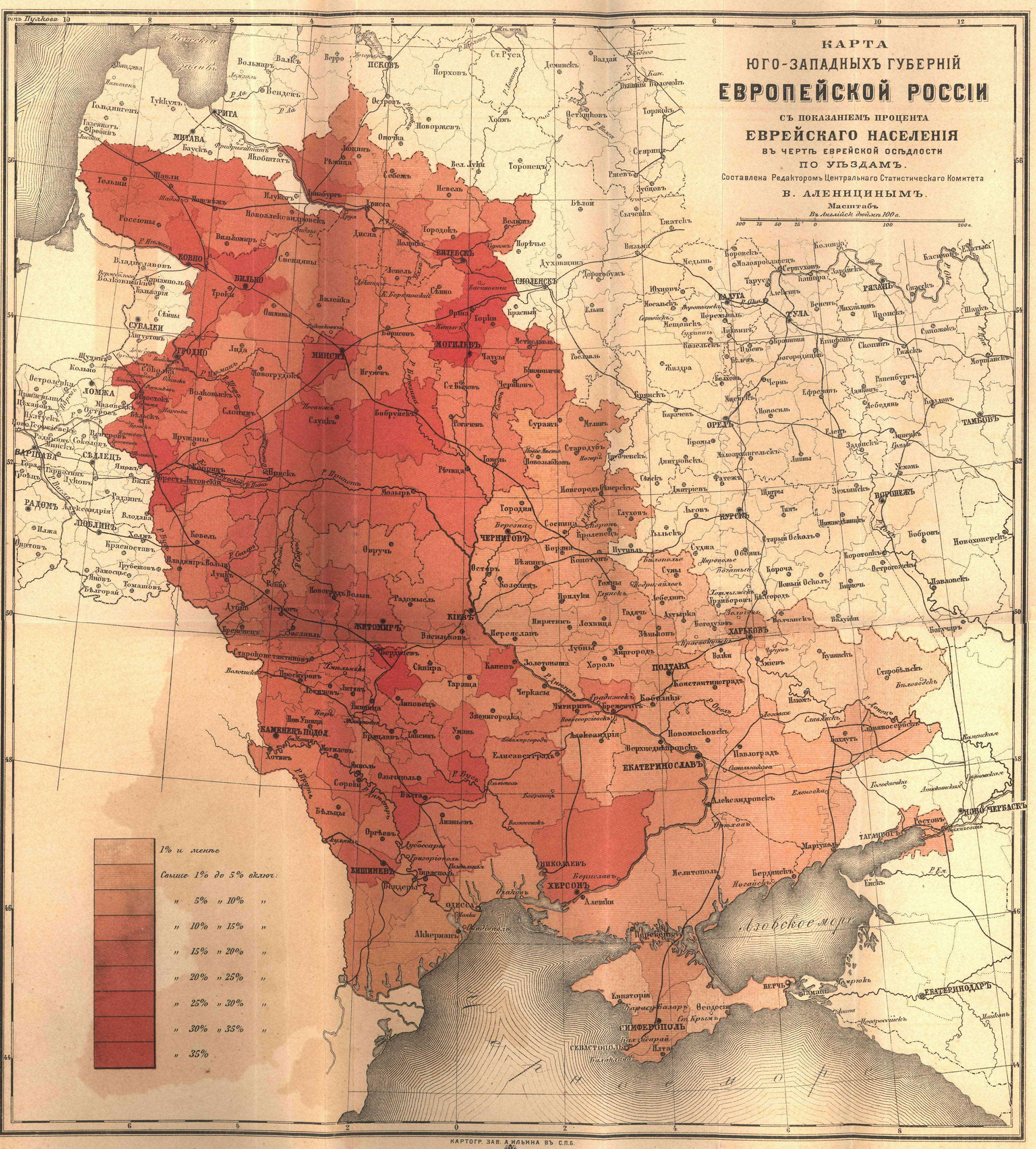
What were the boundaries of the Pale of Settlement?
The Pale of Settlement included all of modern-day Belarus, Lithuania and Moldova, much of Ukraine and east-central Poland, and relatively small parts of Latvia and what is now the western Russian Federation.
Why did they call it the Pale of Settlement?
It is this definition of pale from which the phrase “beyond the pale” is derived. In imperial Russia, what came to be called the Pale of Settlement (Cherta Osedlosti) came into being as a result of the introduction of large numbers of Jews into the Russian sphere after the three partitions of Poland (1772, 1793, 1795).
Was Minsk part of the Pale of Settlement?
In 1835 Minsk was officially included into the Pale of Settlement, which later led to a rise in Jewish population. Throughout the 19th century the city grew and significantly improved.
What does shtetl mean in Yiddish?
townBut according to Shandler, a professor in the Department of Jewish Studies at Rutgers: “In Yiddish, shtetl simply means 'town' – anywhere, at any time, inhabited by anyone. In popular usage, it has acquired all kinds of connotations, especially as the word moves into other languages.”
How did Jews get to the pale?
came to be called the Pale of Settlement (Cherta Osedlosti) came into being as a result of the introduction of large numbers of Jews into the Russian sphere after the three partitions of Poland (1772, 1793, 1795).
Where are Ashkenazi Jews from?
One of two major ancestral groups of Jewish individuals, comprised of those whose ancestors lived in Central and Eastern Europe (e.g., Germany, Poland, Russia). The other group is designated Sephardic Jews and includes those whose ancestors lived in North Africa, the Middle East, and Spain.
What did Minsk used to be called?
Early history By 980, the area was incorporated into the early medieval Principality of Polotsk, one of the earliest East Slavic principalities of Kievan Rus'. Minsk was first mentioned in the name form Měneskъ (Мѣнескъ) in the Primary Chronicle for the year 1067 in association with the Battle on the River Nemiga.
What country was Minsk in?
BelarusMinsk, city, capital of Belarus, and administrative centre of Minsk oblast (region). The city lies along the Svisloch River.
Was Minsk ever part of Poland?
It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland. From 1919 to 1991, after the Russian Revolution, Minsk was the capital of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic within the Soviet Union. Today our tour stops over the city of Minsk.
What's a Shadchan?
Definition of shadchan : a Jewish marriage broker or matchmaker.
What does Goyish mean?
A person who is not Jewish. [Yiddish, from Hebrew gôy, Jew ignorant of the Jewish religion, non-Jew; see gwy in Semitic roots.] goy′ish adj.
What does the term Hasidim mean?
[ (khah-see-dim, hah-see-dim) ] Jews (see also Jews) who observe a form of strict Orthodox Judaism. They generally wear severely plain black and white clothes, and the men, following the requirements of Mosaic law, leave parts of their hair and whiskers untrimmed.
What is the Pale in Irish history?
History. The Pale was a strip of land, centred on Dublin, that stretched from Dundalk in Louth to Dalkey in Dublin; it became the base of English rule in Ireland. The Norman invasion of Ireland, beginning in 1169, brought much of Ireland briefly under the theoretical control of the Plantagenet Kings of England.
When was Dublin called the Pale?
“The Pale” in Ireland (so named after the late 14th century) was established at the time of Henry II's expedition (1171–72) and consisted of the territories conquered by England, where English settlements and rule were most…
What is pale in Old English?
Noun. pale (plural pales) A wooden stake; a picket. quotations ▼ (archaic) Fence made from wooden stake; palisade.
What countries were in the Pale?
Originally formed in 1791 by Russia's Catherine II, the Pale of Settlement was a region designated for Jews. For political, economic, and religious reasons, very few Jews were allowed to live elsewhere. The area mostly falls within today's Poland, Russia, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, and Moldova.