
In financial accounting, a liability is defined as the future sacrifices of economic benefits that the entity is obliged to make to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future.
What is a settlement liability?
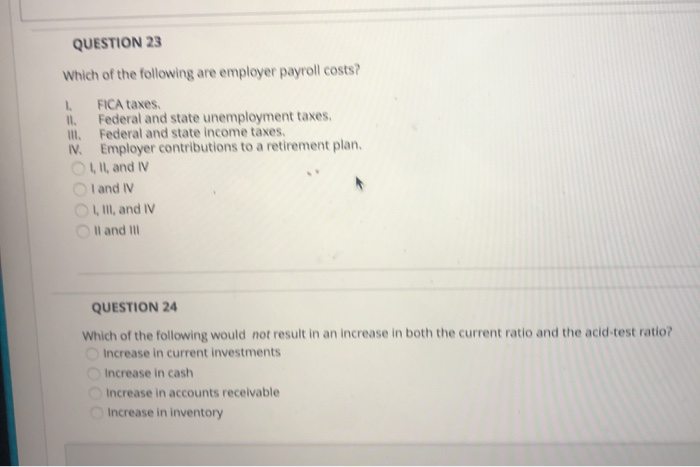
A Settlement Liability shall be computed as the total impact on the net amount to be paid upon final contract settlement, including direct and indirect costs, fees and profits. Settlement Liability. Means: (i) liabilities of the Company described in the Settlement Agreements (of an amount equal to CHF1’693’304.-);
What is a financial liability?
In the world of accounting, a financial liability is also an obligation but is more defined by previous business transactions, events, sales, exchange of assets or services, or anything that would provide economic benefit at a later date.
What is allowable cost audit settlement liability?
Settlement Liability means a net liability due to the final agreement of claims or rights arising out of the settlement of an Allowable Cost Audit, including: (A) final indirect costs and rates for government contracts; (B) Cost Accounting Standards ( CAS) matters; (C) defective pricing matters; or (D) advance agreements with the U.S. Government.
How are liabilities settled on the balance sheet?
Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. Recorded on the right side of the balance sheet, liabilities include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses.
What is a settlement of liability?
Liabilities are legally binding obligations that are payable to another person or entity. Settlement of a liability can be accomplished through the transfer of money, goods, or services. A liability is increased in the accounting records with a credit and decreased with a debit.
What does settlement mean in accounting?
An account settlement generally refers to the payment of an outstanding balance that brings the account balance to zero. It can also refer to the completion of an offset process between two or more parties in an agreement, whether a positive balance remains in any of the accounts.
What does it mean to pay a liability?
Payment of a liability generally involves payment of the total sum of the amount borrowed. In addition, the business entity that provides the money to the borrowing institution typically charges interest, figured as a percentage of the amount that has been lent.
What are the two types of liabilities?
Classification of Liabilities Current liabilities (short-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due and payable within one year. Non-current liabilities (long-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due after a year or more.
How Should settlements be recorded in accounting?
You list it as a liability on the balance sheet and a loss contingency on the income statement. It's possible but not probable you'll lose money. You disclose it in the notes on the financial statement, but you don't include the amount in your statements.
What is difference between payment and settlement?
Settlement in "real time" means payment transaction is not subjected to any waiting period. "Gross settlement" means the transaction is settled on one to one basis without bunching or netting with any other transaction. Once processed, payments are final and irrevocable.
What is liabilities in simple words?
A liability is something a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services.
Is a car a liability or asset?
The vehicle itself is an asset, since it's a tangible thing that helps you get from point A to point B and has some amount of value on the market if you need to sell it. However, the car loan that you took out to get that car is a liability.
Which of the following is not an example of a settlement of a liability?
Which one of the following is not an example of a settlement of a liability? cash payment.
What is the difference between loan and liability?
Bank loans are a form of debt. Hence, it only arises out of borrowing activities. Whereas, liabilities arising out of other business activities as well. For example, accrued wages are payments to employees that have not been paid yet.
What is an asset vs liability?
Assets are what a business owns and liabilities are what a business owes. Both are listed on a company's balance sheet, a financial statement that shows a company's financial health. Assets minus liabilities equals equity, or an owner's net worth.
What are the three types of liabilities?
There are three primary classifications for liabilities. They are current liabilities, long-term liabilities and contingent liabilities. Current and long-term liabilities are going to be the most common ones that you see in your business.
What does settlement amount mean?
Settlement Amount means, with respect to a Transaction and the Non-Defaulting Party, the Losses or Gains, and Costs, including those which such Party incurs as a result of the liquidation of a Terminated Transaction pursuant to Section 5.2.
How do settlement accounts work?
The settlement bank will typically deposit funds into the merchant's account immediately. In some cases, settlement may take 24 to 48 hours. The settlement bank provides settlement confirmation to the merchant when a transaction has cleared. This notifies the merchant that funds will be deposited in their account.
What is the journal entry for settlement of account?
The journal entry is debiting accounts payable and credit cash. The transaction will remove the accounts payable of a specific invoice from the supplier and reduce cash payment.
What does settlement mean in payroll?
an agreement that ends a disagreement between workers and employers about how much the workers should be paid for doing their jobs.
What is settlement liability?
Settlement Liability means a net liability due to the final agreement of claims or rights arising out of the settlement of an Allowable Cost Audit , including: (A)
What is identified contingent liability?
Identified Contingent Liabilities means the maximum estimated amount of liabilities reasonably likely to result from pending litigation, asserted claims and assessments, guaranties, uninsured risks and other contingent liabilities of the Borrower and its Subsidiaries taken as a whole after giving effect to the Transactions (including all fees and expenses related thereto but exclusive of such contingent liabilities to the extent reflected in Stated Liabilities), as identified and explained in terms of their nature and estimated magnitude by responsible officers of the Borrower.
What is excluded hedge liability?
Excluded Hedge Liability or Liabilities means, with respect to each Borrower and Guarantor, each of its Swap Obligations if, and only to the extent that, all or any portion of this Agreement or any Other Document that relates to such Swap Obligation is or becomes illegal under the CEA, or any rule, regulation or order of the CFTC, solely by virtue of such Borrower’s and/or Guarantor’s failure to qualify as an Eligible Contract Participant on the Eligibility Date for such Swap. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in the foregoing or in any other provision of this Agreement or any Other Document, the foregoing is subject to the following provisos: (a) if a Swap Obligation arises under a master agreement governing more than one Swap, this definition shall apply only to the portion of such Swap Obligation that is attributable to Swaps for which such guaranty or security interest is or becomes illegal under the CEA, or any rule, regulations or order of the CFTC, solely as a result of the failure by such Borrower or Guarantor for any reason to qualify as an Eligible Contract Participant on the Eligibility Date for such Swap; (b) if a guarantee of a Swap Obligation would cause such obligation to be an Excluded Hedge Liability but the grant of a security interest would not cause such obligation to be an Excluded Hedge Liability, such Swap Obligation shall constitute an Excluded Hedge Liability for purposes of the guaranty but not for purposes of the grant of the security interest; and (c) if there is more than one Borrower or Guarantor executing this Agreement or the Other Documents and a Swap Obligation would be an Excluded Hedge Liability with respect to one or more of such Persons, but not all of them, the definition of Excluded Hedge Liability or Liabilities with respect to each such Person shall only be deemed applicable to (i) the particular Swap Obligations that constitute Excluded Hedge Liabilities with respect to such Person, and (ii) the particular Person with respect to which such Swap Obligations constitute Excluded Hedge Liabilities.
What is off balance sheet liability?
Off-Balance Sheet Liabilities of any Person shall mean (i) any repurchase obligation or liability of such Person with respect to accounts or notes receivable sold by such Person, (ii) any liability of such Person under any sale and leaseback transactions that do not create a liability on the balance sheet of such Person , (iii) any Synthetic Lease Obligation or (iv) any obligation arising with respect to any other transaction which is the functional equivalent of or takes the place of borrowing but which does not constitute a liability on the balance sheet of such Person .
What are product liability liabilities?
Product Liabilities means all losses, damages, fees, costs and other liabilities incurred by a Party, its Affiliate or its sublicensee and resulting from or relating to the any use of a Compound and/or a Product in a human ( including in Clinical Trials and/or pursuant to Commercialization) in the Territory, other than any losses, damages, fees, costs and other liabilities that are a result of a Party’s, its Affiliates’ or its sublicensee’s negligence, willful misconduct or breach of such Party’s representations and warranties made hereunder. For the avoidance of doubt, Product Liabilities include, reasonable attorneys’ and experts’ fees and costs relating to any claim or potential claim against a Party, its Affiliate, or its sublicensee and all losses, damages, fees, costs. Product Liabilities shall not include liabilities associated with recalls and/or the voluntary or involuntary withdrawal of the Compound and/or a Product.
What is the final reinsurance closing calculation?
The Final Reinsurance Closing Calculation will also include the Ceding Company’s calculation of the difference, if any, between the Initial Reinsurance Premium paid to the Reinsurer and the Reinsurance Closing Date Settlement Liability shown on the Reinsurer’s Final Reinsurance Closing Calculation.
What are current liabilities?
Current Liabilities means, with respect to the Borrower and its Restricted Subsidiaries on a consolidated basis at any date of determination, all liabilities that would, in accordance with GAAP, be classified on a consolidated balance sheet of the Borrower and its Restricted Subsidiaries as current liabilities at such date of determination, other than (a) the current portion of any Indebtedness, (b) accruals of Consolidated Interest Expense (excluding Consolidated Interest Expense that is due and unpaid), (c) accruals for current or deferred taxes based on income or profits, (d) accruals, if any, of transaction costs resulting from the Transactions, (e) accruals of any costs or expenses related to (i) severance or termination of employees prior to the Closing Date or (ii) bonuses, pension and other post-retirement benefit obligations, and (f) accruals for exclusions from Consolidated Net Income included in clause (5) of the definition of such term.
What is a liability in finance?
A liability is a financial obligation of a company that results in the company’s future sacrifices of economic benefits to other entities or businesses. A liability can be an alternative to equity as a source of a company’s financing. Moreover, some liabilities, such as accounts payable.
Why are legal expenses considered contingent liabilities?
The legal expenses may be recognized as contingent liabilities because: The expenses are probable.
What is accounts payable?
Accounts payable: Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit. Accounts payables are. These are the unpaid bills to the company’s vendors. Generally, accounts payable are the largest current liability for most businesses.
What is interest payable?
Interest Payable Interest Payable is a liability account shown on a company’s balance sheet that represents the amount of interest expense that has accrued. Interest expenses that have already occurred but have not been paid. Interest payable should not be confused with the interest expenses.
What is the accounting equation for liabilities?
According to the accounting equation, the total amount of the liabilities must be equal to the difference between the total amount of the assets and the total amount of the equity.
What is a mortgage payable?
Mortgage payable /long-term debt: Long Term Debt Long Term Debt (LTD) is any amount of outstanding debt a company holds that has a maturity of 12 months or longer. It is classified as a non-current liability on the company’s balance sheet.
What is the legal status of a non-human entity that is unable to repay its outstanding debts?
Bankruptcy Bankruptcy is the legal status of a human or a non-human entity (a firm or a government agency) that is unable to repay its outstanding debts. . In addition, liabilities determine the company’s liquidity and capital structure.
Contractual Obligation
A financial liability can be a contractual obligation to deliver cash or similar to another entity or a potentially unfavorable exchange of financial assets or liabilities with another entity.
Equity Settlement
A financial liability can be a contract probably to be settled in the entity's own equity and that is a non-derivative under which the entity may deliver a variable amount of its own equity instruments.
Derivative Settlement
A financial liability can be a derivative that probably will be settled other than through the exchange of cash or similar for a fixed amount of the entity's equity.
What is liability in business?
A liability is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits. Regulations as to the recognition of liabilities are different all over the world, but are roughly similar to those of the IASB.
What is liability in accounting?
In financial accounting, a liability is defined as the future sacrifices of economic benefits that the entity is obliged to make to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future.
What are the characteristics of a liability?
A liability is defined by the following characteristics: 1 Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time; 2 A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a specified or determinable date, on occurrence of a specified event, or on demand; 3 A duty or responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement; and, 4 A transaction or event obligating the entity that has already occurred
What is a current liability?
Current liabilities – these liabilities are reasonably expected to be liquidated within a year. They usually include payables such as wages, accounts, taxes, and accounts payable, unearned revenue when adjusting entries, portions of long-term bonds to be paid this year, and short-term obligations ( e.g. from purchase of equipment). Current liabilities are obligations whose liquidation is reasonably expected to require the use of current assets, the creation of other current liabilities, or the provision of services within the next year or operating cycle, whichever is longer.
What is a long term liability?
Long-term liabilities – these liabilities are reasonably expected not to be liquidated within a year. They usually include issued long-term bonds, notes payables, long-term leases, pension obligations, and long-term product warranties. Liabilities of uncertain value or timing are called provisions.
What is an equitable obligation?
An equitable obligation is a duty based on ethical or moral considerations. A constructive obligation is an obligation that is implied by a set of circumstances in a particular situation, as opposed to a contractually based obligation. The accounting equation relates assets, liabilities, and owner's equity :
When a company deposits cash with a bank, the bank records a liability on its balance sheet?
When a company deposits cash with a bank, the bank records a liability on its balance sheet, representing the obligation to repay the depositor, usually on demand. Simultaneously, in accordance with the double-entry principle, the bank records the cash, itself, as an asset.
What is liability in financial reporting?
Defined by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Framework: “A liability is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits.”
What is contingent liability?
Contingent liabilities#N#Contingent Liability A contingent liability is a potential liability that may or may not occur. The relevance of a contingent liability depends on the probability of the contingency becoming an actual liability, its timing, and the accuracy with which the amount associated with it can be estimated.#N#are liabilities that may occur, depending on the outcome of a future event. Therefore, contingent liabilities are potential liabilities. For example, when a company is facing a lawsuit of $100,000, the company would incur a liability if the lawsuit proves successful.
What are the three types of liabilities?
There are three primary types of liabilities: current, non-current, and contingent li abilities. Liabilities are legal obligations or debt. Senior and Subordinated Debt In order to understand senior and subordinated debt, we must first review the capital stack. Capital stack ranks the priority of different sources of financing.
Why should current liabilities be closely watched?
Current liabilities should be closely watched by management to ensure that the company possesses enough liquidity from current assets. Current Assets Current assets are all assets that a company expects to convert to cash within one year. They are commonly used to measure the liquidity of a.
What is a short term liability?
Current liabilities (short-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due and payable within one year. Non-current liabilities (long-term liabilities) are liabilities that are due after a year or more. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that may or may not arise, depending on a certain event.
Why are long term liabilities important?
Long-term liabilities are crucial in determining a company’s long-term solvency.
What happens if a lawsuit is not successful?
However, if the lawsuit is not successful, then no liability would arise. In accounting standards, a contingent liability is only recorded if the liability is probable (defined as more than 50% likely to happen). The amount of the resulting liability can be reasonably estimated.
Get the treatment you need
If you are settling or have settled your case, Ametros can help you determine what is the most affordable option to get you the treatment you need. Our CareQuote service can look at your life care plan or treatment, and provide transparent pricing available after settlement on our platforms.
Personal insurance may not be enough
While individuals with significant ongoing medical needs may be able to rely on some forms of personal insurance, in many cases there are treatments or items needed for the injury that are not covered. For example, group health insurance will not cover home healthcare and skilled nursing.
How Ametros Can Help
Plaintiff is worried offer is too little to cover future medical care.
What is a liability?
In business, a liability is something that a company owes. This can mean debt or another type of obligation such as taxes or outstanding wages. It can also cover money paid to the company for work which has not yet been carried out. This is known as deferred revenue, as the company cannot count it until they have done the work.
What is a liability on a balance sheet?
A liability is an obligation between two parties for something that is not yet completed or paid for.
What is the difference between liabilities and expenses?
Simply put, liabilities are the obligations and debts that a company owes, while expenses are the costs of a company’s operation. Whereas liabilities are listed on a company’s balance sheet, expenses are listed on an income statement.
What happens when you subtract liabilities from assets?
If we subtract the company’s liabilities from its assets, we will get the owners’ or shareholders’ equity:
What is a loan?
A type of borrowing from a bank or person to improve a business or personal income, which is payable at a predefined short or long period .
What are liabilities used for?
What you need to know about liabilities. Liabilities are used by investors to estimate and compare companies’ performance. This is not always straightforward as the way liabilities are recorded can vary. There are two major types of liability – current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
What is a current liability?
Current liabilities are debts that need to be paid within a year – wages, for example. Long-term liabilities are payable over more than one year. For example, if a company takes a mortgage payable within a 20-year period. A liability has several major characteristics:
What is a liability?
Liability characteristics. A long or short-term loan that a bank provides so that a business has the necessary funds to complete a project. An entity’s duty to provide a future transfer of assets at a specific date, i.e., on demand, to another party. A claim on the assets of a company.
What is liability in accounting?
Definition and examples. In accounting and finance, a liability is a legal debt or obligation that an entity must pay back. An entity could be, for example, a person or a company. Assets are what a company owns, while liabilities are what it owes.
Why are liabilities important?
Liabilities are an important element of the operations of a company. They are key in helping financial operations and achieving growth.
What is long term liabilities?
Long-term liabilities. These are debts or obligations that the company does not liquidate within 12 months, such as long-term leases, long-term bonds, and pension obligations. We refer to liabilities without a specified time due or unknown value as ‘ provisions .’.
What are the two groups of liabilities on a balance sheet?
On a balance sheet, we usually divide liabilities into two groups; current and long-term liabilities.
What does "liability" mean in non-finance?
In non-accounting and non-finance contexts, liability can mean: A hindrance or handicap, as in “After the scandal, the party leader became a liability regarding the forthcoming elections.”. Responsibility, as in “He denies liability for the plane crash.”.
Where are liabilities reported on the balance sheet?
We report liabilities on the right side of the balance sheet. Examples of liabilities include loans, accounts payable, accrued expenses, bonds payable, and interest payable. Wages payable and income taxes payable are also in that category.
What are Liabilities?
Liabilities are legally binding obligations that are payable to another person or entity. Settlement of a liability can be accomplished through the transfer of money, goods, or services. A liability is increased in the accounting records with a credit and decreased with a debit. A liability can be considered a source of funds, since an amount owed to a third party is essentially borrowed cash that can then be used to support the asset base of a business. Examples of liabilities are:
What is contingent liability?
A contingent liability is a potential liability that will only be confirmed as a liability when an uncertain event has been resolved at some point in the future. Only record a contingent liability if it is probable that the liability will occur, and if you can reasonably estimate its amount.
What are some examples of liabilities?
Examples of liabilities are: Accounts payable. Accrued liabilities. Deferred revenue.
When is a liability considered a current liability?
You would classify a liability as a current liability if you expect to liquidate the obligation within one year. All other liabilities are classified as long-term liabilities. If there is a long-term note or bond payable, that portion of it due for payment within the next year is classified as a current liability.
Which is the largest of the preceding liabilities?
Of the preceding liabilities, accounts payable and notes payable tend to be the largest. Liabilities are aggregated on the balance sheet within two general classifications, which are current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Can a company have a negative liability?
It is possible to have a negative liability, which arises when a company pays more than the amount of a liability, thereby theoretically creating an asset in the amount of the overpayment. Negative liabilities tend to be quite small.
Accounting Reporting of Liabilities
Current Liabilities vs. Long-Term Liabilities
- The primary classification of liabilities is according to their due date. The classification is critical to the company’s management of its financial obligations. Current liabilities are those that are due within a year. These primarily occur as part of regular business operations. Due to the short-term nature of these financial obligations, they should be managed with consideration of the company…
Long-Term Liabilities
- Long-term (non-current) liabilities are those that are due after more than one year. It is important that the long-term liabilities exclude the amounts that are due in the short-term, such as interest payable. Long-term liabilities can be a source of financing, as well as refer to amounts that arise from business operations. For example, bonds or m...
Contingent Liabilities
- Contingent liabilities are a special category of liabilities. They are probable liabilities that may or may not arise, depending on the outcome of an uncertain future event. A contingent liability is recognized only if both of the following conditions are met: 1. The outcome is probable. 2. The liability amount can be reasonably estimated. If one of the conditions is not satisfied, a company …
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s explanation of Liability. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Free Reading Financial Statements Course 2. Accrued Expenses 3. Financial Accounting Theory 4. Notes Payable 5. Projecting Balance Sheet Items
Overview
In financial accounting, a liability is defined as the future sacrifices of economic benefits that the entity is obliged to make to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future.
Characteristics
A liability is defined by the following characteristics:
• Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time;
• A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a sp…
Classification
Liabilities are reported on a balance sheet and are usually divided into two categories:
• Current liabilities – these liabilities are reasonably expected to be liquidated within a year. They usually include payables such as wages, accounts, taxes, and accounts payable, unearned revenue when adjusting entries, portions of long-term bonds to be paid this year, and short-term obligations (e.g. from purchase of equipment). Current liabilities are obligations whose liquidation is reasona…
Debits and credits
A debit either increases an asset or decreases a liability; a credit either decreases an asset or increases a liability. According to the principle of double-entry, every financial transaction corresponds to both a debit and a credit.
When cash is deposited in a bank, the bank is said to "debit" its cash account, on the asset side, and "credit" its deposits account, on the liabilities side. In this case, the bank is debiting an asse…
See also
• Assets
• Cost
• Contingent liability
• Depreciation
• Financial Accounting