Pattern refers to the geometrical configuration or the external morphology of a rural settlement. It refers to the geometrical shape or arrangement of rural houses/settlements in an area. It reflects the layout plan as well as the geometrical shape of agricultural lands and the pattern of transportation lines.
Full Answer
What are the types of rural settlement patterns?
Types of rural settlement patterns
- Physical factor: Water availability, terrain, soil fertility
- Communication networks: Road, railways, rivers
- Social factors: caste-based settlement, religious-based settlement
- Political factors: Demorate, Autocrats, also affect the settlement.
What are the types of rural settlements?
What are three types of rural settlement?
- Metro.
- Suburb.
- Big satellite town.
- Mid-size town.
- Small town.
- Village & Settlement cluster.
- Sparse settlement.
What are the different types of settlement patterns?
Linear settlements
- Linear settlements are those settlements where the buildings are constructed in lines, often next to a geographical feature like a lake, a river or around a road.
- Linear settlement is also known as Chain village or ribbon development.
- Linear settlements usually have a long and narrow shape.
What statements describe settlement patterns?
Which statements describe settlement patterns? Resource availability influences where people settle. Politics and economic factors seldom play a role in where people settle. Land use is affected by settlement patterns. Settlement patterns provide information about the people living in specific areas.

What is a rural settlement pattern?
Rural settlement patterns refer to the shape of the settlement boundaries, which often involve an interaction with the surrounding landscape features. The most common patterns are linear, rectangular, circular or semi-circular, and triangular.
What is the settlement pattern?
settlement patterns. Definition English: A settlement pattern refers to the way that buildings and houses are distributed in a rural settlement. Settlement patterns are of interest to geographers, historians, and anthropologists for the insight they offer in how a community has developed over time.
What are the three types of rural settlement patterns?
12.2: Rural Settlement PatternsCompact Rural Settlements.Linear Rural Settlements.Circular Rural Settlements.
What are the 5 types of settlement patterns?
There are 5 types of settlement classified according to their pattern, these are, isolated, dispersed, nucleated, and linear.
What are the 4 types of settlement patterns?
Types of Settlements PatternsFactors.) Radial Pattern.Interpretation.Steps.Gradient.Interpretation.
What are 4 types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed.
What are the characteristics of rural settlement?
Size of the Community: The village communities are smaller in area than the urban communities. ... Density of Population: ... The primacy of Agriculture: ... Close Contact with Nature. ... Homogeneity of Population: ... Social Stratification: ... Social Interaction: ... Social Solidarity:
What are 2 main types of settlement?
Settlements can broadly be divided into two types – rural and urban.
What are the types of rural?
Rural settlements in India can broadly be put into four types: Clustered, agglomerated or nucleated: The clustered rural settlement is a compact or closely built-up area of houses. In this type of village, the general living area is distinct and separated from the surrounding farms, barns and pastures.
What are rural settlements called?
Common types of rural settlements are villages, hamlets and farms.
Where is rural settlement located?
A rural settlement is where displaced populations settle on land outside of cities and towns. The population is often dependent on agricultural and pastoral practices, and has fewer community infrastructure systems than in urban settlements.
Is rural settlement large or small?
In the United States, the Census Bureau classifies a rural area as a town with fewer than 1,000 people per 2.6 square kilometers (square mile), and surrounding areas with fewer than 500 people per 2.6 square kilometers (square mile).
What are settlement patterns examples?
There are three main settlement patterns: nucleated, linear and dispersed. Nucleated settlements comprise of buildings that are situated close together, usually clustering around a central area such as a river crossing or road junction.
What are settlement pattern studies?
The study of settlement patterns in archaeology involves a set of techniques and analytical methods to examine the cultural past of a region. The method allows examination of sites in their contexts, as well as interconnectedness and change across time.
What are the 2 types of settlement?
Settlement is a place where people live and carry out various economic activities on a relatively permanent basis. It can be divided into two types: rural settlement and urban settlement. The two types of settlement are differentiated by their size, density of population and employment pattern.
What is the importance of settlement pattern?
Settlements and the patterns they etch on Earth's surface provide not only information on current economic, political, and social conditions, but also a historical record of past conditions. Today's settlement patterns provide information about past settlement processes and land-use patterns.
What is clustered rural settlement?
A clustered rural settlement is a rural settlement where a number of families live in close proximity to each other, with fields surrounding the collection of houses and farm buildings. The layout of this type of village reflects historical circumstances, the nature of the land, economic conditions, and local cultural characteristics. ...
Where did the dispersed settlement pattern originate?
In the United States, the dispersed settlement pattern was developed first in the Middle Atlantic colonies as a result of the individual immigrants’ arrivals. As people started to move westward, where land was plentiful, the isolated type of settlements became dominant in the American Midwest.
What is a scattered village?
A scattered dispersed type of rural settlement is generally found in a variety of landforms, such as the foothill, tableland, and upland regions. Yet, the proper scattered village is found at the highest elevations and reflects the rugged terrain and pastoral economic life. The population maintains many traditional features in architecture, dress, and social customs, and the old market centers are still important. Small plots and dwellings are carved out of the forests and on the upland pastures wherever physical conditions permit. Mining, livestock raising, and agriculture are the main economic activities, the latter characterized by terrace cultivation on the mountain slopes. The sub-mountain regions, with hills and valleys covered by plowed fields, vineyards, orchards, and pastures, typically have this type of settlement.
What is linear settlement?
Linear Rural Settlements. The linear form is comprised of buildings along a road, river, dike, or seacoast. Excluding the mountainous zones, the agricultural land is extended behind the buildings. The river can supply the people with a water source and the availability to travel and communicate.
What are the two categories of settlements?
Using as classification criteria the shape, internal structure, and streets texture, settlements can be classified into two broad categories: clustered and dispersed.
When was Rundlinge invented?
The current leading theory is that Rundlinge were developed at more or less the same time in the 12th century, to a model developed by the Germanic nobility as suitable for small groups of mainly Slavic farm-settlers.
Where do isolated farms live?
In the United States, the dispersed settlement pattern was developed first in the Middle Atlantic colonies as a result of the individual immigrants’ arrivals. As people started to move westward, where land was plentiful, the isolated type of settlements became dominant in the American Midwest. These farms are located in the large plains and plateaus agricultural areas, but some isolated farms, including hamlets, can also be found in different mountainous areas ( Figures 12.7 and 12.8 ).
What are the two categories of rural settlements?
Using as classification criteria the shape, internal structure, and streets texture, settlements can be classified into two broad categories: clustered and dispersed .
Where did the dispersed settlement pattern originate?
In the United States, the dispersed settlement pattern was developed first in the Middle Atlantic colonies as a result of the individual immigrants’ arrivals. As people started to move westward, where land was plentiful, the isolated type of settlements became dominant in the American Midwest.
What is dispersed settlement?
A dispersed settlement is one of the main types of settlement patterns used to classify rural settlements. Typically, in stark contrast to a nucleated settlement, dispersed settlements range from a scattered to an isolated pattern ( Figure 12.6 ). In addition to Western Europe, dispersed patterns of settlements are found in many other world regions, including North America.
What is a scattered village?
A scattered dispersed type of rural settlement is generally found in a variety of landforms, such as the foothill, tableland, and upland regions. Yet, the proper scattered village is found at the highest elevations and reflects the rugged terrain and pastoral economic life. The population maintains many traditional features in architecture, dress, and social customs, and the old market centers are still important. Small plots and dwellings are carved out of the forests and on the upland pastures wherever physical conditions permit. Mining, livestock raising, and agriculture are the main economic activities, the latter characterized by terrace cultivation on the mountain slopes. The sub-mountain regions, with hills and valleys covered by plowed fields, vineyards, orchards, and pastures, typically have this type of settlement.
What are the compact villages?
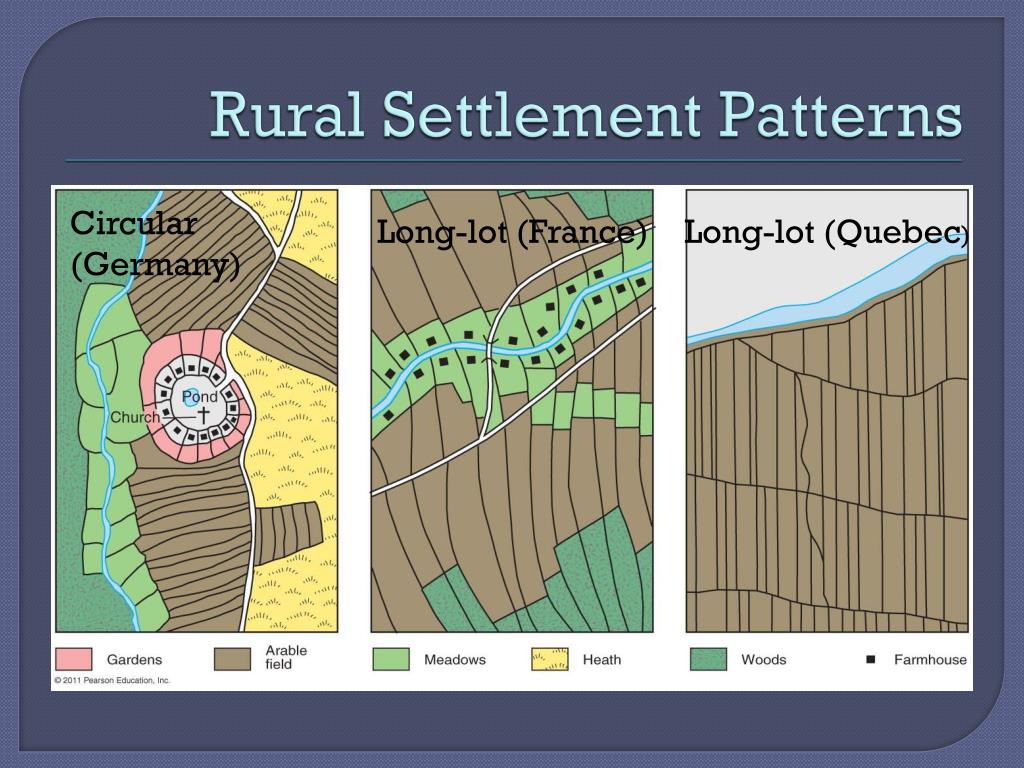
Small garden plots are located in the first ring surrounding the houses, continued with large cultivated land areas, pastures, and woodlands in successive rings. The compact villages are located either in the plain areas with important water resources or in some hilly and mountainous depressions. In some cases, the compact villages are designed to conserve land for farming, standing in sharp contrast to the often isolated farms of the American Great Plains or Australia ( Figure 12.1 ).
Why were roads built in parallel to the river?
Roads were constructed in parallel to the river for access to inland farms. In this way, a new linear settlement can emerge along each road, parallel to the original riverfront settlement ( Figure 12.2 ).
When was Rundlinge invented?
The current leading theory is that Rundlinge were developed at more or less the same time in the 12th century, to a model developed by the Germanic nobility as suitable for small groups of mainly Slavic farm-settlers.
What are the different types of settlements?
There are innumerable geometric possibilities relating to local terrain and location (such as road, canal, riverbank, or spring-line settlements), political conditions, or genesis of the settlements: colonial villages often had defensive functions expressed in linear or circular forms (Figure 2 ). The simpler hamlet clusters which characterized settlement in poorer more difficult agricultural environments were often associated with kinship groups, organic growth of settlements over long periods of time, as well as tribal roots of landownership in the early Middle Ages.
How does urbanization affect grassland ecosystems?
3 ). Urbanization causes the establishment of impermeable surfaces, landscape fragmentation, habitat loss and a loss in natural resource pathways and biodiversity ( Van der Walt et al., 2015 ).
How does grazing affect grassland?
Overutilization in terms of grazing combined with the effect of trampling degrades the grassland habitat making it susceptible for invasion by alien plants and woody species encroachment. Thus, incorrect grazing practices and stocking rates combined with drought events can alter the structure, composition and ecosystem functioning of the grassland areas. Moderate to heavy grazing by domestic animals causes a decrease in forb species richness of up to 84% and even leads to the extirpation of certain perennial forbs ( Scott-Shaw and Morris, 2014 ). In areas where land is left fallow it seldom if ever returns to its original vegetation structure. Bredenkamp and Brown (2003) found that natural grasslands in the Highveld region of South Africa that are degraded due to anthropogenic influences become dominated by thatch grasses ( Hyparrhenia spp.). These Hyparrhenia -dominated grasslands tend to be stable for a very long time (up to 50 years or more) and mostly have low species richness and diversity. In the high-altitude sub-alpine grasslands of Lesotho uncontrolled and ill-managed grazing programs have resulted in the degradation of the grasslands as well as its associated peatlands where large-scale erosion occurs. This has negative impacts on the larger and very important water catchment that is regarded as the most important water catchment area of southern Africa ( Du Preez and Brown, 2011 ).
What is the pattern of settlement in India?
This pattern of settlement is most common in India. The areas having this pattern of settlement have a high degree of clustering and high population density. The shape of the cultivated land is rectangular. Most of North Indian villages have rectangular patterns dominated by caste groups.
What is linear settlement?
Linear settlement. When houses are arranged along the bank of a river or coastline or transportation line, the pattern of settlement formed will be linear. Northern Malabar, Mopla Villages, fisherman villages along roads in Ganga-Yamuna doab.
What are some examples of perforated settlements?
Examples: Bangladeshi villages which are affected by the cyclone, floods, and waterlogging.
What type of settlement is when semi nucleated becomes nucleated?
Checker board type of settlement. When semi nucleated eventually becomes nucleated, the transition phase gives rise to the checkerboard type of settlement. In this type of settlement, the transport networks are developed so that they form a grid over the landscape.
What type of settlement pattern develops when transportation lines appear like a Nebula of circular ring emerging from centre?
Nebular Pattern . This type of settlement pattern develops when transportation lines appear like a Nebula of circular ring emerging from centre. Such patterns are common in south German villages located over highlands.
What is hollow rectangular?
Hollow rectangular. If a village develops along a water body, a religious site, or an open community land in the center, it is called a hollow rectangular. Such villages are typical of wet point settlements. E.g. villages over Tamil Nadu Plateau, Deccan Plateau.
When transportation lines are emerging from a point like over a dome-shaped plateau, what pattern develops?
When transportation lines are emerging from a point like over a dome-shaped plateau, the radial pattern develops and the houses cluster around the roads connecting the top of the plateau.
What are the factors that affect the pattern of rural settlement?
Three factors affect pattern of rural settlement. 1. the kind of resource that attract people to the area e.g . agriculture, forestry. 2. What transportation methods available at time of settlement e.g. before 1800, all settlements near water, after that there was settlement by road, and rail. 3.
What are the two main patterns of settlement in Canada?
There are 2 main patterns, dispersed and concentrated . Two main catgories of settlement in Canada. Rural ,and Urban. Rural – outside of cities and towns, low population density, dispersed settlement pattern. 1. the kind of resource that attract people to the area e.g. agriculture, forestry.
What is the settlement in which houses are constructed along the straight road called?
The settlement, in which houses are constructed along the straight road, is known as Y-Shape pattern. It is further bifurcated into two roads (similar to Y shape).
What is the term for the settlement in which houses are constructed along a road, railway line, river, canal edge?
The settlement in which houses are constructed along a road, railway line, river, canal edge of a valley, or along a levee is known as Linear Pattern.
What is a settlement in a star shape?
The settlements constructed in a star shape are known as Star like Pattern. Such kind of settlement is found around the points where several roads cross each other (making star shape).
Abstract
Much of India’s rural population lives in nucleated villages, which most commonly have a settlement form described as a shapeless agglomerate. Such settlements, though unplanned, are divided by caste into distinct wards and grow outward from a recognizable core area.
References (0)
ResearchGate has not been able to resolve any citations for this publication.
What is rural settlement?
3. RURAL SETTLEMENT A remote and a sparsely populated place People support their livelihood from primary economic activities Facilities that provide goods and service for people are amenities These settlements are mainly concerned with primary activities such as agriculture, mining, fishing, forestry etc. Most of the people (more than 50% of adult male) of rural settlement are engaged in agricultural work. Population density is small and the settlement size is small. Buildings are of non-durable materials in most cases.
What is the pattern of rural settlement in Asia?
Rural Settlement Pattern Of Asia • Disperse Settlement The dispersed settlement, in which each farm or a small group of farms is located at some distance from its neighbors, is increasingly becoming uncommon, but is widespread in hunting-gathering and fishing societies.
