Independently of the small or large strain consolidation, if you have you have constrained boundary conditions like an oedometer, the void ratio SHALL be calculated if SATURATED as e=Gs x V / Wd - 1, where Gs is the density of solid particles, Vc is the corrected volume (therefore the Area of the apparatus x original height - displacement of the LVDT) and Wd is the dry weight of the specimen. if the soil is not saturated then you should use e=Gs x (1+w) / (W/V) - 1, where W is the total weight of the soil and w is the % of water content
What is the void ratio?
The void ratio may be defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of the solid soil mass. It is generally denoted by e. 2. Relation Between Void Ratio and Dry Unit weight 1. The void ratio is calculated for each state of the denseness of the sample. 2. Maximum void ratio takes place at minimum index density. 3.
What happens to the void ratio when soil is saturated?
The void with air of packed dry soil will change when the soil is saturated. If the soil is partially saturated, the saturating water enters the voids and occupy its position. Saturated water and partially left voids will increase its volume and it is called bulk age of soil. If the soil is fully saturated the air ... Can the void ratio be zero?
What is the formula to calculate the volume of soil?
Total Volume of Soil = (Volume of Voids + Volume of Solids)= (Vv +Vs) Hence it is more convenient to use VOID RATIO in which the denominator does not change with the change in the numerator, i.e. the volume of voids, While in the case of POROSITY, change in the numerator further infl
How to calculate bulk density with particle diameter and void ratio?
The formula for bulk density is (mass of dry soil) / (total volume of soil), 1 - (bulk density/particle density) for porosity, and (volume of pores) / (volume of solids) for void ratio. However, I can't find out how to calculate them only with particle diameter and particle density.

What is the void ratio?
Void ratio is the ratio of the open spaces to the volume of the solids.
What is claim settlement ratio?
Claim Settlement Ratio is a measurement used to assess the reliability of an insurance company in paying the claims. It is calculated using the simple formula shown below:
When was the critical void ratio first introduced?
The concept of critical void ratio was first introduced in 1938 by A. Casagrande to study liquefaction of granular soils. When a natural deposit of saturated sand that has a void ratio greater than the critical void ratio is subjected to a sudden shearing stress (due to an earthquake or to blasting, for example), the sand will undergo a decrease in volume. If (i.e., the total stress) remains constant and pore water pressure
What does "change in volume" mean?
Change in volume (increase or decrease) means change in void ration of soil. The nature of the change of the void ratio with strain for loose and dense sands is shown below.
Which has more VR: coarse or fine grained aggregate?
Coarse grained aggregate will have more VR than fine grained aggregate.
What is the void ratio?
The void ratio may be defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of the solid soil mass. It is generally denoted by e.
What happens to soil mass if the void ratio is more than the coefficient of permeability?
For a given soil mass, if the void ratio is more than the value of the coefficient of permeability is higher.
What is the degree of saturation of soil?
The degree of saturation may be defined as the ratio of the volume of water in the soil mass to the volume of voids in the soil mass. It is denoted by ‘ Sr ‘. The degree of saturation is normally expressed in a percentage.
Is a soil a straight line?
Whatever may be the exact relationship, all soils have e Vs log k drawn as a straight line.
Is void ratio parallel to porosity?
The void ratio is normally utilized in parallel with soil porosity.
Most recent answer
Thanks all for your cooperation and suggestion. I have got the answer and hopefully it will work.
Popular Answers (1)
I am a little disturbed by the kind of questions frequently posted. With all due respect Mr. Islam, these are questions for you to answer and perhaps then discuss with your tutor if something doesn't fit. Literature review is about exactly this, i.e. self teaching and digging into the literature and assessing what is suitable.
All Answers (8)
Asalaam aleikum: The answer to your question is as follows: By definition the average degree of consolidation of one-D considation at time t is defined by U (T v) = ∫ (1- u/u o )dz where Tv = C v t/d 2. where t = elapsed time; T v = time factor as defined; d = effective drainage length.
How to determine the settlement of a foundation?
The elastic settlement of a foundation is determined by assuming that the soil behaves as an elastic material. The basic approach employed is to use the traditional Boussinesq solution for stress changes in an isotropic, elastic medium subjected to a point load applied normal to the surface of a half-space (the ground is a half-space because it does not exist above the ground surface). The elastic settlement of the foundation is given by
What is the consolidation settlement?
For fine-grained soils, the consolidation settlement often is the major component of the total settlement. As noted previously, consolidation settlement is the time-dependent volume change that occurs as the excess pore water pressure, developed during load application, gradually dissipates and is transferred to the soil skeleton. The consolidation settlement is given by
What is the pore water pressure of a piezometer?
For the piezometer at GL − 17, the pore water pressure was reduced to − 60 kPa before subjected to embankment load, and became about − 48 kPa at the termination of the vacuum operation. After that, the pore water pressure returned to its hydrostatic condition.
What was the pressure of the airtight sheet during the consolidation settlement?
Vacuum pressure measured under the airtight sheet was maintained constantly at about 80 kPa along to the consolidation settlement between October 2008 and December 2009. The water discharge at the beginning of vacuum pumping was about 400 m 3 /day and gradually decreased during consolidation settlement to about 200 m 3 /day.
What is secondary settlement?
Secondary settlement continues after consolidation settlement is complete, as the soil structure gradually readjusts to the new level of effective stress. This process continues indefinitely. The prediction of secondary settlement is of considerable importance with clays of high plasticity and with micaceous and organic soils, but it typically is of minor concern with coarse-grained soils and overconsolidated, low plasticity, inorganic clays. Secondary settlement often is computed from the relation
What are the phases of settlement?
As stated above, when a load is applied to the foundation, three distinct phases of settlement occur: immediate or elastic (ρ e ), consolidation (ρ c ), and secondary settlement (ρ s ):
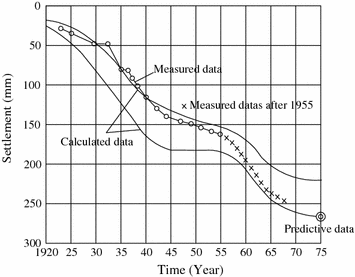
What is the estimated average degree of consolidation in 2024?
The estimated average degree of consolidation in 2024, according to non-Darcian flow, becomes 84%, corresponding to a settlement of 2.1 m.
