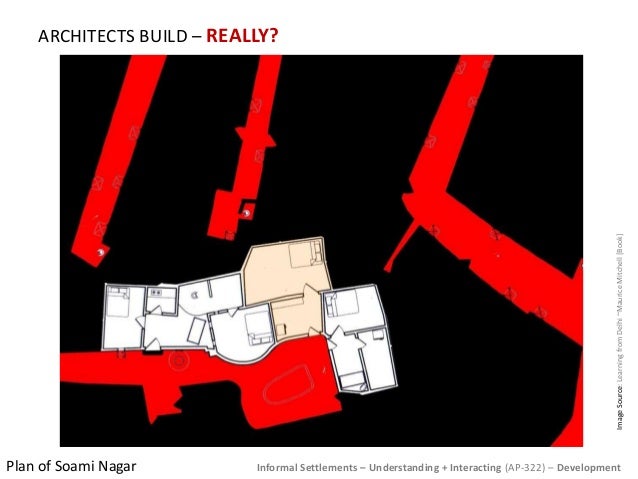
Five Ways “Re-blocking” Helps Improve Informal Settlements (And One Way It Doesn’t)
- 1. By improving access to water, electricity and basic services The failure of local governments to deliver services is a major source of frustration for the country’s poorest citizens. ...
- 2. By preventing shack fires ...
- 3. By creating a passage for emergency vehicles ...
- 4. By preventing flooding ...
- 5. By increasing community engagement
Can upgrading improve quality of life in informal settlements?
When done properly, upgrading can be transformative for residents and their communities. Rather than disrupting vital networks by uprooting and relocating residents, upgrading programmes are the best way to improve quality of life within informal settlements.
How can re-blocking help improve informal settlements?
Five Ways “Re-blocking” Helps Improve Informal Settlements (And One Way It Doesn’t) 1 By improving access to water, electricity and basic services 2 By preventing shack fires 3 By creating a passage for emergency vehicles 4 By preventing flooding 5 By increasing community engagement
What is the difference between formal and informal settlements?
As opposed to the formal settlements, the informal settlements commonly known as slums are characterized by inadequate housing, insufficient living spaces, insecure land tenure, and lack of access to basic services including social services such as clean water and sanitation (33).
What do city governments do about informal settlements?
City government attitudes to informal settlements range from opposition and eviction to reluctant tolerance and support for legalisation and upgrading.

How can informal settlements be prevented?
Five Ways “Re-blocking” Helps Improve Informal Settlements (And One Way It Doesn't)By improving access to water, electricity and basic services. ... By preventing shack fires. ... By creating a passage for emergency vehicles. ... By preventing flooding. ... By increasing community engagement.
How could squatter settlements be improved?
Over time, squatter settlements can be improved by the residents and become more stable permanent dwellings, with brick and concrete used to reinforce the structures. Squatter settlements are found in various locations, but are usually built on the edges of cities in the world's poorest countries or LEDC.
What are the 3 biggest problems of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management.
What is informal settlements upgrading?
Upgrading - or informal settlement improvement means a package of basic services: clean water supply and adequate sewage disposal to improve the well-being of the community. But fundamental is legalizing and 'regularizing' the properties in situations of insecure or unclear tenure.
How do you solve slums?
Solutions common to these programs include:Prioritizing on-site, incremental upgrades. ... Ensuring vulnerable groups have a voice. ... Partnering with NGOs and academic institutions. ... Improving transport networks. ... Avoiding displacement of residents and improving access to services.
Why do informal settlements develop?
According to UN-Habitat (2015:2), informal settlements are caused by a range of interrelated factors, including population growth and rural-urban migration, lack of affordable housing for the urban poor, weak governance (particularly in the areas of policy, planning, land and urban management resulting in land ...
What is the biggest informal settlement in South Africa?
SowetoThose living in informal dwellings – defined as a wood and iron structure – have decreased slightly from 16.2% in 1996 to 13.0% in 2016....These are the 20 biggest townships in the country (Stats SA, 2011)#1TownshipSoweto2011 Population1 271 628Neighbouring townJohannesburg19 more columns•Aug 14, 2016
What is another word for informal settlement?
Shanty town Sometimes called a squatter, informal or spontaneous settlement, shanty towns often lack proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity, hygienic streets, or other basic human necessities.
What are the advantages of informal settlement?
It offers choice, it gives people what they want, it enables individual creativity and it is affordable. It is also simple to build and easy to use. So, a powerful brand — the informal settlement — is in town. And it's reshaping the city.
What physical factors are to be considered in upgrading settlement?
This paper discloses that the basic concept for physical upgrading in a slum settlement consists of three elements: (1) arranging street networks as fundamental systems that structure the settlement, (2) constructing public utility systems that are essential for livelihoods, and (3) providing common space and amenities ...
What is in situ upgrading of informal settlements?
The Department of Housing released a new Informal Settlement Upgrading Programme in 2004 that makes in situ upgrading of informal settlements possible with minimal disruption to residents' lives. To date, the new programme is not necessarily the municipalities' choice when intervening in an informal settlement.
How many informal settlements are there in South Africa?
There are more than 2 700 informal settlements nationwide and the number of households in informal settlements has increased since 1995, rising from 1 170 902 to 1 294 904 by 2011.
What are some solutions to squatter settlements?
Squatter settlements can be improved through urban planning. In 2004, a plan to improve Dharavi was put forward. Vision Mumbai aimed to replace squatter settlement housing with high-quality high-rise tower blocks of flats. In total, only 350 residents moved to new houses.
What are the accepted approaches to improve the quality of life of squatters living in slum?
According to Cockburn (2014), there are four approaches to urban planning of squatter settlements and slums. These are progressive development, security tenure and property rights, urban improvement or urban upgrading, and participation and community development.
Why are squatter settlements growing?
The growing number of slum dwellers is the result of both urbanization and population growth that are outpacing the construction of new affordable homes. Adequate housing is a human right, and the absence of it negatively affects urban equity and inclusion, health and safety, and livelihood opportunities.
How is Dharavi being improved?
The Vision Mumbai project is improving living conditions in Dharavi by replacing squatter settlements with higher quality flats. With this project, there would be more schools, more shops, better health care centers, better roads and more jobs.
What is informal settlement?
Informal settlements are residential areas where ( UN-Habitat, 2015b; Brown, 2015 ): inhabitants often have no security of tenure for the land or dwellings they inhabit ‒ for example, they may squat or rent informally; neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure; housing may not comply with planning and building regulations, ...
How does informal settlement affect women?
For women, for example, this can heighten barriers they face in accessing livelihood opportunities. Home-based workers also face challenges to entrepreneurial activity ( Chant, 2014 ). Women in informal settlements spend more time and energy accessing basic services than other urban counterparts, limiting their ability and time to earn through paid employment ( UNFPA, 2007 ). In addition, the prevalence of male-biased land tenure policies and restrictions on women’s rights to own property decreases the likelihood of alternative housing options. Poor quality housing, or eviction and homelessness, can also increase the risk of insecurity and sexual violence ( Chant, 2013; McIlwaine, 2013 ).
What are the factors that contribute to the emergence of informal settlements?
A number of interrelated factors have driven the emergence of informal settlements: population growth; rural-urban migration; lack of affordable housing; weak governance (particularly in policy, planning and urban management); economic vulnerability and low-paid work; marginalisation; and displacement caused by conflict, natural disasters and climate change ( UN-Habitat, 2015b ).
What is the role of housing in urban development?
Housing. The provision of affordable, adequate housing, including in situ upgrading and avoidance of forced evictions, security of tenure and livelihood and employment generation, all play a role in urban prosperity. Long-term financial investment and inclusive financing options.
What are neighbourhoods lacking?
neighbourhoods usually lack basic services and city infrastructure; housing may not comply with planning and building regulations, and is often situated in geographically and environmentally sensitive areas (see Topic Guide on Provision and Improvement of Housing for the Poor, Patel, 2013). A number of interrelated factors have driven ...
What is the role of government in integration?
Governments must develop and coordinate broader integrated frameworks that are underpinned by urban planning, legislation and finance arrangements; are supported by interconnected institutional arrangements; and ensure the inclusion of marginalised groups and key stakeholders. Participation must be at the heart of this approach, ensuring an understanding of economic and social community dynamics.
How can cities increase population density?
Cities use multiple approaches to increase population density while also improving the quality of housing and providing basic services through land readjustment. One approach to readjustment is land pooling, where rights holders pool their land into a single partnership administered by a government agency, which then, after redevelopment, issues secure ownership rights. Cities can also use land sharing by encouraging the owner of land occupied by an informal settlement to transfer part of the land to the informal occupants at a reduced price.
How many people live in slums in the world?
With urbanization has come growth of the urban poor and informal settlements, also referred to as slums. A whopping 32% of the world's urban population lives in slums. Even with modest successes in poverty reduction and upgrading informal settlements, the world's slum population could still reach 889 million by 2030.
How can reblocking prevent shack fires?
Re-blocking can prevent shack fires as newly constructed shacks are built with fire resistant materials , and allow fire services to better access structures that have caught fire. 3. By creating a passage for emergency vehicles. When shacks are realigned, better roads can be developed.
Why are reblocked shacks built?
Re-blocked shacks are often built on a platform that prevents water from pooling underneath homes and seeping into their interiors . Because there is less dampness, community members have a greater chance of staying healthy. 5. By increasing community engagement.
What is reblocking in shacks?
Developed by Shack Dwellers International (SDI), a network of community-based organizations of the urban poor, re-blocking is a process where shacks are reconstructed and rearranged to “maximise open space”. It allows shacks, which often spring up organically and in unsystematic ways, to be realigned in clusters so that clear spaces can be used ...
Does shack reblocking help?
Shack re-blocking can help uplift communities but only if the government engages with communities and involves them in the process.
How many people live in informal housing in Pakistan?
This is the reality of daily life for many of the 30 million Pakistanis estimated to be living in informal housing in urban Pakistan. In Karachi alone, around 10 million people live in informal housing, spread out over more than 2000 settlements set up wherever possible; from government amenity plots, to land designated for agriculture, ...
What is the requirement for a coloniser to pay a 15–25% rate?
Even the colonisers had some standards though; Article 9 of the Act requires the government to give advance notice to residents about their lands being taken over for a ‘public purpose’, while Article 23 (2) requires residents to be paid 15–25% above a court-determined market rate.
How does slum life affect people?
Effects on the people living in slums: The reduced life expectancy of slum inhabitants. Health problems due to drinking contaminated water. Environment pollution. The low standard of living. Degraded health conditions. Those living in slums get victimized easily by alcohol and drugs.
What are the causes of slums?
Causes of the formation of slums: Increasing rural to urban migration. Urban areas are not being improved enough to accommodate the new inhabitants. Poor planning of cities. Poverty and lack of job opportunities in rural areas are the push factors of migration. The high cost of living in urban areas. Natural disasters.
What are the conditions in slums?
Congested. No access to drinking water and electricity. Most of the inhabitants of the slums can’t be beneficiaries to Govt schemes. Only a few slums are recognized by Govt. Conditions in unrecognized slums are even worse. No drainage system. In most slums, wastewater flow in between houses.
Why should we focus on distribution development?
Besides improving the living conditions in slums, the causes of slums creation should be addressed. Distributive development will serve the purpose and thereby everyone can have a dignified and healthy life.
Who provides medical care in slums?
The little medical facilities available in slums is provided by NGOs.
Does slum upgrading improve living conditions?
Slum upgrading. It improved slum’s living conditions. But it does not address poverty and low wages of the informal economy.
