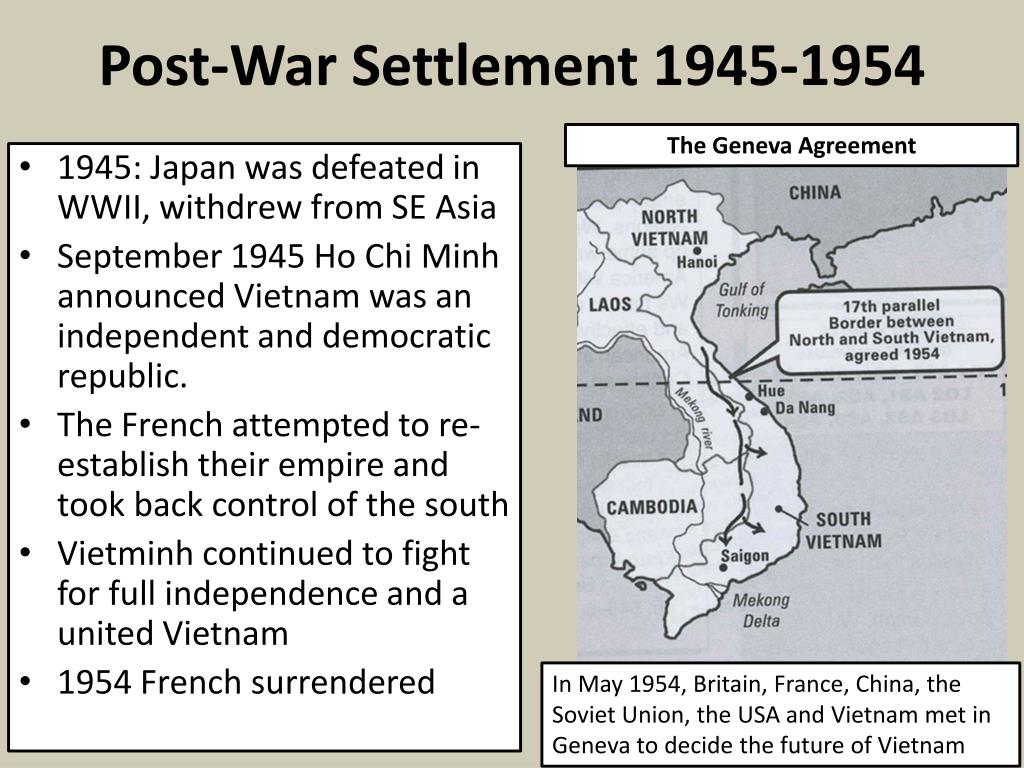
The post-war settlement refers to an era of public policy consensus that included support for collectivism, a mixed economy, access to justice, healthcare, social housing and a broader welfare state. It lasted until the monetarism and privatisation programmes of the New Right government of Thatcher.
Full Answer
What is post-war settlement?
104 THE POST-WAR SETTLEMENT torical adjustment can be made in the direction of justice with suf- ficient rapidity to parry violent revolution and war, requires an enormous amount of faith in the flexibility, adaptability, imagina- tive capacity, and intelligent goodwill of mankind.
What is the postwar history of international politics?
The postwar history of international politics thus became largely a history of Soviet-American rivalry: a cold war between superpowers.
What was the Warsaw Pact and why was it created?
The Soviet coalition founded the Cominform (Communist Information Bureau) in 1947 as a successor to the former Comintern, and created the Warsaw Pact (1955), binding eastern Europe together, as a reply to NATO. The United States and Britain sought in the 1950s and 1960s to prevent the spread of atomic weapons.

What is meant by the post-war consensus?
The post-war consensus was the economic order and social model of which the major political parties in post-war Britain shared a consensus supporting view, from the end of World War II in 1945 to the late-1970s. It was abandoned by Conservative Party leader Margaret Thatcher. Majorities in both parties agreed upon it.
What is the political consensus?
Consensus democracy, consensus politics or consensualism is the application of consensus decision-making to the process of legislation in a democracy.
What factors contributed to America's postwar economic boom?
Driven by growing consumer demand, as well as the continuing expansion of the military-industrial complex as the Cold War ramped up, the United States reached new heights of prosperity in the years after World War II.
What is the liberal consensus?
Liberal consensus may refer to: Embedded liberalism – post World War II international ambitions to combine free market and social policies. Liberal consensus – the post World War II consensus in American politics.
Is the US majoritarian or consensus?
Contrary to popular belief, the USA is not a majoritarian democracy as they can have an elected individual based through points from majority of county and further state votes. This means an individual can be in power in the USA while having a minority vote overall.
Is Canada a consensus democracy?
Consensus government is a form of consensus democracy government in Canada used in two of Canada's three federal territories (Northwest Territories and Nunavut) as well as in Nunatsiavut, an autonomous area in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Is Australia a consensus democracy?
From the perspective of the two-dimensional majoritarian-consensus contrast, this adaptation makes Australian democracy slightly, but by no means insignificantly, more consensual on both dimensions.
Who coined the term party of consensus and parties of pressure?
Rajni Kothari (16 August 1928 – 19 January 2015) was an Indian political scientist, political theorist, academic and writer.
From homes fit for heroes to the end of secure, lifelong social housing tenancies
Social housing arose to supply uncrowded, well-built homes on secure tenancies at reasonable rents to primarily working class people. The First World War indirectly provided a new impetus for house building programmes, when the poor physical health and condition of many urban recruits to the army raised alarm.
Narxism
Socialism is not just about what you believe or what you say, it’s about how you see, treat and relate to OTHERS.
What were the two revolutionary features of the post 1987 arms agreements?
The second revolutionary feature of the post 1987 arms agreements, both conventional and nuclear, is that they establish transparency.
Why should NATO be sustained?
In addition, NATO ought to be sustained because if things go wrong in Russia, as they might, the Atlantic alliance would form the basis of an opposing coalition, just as it did during the Cold War. But if things do go wrong in Russia, they won't go wrong in a hurry.
Did the Cold War end?
The Cold War began and ended there. The danger of a major war in Europe was the central obsession of the American government for much of the 20th century, and rightly so. But that danger is now at its lowest level in decades, perhaps in all of Europe's modern history.
Abstract
The end of the Cold War offered an opportunity to negotiate a major “settlement,” not unlike those following the great wars of the twentieth century. In the 1990s, the plan was to assimilate the former Soviet Union and its East European allies into a great liberal community of states stretching from Vancouver to Vladivostok.
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.