What causes settlement during an earthquake?
Ground settlement. Lowering of the ground surface, known as subsidence or settling, often occurs during an earthquake. Common causes of ground subsidence during an earthquake include consolidation or failure of the ground under a foundation, densification of sand and gravel layers due to the ground shaking and liquefaction. Settlement caused by...
What is subsidence and settlement in geotechnical engineering?
Ground Settlement and subsidence. In geotechnical engineering , settlement is defined as the vertical movement of the ground, generally caused be changes in stresses within the earth. Subsidence is a term often used to described ‘caving in’ or sinking of the ground, that may not be associated within changes in soil stresses.
What are the causes of settlement?
Settlement is most likely to occur when increased vertical stresses are applied to the ground on or above soft or loose soil strata. It is also possible that lowering the ground water, migration of soil fines, deep voids, underground excavation for tunnels, induced ground vibrations and seismic events will cause significant settlement.
What is settlement monitoring instrumentation?
Settlement monitoring instrumentation is typically accomplished using settlement plates which are placed on the ground surface prior to fill placement, extended to the fill surface during ongoing fill placement activities, and surveyed on a regular basis during the monitoring program.

What does ground settlement mean?
Foundation settlement happens when soil shifts beneath a home and it is a serious deal for a homeowner, and often requires that swift action be taken to prevent structural damage from occurring to the home.
What is Surface settlement?
And in the period of construction, surface settlement is mainly caused by soil piling into shield gap in undrained condition. So based on the compar- ison of several computing method, the paper firstly discusses the relationship and applicability of them, and secondly analyzes the issue of parameter selecting.
What are the three types of soil settlement?
There are three main types of soil settlement in geotechnical engineering: Uniform settlement. Differential settlement. Curvature settlement.
What happens when the ground settles?
As the air and water leave the soil, the solid particles are rearranged and 'settle' into a new compact position. Air is released first, and then water flows out at a rate that depends on the materials in the mix. For example, water disperses faster in fine particles like sand, but slower in dense particles like clay.
What is ground settlement in construction?
Introduction. Settlement is the downward movement of the ground caused by a load consolidating the soil below it or causing displacement of the soil. Settlement often refers to the downward movement of the ground around an excavated space, such as that for tunnels, shafts, or basements.
What is static settlement?
Static Settlements are towns or cities that stay immobile on the ground, rather than on caterpillar tracks. Although smaller static settlements are not considered to be with the Anti-Traction League, larger ones such as Zagwa are not considered 'friends' of the Traction Cities. Advertisement.
What causes ground settlement?
What Causes Settlement of Soils? Settlement occurs from soil consolidation due to a reduction in voids or spaces between soil particles due to applied loads or changes in moisture content. The loss of moisture in soils causes consolidation.
What are the types of soil settlement?
The total settlement of the ground consists of 3 components: immediate settlement (commonly referred to as elastic settlement, although this is a misnomer), consolidation settlement (or primary settlement) and creep settlement (or secondary settlement).
What are the types of settlement?
The four main types of settlements are urban, rural, compact, and dispersed. Urban settlements are densely populated and are mostly non-agricultural. They are known as cities or metropolises and are the most populated type of settlement. These settlements take up the most land, resources, and services.
How long does ground take to settle?
In your lawn or around your foundation, however, natural weathering processes will work on the dirt to settle it down and take hold. This usually takes around 7 years in temperate areas.
How much foundation settlement is too much?
How much foundation settlement is too much? The industry standard is 1 inch of differential settlement in 20 feet. Anything greater than this can be considered too much.
How much house settlement is normal?
Settling cracks will be vertical, between two and six inches long, and 1/16 of an inch in width. If the cracks you're seeing are horizontal or wider than 1/16 of an inch, that could indicate improper settling.
What is secondary settlement of soil?
This process of creep is sometimes known as "secondary consolidation" or "secondary compression" because it also involves gradual change of soil volume in response to an application of load; the designation "secondary" distinguishes it from "primary consolidation", which refers to volume change due to dissipation of ...
Which soil has more settlement?
Immediate settlement take place mostly in coarse grained soils of high permeability and in unsaturated fine-grained soils of low permeability.
What is total and differential settlement?
Total settlement refers to the overall change in vertical distance. Differential settlement involves an expected amount that the total settlement will vary between points over a horizontal distance, which can be caused by variations in the foundation soil profile and wall height over a certain distance.
What is secondary settlement?
Secondary settlement areas developed outside the central city district after the end of World War 1 and have established their own distinct identities over time.
What is uniform settlement?
Uniform settlement occurs when a building foundation settles by the same amount over its entire footprint area, effectively lowering the structure in place. A related effect called tilt settlement occurs when the whole building tilts as a solid box.
What is it called when the center of a foundation settles further than the edges?
Where it causes the centre to settle further than the edges, it is known as sagging or dishing (right). Differential settlement can cause an abrupt change in level or cause all corners of the foundation to settle by different amounts. Back to top.
What causes ground to subside?
Common causes of ground subsidence during an earthquake include consolidation or failure of the ground under a foundation, densification of sand and gravel layers due to the ground shaking and liquefaction.
What is differential settlement?
In some cases, only part of the foundation is affected by ground failure, or part of the foundation is affected to a greater extent than other parts. This kind of effect is called differential settlement and can cause much more severe damage to a building than uniform or tilt settlement.
What causes a building to displace?
Settlement caused by ground failure can cause buildings to displace, tilt, stretch, twist, buckle or a combination of all five. How badly the building is damaged depends on: the severity of the settlement (related to ground performance and behaviour) the type and strength of the building’s foundations and structure.
How did groundwater subside?
Notable subsidence occurred in central London between 1865 and 1931 due to water abstraction from the Chalk. Beneath Mexico City, there is an aquifer between 50 and 500 m below ground level. Progressive pumping from this aquifer for over 100 years has resulted in much of the old city settling by 4 m, and in the north-east of the city, settlement of 7.5 m has been recorded.
Which authors demonstrated that the short-term transverse settlement trough shape induced by tunnelling in greenfield conditions?
Martos (1958) and Peck (1969) and many other authors demonstrated that the short-term transverse settlement trough shape induced by tunnelling in greenfield conditions could be expressed by the following Gaussian curve:
What slope is the moving target on?
The moving targets fall on a gently inclined (∼5°) part of a southeast-facing slope, within the middle part of an old, deep earth slide ( Mossa et al., 2005 ). The failed slope has been subjected to stabilization works and currently does not present any obvious signs of instability. However, inclinometer borehole monitoring conducted since 2008 indicated the presence of extremely slow displacements (up to 15 mm/year) occurring in the central portion of the slide at a depth of a few tens of meters (F. Santaloia, CNR-IRPI, unpublished data).
Why are soils bad for construction?
Mechanical properties of soil are mostly undesirable for construction purposes in many parts of the world due to their unstable structure and low mechanical strength. These soils may undergo some unexpected collapse due to some environmental factors. For example, freeze/thaw cycles and overload pressures create some geotechnical problems like landslides, ground settlement, and surface cracks that may lead to failure of human-made infrastructure. Normally some buildings, railways, roads and some monuments may require maintenance and repair because of the loose properties of soil. The strength and stiffness of the loose sediments may be reduced due to earthquake which is harmful to the rest of the soil structure (Jalili et al., 2018; Li et al., 2015 ).
How to simulate segmental lining?
To simulate the process of stepwise segmental lining installation, the construction of each tunnel is executed within two steps. First, an excavation step in which the soil medium within the first tunnel area is removed, and a support pressure is applied to imitate the transient process after installing the lining segments, but before the grout pressure has reached its final stiffness. The relaxation factor λ is set to 0.25, that is, the internal support pressure is reduced to a fraction of 0.25 of the previous in situ stress level ( Potts & Zdravković, 2001 ). In the next step, the internal pressure is removed, and the lining segments are installed without any further support. They are modeled as linear-elastic material with a normal stiffness of 10,389 kN/m and a bending stiffness of 77,918 kNm 2 /m. After the installation of the left tunnel is completed, the procedure is repeated for the right one. The surrounding soil material is modeled using the well-known Mohr-Coulomb constitutive model that assumes a linear elastic and perfect plastic behavior by applying the Coulomb failure criterion. The subsoil is defined with properties typical for dense silty sand following lognormal distribution ( μE = 70, 000 kPa, σE = 7,000 kPa, μΦ = 35 degrees, μC = 5 kPa, σC = 0.25 kPa).
Where was groundwater extraction in California?
Groundwater extraction near Pixley in California caused some 0.75 m of settlement between 1958 and 1963, the surface depression being mainly over the area pumped, with the effect decreasing with distance. In the Houston/Galveston region, the presence of faults has restricted the area affected by the dewatering such that a face up to a metre high has developed over a length of almost 17 km.
Is tunneling a geotechnical project?
In general, mechanized tunneling can be considered as a spacious geotechnical project involving quite a large area. Thereupon, design and analysis of such projects are performed in engineering practice by averaging the characteristics of geomaterials causing uncertainties in evaluations. Due to the different characteristics of lithological composition, stress history and sedimentation, weathering and erosion, probable faults and fractures, almost all properties of subsoil shall be treated as heterogeneous materials. Thereupon, characteristics of the spatial distribution of geotechnical parameters should be quantified and taken into account for every stochastic analysis. Various statistical techniques to estimate spatial variability have been developed that can be classified in three main categories: regression analysis, geostatistics, and random field theory. Regression analyses assume that all sample values within a medium show an equal and independent likelihood, that is, they are not autocorrelated, which contradicts the made observation on the formation of the microscopic structural units within the soil mass ( Yong, 1984 ). Field observations also show a stronger correlation between samples taken at a closer distant compared to samples further apart. Therefore, regression methods are better studied to be utilized in an initial exploration, when only a limited number of samples with large distances between them are taken from the site ( Rendu, 1978 ). However, the other two categories do consider the autocorrelation concept in geomaterials. Geostatistical methods mainly include estimation and simulation methods.
Abstract
There is an ever-growing demand of construction of large-diameter tunnel in Shanghai, China. How to minimize the environmental impact induced by the tunnel construction has been a hot topic of research over the recent years.
1. Introduction
Located in Yangtze River Delta in eastern China, Shanghai is the largest city by population in China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010.
2. Engineering background
The Yingbin San Road tunnel is located at the south side of Shanghai Hongqiao airport. It is one of the most direct and convenient channels to connect the east and west side of Shanghai Hongqiao Airport, and has been considered as a significant part of supporting traffic network serving the Hongqiao transportation hub, as shown in Fig. 1.
3. Numerical modeling and prediction
FLAC 3D is used to establish the numerical model of test section of the project in this paper. It is an explicit finite difference code that has been widely used in the geotechnical analysis field and tunneling modeling ( Liu et al., 2012 ). The model dimension is 126 m × 150 m × 84 m, according to the construction scheme and boundary effect.
4. Empirical method and estimation
A large number of empirical, semi-empirical methods and their revised versions have been developed during the last forty years, such as Peck method ( Peck, 1969 ), Oteo method ( Oteo and Moya, 1979) and the Romo-Diaz method ( Romo and Diaz, 1981 ).
5. Field measurement and test results
A field test has been arranged before the shield machine enters into the critical area of the airport, in order to determine the optimum excavation parameters by which the minimum impact on the environment could be achieved.
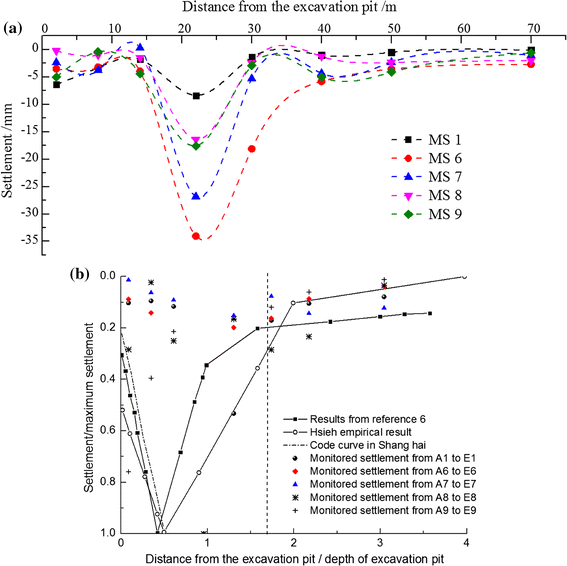
6. Comparison of numerical simulation, empirical prediction and field measurement
The numerical prediction is compared with the field measurement results at cross-section H96 in Fig. 18. The measured data is fewer due to the size difference between the numerical model and testing site, see Fig. 4, Fig. 11.
What is ground surface?
Ground surface means the intended or actual finished grade of the surface of the ground at the well site, which shall be consistent with the surrounding land surface. Ground surface means any horizontal surface at or near ground level, including, but not limited to, bare soil, grass, sidewalks, and driveways.
What is tactile surface?
TACTILE SURFACE3.11.1. Ground surface of a different texture through tactile be provided for allowing/ guiding/warning for persons with vision impairment by a tactile signal.
