
Was the peace settlement of 1919 doomed from the start?
Examination of the readings for this week illustrates the Peace Settlement of 1919 was doomed from the outset.
Who signed the Treaty of Paris in 1919?
Johannes Bell of Germany is portrayed as signing the peace treaties on 28 June 1919 in The Signing of Peace in the Hall of Mirrors, by Sir William Orpen. The Paris Peace Conference was the formal meeting in 1919 and 1920 of the victorious Allies after the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers.
What happened at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919?
The Paris Peace Conference opened on Jan. 18, 1919, in a politically charged atmosphere. The delegations of 27 nations harassed the Great Powers with their various and conflicting complaints and demands. The Great Powers, in turn, sent five delegates each, supported by sprawling staffs of geographers,…
Why is Paris 1919 called Paris 1919?
Paris 1919 (1973), the third studio album by Welsh musician John Cale, is named after the Paris Peace Conference, and its title song explores various aspects of early-20th-century culture and history in Western Europe.

What were the key terms of the 1919 peace settlement?
Introduction. The Treaty of Versailles was signed by Germany and the Allied Nations on June 28, 1919, formally ending World War One. The terms of the treaty required that Germany pay financial reparations, disarm, lose territory, and give up all of its overseas colonies.
What happened at the Paris peace settlements in 1919?
The major decisions were the establishment of the League of Nations; the five peace treaties with defeated enemies; the awarding of German and Ottoman overseas possessions as "mandates", chiefly to members of the British Empire and to France; reparations imposed on Germany; and the drawing of new national boundaries ( ...
Was the peace settlement of 1919 20 A failure?
Thus, the Treaty of Versailles failed to bring about everlasting European stability and peace for which the Allied Powers' governments had hoped.
Was the 1919 Paris Peace Conference successful?
Set against the backdrop of contemporary expectations, the Paris Peace Treaties almost inevitably disappointed everyone and it failed in achieving its ultimate objective: the creation of a secure, peaceful, and lasting world order.
Where was the 1919 International Peace Conference held?
The Paris Peace Conference was an international meeting convened in January 1919 at Versailles just outside Paris. The purpose of the meeting was to establish the terms of the peace after World War.
Why did the US reject the Paris peace settlement of 1919 20?
While it fought alongside the Allies, the United States was not bound to honor pre-existing agreements among the Allied Powers. These agreements focused on postwar redistribution of territories. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson strongly opposed many of these arrangements, including Italian demands on the Adriatic.
Why were the French dissatisfied with the peace settlement?
France was dissatisfied with the conditions of the Treaty of Versailles because they believed that the treaty did not adequately punish Germany.
Why is Treaty of Versailles unfair?
It was unfair because Germany had no say in the creation of the treaty. I agreed with George Clemceau of France on the allied side the most however. His belief was to make sure that Germany's military was restricted to the point where they could not rise and start another war.
What problems did the peacemakers face in 1919?
The first problem faced by the peacemakers at Versailles was the political and social instability in Europe, which necessitated that they act speedily to reach a peace settlement. one Allied observer noted that'there was a veritable race befi,veen peace and anarchy'.
Why did the US reject the Paris peace settlement of 1919 20?
While it fought alongside the Allies, the United States was not bound to honor pre-existing agreements among the Allied Powers. These agreements focused on postwar redistribution of territories. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson strongly opposed many of these arrangements, including Italian demands on the Adriatic.
What event took place at Versailles in 1919?
On June 28, 1919, the Treaty of Versailles was signed at the Palace of Versailles outside Paris, France. The treaty was one of several that officially ended five years of conflict known as the Great War—World War I.
What were the problems at the Paris Peace Conference?
When Wilson returned in mid-March 1919 a tangle of unresolved problems threatened to overwhelm the conference: Germany's responsibility to redress Allied losses; its eastern and western frontiers; Italian claims to Fiume; Polish claims to Danzig and Anglo-French differences in the Middle East.
What was the name of the peace conference that the United States signed in Paris?
United States: The Paris Peace Conference and the Versailles Treaty
What was the Paris Peace Conference?
Paris Peace Conference, (1919–20), the meeting that inaugurated the international settlement after World War I.
When did the League of Nations start?
The formal inauguration of the League of Nations on January 16, 1920, brought the Paris conference to an end, before the conclusion of treaties with Turkey (1920, 1923) or with Hungary (1920).
Why was the Supreme Council of Four reduced to a Council of Four?
In March, however, the Supreme Council was, for reasons of convenience, reduced to a Council of Four, numbering only the Western heads of government, as the chief Japanese plenipotentiary, Prince Saionji Kimmochi, abstained from concerning himself with matters of no interest to Japan.
Who led the Paris Peace Conference?
The Paris Peace Conference was held from January to June 1919. Wilson led the American delegation, which did not include any prominent Republicans. This was a major blunder in light of the midterm elections.
What were the origins of the Cold War?
The Origins of the Cold War. American Foreign Policy. The Civil Rights Movement. The Affluent Society. Johnson and the Great Society. The Counterculture of the 1960s. The Kennedy Years. America in the 1970s . The Nixon Presidency.
What was the purpose of Article 10 of the Treaty of Versailles?
It called on all member states to respect and preserve the independence and territorial integrity of all member nations through collective action. Mindful of the concerns of Senate Republicans, Wilson agreed to amendments to the charter: The League could not interfere in domestic matters, members could withdraw on two‐years' notice, and regional agreements such as the Monroe Doctrine were exempt from League action. These changes were included in the covenant of the League of Nations that was attached to the Treaty of Versailles.
What did Wilson agree to in the charter?
Mindful of the concerns of Senate Republicans, Wilson agreed to amendments to the charter: The League could not interfere in domestic matters, members could withdraw on two‐years' notice, and regional agreements such as the Monroe Doctrine were exempt from League action.
What was the war guilt clause?
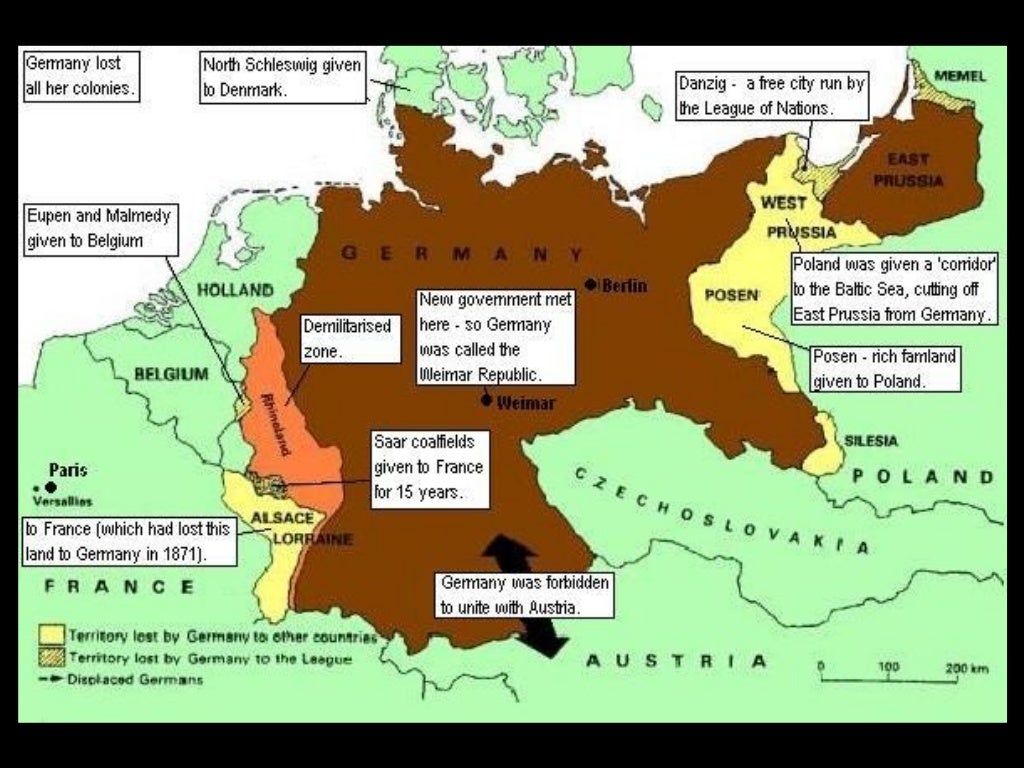
A war guilt clause, which blamed Germany alone for starting the war, was accepted to justify reparations that grew to more than $56 billion. Further, Germany lost all of its colonies and some territory to France and newly independent Poland, and was substantially disarmed. These terms were hardly “peace without victory.”.
What were the 14 points of the War of 1812?
Under the armistice agreement, Wilson's Fourteen Points were the basis for the peace settlement with Germany and the Central Powers. This declaration of American war aims called for open diplomacy (an end to secret treaties), freedom of the seas, removal of trade barriers, impartial adjustment of colonial claims that recognized the interests ...
When was the Treaty of Versailles ratified?
The debate over ratification. The Treaty of Versailles was submitted to the Senate for ratification in July 1919. It was clear from the outset that the Senate was bitterly divided over the League.
What principle should not have been surprised when these were included in the Peace Treaty?
and the principle of reparations. They should not have been surprised when these were included in the peace treaty.
Why did the Treaty of Sevres fail?
The treaties failed in Central Europe as they created states with too many rival minorities, such as the Serbs, Bosnians and Croats forming Yugoslavia.Turkey was treated unfairly to satisfy France, Britain and Greece. The Treaty of Sevres only lasted three years.
What did Clemenceau want?
Clemenceau wanted Germany to pay for the cost of the damage. He wanted the return of Alsace-Lorraine. He wanted to ensure that Germany could not attack France again by taking land, weakening industry and reducing her armed forces. He wanted to split Germany into a number of small states. Germany should lose the Rhineland, the Saarland, Upper Silesia, Danzig and East Prussia. Germany should lose all its colonies. He wanted reparations.
Why did Wilson not want Germany treated harshly?
Wilson did not want Germany treated harshly because he thought that if Germany was punished severely then, in the future, Germany would want revenge. He failed to persuade
Where was Eupen Malmedy handed over?
for fifteen years. Eupen-Malmedy was handed over to Belgium and Northern Schleswig to Denmark. This
Who wanted revenge for the Franco-Prussian War?
Clemenceau, who wanted revenge for the Franco-Prussian War and the fact that most of the fighting in the First World War had taken place in France.
What did the Germans do to Russia?
retreat, the Germans deliberately destroyed mines, railways, factories and bridges. By the end of 1917, Russia was defeated. In March 1918, Russia's new Bolshevik government signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. The Germans inflicted severe punishment on Russia by taking Finland, the Baltic States, its Polish provinces and the Ukraine. It is not surprising the Allies wanted to heavily punish Germany similar to Germany's treatment of
Overview
The Paris Peace Conference was the formal meeting in 1919 and 1920 of the victorious Allies after the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers. Dominated by the leaders of Britain, France, the United States and Italy, it resulted in five treaties that rearranged the maps of Europe and parts of Asia, Africa and the Pacific Islands, and also imposed financial pe…
Overview and direct results
The Conference formally opened on 18 January 1919 at the Quai d’Orsay in Paris. This date was symbolic, as it was the anniversary of the proclamation of William I as German Emperor in 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles, shortly before the end of the Siege of Paris - a day itself imbued with significance in its turn in Germany as the anniversary of the establishment of the Kingdom …
Mandates
A central issue of the conference was the disposition of the overseas colonies of Germany. (Austria-Hungary did not have major colonies, and the Ottoman Empire was a separate issue.)
The British dominions wanted their reward for their sacrifice. Australia wanted New Guinea, New Zealand wanted Samoa, and South Africa wanted South Wes…
British approach
The maintenance of the unity, territories, and interests of the British Empire was an overarching concern for the British delegates to the conference, but they entered the conference with more specific goals with this order of priority:
• Ensuring the security of France
• Removing the threat of the German High Seas Fleet
French approach
French Prime Minister, Georges Clemenceau controlled his delegation, and his chief goal was to weaken Germany militarily, strategically, and economically. Having personally witnessed two German attacks on French soil in the last 40 years, he was adamant for Germany not to be permitted to attack France again. Particularly, Clemenceau sought an American and British joint guarantee of Fr…
Italian approach
In 1914, Italy remained neutral despite the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. In 1915, it joined the Allies to gain the territories promised by the Triple Entente in the secret Treaty of London: Trentino, the Tyrol as far as Brenner, Trieste, Istria, most of the Dalmatian Coast (except Fiume), Valona, a protectorate over Albania, Antalya (in Turkey), and possibly colonies in Africa.
Japanese approach
Japan sent a large delegation, headed by the former Prime Minister, Marquis Saionji Kinmochi. It was originally one of the "big five" but relinquished that role because of its slight interest in European affairs. Instead, it focused on two demands: the inclusion of its Racial Equality Proposal in the League's Covenant and Japanese territorial claims with respect to former German colonies: Shant…
American approach
Until Wilson's arrival in Europe in December 1918, no sitting American president had ever visited the continent. Wilson's 1917 Fourteen Points, had helped win many hearts and minds as the war ended in America and all over Europe, including Germany, as well as its allies in and the former subjects of the Ottoman Empire.