Informal settlement increases public spending for development and financial damage for low income labor because of their funding of illegal construction on public land. Here I introduce 8 effective ways for urban renewal of informal settlement that needs political and economical intervention and development. South Asia informal settlement upgrade
Full Answer
What is informal settlement growth?
The growth of informal settlements, slums and poor residential neighbourhoods is a global phenomenon accompanying the growth of urban populations.
How many people live in informal settlements worldwide?
The growth of informal settlements, slums and poor residential neighbourhoods is a global phenomenon accompanying the growth of urban populations. An estimated 25% of the world’s urban population live in informal settlements, with 213 million informal settlement residents added to the global population since 1990 ( UN-Habitat, 2013b: 126–8 ).
What is eighty20 doing about informal settlements in South Africa?
For the past five years Eighty20 has worked closely with the Housing Development Agency to enumerate and profile informal settlements across South Africa. In part, this research was borne out of the need to fill key gaps in our understanding of informal settlements in South Africa.
How should governments respond to informal settlements?
For decades, governments in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) have responded to informal settlements with a range of approaches, including denying their existence, reacting with benign indifference, evicting residents, and demolishing settlements in whole or in part.
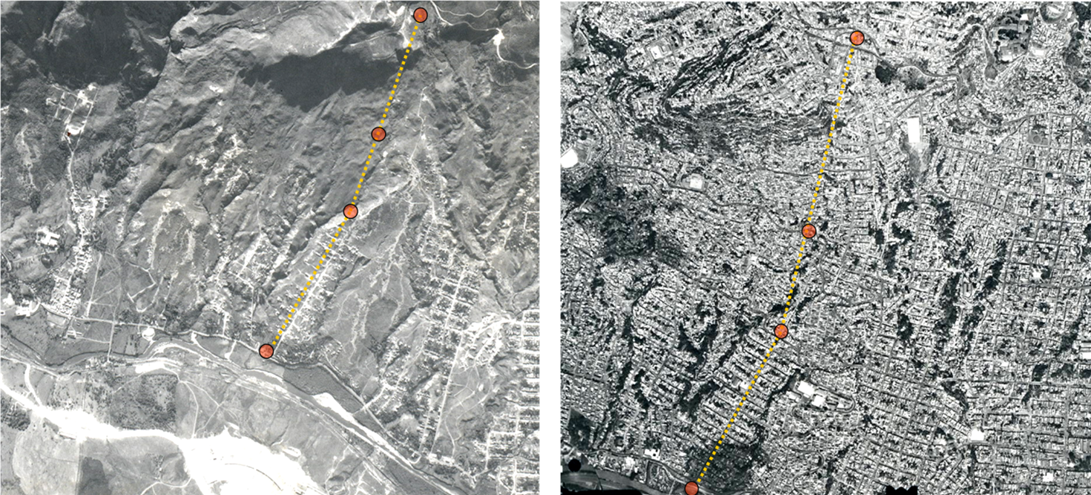

What are examples of informal settlements?
Common categories or terms associated with informal housing include: slums, shanty towns, squats, homelessness, backyard housing and pavement dwellers.
What does informal settlement mean?
Informal settlements are residential areas that do not comply with local authority requirements for conventional (formal) townships. They are, typically, unauthorised and are invariably located upon land that has not been proclaimed for residential use.
How can informal settlement be solved?
Additionally, Janice Perlman4 sets forth eight recommendations for the improvement of informal settlements: (1) provide a variety of housing options in regards to tenure and payment, such as short-term rental, long-term lease, cohousing, and financed purchase; (2) invest in education, healthcare, and social services ...
What are the 3 biggest problems of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management.
What is another word for informal settlement?
Shanty town Sometimes called a squatter, informal or spontaneous settlement, shanty towns often lack proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity, hygienic streets, or other basic human necessities.
Are informal settlements illegal?
Informal settlements are housing areas that are often illegally built on municipal land.
What are the causes of informal settlement?
According to UN-Habitat (2015:2), informal settlements are caused by a range of interrelated factors, including population growth and rural-urban migration, lack of affordable housing for the urban poor, weak governance (particularly in the areas of policy, planning, land and urban management resulting in land ...
What are the advantages of informal settlement?
It offers choice, it gives people what they want, it enables individual creativity and it is affordable. It is also simple to build and easy to use. So, a powerful brand — the informal settlement — is in town. And it's reshaping the city.
What is the problem of informal settlers?
Informal Settlements have been associated with many social problems such as high levels of poverty, illiteracy and crime. Not forgetting the inadequate local services, especially healthcare, education and youth facilities.
What are the consequences of informal settlements?
Informal settlements are characterized by a lack of basic services, pollution, overcrowding and poor waste management. These characteristics impact negatively on the environment posing risk and susceptibility to health problems associated with informal settlements.
What is the biggest informal settlement in South Africa?
SowetoThose living in informal dwellings – defined as a wood and iron structure – have decreased slightly from 16.2% in 1996 to 13.0% in 2016....These are the 20 biggest townships in the country (Stats SA, 2011)#1TownshipSoweto2011 Population1 271 628Neighbouring townJohannesburg19 more columns•Aug 14, 2016
What are the characteristics of informal settlements?
Characteristics include inadequate access to safe water and sanitation, poor quality of housing, overcrowding, and insecure residential status.
Where are informal settlements?
Informal settlements often sit on the periphery of urban areas, lacking access to markets and/or resources. For women, for example, this can heighten barriers they face in accessing livelihood opportunities.
What is formal and informal settlement?
Formal areas have cadastral organization with streets and public services such as electricity, tap water, telephone, school, sanitation. Informal areas are squatter settlements and have no cadastral organization or public services.
What are informal settlements in geography?
Informal settlements are: 1. areas where groups of housing units have been constructed on land that the occupants have no legal claim to, or occupy illegally; 2. unplanned settlements and areas where housing is not in compliance with current planning and building regulations (unauthorized housing).
What is informal settlement in Oxford dictionary?
noun. /ɪnˌfɔːml ˈsetlmənt/ /ɪnˌfɔːrml ˈsetlmənt/ (South African English) a place where people decide to live and build temporary shelters, often followed by more permanent houses.
What are the tenure problems in informal unplanned settlements and shacks?
More important, the tenure problems in informal unplanned settlements and shacks play a direct role in purchasing electrical appliances or other expensive investments in efficiency. Migrant workers continue to play a large role in many countries' urban communities.
How does gender inequality affect sanitation?
Gender inequalities in slums have a cyclical effect on the required know-how of sanitation. Women cannot earn wages independently or make decisions for the household and, as their daily tasks are undertaken in the settlement itself, they experience the worst effects of these poor conditions. Women do not leave their homes of an evening due to the risk of sexual harassment, so toilet waste is often discarded through windows into adjoining alleyways. Women and girls are often denied formal education, which also affects their children’s health, development and skills. Women in many informal settlements spend several hours each day collecting water from a remote source, time which could be invested in building capabilities through education and training (UN-Habitat, 2008: 85).
What are slums in the city?
Slums are highly diverse sites of mobility, in which dwellers’ interactions with the city can lead to economic and social advancement .
What is the importance of sanitation?
It is a key factor in the prevention of disease and is a critical component of socio-technical and chemical systems of urban settlement (cf. ibid.: 107–8; Katukiza et al., 2012).
Does squatting limit migration?
While policies designed to make squatting less attractive can limit rural–urban migration, relocation of slums and squatter areas once they come into being, which allows land to be redeveloped to a higher use, is another policy pursued in some countries. Lall et al. (2008) and Takeuchi et al. (2008) use Indian data to study the preconditions for successful policies of this type. They estimate slum dwellers’ valuations of housing and neighborhood characteristics, with the goal of gauging what characteristics new (titled) settlements must have in order to make relocation welfare improving. 36
What is informal settlement?
Suburbanization and informal settlement in self-grown residences are the words that are increasingly used today in urban planning, urbanization, geography, urban sociology and the ones. Informal settlement is one of the consequences of the modern life and extensive urbanization that is considered as one of the most important problems of metropolitans (Khazaee et al, 91- 2012). During the recent years, for the first time, number of residents of cities has equaled to those of nonurban regions (Egger, 2005- 2). As it was announced by the Head of Informal Settlement Program of the UN, the year 2007 is the first year in human history when over half of the world population lives in cities. In the said year, we have witnessed that number of population living in the poor regions has exceeded 1 billion persons. According to predictions made by the UN, it has been revealed that more than 60% of world population will settle in cities until the year 2030 and the developing world will enjoy an urban rather than rural characteristic until the year 2017 respectively. It may be understood that such urbanization and poverty will be regarded as the greatest world challenges (United Nation, 2004). In case of persistence of the present undesirable condition, number of villagers residing in poor urban regions will be increased to 2 billion individuals within the next three decades.
Why are informal settlements important?
Considering the studies conducted to find the reason of informal settlements, the most important reasons for occurrence of this phenomenon includes expensive lands and shortcoming of housing, immigration and lack of any suitable employment which result in settlement in urban margins. This phenomenon is more obvious in the developing countries. Settlement in the margins of the city has faced several problems including unauthorized constructions and lack of health and security facilities resulting in several bottlenecks in social, economic and environmental fields in the margins of the cities. On the other hand, a look to the approaches for intervention in informal settlements indicates that until before 1960s, governmental investment in low income class housing sector was not often considered necessary; however, the increasing need to solve housing problem for the said class resulted in specific attention to that in terms of policies such as social building construction and empowerment throughout south countries. In 1970s, the service land project was set forth the results of which were accompanied by shortage of land and technical problems. In 1980s, empowerment policy was set forth aiming at public mobilization for improving the conditions of informal settlement which was followed by partnership-based procedures. The current procedure in intervention approaches which has been continued since 2000 is in parallel with guaranty of settlement in slum-free cities which has been formed with the goal of guaranteeing ownership and housing right for all people, public engagement in parallel with sustainable development and unforceful resettlement.
What is informal settlement?
Informal Settlements. definition. Informal Settlements means an area where no sub division of individual erven has taken place in terms of Town planning legislation.
What happens if the infrastructure of the informal settlements change?
Should the infrastructure of the Informal Settlements change, the City will review the service offered and consider rendering a containerised service.
What is a viatical settlement broker?
Viatical settlement broker means a person, including a life insurance producer as provided for in section 508E.3, who, working exclusively on behalf of a viator and for a fee, commission, or other valuable consideration, offers or attempts to negotiate viatical settlement contracts between a viator and one or more viatical settlement providers or one or more viatical settlement brokers. Notwithstanding the manner in which the viatical settlement broker is compensated, a viatical settlement broker is deemed to represent only the viator, and not the insurer or the viatical settlement provider, and owes a fiduciary duty to the viator to act according to the viator’s instructions and in the best interest of the viator. “Viatical settlement broker” does not include an attorney, certified public accountant, or a financial planner accredited by a nationally recognized accreditation agency who is retained to represent the viator and whose compensation is not paid directly or indirectly by the viatical settlement provider or purchaser.
What is contractual settlement date?
Contractual Settlement Date is the earlier of (i) the date upon which all of the required Deposit Securities, the Cash Component and any other cash amounts which may be due are delivered to the Trust and (ii) the latest day for settlement on the customary settlement cycle in the jurisdiction where any of the securities of the relevant Fund are customarily traded. A Creation Unit of Shares will not be issued until the transfer of good title to the Trust of the portfolio of Deposit Securities and the payment of the Cash Component and the applicable Transaction Fee have been completed. When the sub-custodian confirms to the Custodian that the required securities included in the Portfolio Deposit (or, when permitted in the sole discretion of the Trust, the cash value thereof) have been delivered to the account of the relevant sub-custodian, which confirmation shall be done promptly after such delivery, the Custodian shall notify the Distributor and Transfer Agent, and the Trust will issue and cause the delivery of the Creation Unit of Shares via DTC.
How many households were upgraded in the Upgrading of Informal Settlements Programme?
Through the Upgrading of Informal Settlements Programme, 67 548 households were upgraded in partnership with provinces and municipalities, during the review period.
What is structured settlement payment rights?
Structured settlement payment rights means rights to receive periodic payments under a structured settlement , whether from the structured settlement obligor or the annuity issuer, where:
What is a settlement date for a termination?
Termination Settlement Date means, for any Terminated Obligation, the date customary for settlement, substantially in accordance with the then-current market practice in the principal market for such Terminated Obligation (as determined by the Calculation Agent), of the sale of such Terminated Obliga tion with the trade date for such sale occurring on the related Termination Trade Date.
