and sanitation, poor quality of housing, overcrowding, and insecure residential status.
What is the biggest informal settlement in South Africa?
SowetoThose living in informal dwellings – defined as a wood and iron structure – have decreased slightly from 16.2% in 1996 to 13.0% in 2016....These are the 20 biggest townships in the country (Stats SA, 2011)#1TownshipSoweto2011 Population1 271 628Neighbouring townJohannesburg19 more columns•Aug 14, 2016
What are the effects of settlement?
The impact of human settlements on the environment increases with population growth, settlement expansion, economic growth and increased consumption. All indications are that the impact of human settlements on environmental resources is increasing.
What are the 3 biggest problems of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management.
What are the causes of squatter settlement?
Rapid urbanization, poverty and lack of access to land and ownership, in addition to limited or no social housing, have led citizens to build their homes illegally under very poor environmental and social conditions.
Why do some informal settlements and societies successfully adjust and even thrive amid diversity while others fail to do so?
one of the reasons could be as a result of security of tenure. In attaining any sustainable settlements and societies that thrive well security tenure is important as it provides sufficient shelter and infrastructure.
How squatter settlements can be improved?
Squatter settlements can be improved through urban planning . The plan to improve Dharavi is called Vision Mumbai. This involves replacing squatter settlement housing with high-quality high-rise tower blocks of flats.
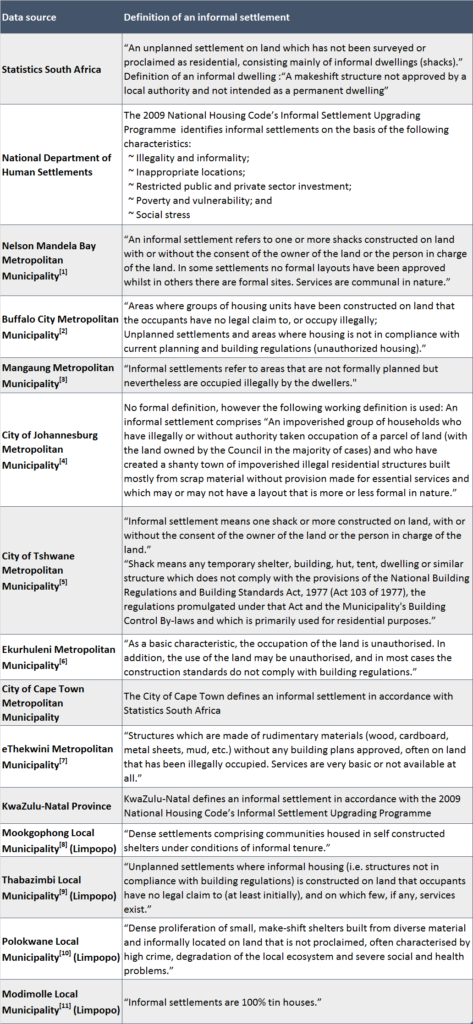
What is informal settlement?
Informal settlements are generally defined as those without a formal right of land to the location in which they are situated. However, this does not mean that informal settlements cannot be fixtures of the urban landscape, with some “slum” areas of cities such as Mumbai having endured for over 60 years.
What is upgrading housing?
Upgrading is a term given to measures to improve housing conditions in the informal settlements or ‘slums’ that house a high proportion of urban dwellers in all low-income and most middle-income nations.
Why is upgrading important?
Upgrading has become an increasingly common response by city and national governments and important because it implies an official acceptance of the rights of the inhabitants in informal settlements to live there and to receive government infrastructure and services.
What is informal settlement?
Informal settlements are residential areas where ( UN-Habitat, 2015b; Brown, 2015 ): inhabitants often have no security of tenure for the land or dwellings they inhabit ‒ for example, they may squat or rent informally; neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure; housing may not comply with planning and building regulations, ...
How does informal settlement affect women?
For women, for example, this can heighten barriers they face in accessing livelihood opportunities. Home-based workers also face challenges to entrepreneurial activity ( Chant, 2014 ). Women in informal settlements spend more time and energy accessing basic services than other urban counterparts, limiting their ability and time to earn through paid employment ( UNFPA, 2007 ). In addition, the prevalence of male-biased land tenure policies and restrictions on women’s rights to own property decreases the likelihood of alternative housing options. Poor quality housing, or eviction and homelessness, can also increase the risk of insecurity and sexual violence ( Chant, 2013; McIlwaine, 2013 ).
What are the factors that contribute to the emergence of informal settlements?
A number of interrelated factors have driven the emergence of informal settlements: population growth; rural-urban migration; lack of affordable housing; weak governance (particularly in policy, planning and urban management); economic vulnerability and low-paid work; marginalisation; and displacement caused by conflict, natural disasters and climate change ( UN-Habitat, 2015b ).
What is UNFPA 2014b?
UNFPA (2014b). Framework of actions for the follow-up to the programme of action of the international conference on population and development beyond 2014. New York: UNFPA.
What is the importance of settlement upgrading?
An important part of settlement upgrading is providing proper sanitation and hygiene systems. These materials outline the process of students took to create a functional sanitation system. Further information on water, sanitation, and hygiene can be found on our Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene in Informal Settlements Page.
Why are informal settlements unsafe?
South African informal settlements are frequently unsafe and develop in haphazard ways as more people move for work and opportunity. Shack houses are made of a variety of materials, vary in size, and present multiple problems, such as flooding, fires, and structural stability. Because of these trends, communities have issues with housing, roads, drainage, and general safety. Within the Cape Town Project Centre, our teams have worked to address these issues and collaborated with communities to upgrade already existing facilities and propose potential new facilities. We have worked through a process known as reblocking, in which communities obtain safer, better built, standardized homes with roads and sometimes even electricity and personal toilets. Although every project seeks to upgrade the community they work in, specific projects throughout past years have focused directly on creating redevelopment strategies to tackle community issues such as infrastructure, housing, and safety.
What is reblocking in housing?
Reblocking is the process of providing uniform housing, roads, and other basic amenities to informal settlement communities. This can be a daunting task. It requires lots of effort, information, and community feedback. Here are resources past students have created to facilitate the reblocking process.
Overview
The national government has identified the upgrading of informal settlements as a key component of its human settlement development approach, targeting (as part of its 2019-2024 outcome based targets for human settlement development) the formalisation/ upgrading of 1,500 informal settlements to phase 3 of the Informal Settlements Upgrading Programme..
Information
Afesis-corplan is collating information relating to the upgrading of informal settlements. Click on the links below for more information on upgrading of informal settlements:
Upgrading of Informal Settlement radio drama
Check out below the radio drama (in English and Xhosa) that Afesis-corplan has developed that aims to educate people upgrading of informal settlements.
Tap and toilet calculator
Afesis-corplan has created a simple calculator (Excel spreadsheet) that one can use to work out how many more taps and toilets are needed in an informal settlement to match the basic minimum norms and standards for a particular municipality. Click the image below to access this calculator page.
Definitions
Informal settlements are residential areas where housing units are constructed on land to which the occupants have no legal claim or which they occupy illegally and unplanned settlements and areas where housing does not comply with statutory plans and building regulations (unauthorized housing) and is often situated in geographically and environmentally hazardous areas (UN-Habitat 2003 ).
How to cite
Matamanda A.R., Mafuku S.H., Mangara F. (2020) Informal Settlement Upgrading Strategies: The Zimbabwean Experience. In: Leal Filho W., Azul A., Brandli L., Özuyar P., Wall T. (eds) Sustainable Cities and Communities. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71061-7_8-1
About this entry
eBook Packages Springer Reference Earth & Environm. Science Reference Module Physical and Materials Science
Definitions
Informal settlements are residential areas where housing units are constructed on land to which the occupants have no legal claim or which they occupy illegally and unplanned settlements and areas where housing does not comply with statutory plans and building regulations (unauthorized housing) and is often situated in geographically and environmentally hazardous areas (UN-Habitat 2003 ).
How to cite
Matamanda A.R., Mafuku S.H., Mangara F. (2020) Informal Settlement Upgrading Strategies: The Zimbabwean Experience. In: Leal Filho W., Marisa Azul A., Brandli L., Gökçin Özuyar P., Wall T. (eds) Sustainable Cities and Communities. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95717-3_8