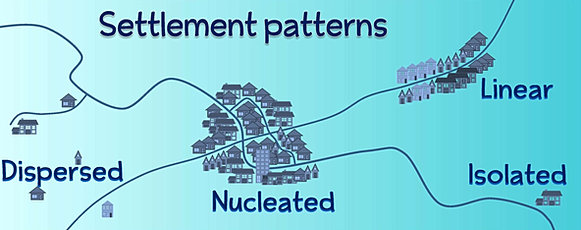
Settlement patterns Colonisation of Australia featured a series of migration waves around the south and south-east regions of Australia. Between 1788 and 1868 about 150 000 convicts arrived in Australia from the United Kingdom.
What is the clustered settlement pattern of Western Australia?
The clustered settlement pattern is demonstrated by the capital of the state, Perth. The city houses about 74% of the states population! Western Australia, the largest state of the country has the second lowest population density of 0.9 people per sq km compared to the other states.
Who coined the term Australian settlement?
As part of the campaign to liberalise the Australian economy in this period, journalist Paul Kelly coined the phrase "Australian Settlement" and blamed those early policy decisions for Australia's economic difficulties of the 1970s and 1980s.
What were the three policies of settlement in Australia?
Australian settlement. They were: the 'White Australia' Policy of immigration restriction; protective tariffs on imports of manufactured goods; a system of compulsory conciliation and arbitration for industrial disputes; and early social welfare policies. The term 'settlement' refers to the way this constellation of policies emerged as...
What was the first European settlement in Australia?
The Dutch first made landfall in Australia in 1606 CE but simply explored and mapped the area and did not establish a settlement. In the late 18th century, the British established their first Australian settlement in what would later become the city of Sydney with the intention of creating an overseas penal colony.

How many settlements are there in Australia?
At the time of the 2016 Census, 2.3 million people were living in small towns, or 9.7% of the Australian population. Australia-wide, there were just over 1,700 small towns. Of these: 88 towns had populations of 5,000 to 9,999, and were home to 613,500 people.
What are the settlements patterns?
There are three main settlement patterns: nucleated, linear and dispersed.
Where in Australia is the population settlement clustered?
Overall, more than half of Australia's population live in the capital cities of Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide; 4.7 million reside in the Greater Metropolitan Region of NSW (Sydney, Newcastle, Wollongong and the Central Coast); 85 per cent of NSW live in urban areas.
What are the 3 settlement patterns?
Population settlement patterns can be separated into to three distinct patterns: Linear. Clustered (or nucleated) Scattered.
What are the 5 types of settlement patterns?
There are 5 types of settlement classified according to their pattern, these are, isolated, dispersed, nucleated, and linear.
What are the 4 types of settlement patterns?
Rural settlement patterns refer to the shape of the settlement boundaries, which often involve an interaction with the surrounding landscape features. The most common patterns are linear, rectangular, circular or semi-circular, and triangular.
Why are most Australian settlements on the coast?
Using slides six to ten: The cities are all located by the coast as the coastal areas of Australia are most accessible for trade and travel, have the best climate and leisure activities, and there is enough water available to meet the needs of a large population.
How is Australia's population distributed?
Australia's population is concentrated in the major cities, which are home to 72% of the total population. By contrast, 26% live in inner and outer regional Australia, with the remainder (around 2%) living in Remote and very remote areas (see Demographic snapshot 2020–21).
How was land distributed in Australia?
Australia was divided into 19 counties in 1829 and the settlers in Australia were permitted to take up land only within these boundaries. Despite the prohibition against settlement outside the permitted area, many people continued occupying lands for pastoral and other purposes.
What are the settlement patterns in Canada?
In Canada, types of human settlement categorized by geographers and the government include urban and rural settlements, census metropolitan areas, First Nation reserves, and Métis settlements. In geography, the term urban describes a concentration of population at a high density.
What are 2 main types of settlement?
Settlements can broadly be divided into two types – rural and urban.
What is the most common type of settlement pattern in the world?
Dispersed, linear and nucleated are the most common. A dispersed pattern is where isolated buildings are spread out across an area, usually separated by a few hundred metres with no central focus. It is typically an area containing buildings rather than a single settlement.
What are the 4 types of rural settlements?
Settlement types (or rurality)Metro.Suburb.Big satellite town.Mid-size town.Small town.Village & Settlement cluster.Sparse settlement.
What are types of Class 7 settlements?
Settlement Transport CommunicationSettlement.Permanent settlement.Temporary settlement.Rural settlement.Urban settlement.
What are the 2 types of settlement?
Settlement is a place where people live and carry out various economic activities on a relatively permanent basis. It can be divided into two types: rural settlement and urban settlement. The two types of settlement are differentiated by their size, density of population and employment pattern.
What are the settlement patterns in Canada?
In Canada, types of human settlement categorized by geographers and the government include urban and rural settlements, census metropolitan areas, First Nation reserves, and Métis settlements. In geography, the term urban describes a concentration of population at a high density.
What were the effects of European settlement on Australia?
European settlement of Australia challenged aboriginal land and water resources, but it was disease that had the most devastating effect on the indigenous population. At the time of British colonization, there were likely between 315,000 and 750,000 Aborigines in Australia. By the start of World War II, diseases like smallpox and measles reduced their numbers to just 74,000.
What happened to the people of Australia when the Europeans arrived?
Life would change dramatically for the people of Oceania with the arrival of Europeans. The Dutch first made landfall in Australia in 1606 CE but simply explored and mapped the area and did not establish a settlement. In the late 18th century, the British established their first Australian settlement in what would later become the city of Sydney with the intention of creating an overseas penal colony. However, many of the prisoners sent to Australia were not hardened criminals who needed to be separated from the British Isles by an expansive ocean. Many were accused of petty crimes like theft and even children who had committed crimes were shipped to Australia. Today, around 20 percent of Australians are the descendants of these imprisoned settlers.
How did the physical landscape of Oceania shape the world?
Much of the physical landscape of Oceania has been directly shaped by human activity and settlement. Although Australia today is known for its origin as a British prison colony, the continent was inhabited long before Europeans arrived. The indigenous people of Australia are known as Aborigines and comprise a number of different ethnolinguistic and cultural groups. Most researchers believe the first aboriginal groups arrived in Australia between 40,000 and 50,000 years ago when sea levels were lower and land bridges and relatively short sea crossings separated Australia, Tasmania, and Papua New Guinea from mainland Southeast Asia.
What were the Pacific islands like in the 19th century?
Some islands were seen as strategic military bases. Others, such as France’s colony of New Caledonia, were transformed into overseas prison colonies following the British model. Still others were occupied for their resources and trade opportunities. In the decades following World War II, a number of islands achieved independence. Australia slowly increased its autonomy throughout the early 20th century, officially dissolving from British control in 1942. New Zealand gained independence from Britain in 1947. In the 1970s and 1980s, another wave of independence occurred, with Fiji, Tonga, and a number of other states gaining independence.
When did the Pacific islands start to be settled?
It took thousands more years and advances in ocean transportation and navigation for the rest of the Pacific islands to be settled (Figure 10.4. 1 ). Humans gradually made their way to the islands of Melanesia, to Fiji by 900 BCE then east and north. The far-reaches of Polynesia, including Hawaii and Easter Island, were not populated until much later due to the long distances separating them from other landmasses. New Zealand, though, was one of the last to be settled, with Eastern Polynesians not arriving on the islands until around 1250 CE. These groups developed their own ethnic and cultural identity known as the Maori.
When did New Zealand become a colony?
New Zealand was originally claimed by the British as a colony of Australia, but then became its own colony in the mid-19th century. Around the same time, representatives of Britain as well as Maori leaders signed the Treaty of Waitangi. This treaty granted British colonists sovereignty over the governing of New Zealand but gave the Maori the rights to their tribal lands and resources and made them British subjects.
What percentage of New Zealand's population is Maori?
The Maori of New Zealand make up a much larger portion of the country’s population at around 15 percent. The Maori have generally kept their traditional cultural and linguistic traditions while partially integrating into more western New Zealand society. Compared to other groups in New Zealand, the Maori have lower life expectancies and average incomes, and make up around 50 percent of New Zealand’s prison population.
History of the Development of Settlements
Aboriginal settlers arrived on the continent from Southeast Asia more than 40 000 years before the first Europeans began exploration in the 17th century. They were a hunting-gathering people known today as Aboriginals and Torres Straight Islanders. They depended on wood, bone and stone weapons to hunt.
Current Major Cities
Today, 82% of people live in urban areas (PRB). Many of these urban areas are along the eastern and southeastern coast, as the map shows, because the areas of central Australia are very arid. Less than 2.5% live in remote or very remote areas (U.S. Department of State).
Which country has a linear, clustered and scattered settlement pattern?
Again, Western Australia also has all characteristics of linear, clustered and scattered settlement pattern.
What percentage of Australia's population lives on the southern coast?
The southern coast is home to more than 75% of the population. This distincts the state as clustered compared to other areas of Australia.
What is the southwest site of Western Australia?
The southwest site of Western Australia is marked by linear and clustered settlement pattern. The cities are positioned and grouped together while some border the coast of the Indian Ocean.
What is Australia's mineral resource?
The country has limited fertile land, half-covered by dry deserts and plains but is with rich mineral resources. Australia is the leading producer of bauxite (aluminum ore); and also mines iron ore, copper, lead, uranium, industrial diamonds, gold, and silver. But the empty, wide land allows for ranches to operate and Australia to account for 70% of the world's wool exports.
What is the mining industry in NSW?
The mining industry of NSW also make up a considerable amount in it's economy; producing coal, silver, lead, and zinc.
Why is Australia more populated than the West?
As reviewed by the population density graph previously, the Pacific coast of Australia is more populated than the west, we can assume this is because the major export partners of Australia is east of the country.
Where are the most populated cities in Australia?
The sole reason of this pattern is becasue the majority of the most populated cities are located in the state New South Wales, including the capital of Australia, Canberra.
What is the Australian settlement?
The Australian settlement was a set of nation-building policies adopted in Australia at the beginning of the 20th century . The phrase was coined by journalist Paul Kelly in his 1992 book The End of Certainty. Kelly identified five policy "pillars" of the settlement: White Australia (a racially exclusive immigration policy); Protection (protective tariffs on imported manufactured goods); Wage Arbitration ( compulsory arbitration for industrial disputes); State Paternalism (interventionist social and economic policies); and Imperial Benevolence (faith in the British Empire ). These pillars profoundly influenced the way Australia developed over the coming decades and were only dismantled towards the end of the century. The term "settlement" refers to the way this constellation of policies emerged as a compromise between major interests in Australian society at that time, namely workers and employers. It has also been referred to as the Deakinite settlement, after its principal architect Alfred Deakin .
What party was involved in the Australian settlement?
The three-cornered contest between Protectionist Liberals, Free Trade Liberals and the Australian Labor Party ( ALP), saw the Protectionists introduce the key "Australian settlement" policies with Labor support.
Why was the protective tariff introduced in 1866?
This was supported and promoted in the Colony of Victoria by a protective tariff that had been introduced in 1866 to help generate local employment for migrants initially attracted to the gold fields.
What is the purpose of the establishment of a national government spanning the continent and the transfer of certain key functions to?
The establishment of a national government spanning the continent and the transfer of certain key functions to that government entailed the establishment of new national policies in regard to a range of important economic and social matters.
When did Australia end its domestic defence policy?
Dismantling the domestic defence framework began with the ending of the White Australia Policy between the mid-1960s and the mid-1970s. Australia persisted, however, with other components such as tariff protectionism while other advanced economies were moving toward more open trade in the post-war years through the GATT process. Weaknesses in Australia's commodity exporting economy combined with steadily increasing competition in world manufacturing thanks to the newly industrialized countries (NICs) put that strategy under great pressure in the 1980s. Under the Hawke-Keating Labor governments (1983–96), both tariff protectionism and centralised wage fixing were wound back. As part of the campaign to liberalise the Australian economy in this period, journalist Paul Kelly coined the phrase "Australian Settlement" and blamed those early policy decisions for Australia's economic difficulties of the 1970s and 1980s. A closer examination makes that interpretation difficult to sustain, but does not alter the reality that by the late 20th century the strategy of domestic defence had become an encumbrance.
Who coined the phrase "Australian Settlement"?
As part of the campaign to liberalise the Australian economy in this period, journalist Paul Kelly coined the phrase "Australian Settlement" and blamed those early policy decisions for Australia's economic difficulties of the 1970s and 1980s.
What was the economic development strategy of Francis Castles?
For theorist Francis Castles, implementation of these policies constituted an economic development strategy of "domestic defence" – using Australia's natural wealth to support an otherwise uncompetitive manufacturing sector, providing a good living to workers and pensions for later life.
Overview
The Australian settlement was a set of nation-building policies adopted in Australia at the beginning of the 20th century. The phrase was coined by journalist Paul Kelly in his 1992 book The End of Certainty. Kelly identified five policy "pillars" of the settlement: White Australia (a racially exclusive immigration policy); Protection (protective tariffs on imported manufactured goods); Wage Arbitration (compulsory arbitration for industrial disputes); State Paternalism (interventionist soci…
Background
Britain's Australian colonies had developed rapidly and successfully in the 19th century to become a major exporter of certain commodities, notably wool. By the 1880s they had become among the wealthiest societies in the world and had also developed unusually strong labour movements. Some manufacturing for local consumption had also become established. This was supported and promoted in the Colony of Victoria by a protective tariff that had been introduced in 1866 to help …
Decade of decision: 1901–1910
There was obviously a lot of business for the new parliament in those first years after Federation took effect on 1 January 1901. The decision-making was complicated, though, by the fact that no single party enjoyed a majority until Labor took office in 1910. The three-cornered contest between Protectionist Liberals, Free Trade Liberals and the Australian Labor Party (ALP), saw the Protectionists introduce the key "Australian settlement" policies with Labor support. This began …
Dismantling
Dismantling the domestic defence framework began with the ending of the White Australia policy between the mid-1960s and the mid-1970s. Australia persisted, however, with other components such as tariff protectionism while other advanced economies were moving toward more open trade in the post-war years through the GATT process. Weaknesses in Australia's commodity exporting economy combined with steadily increasing competition in world manufacturing thank…
See also
• American System (economic plan)
• National Policy (Canada)
Further reading
Origin
• Kelly, Paul (1992). The End of Certainty: The Story of the 1980s. Allen & Unwin.
Journal articles
• Brett, Judith (2007). "The Country, the City and the State in the Australian Settlement". Australian Journal of Political Science. 42 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1080/10361140601158518. S2CID 153485480.