How did Native Americans resist the expansion of the United States?
American Indian Resistance to White Expansion. North American Indians had been accustomed to dealing with Europeans long before the United States came into existence. For two centuries Indians traded, intermarried, allied with, and fought against the various groups of newcomers.
What were the consequences of the Indian Wars of Independence?
The consequences of the wars were that the Natives were pushed West and they were forced to conform to the White's way of life. How did Native Americans resistance to White Settlement end? The Native American resistance to White Settlement ended with the Wounded Knee Battle. What was life like on the Indian reservations?
What was the end of Indian resistance in the west?
Resistance of the Indians in the West. Two weeks later on December 29, 1890, the Seventh Cavalry killed more than 300 Sioux men, women, and children at Wounded Knee Creek in the Dakota Territory. That confrontation marked the end of Indian resistance.
What happened to the Native Americans after the Revolutionary War?
When invading armies left, native people often returned, and in 1783 Indians still controlled most of the interior. The Treaty of Paris, signed that year, ended the Revolutionary War and granted the United States all territory east of the Mississippi, but from an Indian perspective this was a fraud.

How did Native Americans resist white settlers?
During the colonial period, Native Americans had a complicated relationship with European settlers. They resisted the efforts of the Europeans to gain more of their land and control through both warfare and diplomacy.
When did Native American armed resistance end?
December 29, 1890For the most part, armed American Indian resistance to the U.S. government ended at the Wounded Knee Massacre December 29, 1890, and in the subsequent Drexel Mission Fight the next day.
What ended Native American resistance in New England?
Thousands of Indians were killed, wounded or captured and sold into slavery or indentured servitude. The war decimated the Narragansett, Wampanoag and many smaller tribes and mostly ended Indian resistance in southern New England, paving the way for additional English settlements.
How did the Native Americans respond to the loss of land from white settlement of the Great Plains?
How did Native Americans respond to the land lost due to the white settlements on the Great Plains? They killed soldiers, attacked and destroyed wagon trails.
What conflicts ended major Indian resistance?
What rebellions ended major Indian resistance? Red River War, Battle of the Little Big Horn. Indians would become farmer and this into national life by adopting the culture and civilization of whites. Congress passed this, it replaced the reservation system with an allotment system.
When did the last Native American tribe surrender?
September 4, 1886This Date in Native History: On September 4, 1886, the great Apache warrior Geronimo surrendered in Skeleton Canyon, Arizona, after fighting for his homeland for almost 30 years. He was the last American Indian warrior to formally surrender to the United States.
Who are the two main examples of Native American resistors?
Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa, Shawnee brothers, were leading Indian traditionalists, and together they crafted a novel resurgence among native peoples in the west. Tecumseh, a political and military leader, is the better known of the two, but it was their combined skills that made them especially powerful.
What are two ways that Native Americans resisted being relocated?
Answer and Explanation: Native Americans took two approaches to resist the Indian Removal Act of 1830: direct war with the U.S. Army and an effort to work through the U.S. court system.
Why did American settlers feel it was necessary to remove Native Americans?
Most white Americans thought that the United States would never extend beyond the Mississippi. Removal would save Indian people from the depredations of whites, and would resettle them in an area where they could govern themselves in peace.
What caused the loss of Native American land?
During this decade, the U.S. military forcibly removed Natives from their homes and marched over 100,000 people to Indian Territory—up to 25 percent died along the way. For example, the Trail of Tears attributed to the deaths of over 5,000 Cherokee. Disease and famine killed them along the 1,200-mile trek.
What ended Native American resistance on the plains?
Finally, after the army seized female Apaches and deported them to Florida and deprived the warring tribesmen of a food supply, Geronimo was captured. His 1886 defeat marked the end of open resistance by Native Americans in the West.
What is the Dawes Act of 1877?
The Dawes Act of 1877 was a direct sequel to the Indian Appropriations Act of 1851. The Dawes Act furthered the Ameican government's interests in securing land previously owned by Indians and their assimilation to Euro-American culture.
What was the outcome of the Dawes Act of 1887?
As a result of the Dawes Act, tribal lands were parceled out into individual plots. Only those Native Americans who accepted the individual plots of land were allowed to become US citizens. The remainder of the land was then sold off to white settlers.
When was the Indian Removal Act?
May 28, 1830On May 28, 1830, Congress passed the Indian Removal Act, beginning the forced relocation of thousands of Native Americans in what became known as the Trail of Tears.
Where did the first white settlers live?
In the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, the first white settlers in America inhabited the eastern seaboard. There the whites either made treaties with the Native American groups to buy land or they forcibly took Indian land.
What was the end of the American century?
The End of the American Century. 21d. Native American Resistance in the Trans-Appalachian West. Tenskwatawa, also known as Prophet (pictured here), worked with his brother Tecumseh to create a broad-based tribal coalition which would resist American encroachment from the east.
Why did Tecumseh travel to Tukabatchi?
Tecumseh traveled to Tukabatchi, the capital of the Creek people, to try to recruit Natives to join the Indian Confederacy, but he was met with resistance. Legend has it that he said he would return home to Ohio and stamp his foot with such force, they would feel the earth move in Tukabatchi. Several days after he left, a small earthquake did hit the Creek Capital.
What was the Western War?
In fact, the " western war " in many ways represented a continuation of the American Revolution with many autonomous Indian nations again choosing to ally with the British against Americans who fundamentally threatened their survival.
Who were the Shawnee brothers?
Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa, Shawnee brothers, were leading Indian traditionalists, and together they crafted a novel resurgence among native peoples in the west. Tecumseh, a political and military leader, is the better known of the two, but it was their combined skills that made them especially powerful. Tecumseh had fought at Fallen Timbers in 1794, but refused to participate in the peace negotiations that produced the Treaty of Grenville the following year. Instead, he removed to east-central Indiana where he led a band of militant young warriors.
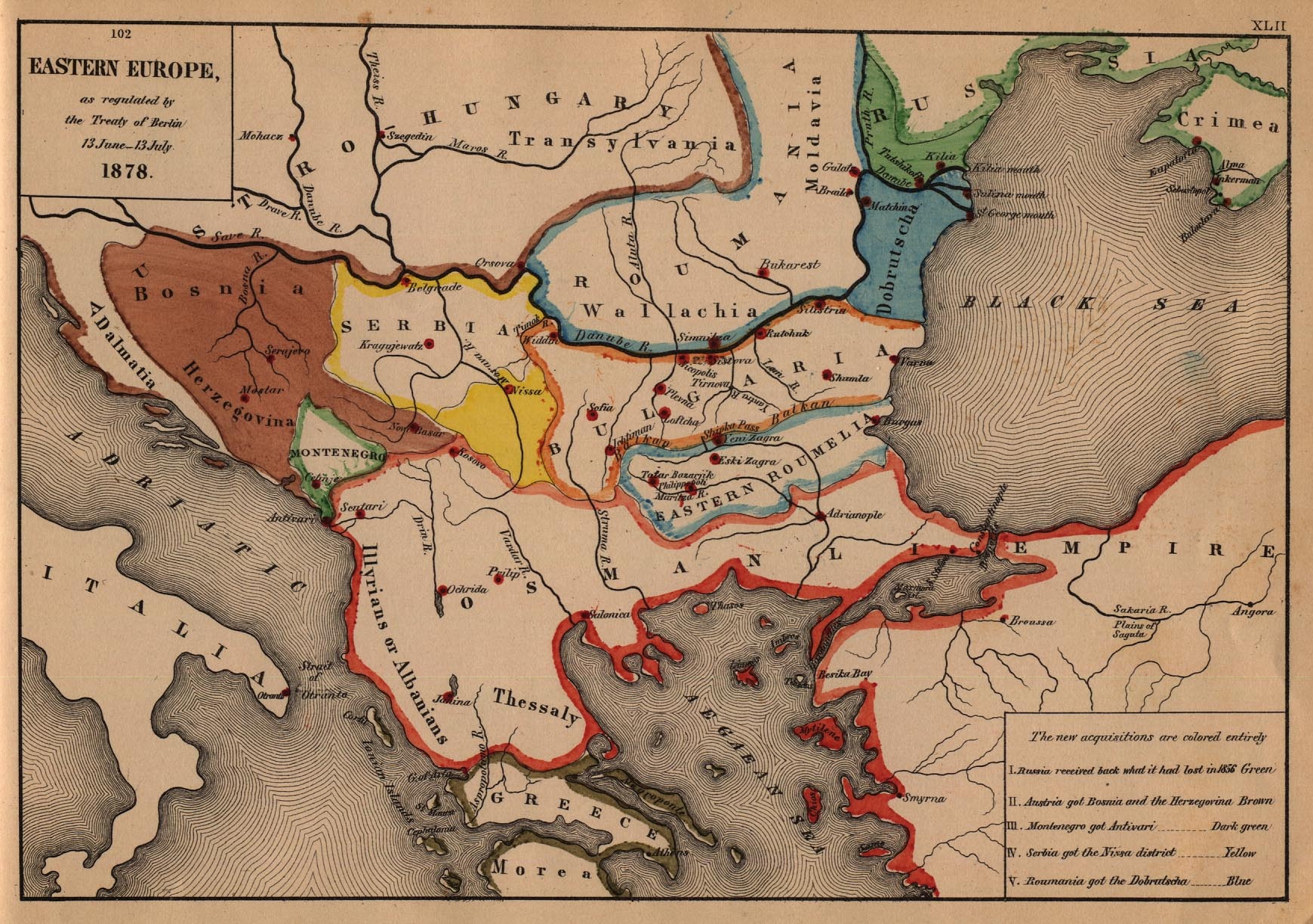
Which Native American tribes were forced to relocate to Oklahoma Territory?
This 1895 map shows many of the Native American tribes which suffered forced relocation to Oklahoma Territory. Among the tribes were the Cherokee, Miami, and Quapaw.
What happened to the Apaches in 1886?
His 1886 defeat marked the end of open resistance by Native Americans in the West.
What happened to the Nez Percé Indians?
Chief Joseph and the Nez Percé. The year after Custer's infamous defeat, the Nez Percé Indians of Idaho fell victim to western expansion. When gold was discovered on their lands in 1877, demands were made for over 90 percent of their land.
What tribe led the war in the Southwest?
Warfare also raged across the American Southwest. The Apache tribe led one of the longest and fiercest campaigns of all. Under the leadership of Geronimo, Apache attackers assaulted settlers in Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico. The army responded slowly but surely. Geronimo was relentlessly hunted, even across the Mexican border.
Why did the West shoot buffalo?
Buffalo robes became fashionable in the East, so profit-seekers slaughtered thousands of bison simply for their hides. Others shot them for sport, leaving their remains for the local vultures.
How many buffalo were there in the Great Plains?
The army was even known to use Gatling guns on the herds to reduce their numbers. The plan was effective. At the end of the Civil War, an estimated 15 million buffalo roamed the Great Plains. By 1900, there were only several hundred, as the species was nearly extinct. The Sioux lost their chief means of subsistence and mourned the loss of the animal, which was revered as sacred according to tribal religion.
Who was the Kiowa chief who was convicted of leading the Warren Wagon Train Massacre in Texas in 18?
A biography of the Kiowa chief Satanta who was convicted of leading the Warren Wagon Train Massacre in Texas in 1871. From the Handbook of Texas Online.
What happened to Indian removal?
As Indian Removal became the law of the land, tribal groups had few choices of how to navigate this. They could comply and either be sent off to reservations out of the way of white expansionism or try to assimilate into white society as best they could, or could defy the ruling and continue to fight for territory. The reactions among tribal people covered all ends of this spectrum.
Why did the Indians hide in plain view?
In Michigan and Indiana, “hiding in plain view” became an effective means of avoiding removal during a period of American settlement leading to state formation. In many cases, Potawatomi and Miami Indians selected from within their communities mixed-race spokespersons with European names who not only mirrored so-called “civilized” behaviors, but also looked white. By representing themselves as whites, these tribes contributed to a sense that Indians had disappeared from the landscape. In fact, often the only Native people who remained visible to whites were those impoverished individuals who had been reduced to begging.
Who led the Winnebago revolt?
In 1827, when false rumors began to spread that the Americans had handed over two Ho-Chunk prisoners to be executed by the Ojibwe, a Ho-Chunk leader named Red Bird led an uprising (known as the Winnebago Revolt) against the Americans.
Where did Black Hawk and his band move to?
Black Hawk and his band contended that they had never signed away their lands in Illinois, and in the spring of 1832, they moved from Iowa east across the Mississippi River to plant corn. The Americans assumed that Black Hawk’s band was hostile and quickly mobilized the Illinois militia, US troops, and Indian allies.
When did the resistance end?
Resistance there came to an end only with the capture of the Chiricahua Apache chief Geronimo in 1886. On the Great Plains, the loss of the bison was an even greater threat to Indian survival than the wars with the U.S. Army.
What was the policy of the United States toward Native Americans?
As new territories and states were organized in the West, it became clear that Native Americans could not roam at will over tens of thousands of square miles that non‐natives were hoping to settle.
What did the Plains Indians rely on?
The Plains Indians relied upon bison for food, clothing, and shelter, and as a source of fuel (burning bison dung, or “buffalo chips”). Although the wanton destruction of the bison was not federal policy, army commanders in the field approved the practice as a means to destroy a key element of Indian life.
What was the Indian reservation system in the 1860s?
Change in federal policy and the end of resistance. The Indian reservation system established during the 1860s was a failure. Many of the reservations were located on marginal agricultural land that made it difficult for the tribes to develop self‐sustaining farming.
What happened to the Sioux in 1890?
Two weeks later on December 29, 1890, the Seventh Cavalry killed more than 300 Sioux men, women, and children at Wounded Knee Creek in the Dakota Territory. That confrontation marked the end of Indian resistance. Throughout the twentieth century, Native Americans have comprised the poorest minority group in the United States.
What was the significance of the Dawes Act?
Although it was hailed as an important humanitarian reform, the Dawes Act actually undercut the communal basis of Native‐American life and resulted in the loss of millions of acres of Indian land.
How many bison were killed by the railroads?
When the railroads were completed, “sportsmen” shot bison from specially chartered cars. By 1875, more than nine million bison had been killed for their hides, which were in demand in the East for lap robes and machine drive belts.
What was the name of the battle that ended the Native American resistance to the White Settlement?
The Native American resistance to White Settlement ended with the Wounded Knee Battle.
Why did the Natives and Whites have conflict?
The Natives believed that you should share the land while the Whites believed you own land, this caused conflict because the whites bought the land the Natives lived on and pushed the to the West.
How many Indians were gathered near the Little Bighorn River?
2,000 Indians were gathered near the Little Bighorn River; They were surrounded and slaughtered here
What invention allowed ranchers to enclose grazing lands?
Invented Barbed wire which allowed ranchers to enclose grazing lands
Why did the cattle boom end?
The cattle boom came to an end because we fell into a depression which declined the demand; farmers would herd the cattle together with barbed wire to keep the cattle from eating the grass so the free plains shrunk, then they had to buy cow feed, which was very expensive, because the cattle could not live off of the land; there was also a drought at the time which kept grass from growing so farmers has to buy more feed. Being in such close proximity, diseases spread quickly there was a harsh winter in which most cattle died.
Why did the Chinese come to California?
Most of the Chinese were farm laborers because they were not allowed to own land.
What were the consequences of the Indian Wars?
The consequences of the wars were that the Natives were pushed West and they were forced to conform to the White's way of life.

A War For Indian Independence
- Many Indians fought in the Revolution, most of them on the side of the British. In joining they acted less out of loyalty to the king than from an awareness that American settlers threatened their land and freedom. Some Cherokees, for example, saw the Revolution as an opportunity to punish squatters and regain territory lost to Virginia and the Carolinas over the previous decade. …
Indian Unity Against The New Republic
- Soon after the Revolution ended, the United States began pressuring tribes for land cessions. Believing they were dealing with conquered peoples, American treaty commissioners tried to dictate new territorial borders. They worked to gain possession of Indian country piece by piece, signing agreements with single tribes and, if that failed, with particular factions or individuals. A…
Prophecy and Resistance
- While white farmers sought to take Indians' land, other Americans pursued their minds and souls. Missionaries, teachers, and government agents worked to "civilize" native peoples, urging them to change their economies and abandon their religions and languages. The men and women involved in this effort assumed that when confronted by a "superior" so...
Different Strategies
- In the Southseveral tribes adopted a different path. As Tecumseh worked to form a confederacy, Cherokees began building a centralized political system for their tribe. This was partly a response to American land hunger. Tribal leaders hoped that a strong national government would prevent individuals and faction leaders from negotiating their own treaties. It also reflected the Cherokee…
Bibliography
- Calloway, Colin G. The American Revolution in Indian Country: Crisis and Diversity in Native American Communities. Cambridge, U.K., and New York: Cambridge UniversityPress, 1995. Champagne, Duane. Social Order and Political Change: Constitutional Governments among the Cherokee, the Choctaw, the Chickasaw, and the Creek. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford UniversityPress…
Decimation of The Buffalo
Chief Joseph and The Nez Percé
- The year after Custer's infamous defeat, the Nez Percé Indians of Idaho fell victim to western expansion. When gold was discovered on their lands in 1877, demands were made for over 90 percent of their land. After a stand-off between tribal warriors and the United States Army, their leader Chief Josephdirected his followers toward Canada to avoid capture. He hoped to join forc…
Geronimo and The Apache Struggle
- Warfare also raged across the American Southwest. The Apache tribe led one of the longest and fiercest campaigns of all. Under the leadership of Geronimo, Apache attackers assaulted settlers in Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico. The army responded slowly but surely. Geronimo was relentlessly hunted, even across the Mexican border. Finally, after the a...
Sooners Grab Oklahoma
- The last land to be claimed by homesteaders was in Oklahoma. Previously dubbed "Indian Territory" by the federal government, Oklahoma had been used as a state-sized reservation of many tribes ranging from the Nez Percé in Idaho to the Cherokee of Georgia. In 1889, the United States Government decided to open two million acres of land unassigned to any particular tribe …