
What was the name of Champlain's first settlement?
After 1603, Champlain's life and career consolidated into the path he would follow for the rest of his life. From 1604 to 1607, he participated in the exploration and creation of the first permanent European settlement north of Florida, Port Royal, Acadia (1605).
Which was Champlain most famous settlement?
He is best known for establishing the first French settlement in the Canadian territory, and founding the city of Quebec. Because of this, Champlain became known as the “Father of New France.”
Where did Champlain build his settlement?
Quebec CityHe sent Champlain to establish a settlement at Quebec (now Quebec City), where the fur trade with First Nations could be controlled more easily. Port-Royal, Nova Scotia, established by Champlain in 1605, was the centre of Acadian life. This reconstruction is a national historic park.
What did Champlain discover?
French explorer Samuel de Champlain began exploring North America in 1603, establishing the city of Quebec in the northern colony of New France, and mapping the Atlantic coast and the Great Lakes, before settling into an administrative role as the de facto governor of New France in 1620.
What land did Samuel de Champlain discover?
Known as the “Father of New France,” Champlain founded Quebec (1608), one of the oldest cities in what is now Canada, and consolidated French colonies. He also made important explorations of what is now northern New York, the Ottawa River, and the eastern Great Lakes.
Who founded the colony of Quebec?
Samuel de ChamplainPermanent European settlement of the region began only in 1608, when Samuel de Champlain established a fort at Cape Diamond, the site of present-day Quebec city, then called Stadacona. A half century later the French settlement had a meagre population of some 3,200 people.
What was the first settlement in Canada?
In 1604, the first European settlement north of Florida was established by French explorers Pierre de Monts and Samuel de Champlain, first on St. Croix Island (in present-day Maine), then at Port-Royal, in Acadia (present-day Nova Scotia). In 1608 Champlain built a fortress at what is now Québec City.
Who founded the first permanent settlement for France?
In 1534, Jacques Cartier planted a cross in the Gaspé Peninsula and claimed the land in the name of King Francis I. It was the first province of New France. The first settlement of 400 people, Fort Charlesbourg-Royal (present-day Quebec City), was attempted in 1541 but lasted only two years.
What was the first permanent settlement in Canada?
Samuel de Champlain's Settlement Samuel de Champlain's impressive settlement was the first permanent European settlement built in Canada. July 1608: Samuel de Champlain arrives near what is now Quebec City. He has been entrusted by the King of France to create a permanent trade settlement and a new nation: New France.
Who discovered Canada?
The survey found that when asked the open-ended question of “who discovered Canada,” 21 per cent of overall respondents named Indigenous people. Some 16 per cent offered up the name of Jacques Cartier, the French explorer who made several voyages to the country's shores and waterways beginning in 1534.
Why is Lake Champlain called that?
About the Water History: Lake Champlain was named in 1609 by Samuel de Champlain, a French explorer. During the Revolutionary War, the lake was an important asset for allowing movement from the colonies to Canada and keeping New England a strong, connected force.
Who found Lake Champlain?
Samuel de Champlain1609. In July, Samuel de Champlain explores the Lake. Champlain traveled up the Richelieu River with his native allies to drive the Iroquois from the Lake. The French explorer gave us the first written account of the region; the first map; and he named the Lake for himself.
Why was Quebec City a good location to develop a settlement?
Economics. As Quebec was settled for its location on the St. Lawrence River with a deep-water harbor, shipping and import/exports dominated the economy. As a port city, Quebec ran a flourishing trade with the French West Indies and with ports in France.
Where is Champlain buried?
“There's one left, and that's Champlain's tomb.” Samuel de Champlain, the French explorer who founded Quebec City in 1608, has been dubbed “the father of New France.” His name graces streets, bridges, and a major lake on the Canada-U.S. border, but his final resting place remains unknown.
When did Samuel de Champlain found Quebec?
1608Not only did he found Québec in 1608, but for 25 years he tirelessly championed the ambitious project to establish a French colony in the St. Lawrence Valley.
Why did early Frenchman settle in Quebec?
They came in hopes of gaining some social mobility or sheltering themselves from religious persecution by a republican and secular France. For the most part, they settled in Montreal and Quebec City.
Where did Champlain settle?
After exploration of the Bay of Fundy, a settlement was established on Saint Croix Island. During the summer and early fall of 1604, Champlain ventured along the mid-Maine coast as far as Georges River.
What did Champlain do in 1606?
In the summer of 1606, Champlain worked on his map of the region, as well as explored around the southern tip of Cape Cod. The winter of 1606/7 was much easier, but just as the small colony seemed to be establishing itself, the French crown revoked De Monts’ charter. In the summer of 1607, all the colonists, except a caretaker, left for France. During their four years of colonization, the French had acquired considerable geographical knowledge of the region, traded with native peoples, and shown that arable cultivation was viable.
Where did De Monts and Champlain go on their expedition?
The following summer, De Monts and Champlain took a small expedition southward along the coasts of present-day Maine and Massachusetts as far as Cape Cod. The party entered the Kennebec and Androscoggin rivers, sailed across Cape Cod Bay, and reached Nauset Harbor on the Cape. On their return, De Monts removed the settlement from St. Croix across the Bay of Fundy to a new location at Port-Royal overlooking Annapolis Basin. The habitation built at Port-Royal was a defensive structure that accommodated the colonists, their supplies, and workshops; it was the forerunner of similar trading posts built by the French elsewhere on the continent during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. During the winter of 1605/6, a further twelve men died of scurvy.
When was Acadia settled?
The Settlement of Acadia 1604-1607. In 1604, a French expedition led by merchant venturer Pierre Du Gua, Sieur de Monts, and including geographer and cartographer Samuel de Champlain, arrived off the coast of what is today southwestern Nova Scotia. After exploration of the Bay of Fundy, a settlement was established on Saint Croix Island.
Why was Saint Croix Island chosen?
Saint Croix Island 1604. The French selected Saint Croix Island because of its good location, safe anchorage, and apparently defensible site. During the summer, houses, stores, and a chapel were hastily erected, while gardens were planted on the island and on a neighboring river bank. However, a bitter winter led to the abandonment ...
What led to the abandonment of the settlement of Saint Croix?
However, a bitter winter led to the abandonment of the settlement. The freezing of the Saint Croix River left the site vulnerable to attack, while a shortage of fresh food led to an outbreak of scurvy and the death of thirty-five men, nearly half of De Monts’ company. The French first settled on Saint Croix Island in the middle ...
What did the French do during their four years of colonization?
During their four years of colonization, the French had acquired considerable geographical knowledge of the region, traded with native peoples, and shown that arable cultivation was viable. In the early twentieth century, French exploration and settlement of Acadia was commemorated in Maine and Nova Scotia.
What did Champlain do in 1606?
In the summer of 1606, Champlain worked on his map of the region, as well as explored around the southern tip of Cape Cod. The winter of 1606/7 was much easier, but just as the small colony seemed to be establishing itself, the French crown revoked De Monts’ charter. In the summer of 1607, all the colonists, except a caretaker, left for France. During their four years of colonization, the French had acquired considerable geographical knowledge of the region, traded with native peoples, and shown that arable cultivation was viable.
When was Champlain's plan for the French settlement on Saint Croix Island?
Champlain’s plan of the French settlement on Saint Croix Island, 1604-05. It is unlikely that such substantial buildings and formal gardens were constructed.
Where did De Monts and Champlain go on their expedition?
The following summer, De Monts and Champlain took a small expedition southward along the coasts of present-day Maine and Massachusetts as far as Cape Cod. The party entered the Kennebec and Androscoggin rivers, sailed across Cape Cod Bay, and reached Nauset Harbor on the Cape. On their return, De Monts removed the settlement from St. Croix across the Bay of Fundy to a new location at Port-Royal overlooking Annapolis Basin. The habitation built at Port-Royal was a defensive structure that accommodated the colonists, their supplies, and workshops; it was the forerunner of similar trading posts built by the French elsewhere on the continent during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. During the winter of 1605/6, a further twelve men died of scurvy.
What is Champlain's Descr?
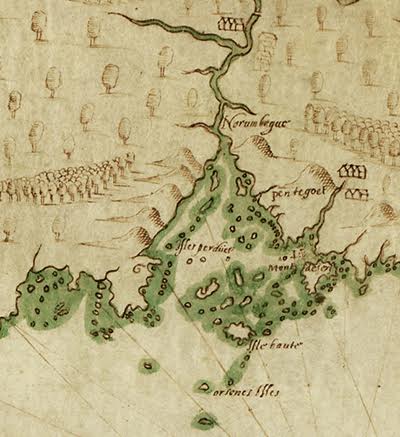
Champlain’s Descr [i]psion des costes – (1607) is the first detailed European map of the Gulf of Maine. Drafted at Port-Royal, the map shows capes, bays, islands, shoals, and rivers along the coast; heights of land useful for navigation; and principal native settlements. Indian guides helped Champlain explore parts of the coast, and also provided information about the interior. Of the French names given to geographical features along the Maine coast, only Mount Desert and Isle au Haut have survived to the present.
Why did the French choose Saint Croix Island?
The French selected Saint Croix Island because of its good location, safe anchorage, and apparently defensible site. During the summer, houses, stores, and a chapel were hastily erected, while gardens were planted on the island and on a neighboring river bank. However, a bitter winter led to the abandonment of the settlement. The freezing of the Saint Croix River left the site vulnerable to attack, while a shortage of fresh food led to an outbreak of scurvy and the death of thirty-five men, nearly half of De Monts’ company.
Where did the French settle in 1605?
This page commemorates the 400th anniversaries of the French settlements on Saint Croix Island (Maine) in 1604 and at Port-Royal ( now Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia) in 1605. Although both settlements were short-lived, they mark the beginnings of a French presence in the area that the French called Acadie (Acadia) and that today comprises eastern Maine and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island.
Who edited the Atlas of Canada?
Jean Daigle, Robert LeBlanc, “Acadian Deportation and Return” in Historical Atlas of Canada, Volume I, From the Beginning to 1800, edited by R. Cole Harris, plate 30. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1987.
How many chiefs did Champlain kill?
In a battle that began the next day, two hundred and fifty Haudenosaunee advanced on Champlain's position, and one of his guides pointed out the three chiefs. In his account of the battle, Champlain recounts firing his arquebus and killing two of them with a single shot, after which one of his men killed the third.
How did Champlain die?
Champlain had a severe stroke in October 1635, and died on 25 December, leaving no immediate heirs. Jesuit records state he died in the care of his friend and confessor Charles Lallemant.
What did Champlain order his men to do?
Upon arriving in Quebec, Champlain later wrote: "I arrived there on the 3rd of July, when I searched for a place suitable for our settlement; but I could find none more convenient or better suited than the point of Quebec, so called by the savages, which was covered with nut-trees." Champlain ordered his men to gather lumber by cutting down the nut-trees for use in building habitations.
What did Samuel Champlain learn?
Born into a family of mariners (both his father and uncle-in-law were sailors, or navigators), Samuel Champlain learned to navigate, draw, make nautical charts, and write practical reports. His education did not include Ancient Greek or Latin, so he did not read or learn from any ancient literature.
What tribes were represented in the engraving of the Battle of Lake Champlain?
Engraving based on a drawing by Champlain of his 1609 voyage. It depicts a battle between Iroquois and Algonquian tribes near Lake Champlain
What is the plaque in Honfleur?
Plaque in Honfleur commemorating Champlain's departures. Painting by George Agnew Reid, done for the third centennial (1908), showing the arrival of Samuel de Champlain on the site of Quebec City.
How did Du Val's plot get foiled?
Du Val's plot was ultimately foiled when an associate of Du Val confessed his involvement in the plot to Champlain's pilot, who informed Champlain . Champlain had a young man deliver Du Val, along with 3 co-conspirators, two bottles of wine and invite the four worthies to an event onboard a boat.
How long did Champlain serve in the army?
In 1593, Champlain served in the army of Henry of Navarre – also known as King Henry IV of France. He served in the army for 5 years, until King Henry’s and France’s victory in 1598.
What was Champlain known for?
He is best known for establishing the first French settlement in the Canadian territory, and founding the city of Quebec. Because of this, Champlain became known as the “Father of New France.”1. Biography.
What was Samuel de Champlain's last voyage?
This discovery would be his last great voyage of exploration. He would spend the next years of his life trying to re-establish and maintain his authority in New France. Later Years and Death. Samuel de Champlain returned to France in July 1616 where he learned his title of lieutenant had been taken away.
What was the goal of Samuel de Champlain?
Once again, the goal was to start a new French colony. Champlain found an area on the shores of the St. Lawrence river and began constructing a fort and other buildings. In July 1608, Samuel de Champlain and his men created the first successful French colony in New France.
Why did Henry IV want to settle in the New World?
King Henry IV wanted to the French to begin settling in the New World in hopes that wealth could be brought back to France. So he sent an expedition to locate a place in the New World to establish a French colony and fur trade settlement. Samuel de Champlain would be among the men who would take part in this venture.
Where was Samuel de Champlain born?
Biography. Early Life. Samuel de Champlain was born in the French village Brouage in the Province of Saintonge. Historians do not know his exact date of birth, but most agree it was between 1567 and 1570.2 His father was Antoine Champlain and his mother was Marguerite Le Roy.
When did Champlain return to New France?
The King agreed, and Champlain returned to New France again in 1620. He spent the rest of his life focusing on governing and growing the territory rather than exploration. In 1628, Champlain became the deputy of the “Company One Hundred Associates” organized by Cardinal Richelieu to colonize New France.
When did Champlain establish Quebec?
Establishing Quebec. In 1608, Champlain was named lieutenant to de Monts, and they set off on another expedition up the St. Lawrence. When they arrived in June 1608, they constructed a fort in what is now Quebec City. Quebec would soon become the hub for French fur trading.
What did Champlain discover?
The group sailed up the St. Lawrence and Saguenay rivers and explored the Gaspé Peninsula, ultimately arriving in Montreal. Although Champlain had no official role or title on the expedition, he proved his mettle by making uncanny predictions about the network of lakes and other geographic features of the region.
Who Was Samuel de Champlain?
French explorer Samuel de Champlain began exploring North America in 1603, establishing the city of Quebec in the northern colony of New France, and mapping the Atlantic coast and the Great Lakes, before settling into an administrative role as the de facto governor of New France in 1620.
Where did Champlain go on his voyage?
Given his usefulness on Du Pont's voyage, the following year Champlain was chosen to be geographer on an expedition to Acadia led by Lieutenant-General Pierre Du Gua de Monts. They landed in May on the southeast coast of what is now Nova Scotia and Champlain was asked to choose a location for a temporary settlement.
What was Champlain's first battle?
When they arrived in June 1608, they constructed a fort in what is now Quebec City. Quebec would soon become the hub for French fur trading. The following summer, Champlain fought the first major battle against the Iroquois, cementing a hostile relationship that would last for more than a century.
When did Champlain retire?
Champlain returned to be its governor. By this time, however, his health was failing and he was forced to retire in 1633. He died in Quebec on Christmas Day in 1635.
When did Champlain and his team sail down the coast of New England?
In the summer of 1605, the team sailed down the coast of New England as far south as Cape Cod. Although a few British explorers had navigated the terrain before, Champlain was the first to give a precise and detailed accounting of the region that would one day become Plymouth Rock.
Overview
Samuel de Champlain was a French colonist, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean, and founded Quebec, and New France, on 3 July 1608. An important figure in Canadian history, Champlain created the first accurate coastal map during his explorations, and founded va…
Birth year, location and family
Champlain was born to Antoine Champlain (also written "Anthoine Chappelain" in some records) and Marguerite Le Roy, in either Hiers-Brouage, or the port city of La Rochelle, in the French province of Aunis.
He was born on or before 13 August 1574, according to a recent baptism record found by Jean-Marie Germe, French genealogist.
Early travels
In year 3 his uncle-in-law , a navigator whose ship Saint-Julien was to transport Spanish troops to Cádiz pursuant to the Treaty of Vervins, gave Champlain the opportunity to accompany him.
After a difficult passage, he spent some time in Cádiz before his uncle, whose ship was then chartered to accompany a large Spanish fleet to the West Indies, …
Founding of Quebec
In the spring of 1608, Dugua wanted Champlain to start a new French colony and fur trading centre on the shores of the St. Lawrence. Dugua equipped, at his own expense, a fleet of three ships with workers, that left the French port of Honfleur. The main ship, called the Don-de-Dieu (French for the Gift of God), was commanded by Champlain. Another ship, the Lévrier (the Hunt Dog), was com…
Relations and war with Native Americans
During the summer of 1609, Champlain attempted to form better relations with the local First Nations tribes. He made alliances with the Wendat (called Huron by the French) and with the Algonquin, the Montagnais and the Etchemin, who lived in the area of the St. Lawrence River. These tribes sought Champlain's help in their war against the Iroquois, who lived farther south. Champlain set off with n…
Marriage
One route Champlain may have chosen to improve his access to the court of the regent was his decision to enter into marriage with the twelve-year-old Hélène Boullé. She was the daughter of Nicolas Boullé, a man charged with carrying out royal decisions at court. The marriage contract was signed on 27 December 1610 in presence of Dugua, who had dealt with the father, and the couple was married three days later. The terms of the contract called for the marriage to be con…
Exploration of New France
On 29 March 1613, arriving back in New France, he first ensured that his new royal commission be proclaimed. Champlain set out on May 27 to continue his exploration of the Huron country and in hopes of finding the "northern sea" he had heard about (probably Hudson Bay). He travelled the Ottawa River, later giving the first description of this area. Along the way, he apparently dropped o…
Military expedition
On 1 September 1615, at Cahiagué (a Wendat community on what is now called Lake Simcoe), he and the northern tribes started a military expedition against the Iroquois. The party passed Lake Ontario at its eastern tip where they hid their canoes and continued their journey by land. They followed the Oneida River until they arrived at the main Onondaga fort on October 10. The exact location of th…