
What was the first Dutch settlement in North America?
↑ Hendrick Christiaensen in 1615 through 1618 built the first Dutch factorij settlement ( Fort Nassau) in North America, in Mahican / Mohawk territory on the North River (upper Hudson), sited at "Castle Island", on ruins of an earlier French fortification from 1540.
Who were the first settlers in New Netherland?
New Netherland Settlers 1609-1640 is the inclusive list, in chronological order, of the reputedly first European pioneers who came to the Dutch colony of Nieuw-Nederland. These are the earliest immigrant arrivals and early births of profiles categorized as Category:New Netherland Settlers.
How did the Dutch colonize the Americas?
Colonialism portal. The Dutch colonization of the Americas began with the establishment of Dutch trading posts and plantations in the Americas, which preceded the much wider known colonisation activities of the Dutch in Asia.
What did the Dutch trade in the 1600s?
A Dutch merchant company chartered in 1602 to carry on trade with Africa, the West Indies, North and South America, and Australia. The sale and exchange of animal furs (like beaver pelts). French and Dutch colonizers focused on trading furs with Native American tribes in North America.
Where were the earliest settlements of the Dutch?
New Netherland was the first Dutch colony in North America. It extended from Albany, New York, in the north to Delaware in the south and encompassed parts of what are now the states of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Connecticut, and Delaware.
What were the names of the Dutch settlements?
Former Dutch colonial possessionsDutch East Indies with company rule (1603–1949), and Dutch New Guinea (until 1962)Dutch India (1605–1825)Dutch Gold Coast (1612–1872)New Netherlands (1614–1667, 1673–1674)Dutch Guianas (1616–1975)Dutch Formosa (1624–1662), and Keelung (Fort Noord-Holland; 1663–1668)More items...
What was Dutch settlement?
The region of the Western Cape which includes the Table Bay area (where the modern city of Cape Town is located) was inhabited by Khoikhoi pastoralists who used it seasonally as pastures for their cattle. When European ships landed on the shores of Table Bay they came into contact with Khoikhoi.
Who were the first settlers in the Netherlands?
The newcomers who stayed in the northern Netherlands would eventually be referred to as "Frisians", although they were not descended from the ancient Frisii. These new Frisians settled in the northern Netherlands and would become the ancestors of the modern Frisians.
Where were the earliest settlements of the Dutch French and English?
Where were the earliest settlements of the Dutch, French, and English in the Americas? New France, Virginia and the Masscheussets Bay Colony, and most of the eastern seaboard of North America.
What were the Dutch settlers called in South Africa?
Boer, (Dutch: “husbandman,” or “farmer”), a South African of Dutch, German, or Huguenot descent, especially one of the early settlers of the Transvaal and the Orange Free State. Today, descendants of the Boers are commonly referred to as Afrikaners.
Why did the Dutch settle at the Cape?
The settlement at Table Bay became Cape Town, whose purpose was to supply fresh food and water to Dutch trading ships rounding the Cape of Good Hope on their voyages to and from the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia).
When did the Dutch settle in South Africa?
1652Dutch has been present in South Africa since the establishment in 1652 of the first permanent Dutch settlement around what is now Cape Town.
What were the Dutch colonies in Africa?
The two major countries in Africa that were colonized by the Dutch were South Africa and Ghana. The colonies that became Ghana were referred to as the Dutch Gold Coast.
When was Holland first settled?
800 to 1000 - The Vikings arrive raiding towns and cities along the coast. They settle in some areas. 1083 - The name Holland first appears in a legal document describing a region that would later become known as the County of Holland.
Who came first Dutch or English?
European Powers That Came To IndiaEuropeansCame to IndiaYearPortuguese14981500Dutch16021605English16001613French16641668Apr 18, 2017
Which city founded Dutch settlers?
A successful Dutch settlement in the colony grew up on the southern tip of Manhattan Island and was christened New Amsterdam.
What were the Dutch colonies in Africa?
The two major countries in Africa that were colonized by the Dutch were South Africa and Ghana. The colonies that became Ghana were referred to as the Dutch Gold Coast.
Where did Dutch immigrants settle in America?
During the early nineteenth century, large numbers of Dutch farmers, forced by high taxes and low wages, started immigrating to America. They mainly settled down in the Midwest, especially Michigan, Illinois and Iowa.
What major Dutch settlement was located at the mouth of the Hudson River?
As such, the Dutch established the colony of New Netherland. The Dutch settled three major outposts: New Amsterdam, Wiltwyck, and Fort Orange. New Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Hudson River, and would later become known as New York City.
Where did the Dutch settle in New York?
Manhattan IslandA successful Dutch settlement in the colony grew up on the southern tip of Manhattan Island and was christened New Amsterdam. To legitimatize Dutch claims to New Amsterdam, Dutch governor Peter Minuit formally purchased Manhattan from the local tribe from which it derives it name in 1626.
Mainland In North America
In 1602, the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered a young and eager Dutch East India Company ( Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie or "VOC") with the mission of exploring North America's Rivers and Bays for a direct passage through to the Indies.
Caribbean Sea
Dutch colonization in the Caribbean started in 1634 on St. Croix and Tobago (1628), followed in 1631 with settlements on Tortuga (now Île Tortue) and Sint Maarten. When the Dutch lost Sint Maarten (and Anguilla where they had built a fort shortly after arriving in Sint Maarten) to the Spanish, they settled Curaçao and Sint Eustatius.
South America
From 1630 onward, the Dutch Republic gained control of a large portion of northeastern Brazil from the Portuguese. The Dutch West India Company set up their headquarters in Recife; it also exported a tradition of religious tolerance to its New World colonies, most notable to Dutch Brazil.
What did the Dutch do to the French refugees?
The Dutch recognising the value of the refugees, encouraged the French families to seek new homes in Dutch settlements.
How many slaves were there in 1657?
1657 & 1658 – The first 150 slaves land at the Cape. A school is established for the male and female slaves. To encourage the slaves to attend, they each received a small glass of brandy and two inches of tobacco, after school. (The beginning of the ‘Dop’ system).
What is the Dutch town of Batavia?
The small town, which Van Riebeeck and his successors established at the Cape, reproduced some of the typical features of Amsterdam. To the Dutch the natural setting of a town was at the water’s edge. When they occupied the Archipelago, they insisted, as far as circumstances permitted, on a similar environment for their lives in the East. Batavia, with its canals and bridges connecting houses and stabling, was modelled on the ground plan of the Netherlands city. In the seventeenth century the sea encroached upon the land to a far greater extent than at present, and the waterfront ran across the lower end of Strand Street. Van Riebeeck intended the heart of his little settlement to lie facing the waterfront, on the bank of a freshwater stream, which flowed from the mountain down the Platteklip Gorge. Here he build his fort and the canalized the lower portion of the freshriver, to fill the moat. Behind and at right angles to the shoreline was the main thoroughfare, named, after its Amsterdam counterpart, the Heerengracht. It was bordered by masonry water canals, fed by a stream from Table Mountain. In time oaks were planted and plank bridges gave access to the gardens of cottages. It resembled the atmosphere of a smaller waterfronted Dutch town. Open canals were constructed down several of the streets, serving as a watersource for irrigations, and despite the diminished flow in summer, as a means of combating fires. The impact of the Dutch presence on the natural flaura and fauna of the Peninsula was not confined to pasture lands and hedges. The natural wildlife was being steadily hunted out. This was encouraged by the premium that the Company paid for the shooting of lions and leopards. Robben Island was populated by sheep, which the Company hoped would breed in isolation from Khoi rivals, while seals on the coastline were hunted for their oil and flesh. Trees in the Table Bay area were swiftly falling to the axe. Brick houses soon began to cluster around the fort, whilst a jetty ran out into the sea. In close proximity was Van Riebeeck’s hospital, later used as a timber store. Sidewalks at right angles to the main street led to the house of Hendrik Boom, the chief gardener, and to various private gardens. The Company’s main vegetable and fruit garden was laid out on the lower slope of the Mountain. Much of it was enclosed. Wheat and barley were sown before the settlement was three months old. With the construction of thatched cottages the wilderness of the sand dunes gave way to a pleasant domesticated scene. Countless waterfowl inhabitated the Lion’s Head area and around the green vlei (Greenpoint). The clusters of melkbos provided very little shelter against the ferocity of the rain bearing Northwesterly wind in Winter and the dry South Easter in Summer.
What tribes lived in the Bergriver?
Living a little distance inland were two other richer and more powerful tribes, the Goringhaikuas, or Kaapmans (Capemen), who numbered about six hundred men, and the Gorachouquas, or Koras, whose strength was about two-thirds of that of the Kaapmans. In time the burgher explorations discovered the existence of other tribes. The most powerful clan was the Cochoqua, or Saldanha men, who lived along the Bergriver towards Malmesbury and Saldanha Bay. The Khoikhoi were of larger physique than the San, with a tawny pigmentation and slight of build. Their houses were crude semi-circular huts of stakes and mats. They used copper and iron. Their weapons consisted of arrows and spears tipped with metal. They were described as mild mannered and friendly.
Why did Van Riebeeck drag yellowwood beams from the mountain kloofs?
Van Riebeeck instructed his men to drag yellowwood beams from the mountain kloofs so that a jetty could be constructed, where ships’ boats could load and unload.
What did the Dutch do on his return to Table Bay?
On his return to Table Bay he acted as interpreter and intermediary between the Khoi and visiting English crews, to obtain cattle and sheep by barter. He continued in this role for the Dutch after the arrival of Van Riebeeck, considerably increasing his own livestock holdings in the process.
What weapons did the Dutch use?
They used copper and iron. Their weapons consisted of arrows and spears tipped with metal. They were described as mild mannered and friendly. Erecting the Fort – Van Riebeeck’s first duties were to erect a fort for the protection of the settlers and to lay out gardens for the growing of vegetables and fruit.
How many communities are there in Space:New_Netherland_Settlements?
Some fifty communities that they then founded will be found in Space:New_Netherland_Settlements .
Why did the colonists return to the homeland in 1628?
Growth of the colony in the early years was very slow. Because of the dangers and hardships of life in the new land some colonists decided to return to the homeland in 1628.
Where did Henry Hudson land his ship?
↑ Henry Hudson in 1609 first explored the coast of western Long Island, and landed his ship the Half Moon at the island known by the natives as Narrioch ( Coney Island ), along the shore of Gravesend Bay, and near what became in 1643 the Dutch-ruled Anabaptist English village of Gravesend, and which is now a neighborhood in south-central Brooklyn, Kings. In 1654 the people of Gravesend purchased the neighboring Dutch-named Conyne Eylandt (Coney Island) from the local natives, but it was not developed until the 1840s.
Is the early settlers a pioneer?
But on the other hand, the legitimate early settlers are famous pioneers. Those famous pioneers have well-researched articles about them in Wikipedia. So they need to be identified and improved in their profiles here in WikiTree.
Who indexed the 1982 Pennsylvania Genealogy Magazine?
1982 Genealogies of Pennsylvania Families from the Pennsylvania Genealogy Magazine, indexed by T. Holloway and E. Antoniak , p. 12
Where did Aldert and Wyntje live?
Aldert and his family subsequently relocated to Hurley where he and Wyntje resided for the remainder of their lives. He died in 1678/79 and she died sometime after 1685 when she was recorded as securing a grant of 320 acres at Hurley.
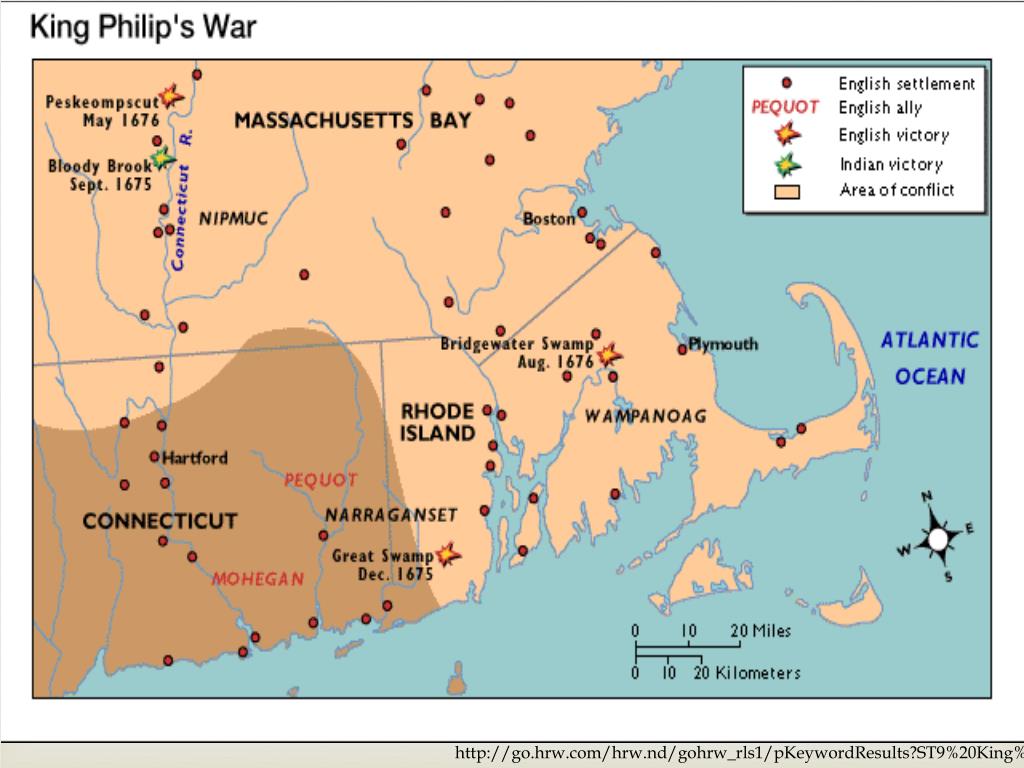
What was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas?
In 1606, the British got serious and King James I formed the Virginia Company to settle North America. It did so in 1607 at Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. Jamestown, located in Virginia, was beset by disease and starvation.
Why did the Dutch explore the Americas?
Like the French, the Dutch were originally exploring the Americas to find a quicker route to the Pacific Ocean, and thus the trade routes of China. They hired the English explorer Henry Hudson in 1609, who ended up at Cape Cod in what is now Massachusetts. Hudson continued along the coast until running into modern-day New York. Later voyages to map the area established it as part of the Dutch Empire under the name New Netherlands.
What did the colonists wear?
They wore sunglasses, and suddenly everybody was rushing to the store to buy those same sunglasses. They got a smartphone, and everybody rushed to trade in their old phones. They started colonizing North America, and everybody rushed across the Atlantic Ocean to start their own colonies.
What were the French interests in the Americas?
For most of the early colonial period, the French interests in the Americas were in fur trapping and trading with the indigenous people, although they also hunted for gold and other treasures.
What was Hudson's first trading fort?
On the island of Manhattan, first surveyed by Hudson, the Dutch built a trading fort called New Amsterdam in 1625.
Which European country was the first to colonize the Americas?
Lesson Summary. Spain was the first European nation to begin colonizing the Americas, starting with Christopher Columbus' discoveries in 1492. Spain was the first European nation of the time to begin exploring North America, mapping out Florida, but their real fame came from defeating the Aztecs of Mexico in 1521.
Where did the British settle in North America?
The first British settlement in North America was St. John's, in Newfoundland, Canada around 1520. However, it could not sustain a year-round population until 1620, a century later. The first major attempt to create a British colony in the modern-day United States was at Roanoke, in present day North Carolina in 1587.
How many French and Dutch settlers were there in 1672?
French settlements were initially made up of fur traders, merchants, and missionaries, so that there were fewer than 5,000 settlers by 1672.
What is the lesson of French and Dutch colonization?
Lesson summary: French and Dutch colonization. A high-level overview of French and Dutch efforts at early colonization. French and Dutch colonization in the Americans focused on the profitable fur trade. Depending on Native Americans to hunt animals for their pelts, French and Dutch colonizers cultivated friendly relationships with Native Americans ...
What did the French and Dutch colonize?
French and Dutch colonization in the Americans focused on the profitable fur trade. Depending on Native Americans to hunt animals for their pelts, French and Dutch colonizers cultivated friendly relationships with Native Americans through intermarriage and military alliances.
What were the goals of the French and Dutch?
Interactions with Native Americans: The goals of both the French and Dutch revolved around the fur trade. Unlike the Spanish and English, the French and Dutch fostered good relationships with Native Americans. The French in particular created alliances with the Hurons and Algonquians.
When was the New Netherlands founded?
New Netherlands was a Dutch colony founded in 1609 by the Dutch East India Company to maintain Dutch fur-trading practices.
When was the first French settlement?
The first permanent French settlement, founded in 1608.
Why did the French colonize North America?
Motivations for colonization: The French colonized North America to create trading posts for the fur trade. Some French missionaries eventually made their way to North America in order to convert Native Americans to Catholicism.
Overview
The Netherlands began its colonization of the Americas with the establishment of trading posts and plantations, which preceded the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. While the first Dutch fort in Asia was built in 1600 (in present-day Indonesia), the first forts and settlements along the Essequibo River in Guyana date from the 1590s. Actual colonization, with the D…
Mainland in North America
In 1602, the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered a young and eager Dutch East India Company (Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie or "VOC") with the mission of exploring North America's rivers and bays for a direct passage through to the Indies. Along the way, Dutch explorers were charged to claim any uncharted areas for the United Provinces, which led to several signifi…
Caribbean Sea
Dutch colonization in the Caribbean started in 1634 on St. Croix and Tobago (1628), followed in 1631 with settlements on Tortuga (now Île Tortue) and Sint Maarten. When the Dutch lost Sint Maarten (and Anguilla where they had built a fort shortly after arriving in Sint Maarten) to the Spanish, they settled Curaçao and Sint Eustatius. They regained half of Sint Maarten in 1648, from then on sharing the island with France. The border between the two portions of the island contin…
South America
From 1630 onward, the Dutch Republic gained control of a large portion of northeastern Brazil from the Portuguese. The Dutch West India Company set up their headquarters in Recife; it also exported a tradition of religious tolerance to its New World colonies, most notable to Dutch Brazil. The governor, Johan Maurits, invited artists and scientists in order to help promote migration to th…
See also
• Atlantic World
• Dutch Empire
• Dutch West India Company
• New York history
• New Amsterdam
Further reading
• Antunes, Catia; Gommans, Jos, eds. (2015). Exploring the Dutch Empire: Agents, Networks and Institutions, 1600-2000. New York: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1474236423.
• Boxer, Charles R. (1989). The Dutch Seaborne Empire: 1600-1800. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0140216004.
• Van Groesen, Michiel (2017). Amsterdam's Atlantic: Print Culture and the Making of Dutch Brazil. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-081224…
• Antunes, Catia; Gommans, Jos, eds. (2015). Exploring the Dutch Empire: Agents, Networks and Institutions, 1600-2000. New York: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1474236423.
• Boxer, Charles R. (1989). The Dutch Seaborne Empire: 1600-1800. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0140216004.
• Van Groesen, Michiel (2017). Amsterdam's Atlantic: Print Culture and the Making of Dutch Brazil. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0812248661.
External links
• Dutch West Indies 1630-1975 documentary
• (in English and Dutch) "Conditions as Created by their Lords Burgomasters of Amsterdam" from 1656, about Dutch goals to populate their New World colonies