- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
- Technical explanation of the DSU
- Rules of Conduct on rules and procedures for settling disputes
- Working Procedures for Appellate Review
Full Answer
Why the WTO is bad?
Sheila Page examined five common criticisms of the WTO:
- First, critics argued that multi-lateral trade agreements made poor countries worse off. ...
- Second, it was argued that the WTO prevented countries from following the same protectionist route that had been followed by developed countries. ...
- Third, it was argued that GATS forced countries to liberalise services. ...
Does WTO Dispute Settlement enforce or inform?
for the argument that WTO dispute settlement primarily serves as an enforcement device. It finds much less support for the argument that dispute settlement reduces complexity and clarifies trade law. These results suggest that the role of WTO dispute settlement in generating information on acceptable
Is the use of the WTO Dispute Settlement system biased?
The larger trading nations have been the main users of the WTO Dispute Settlement system during its first four years of existence (1995-1998). This has prompted a debate about whether the DS system is biased against smaller and poorer countries, for example, because of a lack of legal capacities and retaliatory power.
Is the WTO still relevant?
The multilateral trading system embodied by the WTO remains critical to maintaining global interdependence, something that is vital to the economic and security interests of the United States and the rest of the world.
See more

What is WTO dispute settlement?
Disputes in the WTO are essentially about broken promises. WTO members have agreed that if they believe fellow-members are violating trade rules, they will use the multilateral system of settling disputes instead of taking action unilaterally. That means abiding by the agreed procedures, and respecting judgements.
What is settlement of dispute?
Dispute resolution or dispute settlement is the process of resolving disputes between parties. The term dispute resolution is sometimes used interchangeably with conflict resolution.
Why is the WTO dispute settlement important?
It helps to prevent the detrimental effects of unresolved international trade conflicts and to mitigate the imbalances between stronger and weaker players by having their disputes settled on the basis of rules rather than having power determine the outcome.
How long is WTO dispute settlement?
This appellate process must be completed within 90 days. Appeals are heard by a separate group of experts, who review issues of law covered in the panel report and then issue their own report with their own findings and recommendations. In all, it can take about 15 months to settle a dispute in the WTO.
What are the 4 types of disputes?
Civil cases financial issues - such as bankruptcy or banking disputes. housing. defamation. family law.
What are the main methods of settlement of international disputes?
Techniques used for peaceful settlement of international disputes are negotiation, inquiry, mediation, conciliation, arbitration, judicial settlement, resort to regional agencies or arrangements, or other peaceful means of their own choice (Art.
Is WTO dispute settlement Effective?
If one compares the WTO dispute settlement system with the previous dispute settlement system of GATT 1947, the current system has been far more effective. Moreover, its quasi-judicial and quasi-automatic character enables it to handle more difficult cases.
What trade dispute means?
a disagreement between countries about the products they trade with each other, for example, about import taxes or limits on the number of goods that can be imported: a trade dispute with sb All trade disputes with Japan had been settled.
What are 5 benefits of the WTO trading system?
Benefits of WTO membership— Participation in the development of new rules and principles of international trade. ... — Export diversification. ... — Transparent, predictable and attractive investment regime. ... — Increase of sovereign credit ratings. ... — Strengthening positions in trade disputes.
How are trade disputes resolved?
The WTO's forum for arbitration is called the dispute settlement mechanism, which is run by a rotating staff of judges, as well as a permanent staff of lawyers and administrators. The WTO appoints a panel to hear a case if the opposing parties are unable to resolve the issue through negotiations.
What are the 6 functions of the WTO?
Functionsadministering trade agreements.acting as a forum for trade negotiations.settling trade disputes.reviewing national trade policies.building the trade capacity of developing economies.cooperating with other international organizations.
Where is WTO located?
Geneva, SwitzerlandGeneva, Switzerland, where the WTO headquarters is located, is a unique place, with many United Nations and other international organizations, as well as missions to the WTO. The Centre William Rappard (CWR) is the name of the building that has been home to the WTO Secretariat since the WTO was established in 1995.
How do I settle a dispute without going to court?
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution that provides a final and binding outcome to litigation which does not require recourse to the Courts. It is a consensual process in the sense that it will only apply if the parties agree it should.
How do courts settle disputes?
Settling Cases Most civil cases are settled by mutual agreement between the parties. A dispute can be settled even before a suit is filed. Once a suit is filed, it can be settled before the trial begins, during the trial, while the jury is deliberating, or even after a verdict is rendered.
What is a settlement in contract law?
Settlement Agreement is a document which evidences the agreement between the parties therein binding the parties to a settlement to adhere to the terms and conditions agreed as a result of negotiation between the parties.
How do you settle a trade dispute?
There are two main ways to settle a dispute once a complaint has been filed in the WTO: (i) the parties find a mutually agreed solution, particularly during the phase of bilateral consultations; and (ii) through adjudication, including the subsequent implementation of the panel and Appellate Body reports, which are ...
What is a dispute in the WTO?
A dispute arises when one member country adopts a trade policy measure or takes some action that one or more fellow members consider to be a breach of WTO agreements or to be a failure to live up to obligations.
What is dispute settlement?
Dispute settlement or dispute settlement system ( DSS) is regarded by the World Trade Organization (WTO) as the central pillar of the multilateral trading system, and as the organization's "unique contribution to the stability of the global economy ". A dispute arises when one member country adopts a trade policy measure or takes some action ...
How long does it take to resolve a dispute with the DSB?
If consultations fail to resolve the dispute within 60 days after receipt of the request for consultations, the complainant state may request the establishment of a Panel. It is not possible for the respondent state to prevent or delay the establishment of a Panel, unless the DSB by consensus decides otherwise. The panel, normally consisting of three members appointed ad hoc by the Secretariat, sits to receive written and oral submissions of the parties, on the basis of which it is expected to make findings and conclusions for presentation to the DSB. The proceedings are confidential, and even when private parties are directly concerned, they are not permitted to attend or make submissions separate from those of the state in question. Disputes can also arise under Non-violation nullification of benefits claims.
How long does an appeal last in the WTO?
Normally appeals should not last more than 60 days, with an absolute maximum of 90 days. The possibility for appeal makes the WTO dispute resolution system unique among the judicial processes of dispute settlement in general public international law.
When did the WTO start settling trade disputes?
In 1994, the WTO members agreed on the Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes or Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) (annexed to the "Final Act" signed in Marrakesh in 1994 ). Pursuant to the rules detailed in the DSU, member states can engage in consultations to resolve trade disputes pertaining to a "covered agreement" or, if unsuccessful, have a WTO panel hear the case. The priority, however, is to settle disputes, through consultations if possible. By January 2008, only about 136 of the nearly 369 cases had reached the full panel process.
Is the WTO dispute settlement system weak?
Bown of the Peterson Institute for International Economics and Petros Mavroidis of Columbia Law School remarked on the 20th anniversary of the dispute settlement system that the system is "going strong" and that "there is no sign of weakening".
Is the Office of the United States Trade Representative re-appointment?
According to an article by the Waterloo, Ontario-based independent think tank Centre for International Governance Innovation (CIGI)—supported by the Canadian federal government, the Office of the United States Trade Representative, which is seeking WTO reforms, has blocked any re-appointments.
What is a dispute settlement body?
The Dispute Settlement Body is hereby established to administer these rules and procedures and, except as otherwise provided in a covered agreement, the consultation and dispute settlement provisions of the covered agreements. Accordingly, the DSB shall have the authority to establish panels, adopt panel and Appellate Body reports, maintain surveillance of implementation of rulings and recommendations, and authorize suspension of concessions and other obligations under the covered agreements. With respect to disputes arising under a covered agreement which is a Plurilateral Trade Agreement, the term “Member” as used herein shall refer only to those Members that are parties to the relevant Plurilateral Trade Agreement. Where the DSB administers the dispute settlement provisions of a Plurilateral Trade Agreement, only those Members that are parties to that Agreement may participate in decisions or actions taken by the DSB with respect to that dispute.
Who draws up the working procedures?
9. Working procedures shall be drawn up by the Appellate Body in consultation with the Chairman of the DSB and the Director-General, and communicated to the Members for their information.
Is conciliation considered contentious?
10. It is understood that requests for conciliation and the use of the dispute settlement procedures should not be intended or considered as contentious acts and that, if a dispute arises, all Members will engage in these procedures in good faith in an effort to resolve the dispute.
Is conciliation and mediation confidential?
Proceedings involving good offices, conciliation and mediation, and in particular positions taken by the parties to the dispute during these proceedings, shall be confidential, and without prejudice to the rights of either party in any further proceedings under these procedures.
How to settle a dispute in the WTO?
There are two main ways to settle a dispute once a complaint has been filed in the WTO: (i) the parties find a mutually agreed solution, particularly during the phase of bilateral consultations; and (ii) through adjudication, including the subsequent implementation of the panel and Appellate Body reports, which are binding upon the parties once adopted by the DSB. There are three main stages to the WTO dispute settlement process: (i) consultations between the parties; (ii) adjudication by panels and, if applicable, by the Appellate Body ; and (iii) the implementation of the ruling, which includes the possibility of countermeasures in the event of failure by the losing party to implement the ruling.
When was the WTO dispute settlement system published?
This interactive training module is based on the “Handbook on the WTO Dispute Settlement System” published in 2004. The second edition of this handbook published in 2017 can be found at here.
What is the WTO dispute settlement system?
The WTO’s dispute settlement system has as its foundation the rules, procedures and practices developed under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 1947. However, it improves upon the previous system in a number of ways, including by being more accessible.
Why is dispute settlement important in the WTO?
This in turn leads to more harmonious trade relations between members and promotes economic growth.
What is WTO analysis index?
The WTO Analytical Indexis a comprehensive guide to the interpretation and application of the WTO Agreements by the Appellate Body, dispute settlement panels and other WTO bodies. It contains extracts of key pronouncements and findings from tens of thousands of pages of WTO jurisprudence, including panel reports,Appellate Body reports,Article 21.3(c) awards and Article 22.6 decisions.This unique work will be of assistance to anyone working in the field of WTO law, including lawyers, economists, academics and students. It is produced by the Legal Affairs Division of the WTO Secretariat with contributions from other divisions of the Secretariat and the Appellate Body Secretariat. The third edition of theWTO Analytical Indexcovers developments in WTO law and practice over the period January 1995 through September 2011.
What is the third edition of WTO Dispute Settlement Procedures?
BLK The third edition of The WTO Dispute Settlement Procedures collects together the treaty texts,decisions and agreed practices relating to the procedures that apply in the settlement of WTO disputes.It affords ready answers to technical questions relating to matters such as:how disputes are initiated and conducted,including at the appellate stage;what deadlines apply and how to calculate them;what rules of conduct bind individuals involved in WTO dispute settlement;and what rules of procedure apply to meetings of the Dispute Settlement Body.This highly practical work,which includes cross-references and a subject index,will prove to anyone working in WTO dispute settlement,including lawyers,civil servants working in the field of trade,economists,academics and students.This edition has been fully updated to take account of revised rules and procedures. W
What is a DSU in WTO?
The DSU allows for the possibility of establishing a single panel where more than one WTO member has complained about the same issues. These efficiencies are appreciated by members, who may collaborate in preparing their cases, and allows the disputes to be examined more quickly.
How long does it take to get a dispute resolved in the WTO?
Over the past 20 years, nearly 500 disputes have been brought to the WTO. About half of these were resolved during bilateral discussions while the other half proceeded to a panel process, which in recent years generally takes about 14 months. Appeals are considered by the WTO’s Appellate Body and – excluding exceptionally busy periods – are completed within three months. This makes the WTO’s dispute system one of the fastest in the world.
How long does it take to comply with WTO rules?
The member is generally given a “reasonable period of time” – ranging from eight to 15 months – to implement the dispute settlement rulings. During the implementation period, the member who is required to comply with the rulings must provide a status report at each meeting of the DSB. If the member does not bring its measures into conformity with the relevant WTO agreements within the allotted time, the complainant may request the DSB to authorize retaliation in the form of trade sanctions, such as restrictions on imports, for an amount equivalent to the level of trade affected by the offending measure. The DSB continues to keep the member’s compliance efforts under review, even when retaliation has been authorized. If there is disagreement about compliance, the matter remains on the agenda of the DSB.
When was the WTO dispute settlement system published?
This interactive training module is based on the “Handbook on the WTO Dispute Settlement System” published in 2004. The second edition of this handbook published in 2017 can be found at here.
What is consultation in the WTO?
Together with good offices, conciliation and mediation 3, consultations are the key non-judicial/diplomatic feature of the dispute settlement system of the WTO. Consultations also allow the parties to clarify the facts of the matter and the claims of the complainant, possibly dispelling misunderstandings as to the actual nature of the measure at issue. In this sense, consultations serve either to lay the foundation for a settlement or for further proceedings under the DSU.
What is a request for consultation?
The request for consultations formally initiates a dispute in the WTO and triggers the application of the DSU. Very often, informal discussions on the matter between capital-based officials or between the Geneva delegations of the Members involved precede the formal WTO consultations. However, even where prior consultations occurred, it remains necessary for the complainant to go through the consultation procedure set forth in the DSU as a prerequisite for further proceedings in the WTO.
What are the two legal bases for launching a dispute with a request for consultation?
Under GATT 1994 and those covered agreements that refer to the consultations and dispute settlement provisions of GATT 1994 , two legal bases are available for launching a dispute with a request for consultations, that is, either Articles XXII:1 or XXIII:1 of GATT 1994. Similarly, under GATS ), consultations can be initiated under either Articles XXII:1 or XXIII:1.
What is the purpose of Article 3.7 of the WTO?
By its express terms, Article 3.7 of the DSU entrusts the Members of the WTO with the self-regulating responsibility of exercising their own judgement in deciding whether they consider it would be fruitful to bring a case.
Can a party to a dispute depart from the requirement of consultations through mutual agreement?
The parties to a dispute can depart from the requirement of consultations through mutual agreement under Article 25.2 of the DSU if they resort to arbitration as an alternative means of dispute settlement. back to text
Is dispute resolution a prerequisite for judicial action?
2. It is not this possibility of, and preference for, mutually agreeable solutions, which distinguishes the dispute settlement system of the WTO from typical domestic judicial systems, but the formal prerequisite of prior consultations. However, many of these domestic systems are moving towards the inclusion of alternative means of dispute resolution as a formal prerequisite for judicial action such as, for instance, a prior attempt to find an amicable solution with a mediator. back to text
Why do WTO members want to settle disputes?
The WTO members agree that if a country has some measure which is violative of the WTO agreement, they will resort to a multilateral trade system to settle disputes rather than solving them unilaterally. It ensures that the members abide by the rules and regulations.
What to do if the WTO is not able to settle the dispute?
The parties sit together, talk to each other, and even after that, if they are not able to settle the differences, they can either ask the WTO Director-General to mediate or help in any other way possible .
What does the WTO believe?
The WTO believes that to ensure a reliable multilateral trade settlement system ; all the members must respect the rules. The members have also agreed that the same shall be referred to the dispute settlement system whenever a matter arises.
What is the process of dispute settlement?
The process is the duty of the Dispute Settlement Body, which consists of the WTO members. They have the authority to appoint the panels for a case and accept or reject their findings. The body also keeps a check on the proper implementation of the rules and regulations established during the process of dispute settlement.
What is the function of a dispute panel?
The primary function of the panel is to help the Dispute Settlement Body in laying down rulings and regulations. Though the panel’s role is to help, overturning its decisions is hardly impossible. The consensus of the members of the Dispute Settlement Body only can reject the recommendations of the panel. The findings of the panel should be following the agreements cited. The period of appointing a panel is up to 45 days. (Article 6 of DSU).
What is the procedure for presenting a dispute before a panel?
1. Before the Hearing: Before presenting in front of the panel, each country of the dispute has to put forward its case before the panel in writing.
How long does it take to get a final report from the WTO?
8. Final Report: After reviewing, the panel submits the final report to both sides. After three weeks , the same is given to all the WTO members. If in the report, the panel concludes that the trade measure in dispute breaks a WTO agreement, it recommends that the same must conform with WTO rules, and the panel might suggest some measures on how it is to be done.

Introduction to Dispute Settlement in The WTO
Dispute Settlement Process
- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU)is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
- Technical explanationof the DSU
- Rules of Conducton rules and procedures for settling disputes
- Working Procedures for Appellate Review
- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU)is the main WTO agreement on settling disputes.
- Technical explanationof the DSU
- Rules of Conducton rules and procedures for settling disputes
- Working Procedures for Appellate Review
The Appellate Body
- Appeals are handled by the permanent seven-member Appellate Bodywhich is set up by the Dispute Settlement Body and broadly represents the range of WTO membership.
Dispute Settlement Activity — Some Figures
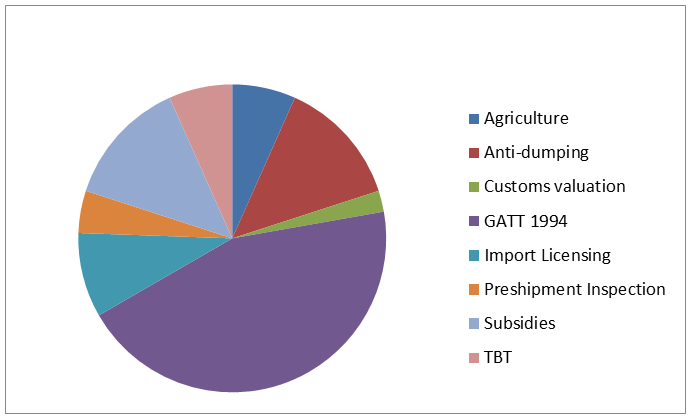
- As of end-2020, WTO members had submitted 598 requests for consultations, the first stage in the dispute settlement process.
Documents
Interpretation of WTO Agreements
- The WTO Analytical Indexis a comprehensive guide to the interpretation and application of the WTO agreements by the Appellate Body, dispute settlement panels and other WTO bodies. It contains extracts of key pronouncements and findings from tens of thousands of pages of WTO jurisprudence, including panel reports, Appellate Body reports, arbitral decisions and awards, an…
Negotiations to Improve Dispute Settlement Procedures
- At the Doha Ministerial Conference, in 2001, WTO members agreed to negotiate to improve and clarify the DSU— the rules and procedures governing the settlement of WTO disputes.
Secretariat's Informal Consultations Concerning The Panel Process
- At the request of the Director-General, the Secretariat initiated in 2010 a process of informal consultationswith a view to exploring whether it is possible to find efficiency gains in the panel process.
Overview
Dispute settlement or dispute settlement system (DSS) is regarded by the World Trade Organization (WTO) as the central pillar of the multilateral trading system, and as the organization's "unique contribution to the stability of the global economy". A dispute arises when one member country adopts a trade policy measure or takes some action that one or more fellow members consider to be a breach of WTO agreements or to be a failure to live up to obligations…
WTO Appellate Body
The WTO Appellate Body of judges was first established in 1995. While a full complement consists of seven judges, the Appellate Body can hear an appeal with a minimum of three. The full term for an Appellate Body judge's appointment lasts four years with the a possibility of a reappointment for a second term.
By July 2018, there were only four judges remaining, as others had completed their 4-year term…
Dispute Settlement Understanding
Prompt compliance with recommendations or rulings of the DSB is essential in order to ensure effective resolution of disputes to the benefit of all Members.— World Trade Organization, Article 21.1 of the DSU
In 1994, the WTO members agreed on the Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes or Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) (annexed to the "Final A…
From complaint to final report
If a member state considers that a measure adopted by another member state has deprived it of a benefit accruing to it under one of the covered agreements, it may call for consultations with the other member state. If consultations fail to resolve the dispute within 60 days after receipt of the request for consultations, the complainant state may request the establishment of a Panel. It is not possible for the respondent state to prevent or delay the establishment of a Panel, unless the D…
Compliance
The DSU addresses the question of compliance and retaliation. Within thirty days of the adoption of the report, the member concerned is to inform the DSB of its intentions in respect of implementation of the recommendations and rulings. If the member explains that it is impracticable to comply immediately with the recommendations and rulings, it is to have a "reasonable period of time" in which to comply. This reasonable amount of time should not exce…
Compensation and retaliation
If all else fails, two more possibilities are set out in the DSU:
• If a member fails within the "reasonable period" to carry out the recommendations and rulings, it may negotiate with the complaining state for a mutually acceptable compensation. Compensation is not defined, but may be expected to consist of the grant of a concession by the respondent state on a product or service of interest to the complainant state.
Developing countries
Like most of the agreements adopted in the Uruguay Round, the DSU contains several provisions directed to developing countries. The Understanding states that members should give "special attention" to the problems and interests of developing country members. Further, if one party to a dispute is a developing country, that party is entitled to have at least one panelist who comes from a developing country. If a complaint is brought against a developing country, the time for consult…
WTO bias
President Trump raised concerns that the WTO's dispute settlement system was biased against the US. Economists Jeffry Frieden and Joel Trachtman found that the United States wins the vast majority of disputes it brings against other countries, winning "more than the average when it is complainant". Other countries lose most of the cases brought against the US, losing "less than the average when it is [the] respondent". Frieden and Trachtman explain that the US would only brin…
Article 1
- Coverage and Application 1. The rules and procedures of this Understanding shall apply to disputes brought pursuant to the consultation and dispute settlement provisions of the agreements listed in Appendix 1 to this Understanding (referred to in this Understanding as the “covered agreements”). The rules and procedures of this Understanding shall also apply to consultations …
Article 2
- Administration 1. The Dispute Settlement Body is hereby established to administer these rules and procedures and, except as otherwise provided in a covered agreement, the consultation and dispute settlement provisions of the covered agreements. Accordingly, the DSB shall have the authority to establish panels, adopt panel and Appellate Body reports, maintain surveillance of i…
Article 3
- General Provisions 1. Members affirm their adherence to the principles for the management of disputes heretofore applied under Articles XXII and XXIII of GATT 1947, and the rules and procedures as further elaborated and modified herein. 2. The dispute settlement system of the WTO is a central element in providing security and predictability to the ...
Article 4
- Consultations 1. Members affirm their resolve to strengthen and improve the effectiveness of the consultation procedures employed by Members. 2. Each Member undertakes to accord sympathetic consideration to and afford adequate opportunity for consultation regarding any representations made by another Member concerning measures affecting the operation of any c…
Article 5
- Good Offices, Conciliation and Mediation 1. Good offices, conciliation and mediation are procedures that are undertaken voluntarily if the parties to the dispute so agree. 2. Proceedings involving good offices, conciliation and mediation, and in particular positions taken by the parties to the dispute during these proceedings, shall be confidential, and without prejudice to the rights …
Article 6
- Establishment of Panels 1. If the complaining party so requests, a panel shall be established at the latest at the DSB meeting following that at which the request first appears as an item on the DSB's agenda, unless at that meeting the DSB decides by consensus not to establish a panel (5). 2. The request for the establishment of a panel shall be made in writing. It shall indicate whethe…
Article 7
- Terms of Reference of Panels 1. Panels shall have the following terms of reference unless the parties to the dispute agree otherwise within 20 days from the establishment of the panel: “To examine, in the light of the relevant provisions in (name of the covered agreement(s) cited by the parties to the dispute), the matter referred to the DSB by (name of party) in document ... and to …
Article 8
- Composition of Panels 1. Panels shall be composed of well-qualified governmental and/or non-governmental individuals, including persons who have served on or presented a case to a panel, served as a representative of a Member or of a contracting party to GATT 1947 or as a representative to the Council or Committee of any covered agreement or its predecessor agree…
Article 9
- Procedures for Multiple Complainants 1. Where more than one Member requests the establishment of a panel related to the same matter, a single panel may be established to examine these complaints taking into account the rights of all Members concerned. A single panel should be established to examine such complaints whenever feasible. 2. The single panel shall …
Article 10
- Third Parties 1. The interests of the parties to a dispute and those of other Members under a covered agreement at issue in the dispute shall be fully taken into account during the panel process. 2. Any Member having a substantial interest in a matter before a panel and having notified its interest to the DSB (referred to in this Understanding as a “third party”) shall have an …