
What is considered a settlement in Israel?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War —the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are 126 Israeli settlements in the West Bank (excluding East Jerusalem), according to the September 2016 report from the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Geographically, these settlements are all across the West Bank.
What do left-wing Israelis think of the Israeli settlement project?
The majority of Israeli Zionist leftists who oppose the settlement project, however, believe in the Jewish state along 1948 borders and reject Israel's expansion into the occupied territories.
Why did Israel build settlements in the Old Testament?
Israeli settlements were erected for a variety of reasons. In some cases, Israelis sought to recover property lost in the 1948 war and the hostilities leading up to it, such as the core settlements of Gush Etzion between Jerusalem and Hebron.

When did Israel start settlements?
After the capture of the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt in the 1967 Six-Day War, settlements were established along the Gulf of Aqaba and in northeast Sinai, just below the Gaza Strip.
How many settlements has Israel built?
From 1967 through 2017, over 200 Israeli settlements were established in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem); their current population is almost 620,000.
Why is Israel allowed to have settlements?
Israel has justified its civilian settlements by stating that a temporary use of land and buildings for various purposes appears permissible under a plea of military necessity and that the settlements fulfilled security needs.
When was the Israel settlement in Palestine?
June 1967Since the occupation first began in June 1967, Israel's ruthless policies of land confiscation, illegal settlement and dispossession, coupled with rampant discrimination, have inflicted immense suffering on Palestinians, depriving them of their basic rights.
How much land has Palestine lost to Israel?
During and immediately following the state's creation in 1948, Israel expropriated approximately 4,244,776 acres of Palestinian land. In the process, more than 400 Palestinian cities and towns were systematically destroyed by Israeli forces or repopulated with Jews.
Are there still Israeli settlements on the West Bank?
Today, there are upwards of 450,000 Israeli settlers in the West Bank, excluding East Jerusalem.
Is Israel occupying Palestine land?
BACKGROUND: Palestinian territory – encompassing the Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East Jerusalem – has been illegally occupied by Israel since 1967.
How many times has Israel broken international law?
SECURITY COUNCIL RESOLUTIONS: Laws Violated: Israel has violated 28 resolutions of the United Nations Security Council (which are legally binding on member-nations U.N.
Does Israel have a right to the West Bank?
Israel claims historical and religious rights to the West Bank as the ancestral land of the Jewish people. It also says its presence there - especially in the Jordan Valley - is strategically vital for its self-defence.
What was Israel before 1948?
In 1517, the Ottoman Empire conquered the region, ruling it until the British conquered it in 1917. The region was ruled under the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948, when the Jewish State of Israel was proclaimed in part of the ancient land of Israel.
What was Palestine before 1948?
In modern times, the area was ruled by the Ottoman Empire, then the United Kingdom and since 1948 it has been divided into Israel, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip.
Why did Israel occupy Palestine?
Israel says the occupation is necessary for security given its tiny size: to protect Israelis from Palestinian attacks and to provide a buffer from foreign invasions.
Are there Israeli settlements in Gaza?
According to the report of the Security Council Commission established under resolution 446 (1979): "Between 1967 and May 1979, Israel has established altogether 133 settlements in the occupied territories, consisting of 79 in the West Bank, 29 in the Golan Heights, 7 in the Gaza Strip and 18 in the Sinai.
Why does Israel have settlements in the West Bank?
Israel has cited several reasons for retaining the West Bank within its ambit: a claim based on the notion of historic rights to this as a homeland as affirmed in the Balfour Declaration of 1917; security grounds, both internal and external; and the deep symbolic value for Jews of the area occupied.
Who were the first settlers in Israel?
3,000 to 2,500 B.C. — The city on the hills separating the fertile Mediterranean coastline of present-day Israel from the arid deserts of Arabia was first settled by pagan tribes in what was later known as the land of Canaan. The Bible says the last Canaanites to rule the city were the Jebusites.
How many intifadas were there?
The intifadas were two Palestinian uprisings against Israel, the first in the late 1980s and the second in the early 2000s.
How many Israeli colonies are there in the occupied Palestinian territories?
There are three main types of Israeli colonies in the occupied Palestinian territories, all of which involve seizing Palestinian land and are all illegal under international law.
Why do settlements matter in the West Bank?
Why the locations of settlements matter. Settlements are scattered across the West Bank in a way that makes a contiguous Palestinian state impossible, while in Jerusalem the Israeli government has built settlements around the city to consolidate control over it.
What happened in 1948?
As European Jews began to colonise Palestine - many pushed by anti-Semitic persecution in Europe - the balance of land control between Palestinians and immigrant Jews shifted significantly.
How do they impact Palestinians?
Besides being built illegally on private and public Palestinian land, settlements impact the day-to-day life of Palestinians in many ways.
How many Israelis live in Israel?
Today, between 600,000 and 750,000 Israelis live in these sizeable settlements, equivalent to roughly 11 percent of the total Jewish Israeli population. They live beyond the internationally recognised borders of their state, on Palestinian land that Israel occupied in 1967, comprising East Jerusalem and the West Bank.
Why does Israel have a policy of demolition?
While building homes for settlers, Israel employs a policy of home demolitions to restrict the expansion of Palestinian communities on the pretext that homes were built without necessary permits, while refusing to issue them.
What was the Jewish settlement in the 1880s?
In the 1880s, the community of Palestinian Jews, known as the Yishuv , amounted to three percent of the total population. They were apolitical and did not aspire to build a modern Jewish state.
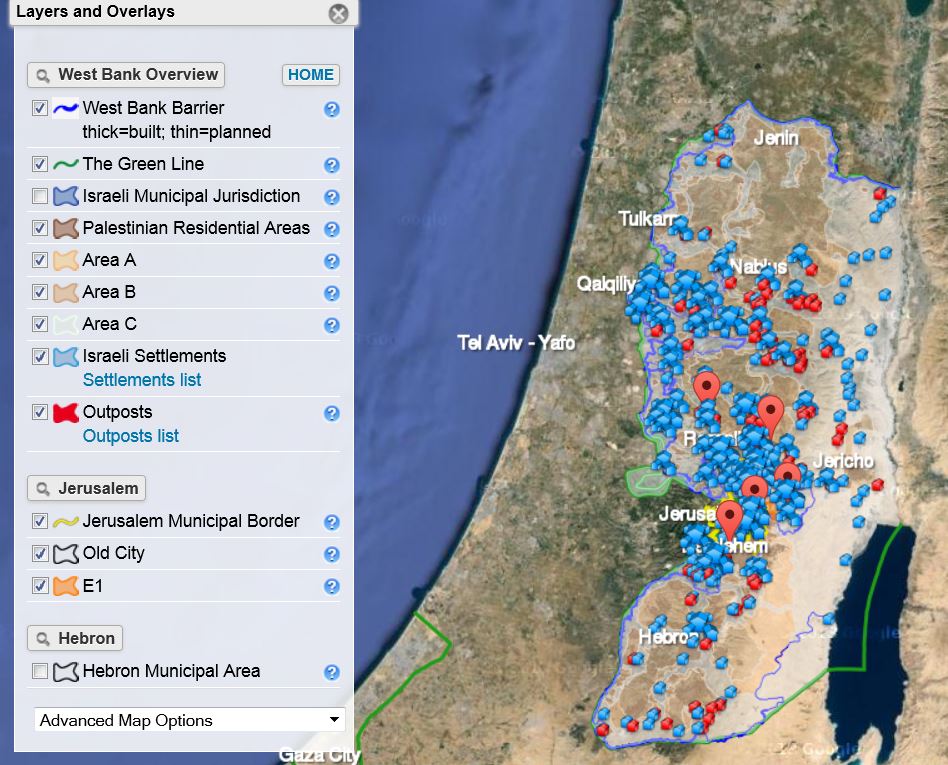
Where are the Israeli settlements?
This is a list of Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights. Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement ...
When did Israel start building settlements in the Golan Heights?
Golan Heights. Construction of Israeli settlements began in the portion of the Golan Heights held by Israel in 1967, which was under military administration until Israel passed the Golan Heights Law extending Israeli law and administration throughout the territory in 1981.
What happened to East Jerusalem?
Following the capture and occupation of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem in 1967, the Israeli government effectively annexed the formerly Jordanian occupied territory and extended the Jerusalem municipality borders by adding 70,500 dunams of land with the aim of establishing Jewish settlements and cementing the status of a united city under Israeli control. The Jerusalem Master Plan 1968 called for increasing the Israeli population of Arab East Jerusalem, encircling the city with Israeli settlements and excluding large Palestinian neighborhoods from the expanded municipality. Jerusalem was effectively annexed by Israel in 1980, an act that was internationally condemned and ruled "null and void" by the United Nations Security Council in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478. The international community continues to regard East Jerusalem as occupied territory and Israel's settlements there illegal under international law.
What resolution did the UN adopt in 2008?
In 2008, a plenary session of the United Nations General Assembly voted by 161–1 in favour of a motion on the "occupied Syrian Golan" that reaffirmed support for UN Resolution 497. ( General Assembly adopts broad range of texts, 26 in all, on recommendation of its fourth Committee, including on decolonization, information, Palestine refugees, United Nations, 5 December 2008.)
Is the Israeli settlement illegal?
The international community considers Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories illegal under international law, violating the Fourth Geneva Convention 's prohibition on the transfer of a civilian population to or from occupied territory, though Israel disputes this.
Did Israel have settlements in the Sinai Peninsula?
Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement from Gaza in 2005 and the Sinai settlements were evacuated with the Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty and the return of the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. This list does not include West Bank ...
Does Israel have a right to the Golan?
Israel maintains it has a right to retain the Golan, citing the text of UN Resolution 242, which calls for "safe and recognised boundaries free from threats or acts of force". However, the international community rejects Israeli claims to title to the territory and regards it as sovereign Syrian territory.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are 126 Israeli settlements in the West Bank (excluding East Jerusalem), according to the September 2016 report from the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Geographically, these settlements are all across the West Bank. The West Bank is broken down into Areas A, B, and C, according to the Oslo Accords, ...
What is the legal status of settlements?
The settlements are illegal under international law. The Fourth Geneva Convention, which concerns civilian populations during a time of war, states in Article 49 that, “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
What are settlements?
Settlements are Israeli cities, towns and villages in the West Bank and the Golan Heights. (We will deal with East Jerusalem a bit later.) They tend to be gated communities with armed guards at the entrances. Why are they settlements and not simply Israeli residential areas? Because Israel is widely considered to be an occupying force in the territories. It is land that Palestinians, along with the international community, view as territory for a future Palestinian state.
Why are the West Bank and East Jerusalem considered occupied territory?
Israel began its occupation of the West Bank and East Jerusalem in 1967 during the Six-Day War. Seeing a military buildup in the surrounding Arab countries, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, after which Jordan, in turn, attacked Israel. Israel annexed East Jerusalem shortly thereafter, unifying the city under Israel’s authority. But Israel has never annexed the West Bank, part of which remains under military law.
Who are the settlers?
This is a very broad question, and requires a fair amount of generalization.
Why are the settlements controversial?
The settlements are built on land the Palestinians and the international community, along with some in the Israeli community, see as a future Palestinian state. Some of the settlements – especially the blocs – may be a part of Israel in a two-state solution through land swaps between Israelis and Palestinians. One concern, expressed by the European Union, and in the past by the US State Department, is that settlement expansion may make a contiguous, whole Palestinian state in the West Bank impossible.
What about East Jerusalem? And what is East Jerusalem anyway?
From 1948 to 1967, Jerusalem was divided by the Green Line, which is the cease-fire line of 1948 between Israel and Jordan. Although the city is now under Israeli governance, the distinction remains.
Who conquered Israel?
For the next several centuries, the land of modern-day Israel was conquered and ruled by various groups, including the Persians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, Fatimids, Seljuk Turks, Crusaders, Egyptians, Mamelukes, Islamists and others.
How many people are in Israel?
The nation of Israel—with a population of more than 9 million people, most of them Jewish—has many important archaeological and religious sites considered sacred by Jews, Muslims and Christians alike, and a complex history with periods of peace and conflict.
What is the area between Israel and Egypt?
Much of the conflict in recent years has centered around who is occupying the following areas: Gaza Strip : A piece of land located between Egypt and modern-day Israel. Golan Heights: A rocky plateau between Syria and modern-day Israel. West Bank: A territory that divides part of modern-day Israel and Jordan.
Why did Arabs oppose the Balfour Declaration?
Arabs vehemently opposed the Balfour Declaration, concerned that a Jewish homeland would mean the subjugation of Arab Palestinians. The British controlled Palestine until Israel, in the years following the end of World War II, became an independent state in 1947.
What was the Balfour Declaration?
The Balfour Declaration. From 1517 to 1917, Israel, along with much of the Middle East, was ruled by the Ottoman Empire. But World War I dramatically altered the geopolitical landscape in the Middle East.
What was the name of the country that took control of Palestine?
When World War I ended in 1918 with an Allied victory, the 400-year Ottoman Empire rule ended, and Great Britain took control over what became known as Palestine (modern-day Israel, Palestine and Jordan).
Where is Israel located?
Israel is small country in the Middle East, about the size of New Jersey, located on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea and bordered by Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria.
What was the economy of Israel in the 1970s?
In the 1970s and 1980s, the economy underwent a series of free market reforms and was gradually liberalized.
What is the land of Israel?
The Land of Israel, also known as the Holy Land or Palestine, is the birthplace of the Jewish people, the place where the final form of the Hebrew Bible is thought to have been compiled , and the birthplace of Judaism and Christianity. It contains sites sacred to Judaism, Samaritanism, Christianity, Islam, Druze and the Baháʼí Faith.
What is the name of the first instance of the name Israel?
The Merneptah Stele. While alternative translations exist, the majority of biblical archeologists translate a set of hieroglyphs as "Israel," representing the first instance of the name in the historical record.
How did the British respond to the revolt?
The British responded to the revolt with the Peel Commission (1936–37), a public inquiry that recommended that an exclusively Jewish territory be created in the Galilee and western coast (including the population transfer of 225,000 Arab s); the rest becoming an exclusively Arab area.
When did Solomon and David split?
Both David and Solomon are widely referenced in Jewish, Christian and Islamic texts. Standard Biblical chronology suggests that around 930 BCE, following the death of Solomon, the kingdom split into a southern Kingdom of Judah and a northern Kingdom of Israel.
When did humans first appear in Israel?
The oldest evidence of early humans in the territory of modern Israel, dating to 1.5 million years ago , was found in Ubeidiya near the Sea of Galilee.
Who was the prime minister of Israel during the Six Day War?
Following Meir's resignation, Yitzhak Rabin (Chief of Staff during the Six Day War) became prime minister. Modern Orthodox Jews ( Religious Zionist followers of the teachings of Rabbi Kook ), formed the Gush Emunim movement, and began an organized drive to settle the West Bank and Gaza Strip. In November 1975 the United Nations General Assembly, under the guidance of Austrian Secretary General Kurt Waldheim, adopted Resolution 3379, which asserted Zionism to be a form of racism. The General Assembly rescinded this resolution in December 1991 with Resolution 46/86. In March 1976 there was a massive strike by Israeli-Arabs in protest at a government plan to expropriate land in the Galilee.
When was Israel created?
When Israel was created in 1948 , the previous legal state was the Palestinian Mandate (Israel, West Bank, Gaza). The presumptive borders of Israel are those of the Mandate. The Palestinian Mandate explicitly permits Jewish settlement on the land.
Where were Jewish settlements in 1948?
Throughout the “West Bank”, there were numerous Jewish settlements prior to 1948, some dating back to long before the fall of the Ottoman Empire. The same is true for homes in neighborhoods in and around the eastern part of Jerusalem (the Silwan and Sheikh Jarrah neighborhoods, for example).
What is the earliest textual reference to Israel?
The stele represents the earliest textual reference to Israel and the only reference from ancient Egypt. [4] . It is one of four known inscriptions, from the Iron Age , that date to the time of and mention ancient Israel , under this name, the others being the Mesha Stele , the Tel Dan Stele , and the Kurkh Monolith .
What was the dichotomy between Israel and the Arab nations?
The dichotomy between Israel and the Arab nations was not nearly as strong in terms of military and economic power as it is today. Israel’s population was 3.5 million and the Arabs were 50+ million, military tech was almost parity. The liberal Zionists felt settling the land was their right.
What happens if ceasefire lines become legal borders?
If cease fire lines become legal borders, or there is a fear this will happen, then no ceasefire will every be reached without total victory. Jerusalem is a good example, Israel would not have agreed to a ceasefire so long as Jordan held Jerusalem and Jordan would not have agreed so long as Israel held it.
Does Israel want to give up settlements?
Israel does not want to give up the small settlements and the PA wants to evict even the larger areas town like the city of ma-aleh edomeed (37k people). The next major issue is private land ownership, if some one specific owns the land, it's a problem, and these settlements are often removed.
Who signed the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt?
1979 - President Jimmy Carter hosts signing of peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, concluded in talks at Camp David.
Who was the first leader to recognize Israel?
1948 - President Harry Truman becomes the first world leader to recognize the newly-born Israel.
How many American seamen died in the Yom Kippur war?
Thirty-four American seamen are killed and 174 wounded. 1973 - President Richard Nixon rushes to Israel’s aid with an airlift of military hardware after Egypt and Syria, which lost territory in the 1967 conflict, launch the Yom Kippur war.
Who was the president of Israel in 1993?
1993 - President Bill Clinton hosts, on the White House lawn, a handshake between Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat at the signing of a Declaration of Principles on interim Palestinian self-government.
What Are Settlements?
Why Are The West Bank and East Jerusalem Considered Occupied Territory?
Where Are The Settlements?
Who Are The Settlers?
What’s The Difference Between Settlements and Outposts?
Why Are The Settlements Controversial?
What Does President Donald Trump Think of The Settlements?
What Is The Legal Status of Settlements?
What About East Jerusalem? and What Is East Jerusalem Anyway?
- From 1948 to 1967, Jerusalem was divided by the Green Line, which is the cease-fire line of 1948 between Israel and Jordan. Although the city is now under Israeli governance, the distinction remains. Under international law, settlements in East Jerusalem are no different than settlements in the West Bank. So why consider them separately? Because Je...
What About The Golan Heights?
Early History of Israel
King David and King Solomon
The Balfour Declaration
- From 1517 to 1917, what is today Israel, along with much of the Middle East, was ruled by the Ottoman Empire. But World War I dramatically altered the geopolitical landscape in the Middle East. In 1917, at the height of the war, British Foreign Secretary Arthur James Balfour submitted a letter of intent supporting the establishment of a Jewish home...
Conflict Between Jews and Arabs
The Zionism Movement
Israeli Independence
1948 Arab-Israeli War
Arab-Israeli Conflict
Israel Today
The Two-State Solution