Cracks from soil settlement will often be much wider than a shrinkage crack. Cracks in a concrete slab-on-grade or other horizontal concrete slab caused by soil settlement will often have a vertical displacement across the crack, in other words, one side of the crack will be higher than the other side.
Can shrinkage cracks happen in concrete?
Shrinkage cracks can happen in concrete. For every ten feet of concrete that are poured, be it a wall or a slab, it will shrink 1/16th of an inch in about a year's time. But people see a crack in a concrete wall and immediately think it's a settlement crack. Different construction materials have different expansion and contraction coefficients.
How important are settlement cracks in concrete?
VERY IMPORTANT! Concrete Shrinks! Shrinkage cracks can happen in concrete. For every ten feet of concrete that are poured, be it a wall or a slab, it will shrink 1/16th of an inch in about a year's time. But people see a crack in a concrete wall and immediately think it's a settlement crack.
What is the path of concrete shrinkage?
As the path of cracking caused by concrete shrinkage wanders and stops and starts across an area of wall or floor, you will often see overlapping or roughly parallel nearby cracks that represent the end of one crack line and the beginning of another.
How do plastic settlement cracks affect structural integrity?
Plastic settlement cracks rarely pass through the full section, except in cases similar to trough and waffle slabs, mainly because they stop at the reinforcement that causes the restraint. Structural integrity is therefore not compromised, however the cracks need to be sealed especially on slabs, to reduce the risk of reinforcement corrosion.

How can you tell if shrinkage is cracked?
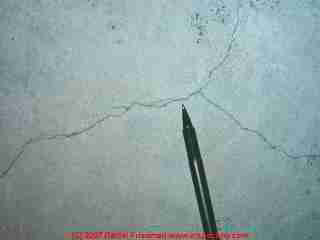
They may appear larger. What is unique about shrinkage cracks in concrete is that they usually appear to be discontinuous, as shown in this photo. The crack will meander along in the concrete, taper to a stop, and then continue beginning in a parallel line to the first crack, meandering again through the concrete.
How can you tell if concrete is cracked?
Crack severity on the surface of concrete is normally measured using a crack width ruler (crack gauge). Depending on the opening of the cracks on the surface, cracks can be described (as tiny as hairline, or severe (few millimetres opening).
How do you know if plastic shrinkage cracks in concrete?
Plastic shrinkage cracks appear in the surface of fresh concrete soon after it is placed and while it is still plas- tic. These cracks appear mostly on horizontal surfaces.
Does shrinkage cause cracking?
Because of the many factors which can influence the locations at which cracks develop, they sometimes appear in areas other than at control joints. According to the Portland Cement Association, restraint to shrinkage is the most common cause of concrete cracking.
What is acceptable concrete cracks?
A crack in a slab of 1/8 inch or less is typically a normal shrinkage crack and not a cause for concern. If the crack is larger or growing larger (an “active” crack), or one side of the crack is higher than the other, then you may need to have the work reviewed by a structural engineer.
What are settlement cracks?
Settlement. A home may experience some minor cracking as it settles down on its new foundations. The ground underneath the home can compact under the weight of the structure, which causes the home to move downwards. Settlement usually occurs in newer properties, but it soon stabilises.
What is the difference between drying shrinkage and plastic shrinkage?
If the volume reduction occurs before the concrete hardens, it is called plastic shrinkage. The volume reduction that occurs primarily due to moisture loss after the concrete has hardened is known as drying shrinkage.
How wide are shrinkage cracks?
The cracks tend to be 1-2 mm wide, 300-500 mm long and 20-50 mm deep, though, in some circumstances, they may extend through the full depth of a member. The occurrence of plastic shrinkage cracks can be significantly reduced by adequate curing.
Are shrinkage cracks normal in concrete?
Cracks in concrete are common and they develop when stresses in the concrete exceed its strength. Cracks are often caused by normal shrinkage of the concrete when hardening and drying.
How do you prevent shrinkage from cracking?
Methods of Preventing Plastic Shrinkage Cracking of ConcreteErecting Temporary Wind Breaks. ... Providing Sunshades. ... Proper Placement Timing. ... Using Fog Sprays. ... Dampening the Subgrade. ... Using Evaporation Retarder. ... Start Curing Immediately. ... Accelerating Setting Time of Concrete.More items...•
What are the main causes of shrinkage cracking?
Plastic shrinkage cracks occur when wind velocity, low relative humidity, high ambient temperature, or a combination of all three, cause water to evaporate from a concrete surface faster than it can be replaced by bleeding to the surface.
How do you deal with shrinkage cracks?
Shrinkage Cracks in Masonry Cracks caused due to shrinkage in masonry walls can be minimized by avoiding the use of rich cement mortar in masonry. It can also be reduced by delaying plasterwork until masonry has dried after proper curing has undergone most of its initial shrinkage.
Will hairline cracks in concrete get worse?
Yes, in about a month, hairline cracks should subside. While shrinkage cracks can show up on the surface within hours of having concrete poured, it takes a full monthfor new concrete to fully settle. Don't be surprised if cracks that seemed visible at first are nearly impossible to see after a month of settling.
What is the most common cause of cracking in concrete?
Shrinkage is a main cause of cracking. As concrete hardens and dries it shrinks. This is due to the evaporation of excess mixing water. The wetter or soupier the concrete mix, the greater the shrinkage will be.
Should I worry about cracks in my concrete floor?
Generally, cracks in your floor are nothing to worry yourself over. The only time that you might be concerned is if the cracks start changing vertically, suggesting that there is some settling happening.
How do you fix cracks in concrete?
0:412:34How to Repair Concrete Cracks - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then load the tube into a standard caulk gun slowly draw the gun down the crack. Forcing a beadMoreAnd then load the tube into a standard caulk gun slowly draw the gun down the crack. Forcing a bead of concrete or pair caulk deep into the crack. Conquer.
What causes cracks in concrete?
Cracks in a concrete slab-on-grade or other horizontal concrete slab caused by soil settlement will often have a vertical displacement across the crack, in other words, one side of the crack will be higher than the other side. Cracks in vertical surfaces caused by soil settlement will often be stair-step cracks.
What is the term for the thin hairline cracks in concrete?
As they undergo the chemical reaction, the materials can shrink as water is lost from the mix. That shrinkage causes the hardening material to crack. These types of cracks are known as shrinkage cracks . Shrinkage cracks are thin, hairline cracks on the face of the concrete or mortar.
Why are cracks in stair steps called that?
Cracks in vertical surfaces caused by soil settlement will often be stair-step cracks. Stair-step cracks have that name because they resemble a set of stairs. Stair-step cracks travel horizontally, then travel vertically, then travel horizontally again. If a crack runs through a brick or other masonry unit, rather than just through ...
Why does my house have cracks in the walls?
Additionally, if a home has cracks in concrete or masonry accompanied by stair-step or diagonal cracks in the drywall on the interior or accompanied by doors and windows that stick or will not open, there is a greater chance that the cracking is caused by soil settlement.
What does it mean when a brick cracks?
If a crack runs through a brick or other masonry unit, rather than just through the mortar holding the bricks or other masonry together, that is a sign of a settlement crack. Bricks and masonry units typically do not crack unless subjected to the stress of soil settlement.
Is shrinkage cracking a problem in concrete?
Shrinkage cracks are common, but can be minimized by proper mixing and placement of the concrete. While they are not pleasing to the eye, shrinkage cracks are generally not harmful to the structure of a home. The standards that govern concrete construction permit shrinkage cracks in concrete up to a certain crack width.
Is soil settlement a good idea?
Soil settlement will damage the structure of your home, will reduce the useful life of your home, will require costly repairs and will prevent you from selling your home. Soil settlement is entirely avoidable.
What is unique about shrinkage cracks in concrete?
What is unique about shrinkage cracks in concrete is that they usually appear to be discontinuous, as shown in this photo.
Why does cement have shrinkage cracks?
Shrinkage Cracks or "Contraction Cracks" are due to faulty workmanship, and may occur in the best of cements if mixed too rich or if allowed to dry out too quickly, or if not thoroughly mixed and trowelled (A, in Fig. I.) Expansion cracks are due to too much free lime or magnesia in the cement. (B, Fig I.)
What is the significance of differences in concrete height on opposite sides of a crack?
Why are some "shrinkage cracks" at different heights on either side of the crack?
What is a small crack in a concrete foundation?
Small shrinkage cracks that are above ground level in a foundation wall, such as the cracks in the inside corner of this poured concrete foundation are unlikely to be much of a problem except for a few less common cases where water running down the wall is leaking in at the shrinkage crack.
How are concrete walls, foundations, or floor slabs shrinkage avoided or repaired?
How are concrete wall, foundation, or floor slab shrinkage cracks avoided or repaired. While shrinkage in poured concrete walls or floor slabs is a normal property of curing concrete, shrinkage cracks can be controlled, or where they have occurred, in some cases repairs are needed.
What causes concrete to cure?
Multiple forces and movements may be present as a poured concrete foundation cures, such as a combination of shrinkage and settlement, or shrinkage and outside pressures on a wall from backfill.
Where do cracks in concrete come from?
Concrete cracks often occur at natural stress points where the uniformity of a poured concrete wall or floor has been interrupted by placement of a window (in walls of course) or inside corners (in floors). You may often find shrinkage cracks that trace across the concrete to these stress points.
Why do settlement cracks need to be separated?
Settlement cracks need to be separated into initial settlement due to construction or site factors and ongoing settlement due to site factors.
What is shrinkage crack?
Shrinkage cracks in poured concrete are easily recognizable and can be distinguished from other types of cracks that occur later in the life of a foundation wall or floor slab.
What is a crack in a concrete foundation?
Cracks in a poured concrete foundation which are diagonal or vertical and which are generally uniform in width, or which taper to an irregular hairline form and stop entirely, which are usually discontinuous in the crack's finest or hairline area (the crack "stops and starts" in the same area), are usually shrinkage cracks and should not be ongoing nor of structural significance, though they may invite water entry through the wall.
Why do masonry blocks crack?
Solid materials may be cracked by pressure from loading. In masonry foundations, bricks actually expand indefinitely, though probably at a decreasing rate. Poured concrete shrinks after pouring. Masonry blocks may shrink and expand.
Why do foundations crack?
Speaking generally, foundations may be damaged and cracks may appear from innocent causes unlikely to affect the structure such as concrete shrinkage cracks, initial settlement, or from potentially more serious causes such as ongoing settlement, unusual pressures or loading, or from improper construction.
What does a diagonal crack mean?
However a diagonal crack may also indicate upwards wall-lift such as by frost or expansive clay soils which are more active under one portion of a foundation wall than another.
Where do shrinkage cracks occur?
Common areas for a shrinkage concrete crack to develop are under a basement window, above a doorway in the middle of a long wall or where the foundation "steps down." Shrinkage cracks also often occur near the middle of a large poured concrete wall [or floor] if no control joints were used. [Concrete control joints are very often omitted in residential construction.
What causes concrete to crack?
Just like a balloon, heat causes concrete to expand. When concrete expands, it pushes against anything in its way (a brick wall or adjacent slab for example). When neither has the ability to flex, the expanding force can be enough to cause concrete to crack.
What does it mean when you see cracks in concrete?
When you see a crack in your concrete slab or wall, your first assumption is typically that something has been done wrong–but that’s not always the case. Actually, concrete cracks are very common, some are even inevitable.
What are the cracks in concrete that are caused by premature drying?
There are two common types of cracks brought on by premature drying. Crazing cracks are very fine, surface cracks that resemble spider webs or shattered glass. When the top of a concrete slab loses moisture too quickly, crazing cracks will likely appear. While unsightly, crazing cracks are not a structural concern.
What causes cracks in concrete slabs?
Instead, what is more likely to occur is excess overload on the ground below the slab. After a heavy rain or snowmelt when the ground below is soft and wet, excessive weight on the slab can press the concrete down and result in cracks .
Why does concrete crack when it freezes?
When the ground freezes, it can sometimes lift many inches before thawing and settling back down. This ground movement brought on by the freezing and thawing cycle is a huge factor contributing to concrete cracking. If the slab is not free to move with the ground, the slab will crack.
Why is my concrete slab shrinking?
An excessively wet mix is a contributing factor to shrinkage in concrete. While water is an essential ingredient in every concrete mix, there is such a thing as too much water. When the mix contains too much water, the slab will shrink more than if the correct amount of water was used. Hot weather is another big reason for plastic shrinkage cracks.
Why does plastic shrink?
Hot weather is another big reason for plastic shrinkage cracks. Control joints can be incorporated into the slab to prevent shrinkage cracking. The joints will open up as the concrete slab gets smaller. 2. Expansion concrete cracks. Just like a balloon, heat causes concrete to expand.
How much does a crack in concrete shrink?
For every ten feet of concrete that are poured, be it a wall or a slab, it will shrink 1/16th of an inch in about a year's time. But people see a crack in a concrete wall and immediately think it's a settlement crack.
What is settling crack?
House settling cracks come in all types and sizes. Settling cracks can often just be lumber shrinkage cracks in new homes. True settlement cracks tend to get larger over time.
Why do people name cracks in their houses?
Cracks happen for all sorts of reasons. But all too often people name every crack in their house as a settlement crack.
Where is the Kope and Lower Fairview formation?
The Kope and Lower Fairview formations are the light pink rock just above the magenta alluvium that's north of the Ohio River. (C) Copyright 2017 USGS and every US taxpayer that owns the maps. CLICK THE IMAGE TO BUY GEOLOGIC MAPS FOR YOUR AREA.
Where do you see cracks in a house?
These are places where the house relieves movement, just like the joints in our fingers, arms and legs. I often see cracks in modern homes where columns support beams. You can see cracks right where the contact point between these two structural members meet.
Did they patch settling cracks?
House settling cracks were patched here. See all the white lines? The person who repaired the cracks made several critical mistakes. The stucco should have been washed first. The patching material should have been tested on the side or rear of the home for a perfect match. Copyright 2018 Tim Carter
Can cracks be repaired?
If you have an understanding as to why cracks happen, then you can often work to make permanent repairs. There are some cracks that can't be easily repaired.
What is a shrinkage crack?
But 99 times out of 100, the cracks that you might see in a foundation wall, a concrete slab or in floors, walls, ceilings, ceramic tile grout, etc. are shrinkage cracks. Water is an ingredient of many building materials. It can be a natural ingredient as in the case of wood, or it can be added in the manufacturing process much like milk is added to a powder when making pancake batter. When this water evaporates from the material, the loss in volume can create a tension or tearing force within the building material.
How do you prevent settlement cracks?
In almost all areas of the nation, building inspectors are responsible for doing a visual inspection of the soil just before the foundation footer is poured. A trained inspector can often see or smell soil that may not be strong enough to support the weight of the new home.
How Do You Repair Concrete Cracks?
CLICK or TAP HERE to discover the best product to use to repair concrete cracks. I use it all the time.
What is a foundation footing?
The footing is perhaps the most fundamental aspect of a home foundation. It's a structural element not much different than a beam or a column. The footing is that part of a house or building that contacts the ground. Everything is built up from a footing.
Is Steel Reinforcing Important in Foundation Walls?
Steel reinforcing is also important in foundation walls. Typically, a builder might place two rows of steel in the lower and upper portion of the wall. If you want bulletproof concrete walls that will stand the test of time, give serious consideration to extra horizontal steel as well as vertical steel bars that lock into the footer and continue up into the top of the foundation wall. Vertical steel bars help prevent horizontal cracks in the foundation walls.
Is it possible to help prevent foundation cracks once the house is built?
Yes. You can prevent foundation cracks by keeping the clay soil damp all year. You can install simple vertical watering holes to deep water the soil using a hand auger and filling the holes with rounded pea gravel.
How much concrete should I use for a footing?
It costs just a little bit more money to add strength. Specify 3,000 pounds per square inch (psi) at a bare minimum. If you can afford 3,500 psi concrete for the footing, order or specify it.
Why is my concrete cracking?
According to the Portland Cement Association, restraint to shrinkage is the most common cause of concrete cracking. This condition is inherent in continuously-poured concrete slabs. In applications such as concrete slabs and residential foundation walls, cracking is inevitable and expected.
What causes cracks in concrete?
Cracks which are caused by soil settlement or heaving typically exhibit vertical displacement of the concrete; concrete on one side of the crack will be higher than concrete on the other side. Cracks caused by shrinkage are typically not linearly continuous.
What happens when concrete dries?
As the surface of concrete dries, water evaporates from the spaces between particles. As this water dissipates, the particles move closer together, resulting in shrinkage of the concrete. Because the surface of a concrete slab is exposed to air but the underlying concrete is not, concrete near the surface dries and shrinks at a rate different from that of the underlying concrete. The underlying concrete acts as a restraint to shrinkage, resulting in cracking of the surface layer.
How does concrete expand?
The chemical hydration process through which concrete hardens produces heat which causes concrete to expand. At the same time, concrete at the surface of the slab is exposed to air and loses water through evaporation. Both of these conditions contribute to cooling and shrinking of the concrete near the surface.
Why does concrete have tensile stresses?
Newly-placed concrete develops tensile stresses as differences in temperature and moisture content develop in the drying concrete. These stresses are relieved by cracking. A number of factors can influence the development of such stresses.
What is control joint?
Control joints are grooves pressed into the concrete during the finishing process. Because the concrete slab is thinner and weaker at these grooved areas, it tends to develop cracks in these grooves first. Because of the many factors which can influence the locations at which cracks develop, they sometimes appear in areas other than ...
What happens when reinforcement steel is placed too close to the surface?
Corrosion: When reinforcement steel is placed too near the surface, it can corrode. Expansion results as steel is converted to iron oxide through corrosion. This expansion can crack the concrete surface. When the crack is caused by corroding steel, corrosion is typically visible at the slab surface.
How to identify shrinkage cracks in concrete?
In appearance, plastic shrinkage cracks are generally isolated and narrow. Sometimes, these can pass through the section. Random, cracks following the reinforcement pattern or parallel cracks are possible with plastic shr inkage cracks in concrete slabs.
Why does concrete have shrinkage cracks?
Even with no restrains, drying shrinkage cracks appear due to different shrinkages at the end. Imagine using two mix proportions of concrete having different shrinkage properties. If they use to cast one element there can be drying shrinkage cracks between them. Here the concrete itself creates a restrain inside of it.
How to fix cracks in concrete slab?
The reason for this kind of crack is the high evaporation rate, the best-known method to solve these cracks by reducing the evaporation rate. The most common method is to use a windbreaker and sun blinds to cover the work area. If the slab is thick (imagine a raft foundation), you can also try to cool the concrete. This will help keep the internal temperature within limits. Misting the slab is another practical method to reduce the risk of plastic shrinkage cracks in concrete slabs. This will saturate the air and the evaporation rate will decrease.
Why does concrete crack?
These cracks occur due to the water loss from the concrete. When the evaporation rate is higher than the bleeding rate, the top of the slab surface shrinks due to drying and cracks at the end. Usually, concrete slabs undergo high evaporation due to their large surface area. Plastic shrinkage cracks can appear on the slab surface within the setting time mostly. So, these are classified as very early age cracks.
What is shrinkage crack?
Shrinkage cracks in concrete slabs – what you must know! concrete slabs are the severely vulnerable to some thin cracks called shrinka ge cracks. Due to its thin sections and high surface area, the evaporation rate is high in concrete slabs. This is favorable for early shrinkage cracks in concrete slabs.
Why is the evaporation rate high in concrete?
Due to its thin sections and high surface area, the evaporation rate is high in concrete slabs. This is favorable for early shrinkage cracks in concrete slabs. There are two types of shrinkage actions possible in concrete slabs. Namely, plastic shrinkage and drying shrinkage actions. Both these contract the concrete due to moisture evaporation loss.
What is the most significant factor for drying shrinkage cracks?
So these cracks are late than thermal cracks. The most significant factor for drying shrinkage cracks is the water content in the mix. Calcium silicate gel formed during hydration has moisture inside.
How to prevent plastic settlement cracks in concrete?
In simple terms prevention of plastic settlement cracks in concrete can be achieved by increasing the sand content. However, there is a limit to this at which the bleeding will increase. Very clean (marine-dredged) sand tend to assist water movement, so blending with ‘dirtier’ sand with a higher fines (<150 micron) content can be beneficial.
How wide are plastic settlement cracks?
Plastic settlement cracks are typically 1 mm wide and usually run from the surface to the bars (see Figures 2 and 3). The settlement may also result in visible undulations on the concrete surface, with the high points over the top reinforcing bars.
What happens when solids settle in concrete?
If the settlement of solids in the concrete can freely take place without hindrance there will be a reduction in depth and volume of the cast concrete but no cracking. However, any restraint to this movement, e.g. reinforcement, can result in plastic settlement cracks. Where the solids continue to settle in comparison to those which are prevented from further downward movement, the concrete will ‘break its back’ and a tear appears in the surface as it is forced into tension. Cracks may develop at regular spacing reflecting the reinforcement layout. Cracks in concrete often occur in conjunction with voids under the bars as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 (a) shows initiation and Figure 1 (b) the condition after a few hours. These crescent-shaped voids may initially be filled with bleed water. The region of bond between the bar and concrete is thus reduced.
How wide is a concrete slab?
They are also typically 1 mm wide and can cross the full section. If the sub-base or other material against which the concrete is placed has a high absorbency (dry soil, permanent forms) the settlement can be exaggerated, again the cracking following the reinforcement layout.
What is settlement below restrained concrete?
Settlement below the restrained concrete results in a crack being formed, generally coinciding with the links. It is sometimes possible for plastic settlement cracks to form on a vertical face where reinforcement has restricted the free flow of concrete within the formwork.
Can you treat cracks in concrete?
exposure class, and the severity of the cracking. They can be treated with resin injection although in some instances full-depth breaking out and reinstatement may be necessary.
Do cracks in concrete pass through aggregate?
Unlike cracks in hardened concrete, due to overloading for instance, these cracks form at a very early age and pass through the cement paste and do not pass through aggregate particle pieces. The path is therefore more tortuous.

Distinguishing Among Shrinkage, Expansion, and Settlement Cracks
- General Comments about foundation expansion or shrinkage Cracks will occur in masonry structures:Most solid materials may both expand and contract in response to temperature variations. Solid materials may be cracked by pressure from loading. In masonry foundations, bricks actually expand indefinitely, though probably at a decreasing rate. Poured c...
Evidence of Foundation Shrinkage
- A variety of site conditions can lead to cracks in a concrete or other masonry foundation walls or floor slabs. Speaking generally, foundations may be damaged and cracks may appear from innocent causes unlikely to affect the structure such as concrete shrinkage cracks, initial settlement, or from potentially more serious causes such as ongoing settlement, unusual pressu…
Evidence of Foundation Expansion
- Brick, in particular, whether used in a foundation or as a building wall, expands over time and as moisture, temperature, and other conditions vary. Dave Wickersheimer, P.E. and R.A., who is a masonry failures expert from the SHC, informs us that brick "grows" or expands indefinitely. However if we exclude heating effects of sun exposure (discussed below), most brick expansio…
Foundation Settlement: Crack Patterns, Other Evidence
- The photograph shows a significant settlement crack in a poured concrete foundation of a new (modular) home. This crack appeared first as a fine hairline crack. The owner monitored the crack as it expanded to a significant width over the ensuing year. A combination of poor site preparation of soils below the building footings (un compacted fill), portions of footings sitting on bedrock, a…