- West Bank (about one and a half times the size of Goa) is a landlocked territory in West Asia. ...
- It was captured by Jordan after the Arab-Israeli War (1948) but Israel snatched it back during the Six-Day War of 1967 and has occupied it ever since.
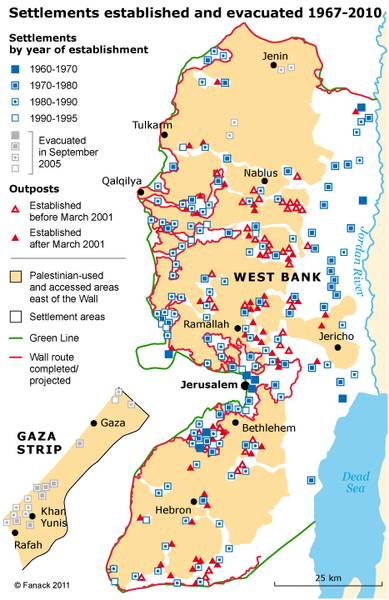
- At present, there are around 130 formal Israeli settlements along with 26 lakh Palestinians at West Bank.
Does Israel have rights to settlements in the West Bank?
Settlements on “state land” often expand into surrounding, privately owned, Palestinian land. As an occupying power, Israel does not own the West Bank and is not permitted under international law to seize land in this manner. Based on the law in the West Bank, a state is only allowed to expropriate private land for public Palestinian needs.
How much land do West Bank settlements take up?
The overall area in dispute is very small. According to one organization critical of settlements, the built-up areas constitute only 1.7% of the West Bank. That is less than 40 square miles. Even if you add the unbuilt areas falling within the municipal boundaries of the settlements, the total area is only 152 square miles. Outposts
Are the Israeli settlements on the West Bank legal?
Israeli settlements in the West Bank are legal both under international law and the agreements between Israel and the Palestinians. Claims to the contrary are mere attempts to distort the law for political purposes. Yet whatever the status of the settlements, their existence should never be used to justify terrorism.
Is West Bank and Palestine the same?
The term "Palestinian territories" has been used to describe the territories delimited by the 1949 Armistice borders within the former British Mandate for Palestine, that were occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip.The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has referred to the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, as ...
See more
Why does Israel settle the West Bank?
Israel has cited several reasons for retaining the West Bank within its ambit: a claim based on the notion of historic rights to this as a homeland as affirmed in the Balfour Declaration of 1917; security grounds, both internal and external; and the deep symbolic value for Jews of the area occupied.
Who does the West Bank belong to?
IsraelPresently, most of the West Bank is administered by Israel though 42% of it is under varying degrees of autonomous rule by the Fatah-run Palestinian Authority. The Gaza Strip is currently under the control of Hamas.
Who has claim to the West Bank?
Political geographyAreaSovereignty claimed byWest BankArea CState of PalestineEast JerusalemWest JerusalemUnited Nations as an international city along with East JerusalemGolan HeightsSyria3 more rows
What is the purpose of the West Bank?
Israel claims historical and religious rights to the West Bank as the ancestral land of the Jewish people. It also says its presence there - especially in the Jordan Valley - is strategically vital for its self-defence.
Is West Bank and Gaza the same as Palestine?
The Gaza Strip and the West Bank are two Palestinian territories that were part of Mandate Palestine and were captured by Israel during the Six-Day War in 1967. There are over 5 million Palestinians combined living in the two territories.
What's the difference between Gaza and the West Bank?
Gaza is separated from the West Bank, while in the West Bank, Areas A and B are themselves divided among 227 separate areas (199 of which are smaller than 2 square kilometers) that are separated from one another by Israeli-controlled Area C. All but 40,000 West Bank Palestinians live in Areas A and B.
How much land has Israel taken from Palestine?
Shortly after Israel declared statehood, units of the neighbouring Arab country armies came in to fight for the Palestinian nation. The 1948 war ended with Israeli forces controlling approximately 78 percent of historical Palestine. The remaining 22 percent fell under the administration of Egypt and Jordan.
Is Israel occupying Palestine land?
BACKGROUND: Palestinian territory – encompassing the Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East Jerusalem – has been illegally occupied by Israel since 1967.
Was Palestine a country before Israel?
Israel Becomes a State In May 1948, less than a year after the Partition Plan for Palestine was introduced, Britain withdrew from Palestine and Israel declared itself an independent state, implying a willingness to implement the Partition Plan.
What is Israel claim to the land?
Evangelical Zionists variously claim that Israel has title to the land by divine right, or by a theological, historical and moral grounding of attachment to the land unique to Jews (James Parkes).
Which country does Gaza belong to?
Gaza StripGaza Strip قِطَاعُ غَزَّةَ Qiṭāʿu ĠazzahPalestinian flagStatusUnder the Palestinian National Authority according to the Oslo Accords De facto administrated by Hamas since July 2007 Claimed by the State of PalestineaCapital and largest cityGaza City 31°31′N 34°27′EOfficial languagesArabic14 more rows
Is Jerusalem in Israel or Palestine?
Israel claims the whole of Jerusalem as its capital, while the Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state. The US is one of only a handful of countries to recognise the city as Israel's capital.
Which country does Gaza belong to?
Gaza StripGaza Strip قِطَاعُ غَزَّةَ Qiṭāʿu ĠazzahPalestinian flagStatusUnder the Palestinian National Authority according to the Oslo Accords De facto administrated by Hamas since July 2007 Claimed by the State of PalestineaCapital and largest cityGaza City 31°31′N 34°27′EOfficial languagesArabic14 more rows
Is Jerusalem in Israel or Palestine?
Israel claims the whole of Jerusalem as its capital, while the Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state. The US is one of only a handful of countries to recognise the city as Israel's capital.
Why did Israel occupy Palestine?
Israel says the occupation is necessary for security given its tiny size: to protect Israelis from Palestinian attacks and to provide a buffer from foreign invasions.
Is the West bank an Arab state?
The West Bank, as demarcated by the Jordanian-Israeli armistice of 1949, was broadly similar to (but smaller than) one of the zones designated as an Arab state by the United Nations (UN) partition plan for Palestine in 1947 (see United Nations Resolution 181).
How many settlements are there in the West Bank?
The Government of Israel has invested and continues to invest heavily in the construction and defense of settlements. • Number of settlements: 120 official settlements in the West Bank (not including East Jerusalem) • Area of the settlements: The official jurisdiction of the settlements stands ...
Where are the settlements in Israel?
During the disengagement program in the summer of 2005, 17 Gaza Strip settlements and four settlements in northern West Bank were dismantled. Today, all settlements are in the West Bank.
What percentage of West Bank residents are Palestinians?
About 90% of West Bank residents are Palestinians (and about 10% Jewish settlers). To download the full list of settlements. Outposts are, essentially, settlements established by governments of Israel since the 1990s in an unofficial and illegal manner.
When was the separation barrier built?
The Separation Barrier. In June 2002, the Israeli government approved the construction of a separation fence with the declared intention of preventing the uncontrolled entry of Palestinians from the West Bank into Israel.
Where is the West Bank?
The West Bank ( Arabic: الضفة الغربية aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; Hebrew: הגדה המערבית HaGadah HaMa'aravit or יהודה ושומרון Yehuda VeShomron) is a landlocked territory near the Mediterranean coast of Western Asia, bordered by Jordan and the Dead Sea to the east and by Israel to the south, west and north.
Which country occupied the West Bank in 1948?
In 1948, Jordan occupied the West Bank and annexed it in 1950. In 1967, Israel captured the West Bank from Jordan in the Six-Day War.
What is the Jerusalem law?
Through the Jerusalem Law, Israel extended its administrative control over East Jerusalem. This has often been interpreted as tantamount to an official annexation, though Ian Lustick, in reviewing the legal status of Israeli measures, has argued that no such annexation ever took place. The Palestinian residents have legal permanent residency status. Rejecting the Jerusalem Law, the UN Security Council passed UN Security Council Resolution 478, declaring that the law was "null and void". Although permanent residents are permitted, if they wish, to receive Israeli citizenship if they meet certain conditions including swearing allegiance to the State and renouncing any other citizenship, most Palestinians did not apply for Israeli citizenship for political reasons. There are various possible reasons as to why the West Bank had not been annexed to Israel after its capture in 1967. The government of Israel has not formally confirmed an official reason; however, historians and analysts have established a variety of such, most of them demographic. Among those most commonly cited have been: 1 Reluctance to award its citizenship to an overwhelming number of a potentially hostile population whose allies were sworn to the destruction of Israel. 2 To ultimately exchange land for peace with neighbouring states 3 Fear that the population of ethnic Arabs, including Israeli citizens of Palestinian ethnicity, would outnumber the Jewish Israelis west of the Jordan River. 4 The disputed legality of annexation under the Fourth Geneva Convention
Why does the Palestinian public oppose Israeli military and settler presence on the West Bank?
Palestinian public opinion opposes Israeli military and settler presence on the West Bank as a violation of their right to statehood and sovereignty. Israeli opinion is split into a number of views:
What was the Oslo agreement?
The Oslo Accords, signed between the Palestine Liberation Organization and Israel, created administrative districts with varying levels of Palestinian autonomy within each area. Area C, in which Israel maintained complete civil and security control, accounts for over 60% of the territory of the West Bank.
What is the name of the city in the West Bank?
City of Bethlehem, West Bank. The name West Bank is a translation of the Arabic term ad-Diffah I-Garbiyyah, given to the territory west of the Jordan River that fell, in 1948, under occupation and administration by Jordan, which subsequently annexed it in 1950.
Why is the West Bank called the West Bank?
The "West Bank" name was given to the territory after it was captured by Jordan in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War because it sits on the west side of the Jordan River. Jordan subsequently annexed the territory in 1950 and held it until 1967 when it was occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War .
Where are the settlements in the West Bank?
Facts About Jewish Settlements in the West Bank. The term “ Settlements ” usually refers to the towns and villages that Jews established in Judea and Samaria (the West Bank) and the Gaza Strip (prior to the disengagement) since Israel captured the area in the Six-Day War of 1967. In some cases, the settlements are in the same area ...
How much of the West Bank is built up?
The overall area in dispute is very small. According to one organization critical of settlements, the built-up areas constitute only 1.7% of the West Bank. That is less than 40 square miles. Even if you add the unbuilt areas falling within the municipal boundaries of the settlements, the total area is only 152 square miles.
What percentage of the West Bank was annexed by Israel?
Instead of calling for the establishment of a Palestinian state in more than 90% of the West Bank, the plan envisioned a state in 70% and, rather than expecting Israel to dismantle and evacuate a majority of settlements, it approved of Israel’s annexation of all the settlements.
How many settlements are there in Israel in 2021?
The estimate for the Jewish population in 128 West Bank settlements at the beginning of 2021 was 475,481, roughly 5 percent of Israel’s total population.
Why did Jews move to the West Bank?
A third group of Jews who are today considered “settlers,” moved to the West Bank primarily for economic reasons ; that is, the government provided financial incentives to live there, and the towns were close to their jobs.
Which country has the strongest claim to the West Bank?
The Palestinians never had sovereignty in the West Bank whereas the Jews did for hundreds of years; therefore, “Israel has the strongest claim to the land,” according to legal scholar Eugene Kontorovich. “International law holds that a new country inherits the borders of the prior geopolitical unit in that territory.
When were the first settlements built?
The first settlements were built by Labor governments from 1968 to 1977, with the explicit objective to secure a Jewish majority in key strategic regions of the West Bank - such as the Tel Aviv - Jerusalem corridor - that were the scene of heavy fighting in several of the Arab-Israeli wars.
Where do the West Bank settlers live?
Still, these fervent settlers are a vocal and highly visible minority. They generally live in smaller settlements, located deep inside the West Bank.
What are the Palestinians' claims to the West Bank?
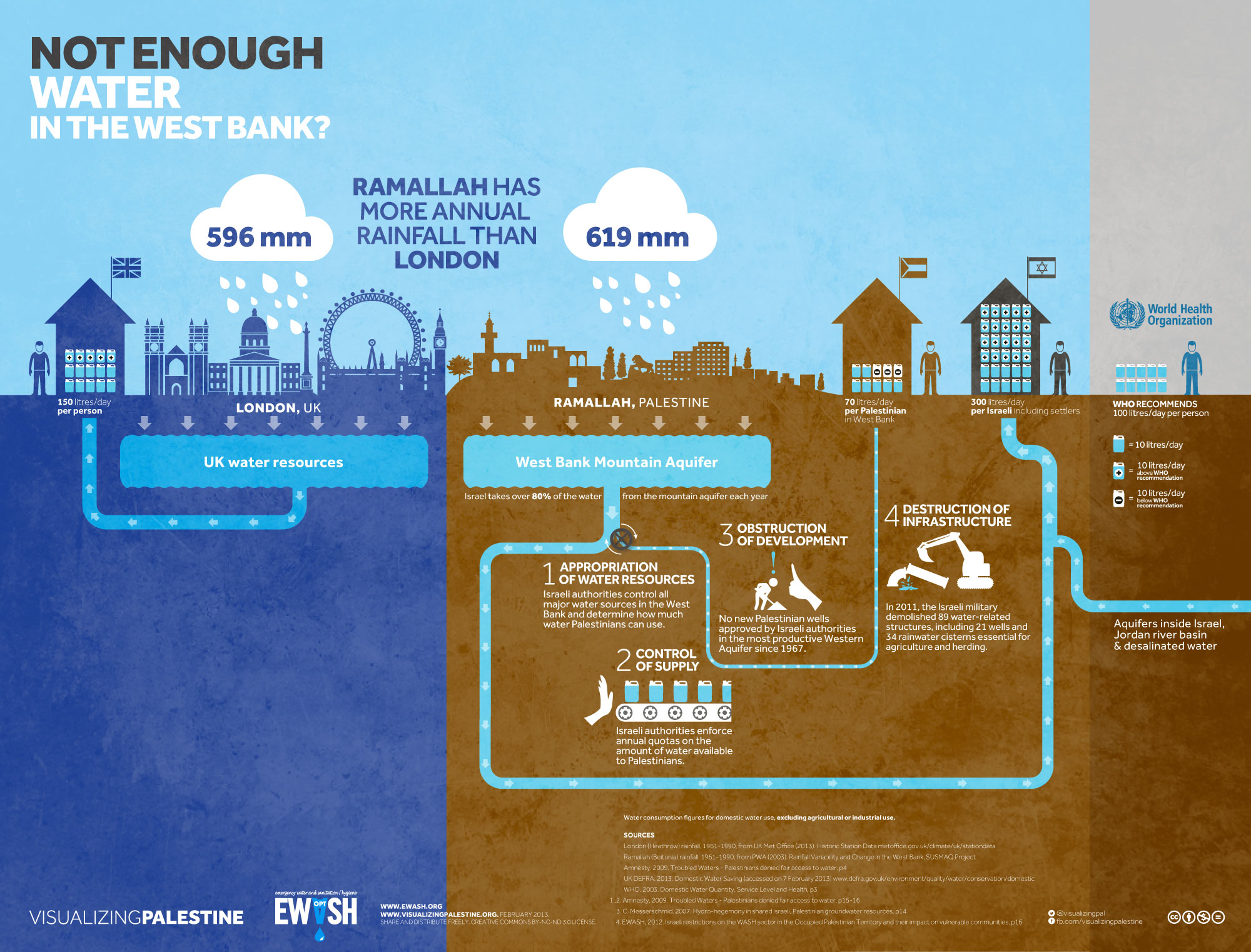
Palestinians contend that Israeli settlements in the West Bank are built on stolen land and that the settlers’ use of water – a scarce resource – is likewise illegal.
How many Israelis live in the West Bank?
The population of Israelis living in the West Bank has mushroomed over the years. An estimated 430,000 Israeli Jews now live in 132 officially recognized “settlements” and in 121 unofficial “outposts” that require, but haven’t yet received, government approval.
Why are there checkpoints in the West Bank?
The Israeli army security checkpoints that dot the West Bank, which are meant to protect Israelis from terror attacks, also restrict and complicate the ability of Palestinian people to move around.
Why is the West Bank considered occupied territory?
According to the International Court of Justice, the UN’s main judicial body, the West Bank is considered occupied territory because it was not part of Israel before the Israeli army conquered it in 1967. Territorial conquest is also forbidden by international law. The Israeli government says that the Geneva Convention is not applicable to ...
Why do Jews live in the West Bank?
Most Jewish settlers in the West Bank, however, live there for economic reasons. Israeli government investment and incentives aimed at encouraging Jews to settle there make the cost of living lower than inside Israel.
Why is the Geneva Convention not applicable to the West Bank?
The Israeli government says that the Geneva Convention is not applicable to the West Bank because it only refers to a state occupying another state’s land. Israel considers the West Bank “disputed territory,” not occupied territory.
Which country occupied the West Bank?
Israel captured the West Bank from Jordan in the 1967 war and has occupied the territory ever since. The Fourth Geneva Convention, ratified by 192 nations in the aftermath of World War II, says that an occupying power “shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”.
What is the birthright of the West Bank?
Some of the settlements are home to religious Zionists who believe that the West Bank, which Israel refers to by its biblical names of Judea and Samaria, is their biblical birthright . Many secular and ultra-Orthodox Jews also moved there largely for cheaper housing.
How many settlements have been built in Israel?
Israel has built about 130 formal settlements in the West Bank since 1967. A similar number of smaller, informal settlement outposts have gone up since the 1990s, without government authorization but usually with some government support.
Is it illegal to build a settlement in Israel?
The Israeli Supreme Court and the government do consider settlement construction on privately owned Palestinian land to be illegal. Under the Oslo Accords, signed by Israel and the Palestinians in the 1990s, both sides agreed that the status of Israeli settlements would be resolved by negotiation.
When did the International Court of Justice reject the settlements?
The International Court of Justice rejected that argument in an advisory opinion in 2004, ruling that the settlements violated international law.
Who is the secretary general of the Palestine Liberation Organization?
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel applauded the announcement as a “policy that rights a historical wrong,” while Saeb Erekat, the secretary general of the Palestine Liberation Organization, said it was an attempt by the Trump administration “to replace international law with the ‘law of the jungle.’”.
Who said Israel has a right to retain the West Bank?
In June, the American ambassador to Israel, David M. Friedman, said that Israel had a right to retain at least some of the West Bank.
Why is it impossible for Israel to occupy the West Bank?
For one thing, it was impossible for Israel to “occupy” Palestinian territories because no such nation has ever existed.
Where is the Jewish settlement of Ofra?
A view shows Palestinian houses in the village of Ein Yabrud with the Jewish settlement of Ofra seen in the background, in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, September 3, 2019. (Raneen Sawafta/Reuters)
Did Israel take the West Bank?
Israel spilled much blood taking the West Bank in self-defense from Jordan after that nation joined Egypt and Syria in the attempted destruction of Israel in 1967. Even then, Jordan had no legal claim to the territory. Israel offered 98 percent of the West Bank back right after the 1967 war, and on numerous occasions afterward.
Who encouraged the settlement of the West Bank?
As early as September 1967, Israeli settlement policy was progressively encouraged by the Labor government of Levi Eshkol. The basis for Israeli settlement in the West Bank became the Allon Plan, named after its inventor Yigal Allon. It implied Israeli annexation of major parts of the Israeli-occupied territories, especially East Jerusalem, Gush Etzion and the Jordan Valley. The settlement policy of the government of Yitzhak Rabin was also derived from the Allon Plan.
Who vetoed the West Bank settlement?
On 19 June 2011, Haaretz reported that the Israeli cabinet voted to revoke Defense Minister Ehud Barak 's authority to veto new settlement construction in the West Bank, by transferring this authority from the Agriculture Ministry, headed by Barak ally Orit Noked, to the Prime Minister's office.
How many settlements were there in the Gaza Strip?
Before Israel's unilateral disengagement plan in which the Israeli settlements were evacuated, there were 21 settlements in the Gaza Strip under the administration of the Hof Aza Regional Council. The land was allocated in such a way that each Israeli settler disposed of 400 times the land available to the Palestinian refugees, and 20 times the volume of water allowed to the peasant farmers of the Strip.
What was the Allon Plan?
It implied Israeli annexation of major parts of the Israeli-occupied territories, especially East Jerusalem, Gush Etzion and the Jordan Valley. The settlement policy of the government of Yitzhak Rabin was also derived from the Allon Plan.
How was Kiryat Arba established?
According to a secret document dating to 1970, obtained by Haaretz, the settlement of Kiryat Arba was established by confiscating land by military order and falsely representing the project as being strictly for military use while in reality, Kiryat Arba was planned for settler use.
What territories did Israel control?
It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and from Syria it captured most of the Golan Heights, which since 1981 has been administered under the Golan Heights Law .
How does settlement affect the economy?
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the security of the Israeli citizens living there.
Overview
The West Bank (Arabic: الضفة الغربية, romanized: aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; Hebrew: הגדה המערבית, romanized: HaGadah HaMaʽaravit), also referred to by some Israelis as Judea and Samaria (יהודה ושומרון, Yehuda VeShomron), is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediterranean in Western Asia. It is bordered by Jordan and the Dead Sea to the east and by Israel (see Green Line) to the south, …
Etymology
The name West Bank is a translation of the Arabic term aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah, which designates the territory situated on the western side of the Jordan River that was occupied in 1948 and subsequently annexed in 1950 by the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. This annexation was widely considered to be illegal, and was recognized only by Iraq, Pakistan, and the United Kingdom.
History
From 1517 through 1917, the area now known as the West Bank was under Turkish rule as part of Ottoman Syria.
At the 1920 San Remo conference, the victorious Allies of World War I allocated the area to the British Mandate of Palestine (1920–1948). The San Remo Resolution, adopted on 25 April 1920, incorporated the Balfour Declaration of 1…
Public opinion
Palestinian public opinion opposes Israeli military and settler presence on the West Bank as a violation of their right to statehood and sovereignty. Israeli opinion is split into a number of views :
• Complete or partial withdrawal from the West Bank in hopes of peaceful coexistence in separate states (sometimes called the "land for peace" position); (In a 2003 poll, 76% of Israelis supported a peace agreement based on that principle).
Geography
The West Bank has an area of 5,628 square kilometres (2,173 sq mi), which comprises 21.2% of former Mandatory Palestine (excluding Jordan) and has generally rugged mountainous terrain. The total length of the land boundaries of the region are 404 kilometres (251 miles). The terrain is mostly rugged dissected upland, some vegetation in the west, but somewhat barren in the ea…
Crossing points
Allenby Bridge, or ‘King Hussein Bridge’, is the main port for the Palestinian in the West Bank to the Jordanian borders. This crossing point is controlled by Israel since 1967. It was inaugurated on 11 December 2011 under the military order "175" entitled ‘An order concerning transition station’. Later, Order ‘446’ was issued which annexed the Damia Bridge crossing point to the Allenby Bridge as a commercial crossing point only. Goods were exported to Jordan, while the i…
Economy
As of the early-21st century, the economy of the Palestinian territories is chronically depressed, with unemployment rates constantly over 20% since 2000 (19% in the West Bank in first half of 2013).
Consequences of occupation
According to a 2013 World Bank report, Israeli restrictions hinder Palestinian economic development in Area C of the West Bank. A 2013 World Bank report calculates that, if the Interim Agreement was respected and restrictions lifted, a few key industries alone would produce US$2.2 billion per annum more (or 23% of 2011 Palestinian GDP) and reduce by some US$800 million (50%) the Palestinian Authority's deficit; the employment would increase by 35%.
History of The Settlement Movement
Outposts
- Outposts are settlements typically constructed by a handful of people without government authorization. In 2003, President George W. Bush asked Israel to remove illegal outposts as part of the road map for peace. Israel subsequently removed some outposts; however, in February 2017, the Knessetpassed the Regularization Law, which legalized outposts, including those built …
Legalities
- Another charge is that settlements are “illegal.” On November 18, 2019, Secretary of State Michael Pompeo expressed the Trump administration’s position that “the establishment of Israeli civilian settlements in the West Bankis not per se inconsistent with international law.” The idea that settlements are illegal derives primarily from UN resolutions and the International Court of Justi…
Obstacles?
- Since 1967, Israelis have been divided over two competing ideas of what to do with the territories captured in the war. The Land for Peace advocates argue that Israel should evacuate most of the area in exchange for a peace agreement that provides Israelis with peace and security. By contrast, the proponents of Greater Israel insist that the land is part of the biblical homeland of t…
Rights Versus Wisdom
- The implication of many settlement critics is that it would be better for peace if the West Bank were Judenrein. It would certainly be called racist if Jews were barred from living in New York, Paris or London; barring them from living in the West Bank, the cradle of Jewish civilization, would be no less objectionable. On the other hand, though Jews may have the right to live in the territor…
Why Is Ownership of The West Bank So Contested?
Why Do Palestinians Object to The Israeli Settler Movement?
- Though they are neighbors and sometimes co-workers, relations between Jews and Palestinians on the West Bank are seldom friendly. West Bank Palestinians, who are majority Muslim, see themselves as the area’s indigenous inhabitants; many of their ancestors have lived and farmed in the West Bank for many centuries. Palestinians contend that Israeli settlements in the West Ban…
Why Do Israelis Want to Live in The West Bank?
- Israelis choose to live in the West Bank for many reasons. The popular stereotype of Jewish settlers as religious fanatics determined to reclaim the entire ancient homeland they believe was given to Jews by God is not quite accurate. It’s estimatedthat only about a quarter of West Bank settlers live there out of ideological conviction. Still, these fervent settlers are a vocal and highly …
Are Israel’s West Bank Settlements Legal Or Not?
- Most legal experts and the United Nations agree that Israeli settlements in the West Bank violate international law. The 1949 Geneva Convention, which Israel signed, prohibits an occupying state from moving its own civilians into the territory it occupies. According to the International Court of Justice, the UN’s main judicial body, the West Bank i...