
What is the northernmost human settlement in Canada?
Located in the Ellesmere Island’s northeastern tip in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut, Alert is the country’s and the world’s northernmost permanent human settlement. It is only 817 km away from the North Pole. It is located at a latitude of 82°28' N. Alert is home to around 62 individuals.
What is the northernmost populated area in Canada?
However, the northernmost 'populated' area in Canada (and in the world) is Canadian Forces Station (CFS) Alert (just north of Alert, Nunavut) on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island - latitude 82.5°N - just 834 kilometres (518 mi) from the North Pole. ===============================================================================
How did people settle in Canada?
Permanent settlement depended on agricultural land—which in Canada occurs in patches, separated by physical barriers. Different patches were settled by people from various European countries, so that a diversity of cultures and settlement patterns developed across the country.
What are settlement patterns in Canada?
( See also Human Geography and Canada .) A human settlement is a place where people live. Settlement patterns describe the ways in which villages, towns, cities and First Nation reserves are distributed, as well as the factors that influence this arrangement.

What is the most northern settlement in the world?
LongyearbyenEvery winter the community of Longyearbyen, the world's northernmost town at 78 degrees North latitude, holds a jazz festival to liven up the perpetual darkness.
What is the northern region of Canada called?
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut.
What are the most northern lands in Canada?
Canada's north is a vast area, the three territories alone, Nunavut, Yukon and Northwest Territories, encompass approximately 40% of the total area of Canada.
What is Northern Canada known for?
The Northern Territories. Occupying nearly 40 per cent of the country's total landmass, the North is an iconic yet mysterious region of Canada. Igloos, icebergs, polar bears, seal hunters and the Northern Lights may be some of Canada's best-known symbols, but they're found in a part of the country few will ever visit.
Where is the northern region in Canada?
The North encompasses the territories as well as the northern regions of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia. The South refers to the southern regions of these provinces and includes Prince Edward Island, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
What country is directly north of Canada?
Answer and Explanation: The country of Russia can be reached traveling due north from Canada.
Who owns Nunavut?
On April 1, 1999 the map of Canada was re-drawn: the Northwest Territories divided into two territories to allow for the creation of Nunavut, a homeland for Canada's Inuit.
Does anyone live in Nunavut?
The total current population of Nunavut (as of 2011) is estimated to be around 33,330 people, the vast majority (84%) of whom are Inuit. Of the approximately 28,000 Inuit living in Nunavut, more than half of them reside in the eastern Qikiqtaaluk region of the territory and, remarkably, they are mostly young people.
What are the regions of Canada called?
PopulationRegionProvince/TerritoryAtlantic regionNewfoundland and Labrador Prince Edward Island Nova Scotia New BrunswickCentral CanadaQuebec OntarioPrairie ProvincesManitoba Saskatchewan AlbertaWest CoastBritish Columbia1 more row•Jul 1, 2012
What are the 7 regions in Canada?
Canada may be divided into seven physiographic regions: Arctic Lands, Cordillera, Interior Plains, Hudson Bay Lowland, Canadian Shield Forest Lands, St Lawrence Lowlands and Appalachia. Divisions are based on each area's relatively similar physical geography and landforms.
What are the Canadian regions?
Canada is the second largest country in the world. Canada is made up of five geographic regions, the Atlantic Provinces, Central Canada, the Prairies, the West Coast, and the Northern Territories.
How is Canada divided into 5 regions?
Canada, the strong north, stretches 9,984670 sq km in area and is made up of five distinct regions. Atlantic, Central, Prairie, West coast and North. Ottawa is the capital of Canada and is situated in the province of Ontario.
All locations
Northernmost civilian and functional settlement; home to the northernmost post office
Larger cities
Northernmost cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants. The population data may include municipalities, urban areas or metropolitan areas.
What is the northernmost region of Canada?
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 per cent of Canada's population .
What is Northern Canada?
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, ...
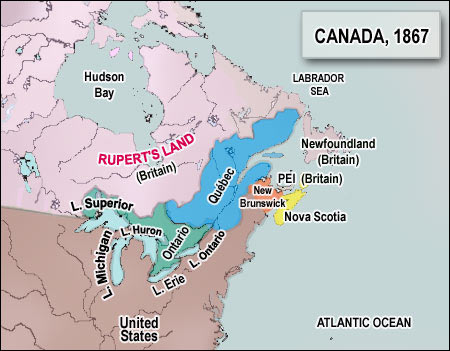
What was the HBC claim to Rupert's Land?
The HBC's claim to Rupert's Land, which, as the company was the de facto administrator, included the North-Western Territory , was purchased by the Canadian government in 1869. After buying Rupert's Land, Canada renamed the area it had purchased the Northwest Territories. Shortly thereafter the government made a series of treaties with the local First Nations regarding land title. This opened the region to non-Native settlement, as well as to forestry, mining, and oil and gas drilling. In 1896, gold was discovered in the Yukon, leading to the Klondike Gold Rush in 1896-1899 and the first substantial white settlements were made in the near north. To deal with the increased settlement in the Klondike, the Yukon Territory was created in 1898.
What provinces did Canada create out of the Northwest Territory?
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Canada reduced the size of the Northwest Territory by carving out new provinces out of it such as Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba together with the new territory of the Yukon while transferring other parts of the Northwest Territory to Ontario and Quebec.
How much of Canada is north?
Using the political definition of the three northern territories, the north, with an area of 3,921,739 km 2 (1,514,192 sq mi), makes up 39.3% of Canada.
Why is Canada so poor?
Though GDP per person is higher than elsewhere in Canada, the region remains relatively poor, mostly because of the extremely high cost of most consumer goods, and the region is heavily subsidised by the government of Canada .
When did Nunavut become a territory?
In 1982 a referendum was held to decide on splitting the Northwest Territories. This was followed by the 1992 Nunavut creation referendum with the majority of the people in far north voting to leave the Northwest Territories, leading to the new territory of Nunavut being created in 1999. Very few non-Indigenous people have settled in these areas, and the residents of the far north represent less than 1% of Canada's total population.
What were the main resources of Europeans?
Different groups of Europeans came at different times to develop and export the abundant fish, furs, forests, and minerals. With the development of each new resource, new settlements were established. Most of the settlements based on these resources remained small, however, and some of them disappeared when their resources were depleted. A few port cities—including the eastern cities of St. John’s, Newfoundland; Halifax, Nova Scotia; and Saint John, New Brunswick—continued to grow as they benefited from the export of successive resources. Montreal owed its early growth to the fur trade, but later it became an important entrepôt for exporting a succession of raw and processed materials and importing manufactured goods from Europe. Later Toronto and the west-coast city of Vancouver also grew quickly because of entrepôt activities. Winnipeg, Manitoba, owed its early growth to its gateway role in the agricultural development of the interior plains.
What were the settlement patterns of the Europeans?
Settlement patterns. When Europeans began exploring and developing resources in what is now Canada, they found the land sparsely populated by many different First Nations in the south and the Inuit in the north. The indigenous peoples were primarily hunters and gatherers and often were nomadic. Because they were few in number, ...
What is the impact of urbanization on Canada?
In the Niagara Peninsula of southwestern Ontario, the area with the best climate in Canada for producing soft fruits and grapes, urbanization has destroyed some one-third of the fruit land. To prevent further reduction, the Ontario Municipal Board in the 1980s delineated permanent urban boundaries and ordered that urban growth be directed away from fruit-growing areas.
Where did the Appalachian settlers live?
In the Appalachian region, farms are spaced along the roads at irregular intervals wherever land can be cultivated. In Quebec the first settlers laid off long, narrow tillage strips from the shores of the Gulf of St. Lawrence or the St. Lawrence River into the interior. As settlement moved farther inland, roads were built parallel to the waterways, from which further narrow lots extended on either side. The same pattern occurred in the Red River valley of Manitoba and even parts of Ontario, where the early settlers were also French.
Where is the French farmland?
Long narrow strips of farmland, typical of French Canada, lie along the roads in the St. Lawrence River valley near Montreal.
Did settlement occur in patches?
Settlement did not proceed sequentially westward from an Atlantic beginning. Permanent settlement depended on agricultural land—which in Canada occurs in patches, separated by physical barriers. Different patches were settled by people from various European countries, so that a diversity of cultures and settlement patterns developed across the country.
What Factors Influence Human Settlement?
They are: the kind of natural resources found in the area, the types of transportation methods available at the time of settlement, and government policy.
What are the types of settlements in Canada?
In Canada, types of human settlement categorized by geographers and the government include urban and rural settlements, census metropolitan areas, First Nation reserves , and Métis settlements.
How did government policy affect settlement in Canada?
They set the rules for the size and shapes of farms and aided in the development of primary source industries like mining. Governments also determined where roads, canals and bridges would be built, as well as the location of town sites, military bases, and First Nation reserves .
What is a human settlement?
A human settlement is a place where people live. Settlement patterns describe the ways in which villages, towns, cities and First Nation reserves are distributed, as well as the factors that influence this arrangement.
How does human settlement affect the environment?
Human settlement affects the environment in many ways. Growing and concentrated populations need land, food and water, as well as other necessities like heat and sewage disposal. In Canada’s urban and rural communities these needs put stress on the natural environment.
What was the resource based economy of Canada?
The resource-based economy on which the original settlement was based on may change over time. Areas in Canada that were settled before 1800 are typically situated on water. At this time, lakes and rivers were the main methods of transportation.
What is a census metropolitan area?
A census metropolitan area (CMA) is an urban area made up of one of more neighbouring municipalities located around a central core. A CMA must have a total population of at least 100,000.
Overview
Demographics
Using the political definition of the three northern territories, the north, with an area of 3,921,739 km (1,514,192 sq mi), makes up 39.3% of Canada.
Although vast, the entire region is very sparsely populated. As of 2021, only about 118,160 people lived there compared to 36,991,981 in the rest of Canada.
The population density for Northern Canada is 0.03/km (0.078/sq mi) (0.08/km (…
Subdivisions
As a social rather than political region, the Canadian North is often subdivided into two distinct regions based on climate, the near north and the far north. The different climates of these two regions result in vastly different vegetation, and therefore very different economies, settlement patterns, and histories.
The "near north" or sub-Arctic is mostly synonymous with the Canadian boreal f…
Territoriality
Since 1925, Canada has claimed the portion of the Arctic between 60°W and 141°W longitude, extending all the way north to the North Pole: all islands in the Arctic Archipelago and Herschel, off the Yukon coast, form part of the region, are Canadian territory and the territorial waters claimed by Canada surround these islands. Views of territorial claims in this region are complicated by disagreements on legal principles. Canada and the Soviet Union/Russia have long claimed that t…
Topography (geography)
While the largest part of the Arctic is composed of permanent ice and the Canadian Arctic tundra north of the tree line, it encompasses geological regions of varying types: the Innuitian Mountains, associated with the Arctic Cordillera mountain system, are geologically distinct from the Arctic Region (which consists largely of lowlands). The Arctic and Hudson Bay Lowlands comprise a s…
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, much of mainland Northern Canada has a subarctic climate, with a tundra climate in most of the Arctic Archipelago and on the northern coasts, and an Ice cap climate in some parts of the Arctic Cordillera. For more than half of the year, much of Northern Canada is snow and ice-covered, with some limited moderation by the relatively warmer waters in coastal areas with temperatures generally remaining below the freezing mark from Oct…
Recent
Although it has not been on the same scale, some towns and cities have experienced population increases not seen for several decades before. Yellowknife has become the centre of diamond production for Canada (which has become one of the top three countries for diamonds).
In the 2006 Canadian Census, the three territories posted a combined population of over 100,000 people for the first time in Canadian history.
See also
• Arctic policy of Canada
• Geography of Canada
• Northern Alberta
• Northern Manitoba
• Northern Ontario