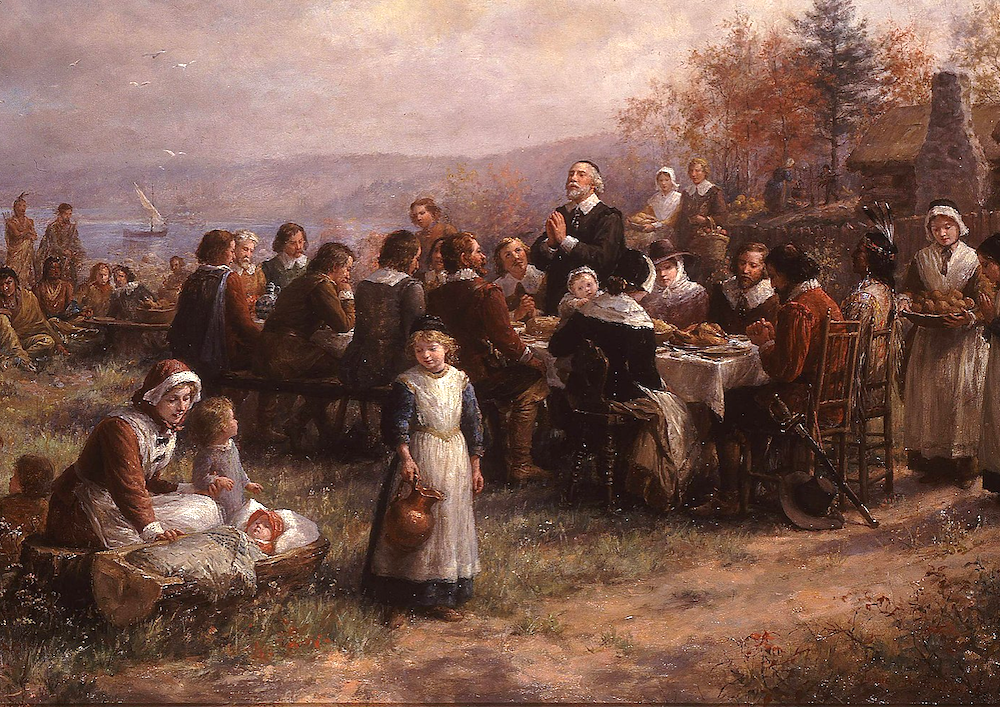
Full Answer
What happened during the settlement of New England colonies?
Settling of America – New England Settlements. It took its part bravely in the defense of the New England settlements against the Indians and saw half its towns destroyed in King Phillip’s War in 1675. Years later, in 1691, Plymouth would be annexed to the powerful neighboring colony of Massachusetts Bay.
How many Native Americans lived in the New England colonies?
In the 1600s, when the first English settlers began to arrive in New England, there were about 60,000 Native Americans living in what would later become the New England colonies (Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, New Hampshire, Connecticut, New Haven, and Rhode Island).
What was life like in the New England colonies?
Life in the New England Colonies. Men made the decisions in church and government matters. Women were obedient, quiet and deeply devout. Fathers served as the uncontested head of the household, with mothers acting in a subordinate role.
Why did the pilgrims settle in New England?
The New England colonies were settled by Pilgrim families who landed at Plymouth Rock after separating from the Anglican church over differences in theology. Their goal was to settle in a new land where they could practice their religion as they wished without pressure to conform.

What was life like in the early New England colonies?
Most people in New England lived by farming. It was back-breaking work and usually lasted from dawn to dusk. However in the south by the 18th century, great plantations existed alongside the many small farms. From 1612 tobacco was grown in Virginia and in 1619 the first black slaves arrived.
What was the settlement of New England?
The first European settlement in New England was a French colony established by Samuel de Champlain on Saint Croix Island, Maine in 1604. As early as 1600, French, Dutch, and English traders began to trade metal, glass, and cloth for local beaver pelts.
What was the New England land like?
The New England region included Connecticut, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire. The geography consisted of forests and hills. Combined with the hard rocky land, cold climate and long winters, New England's land was poor for large farming. Those who had small family owned farms were called Yeoman farmers.
Who settled the earliest New England colonies and why?
Establishing the New England Colonies. A group of Puritans known as the Pilgrims arrived on the Mayflower from England and the Netherlands to establish Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts, the second successful English colony in North America following Jamestown, Virginia.
Who settled the New England colony?
The original settlers of the New England colonies emigrated from Britain to the Americas for religious freedom. They fell into two categories: pilgrims and puritans. Pilgrims were separatists – they wanted to distance themselves from the Church of England and practice their own religion.
What was bad about the New England colonies?
Some of the problems were unintentionally introduced by the colonists, like smallpox and other diseases that the English settlers had unwittingly brought over on their ships. Although the colonists suffered diseases of their own early on, they were largely immune to the microbes they brought over to the New World.
What are 4 facts about the New England colonies?
Shortly after the Mayflower, the Puritans settled Massachusetts Bay. Massachusetts Bay became the most influential colony in New England. Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire can trace their beginnings back to it. New England's main source of commerce was its fish and timber.
What are 3 facts about the New England colonies?
The New England Colonies got their names for a variety of reasons. Massachusetts was named after a tribe, with the name meaning 'large hill place'. Connecticut was named for an Algonquin word meaning 'beside the long tidal river. ' Rhode Island was named for a Dutch word meaning 'red island.
What were the New England colonies known for?
In the New England towns along the coast, the colonists made their living fishing, whaling, and shipbuilding. The fish included cod, mackerel, herring, halibut, hake, bass and sturgeon. Whale oil was a valuable resource as it could be used in lamps....New England Colonies.●New England Colonies●Middle Colonies●Southern Colonies
Which settlers were attracted to New England in its earliest years?
Which settlers were attracted to New England in its earliest years? Religious people. The first settlers of New England were Puritans who mostly attracted other religious Puritan families.
What made the English settlement of New England distinctive?
What made the English settlement of New England distinctive? In the English settlement of New England a different social order emerged, a religious movement known as "Puritanism." The Puritans had different beliefs for the family, government and society, and the relationship between the church and state.
What caused the Pilgrims to settle in New England?
Due to economic difficulties, as well as fears that they would lose their English language and heritage, they began to make plans to settle in the New World. Their intended destination was a region near the Hudson River, which at the time was thought to be part of the already established colony of Virginia.
Why did Puritans settle in New England?
Puritans felt that they had a direct covenant with God to enact these reforms. Under siege from Church and crown, certain groups of Puritans migrated to Northern English colonies in the New World in the 1620s and 1630s, laying the foundation for the religious, intellectual and social order of New England.
What were the New England colonies known for?
In the New England towns along the coast, the colonists made their living fishing, whaling, and shipbuilding. The fish included cod, mackerel, herring, halibut, hake, bass and sturgeon. Whale oil was a valuable resource as it could be used in lamps....New England Colonies.●New England Colonies●Middle Colonies●Southern Colonies
What was the influence of the Pilgrims on New England?
Politically, the little colony was of slight importance, but its moral and religious influence on New England was great. The Pilgrims demonstrated that industry and courage could conquer even the inhospitable soil and climate of the Massachusetts shore and that unflinching devotion to an ideal could make of the wilderness, a home.
Why was the Plymouth colony allowed to continue undisturbed?
However, because of its small size and quiet demeanor, the colony of Plymouth was allowed to continue undisturbed by the Stuarts.
What was the first instance of self-government in the nation's history?
It was the first instance of complete self-government in the nation’s history, as the assembly which met at Jamestown the year before the landed, was called together by orders from the Virginia Company in England. The first winter of 1620-1621 was difficult for the immigrants.
What colony was founded in 1628?
Massachusetts. Massachusetts Bay Colonists. In 1628 a company of Puritan gentlemen secured a grant of land from the council and began the largest and most important of the English settlements in America — the colony of Massachusetts Bay.
When did the Mayflower return to England?
The first winter of 1620-1621 was difficult for the immigrants. Yet, when the Mayflower returned to England in the spring, not one of the colonists went with her. Their home was in America. The first Thanksgiving with the Pilgrims. 1921 painting by Jean Leon Gerome Ferris.
When was Plymouth annexed?
Years later, in 1691, Plymouth would be annexed to the powerful neighboring colony of Massachusetts Bay. While the settlement at Plymouth was slowly growing, several attempts were made by Gorges and other members of the Massachusetts Council for New England to plant colonies in the New World. About 50 scattered settlements were established by March ...
Where did the separatists settle in 1608?
Many of these separatist congregations took refuge in Holland in 1608 but were not content to be absorbed into the Dutch nation and have their children forget the customs and speech of England. Determined to migrate to the new land of America, they got permission from the London Company to settle in; but their pilot brought them to the shores of Cape Cod, where they landed December 21, 1620.
What is a glimpse at everyday life in the New England colonies?
A Glimpse at Everyday Life in the New England Colonies, 1763-1774. A depiction of a town meeting being held in a church. Library of Congress.
Why did the New England colonies have a strong cohesion?
The makeup of most New Englanders came from the British Isles and portions of the Netherlands. Because of this makeup, along with commonalities in religion, cultural practices, and intermarrying, led to a strong cohesion among the commonwealths. It also explains why so many first defended their natural rights as Englishmen, and then openly objected when these rights were being violated because they were Englishmen. For the majority of colonists, daily life consisted of supporting the profession the family was centered around. Nearly all rural communities were supported by farming while the larger, more concentrated port cities were hubs for mercantile businesses and artisan trades. Women were primarily responsible for the rearing of children at home, but many also were forced to work jobs such as cooks, washers, spinsters, and seamstresses if widowed or necessity demanded it. Others served as prostitutes and camp-followers to the colonial militia and British regulars. Though the early push for abolition did partially arise in New England, slavery was still the common practice in the colonies through the years leading to the Revolution. The streets of Boston yielded a mixture of both free and enslaved black Americans during the period. It was also common for farms and plantations (yes, they did exist in the North) to have enslaved people working them. The most tedious relationship between white colonists was that with Native Americans to their immediate west. Relations had been mixed throughout the two centuries of cohabitation, with a handful of Indian raids that left permanent stains on community memories.
What was the most tedious relationship between white colonists and Native Americans?
The most tedious relationship between white colonists was that with Native Americans to their immediate west. Relations had been mixed throughout the two centuries of cohabitation, with a handful of Indian raids that left permanent stains on community memories.
What jobs did women have to do with their children?
Women were primarily responsible for the rearing of children at home, but many also were forced to work jobs such as cooks, washers, spinsters, and seamstresses if widowed or necessity demanded it. Others served as prostitutes and camp-followers to the colonial militia and British regulars.
What was the primary destination for the majority of imported goods in the Middle and Southern colonies?
While this was also true for the middle and southern colonies, New England’s established trade routes and closer proximity to Europe allowed for it to be the primary destination for the majority of imported goods.
Why did so many first defended their natural rights as Englishmen, and then openly objected when these rights?
It also explains why so many first defended their natural rights as Englishmen, and then openly objected when these rights were being violated because they were Englishmen. For the majority of colonists, daily life consisted of supporting the profession the family was centered around.
Why was the Boston area considered ground zero?
This created wealth and prosperity throughout the region and explains why it became ground zero for resistance to British taxation in the 1760s. While port cities like Boston, Gloucester, and New Haven defined the region’s main economy, it was the several rural villages that made up the backcountry and interior landscape.
Introduction
Much of American Genealogy can be traced to about 4,000 core families that first settled in the New England area between 1620-1640. The first group was parted of Plymouth Colony started by the Mayflower pilgrims in 1620. The second and much larger group came over between 1630-1638 with Gov John Winthrop to settle the Massachusetts Bay Colony.
New England Founding Fathers
Trace major founders families from first landing to the 1880 US Census.
What was the life like in the New England colonies?
Life in the New England Colonies. Men made the decisions in church and government matters. Women were obedient, quiet and deeply devout. Fathers served as the uncontested head of the household, with mothers acting in a subordinate role. Under the father's authority, the mother oversaw the upkeep of the home and the raising of the children.
What did the New England colonists bring to the colonies?
Unlike previous attempts at colonization by the British, which consisted of companies of men seeking resources and a passage to the Northwest, the New England colonists brought over entire families to establish permanent homes and congregations.
What did the colonists do to help the family?
Men of the family were responsible largely for tending livestock, hunting wild game, and working at various trades that supported the family. A mid-day meal might consist of ox tongue, mince meat pie, roast pigeons, cucumbers and sweet potato pudding. Fresh caught fish also made for a tasty meal. To prevent spoiling, the colonists smoked their meat or used salt as a preservative. Women took care of the children, prepared foods, tended the family garden, and making necessary items such as soap, candles, clothing and blankets. Children were given chores from a very young age. Growing boys would work with their fathers raise crops in the fields, while young girls were trained by their mothers to help with the domestic work.
What did the colonists do to prevent spoiling?
To prevent spoiling, the colonists smoked their meat or used salt as a preservative. Women took care of the children, prepared foods, tended the family garden, and making necessary items such as soap, candles, clothing and blankets. Children were given chores from a very young age.
What was the Puritans' goal?
Their goal was to settle in a new land where they could practice their religion as they wished without pressure to conform. The Puritans arrived about a decade later. They remained loyal to the Church of England but advocated for significant religious reform. Unlike previous attempts at colonization by the British, ...
How did the family bond?
The family bonded together by their efforts to work cooperatively, protect and shelter each other, and celebrate life together, sharing and passing on their morals and values to each new generation. However, disciplinary techniques have changed substantially.
Who built the American family?
The structure for the traditional American family as it is defined in modern times was built by the New England colonists. Colonial families developed the structure of the essentially nuclear, child-centered, loving, close-knit family that works as a unit for the benefit of all.
Why was New England established?
New England was established out of a need for those separated from the English Protestant Church. In 1530, the English decided a separate from the Roman Catholic Church was necessary, and reform in belief soon followed. Roughly 30 years later, those who still believed in the 'purification' the Church - the Puritans - eventually decided ...
What was life like in the early colonies?
Life in the early colonies was an interesting one for the earliest American settlers. Being a Puritan meant following a strict lifestyle and one that was not necessarily approved by the Church of England, which is part of the reason for the early settlement in what would become known as colonial New England. This separation of religions is ...
Why was the Scarlet Letter inspired by the Puritan religion?
While it's true that this was a big cause for paranoia, it was also the inspiration for novels such as The Scarlet Letter, as Puritan life had strict punishment for those who went against the church or their faith. Life was vastly different for men, women, children, and teens, and each person had a role in society as well as a role to serve in ...
What was it like to be a Puritan?
During a time when the separation of church and state was far from anyone's minds, Puritan life was physically healthier but mentally taxing. Life in the early colonies was an interesting one for the earliest American settlers.
What were the consequences of missing the church?
Harsh Consequences. Those who didn't follow the rules of the church or respect the rules society had set in place would be subject to serious consequences. Routinely missing church meant that those in defiance would be fined, as the church was a place where meetings were held and important issues were discussed.
Why was New England the birthplace of grandparents?
This was so prevalent that it's said, according to ushistory.org, that New England was the 'birthplace of grandparents.'. Thanks to Massachusetts law which required a high tax, literacy rates were up as well, and the sole purpose of this was so that children would be able to read the Bible.
Did the colonies have longer lives than England?
It soon became known that those living in the colonies would have longer lives than those who lived in England, and many even lived to watch their future generations grow up. This was nearly unheard of until that time and can be attributed to a healthier lifestyle all around (harsh winters aside) as well as better air quality and other improvements that did not come with living in England. Additionally, pregnancy rates were up and it was soon not uncommon for families to grow to large sizes, especially in Maryland and Virginia. This was so prevalent that it's said, according to ushistory.org, that New England was the 'birthplace of grandparents.'
How did slavery grow in New England?
While slavery grew exponentially in the South with large-scale plantations and agricultural operations , slavery in New England was different. Most of those enslaved in the North did not live in large communities, as they did in the mid-Atlantic colonies and the South. Those Southern economies depended upon people enslaved at plantations to provide labor and keep the massive tobacco and rice farms running. But without the same rise in plantations in New England, it was more typical to have one or two enslaved people attached to a household, business, or small farm.
Why did enslaved people work in New England?
In New England, it was common for individual enslaved people to learn specialized skills and crafts due to the area’s more varied economy. Ministers, doctors, tradesmen, and merchants also used enslaved labor to work alongside them and run their households. As in the South, enslaved men were frequently forced into heavy or farm labor. Enslaved women were frequently forced to work as household servants, whereas in the South women often performed agricultural work.
What were the forced labors in the South?
As in the South, enslaved men were frequently forced into heavy or farm labor. Enslaved women were frequently forced to work as household servants, whereas in the South women often performed agricultural work. New England’s Forced Laborers: the Enslaved, Indentured Servants, and Native Americans. Part of the reason slavery evolved differently in ...
Why did slavery evolve differently in New England than in the middle and southern colonies?
Part of the reason slavery evolved differently in New England than in the middle and southern colonies was the culture of indentured servitude. As a carryover from English practice, indentured servants were the original standard for forced labor in New England and middle colonies like Pennsylvania and Delaware.
How long did indentured servants work?
These indentured servants were people voluntarily working off debts, usually signing a contract to perform slave-level labor for four to seven years. Historians estimate that more than half of the original population of the American colonies was brought over as indentured servants.
Why did Southern economies depend on slaves?
Those Southern economies depended upon people enslaved at plantations to provide labor and keep the massive tobacco and rice farms running. But without the same rise in plantations in New England, it was more typical to have one or two enslaved people attached to a household, business, or small farm.
What was the Free North?
Becoming the “Free North”. The use of slavery throughout the colonies (particularly the southern ones) continued to grow throughout the 18 th century, but as the colonies moved closer to revolution against England, there was a growing trend of questioning slavery and its practices in New England.
What were the Puritans' motives for settling in New England?
Many of the Puritans crossing the Atlantic were people who brought families and children. Often they were following their ministers in a migration “beyond the seas,” envisioning a new English Israel where reformed Protestantism would grow and thrive, providing a model for the rest of the Christian world and a counter to what they saw as the Catholic menace. While the English in Virginia and Maryland worked on expanding their profitable tobacco fields, the English in New England built towns focused on the church, where each congregation decided what was best for itself. The Congregational Church is the result of the Puritan enterprise in America. Many historians believe the fault lines separating what later became the North and South in the United States originated in the profound differences between the Chesapeake and New England colonies.
Why did the English settle in Virginia?
In the early seventeenth century, thousands of English settlers came to what are now Virginia, Maryland, and the New England states in search of opportunity and a better life.
Why were Puritans a threat to the Church of England?
In the Church’s view, Puritans represented a national security threat, because their demands for cultural, social, and religious reforms undermined the king’s authority. Unwilling to conform to the Church of England, many Puritans found refuge in the New World. Yet those who emigrated to the Americas were not united. Some called for a complete break with the Church of England, while others remained committed to reforming the national church.
Why did the Puritans escape England?
Although many people assume Puritans escaped England to establish religious freedom , they proved to be just as intolerant as the English state church. When dissenters, including Puritan minister Roger Williams and Anne Hutchinson, challenged Governor Winthrop in Massachusetts Bay in the 1630s, they were banished. Roger Williams questioned the Puritans’ taking of Indian land. Williams also argued for a complete separation from the Church of England, a position other Puritans in Massachusetts rejected, as well as the idea that the state could not punish individuals for their beliefs. Although he did accept that nonbelievers were destined for eternal damnation, Williams did not think the state could compel true orthodoxy. Puritan authorities found him guilty of spreading dangerous ideas, but he went on to found Rhode Island as a colony that sheltered dissenting Puritans from their brethren in Massachusetts. In Rhode Island, Williams wrote favorably about native peoples, contrasting their virtues with Puritan New England’s intolerance.
How did Puritans differ from Catholics?
This attitude was in stark contrast to that of Catholics, who refused to tolerate private ownership of Bibles in the vernacular. The Puritans, for their part, placed a special emphasis on reading scripture, and their commitment to literacy led to the establishment of the first printing press in English America in 1636. Four years later, in 1640, they published the first book in North America, the Bay Psalm Book. As Calvinists, Puritans adhered to the doctrine of predestination, whereby a few “elect” would be saved and all others damned. No one could be sure whether they were predestined for salvation, but through introspection, guided by scripture, Puritans hoped to find a glimmer of redemptive grace. Church membership was restricted to those Puritans who were willing to provide a conversion narrative telling how they came to understand their spiritual estate by hearing sermons and studying the Bible.
What was the result of the Puritan enterprise in America?
While the English in Virginia and Maryland worked on expanding their profitable tobacco fields, the English in New England built towns focused on the church, where each congregation decided what was best for itself. The Congregational Church is the result of the Puritan enterprise in America.
What were the English colonies like in the seventeenth century?
The English encouraged emigration far more than the Spanish, French, or Dutch. They established nearly a dozen colonies, sending swarms of immigrants to populate the land. England had experienced a dramatic rise in population in the sixteenth century, and the colonies appeared a welcoming place for those who faced overcrowding and grinding poverty at home. Thousands of English migrants arrived in the Chesapeake Bay colonies of Virginia and Maryland to work in the tobacco fields. Another stream, this one of pious Puritan families, sought to live as they believed scripture demanded and established the Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, New Haven, Connecticut, and Rhode Island colonies of New England ( [link] ).
