
Israeli settlement
Israeli settlements are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Jewish ethnicity, built predominantly on lands within the Palestinian territories, which Israel has militarily occupied since the 1967 Six-Day War, and partly on lands considered Syrian territory also m…
Full Answer
What is considered a settlement in Israel?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War —the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
Why did Israel build settlements in the Old Testament?
Israeli settlements were erected for a variety of reasons. In some cases, Israelis sought to recover property lost in the 1948 war and the hostilities leading up to it, such as the core settlements of Gush Etzion between Jerusalem and Hebron.
Do Israel’s settlements violate international law?
In order to find Israel’s settlements to be a violation of international law, first, Israel must be considered an occupier of foreign territory. Yet, Israel’s legal claim to the territory in question was recognized by the international community on several occasions.
Are Israeli settlements an obstacle to peace?
The Israeli government’s position, under Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, is that settlements are not an obstacle to peace and that settlement expansion is a function of natural growth within existing settlements.
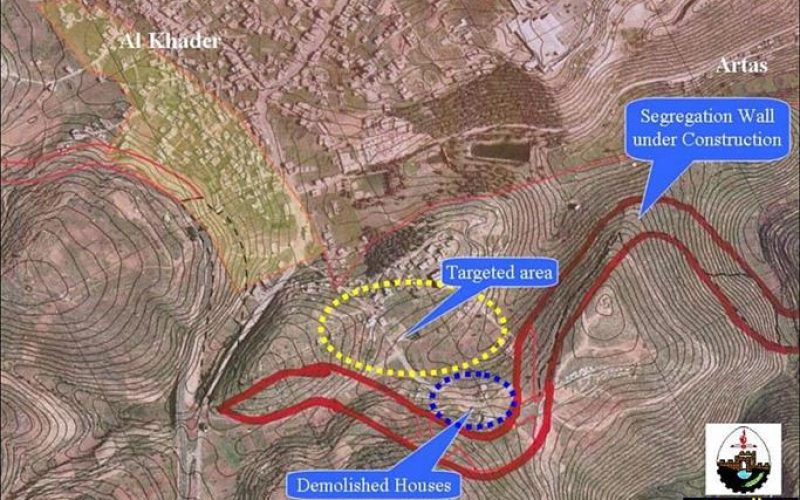
What is the goal of Israeli settlements?
Israel wanted "a Palestinian entity, less than a state, which will be a home to most of the Palestinian residents living in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank". It wanted to keep settlements beyond the Green Line including Ma'ale Adumim and Givat Ze'ev in East Jerusalem.
How are Israeli settlements justified?
Israel has justified its civilian settlements by stating that a temporary use of land and buildings for various purposes appears permissible under a plea of military necessity and that the settlements fulfilled security needs.
Why are there Israeli settlements in Palestine?
After the military assaults of 1948-'50, Zionist armed forces, subsequently transformed into the Israeli army, constructed Jewish settlements over the ruins of Palestinian towns and villages throughout the 78 percent of historic Palestine they controlled.
What are Israeli settlements called?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War—the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
Is Israel occupying Palestine land?
BACKGROUND: Palestinian territory – encompassing the Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East Jerusalem – has been illegally occupied by Israel since 1967.
How much land has Palestine lost to Israel?
During and immediately following the state's creation in 1948, Israel expropriated approximately 4,244,776 acres of Palestinian land. In the process, more than 400 Palestinian cities and towns were systematically destroyed by Israeli forces or repopulated with Jews.
Who Owns the West Bank?
Presently, most of the West Bank is administered by Israel though 42% of it is under varying degrees of autonomous rule by the Fatah-run Palestinian Authority. The Gaza Strip is currently under the control of Hamas.
When did Israel take Palestine?
The Arab-Israeli War of 1948 broke out when five Arab nations invaded territory in the former Palestinian mandate immediately following the announcement of the independence of the state of Israel on May 14, 1948.
Are there Israeli settlements in Gaza?
According to the report of the Security Council Commission established under resolution 446 (1979): "Between 1967 and May 1979, Israel has established altogether 133 settlements in the occupied territories, consisting of 79 in the West Bank, 29 in the Golan Heights, 7 in the Gaza Strip and 18 in the Sinai.
How many Israelis live in Palestinian lands?
Roughly 10 percent of Israel's 6.8 million Jewish population lives in these occupied Palestinian territories. Despite being outside of Israel proper, these settlers are granted Israeli citizenship and receive government subsidies that significantly lower their cost of living.
Why is Israel blockading Gaza?
Israel said that the blockade was necessary to protect Israeli citizens from "terrorism, rocket attacks and any other hostile activity" and to prevent dual use goods from entering Gaza.
Who were the first settlers in Israel?
3,000 to 2,500 B.C. — The city on the hills separating the fertile Mediterranean coastline of present-day Israel from the arid deserts of Arabia was first settled by pagan tribes in what was later known as the land of Canaan. The Bible says the last Canaanites to rule the city were the Jebusites.
What is the illegality of settlements in Israel?
The illegality of Israel’s civilian settlements in territories it occupied in 1967 is one of the few clearly settled issues in international law. The Geneva Conventions provisions on this issue are clear and explicit: civilian settlement activities are considered grievous breaches and war crimes. Furthermore, the issue was litigated and decided by the International Court of Justice in a rare, almost unanimous ruling of 15 judges in the case of Israel’s Separation Wall in 2004. The lone dissenting judge in that case wrote that even he agrees with the majority on the issue of the applicability of the Geneva Conventions.
Why were the Geneva Conventions important?
Apart from the difficulty of establishing which wars are “aggressive” and which are “defensive,” particularly when the army that starts hostilities claims it is acting in a “preemptively defensive” fashion, the Geneva Conventions were concerned with protecting civilians who fall under the rule of another army.
What is an Israeli settlement?
Israeli settlement. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree.... Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the disputed territories captured by Israel in ...
What was the purpose of the settlements in the Jordan Valley?
Israel’s political and defense establishments, meanwhile—inspired in part by the peace plan of Yigal Allon, the deputy prime minister (1967–77)—spurred the development of settlements in strategic locations such as the Jordan Valley that would bolster Israel’s security and strengthen its hand in negotiations .
How many people lived in settlements in 1993?
Settlements continued to expand in the decades that followed, and by 1993 there were more than 280,000 people living in settlements (130,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded).
When were the settlements in the Sinai Peninsula evacuated?
Settlements in the Sinai Peninsula were either dismantled or evacuated in 1982, and settlements in the Gaza Strip were dismantled in 2005. It is disputed, moreover, whether communities in the formally annexed territories of East Jerusalem (part of the West Bank territory under Jordanian rule from 1949 to 1967) and the Golan Heights constitute ...
How many settlers were there in 2019?
Despite the agreement, settlement building proliferated, especially in the West Bank, and in 2019 the number of settlers reached nearly 630,000 (413,000 if East Jerusalem is excluded). Most of these newer settlers were motivated less by reasons of ideology or recovering lost property, however, than by cheaper housing and financial incentives ...
Where is Israel located?
Israel, country in the Middle East, located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bounded to the north by Lebanon, to the northeast by Syria, to the east and southeast by Jordan, to the southwest by Egypt,…
Where is Gilo in the West Bank?
Since 2005 these communities have existed almost exclusively in the West Bank, with a handful located in the Golan Heights.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are 126 Israeli settlements in the West Bank (excluding East Jerusalem), according to the September 2016 report from the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Geographically, these settlements are all across the West Bank. The West Bank is broken down into Areas A, B, and C, according to the Oslo Accords, ...
Why are the settlements controversial?
The settlements are built on land the Palestinians and the international community, along with some in the Israeli community, see as a future Palestinian state. Some of the settlements – especially the blocs – may be a part of Israel in a two-state solution through land swaps between Israelis and Palestinians. One concern, expressed by the European Union, and in the past by the US State Department, is that settlement expansion may make a contiguous, whole Palestinian state in the West Bank impossible.
What are settlements?
Settlements are Israeli cities, towns and villages in the West Bank and the Golan Heights. (We will deal with East Jerusalem a bit later.) They tend to be gated communities with armed guards at the entrances. Why are they settlements and not simply Israeli residential areas? Because Israel is widely considered to be an occupying force in the territories. It is land that Palestinians, along with the international community, view as territory for a future Palestinian state.
Why are the West Bank and East Jerusalem considered occupied territory?
Israel began its occupation of the West Bank and East Jerusalem in 1967 during the Six-Day War. Seeing a military buildup in the surrounding Arab countries, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, after which Jordan, in turn, attacked Israel. Israel annexed East Jerusalem shortly thereafter, unifying the city under Israel’s authority. But Israel has never annexed the West Bank, part of which remains under military law.
Who are the settlers?
This is a very broad question, and requires a fair amount of generalization.
What is the legal status of settlements?
The settlements are illegal under international law. The Fourth Geneva Convention, which concerns civilian populations during a time of war, states in Article 49 that, “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
What about East Jerusalem? And what is East Jerusalem anyway?
From 1948 to 1967, Jerusalem was divided by the Green Line, which is the cease-fire line of 1948 between Israel and Jordan. Although the city is now under Israeli governance, the distinction remains.
Why was the re-acquisition of the territory by Israel legal?
This re-acquisition of the territory by Israel was legal because article 51 of the U.N. charter permits a nation to defend itself from attack. It is understood that national self-defense often necessitates control of any territory from which the initial aggression was launched.
Which article of the Fourth Geneva Convention gives the Palestinian Authority the right to live and build in their allotted jurisdictions?
Lastly, even if Israel’s settlements were a violation of article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention, the Oslo Accords have given both Israel and the Palestinian Authority the right to live and build in their allotted jurisdictions.
Why can't Israel be an occupier?
Israel can’t be an occupier because it likely has superior title to the territory in the first place. Even if it had no title to the territory, the Fourth Geneva Convention can’t apply here. And even if it could apply here, Israel would be a legal occupier rather than an illegal one, since Israel hasn’t violated the provisions of the Fourth Geneva Convention (making the settlements legal rather than illegal). Lastly, even if Israel’s settlements were a violation of article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention, the Oslo Accords have given both Israel and the Palestinian Authority the right to live and build in their allotted jurisdictions.
What article of the UN charter forbids the acquisition of territory through war?
Furthermore, article 2 of the UN charter forbids the acquisition of territory through war. Thus, Jordan’s acquisition and annexation of the territory was illegal under international law. In 1967, Jordan again initiated war against Israel (along with two other Arab states) but Jordan was pushed out of the territory ...
Why did the Second World War require the transfer of populations to occupied territories?
Intended to prevent a practice adopted during the Second World War by certain Powers, which transferred portions of their own population to occupied territory for political and racial reasons or in order, as they claimed, to colonize those territories. Such transfers worsened the economic situation of the native population and endangered their separate existence as a race.”
Is Israel an occupier of the Oslo Agreement?
So there you have it, in all the possible stages of the legal argument: Israel can’t be an occupier because it likely has superior title to the territory in the first place.
When did Israel become a state?
When Israel’s leaders declared sovereignty in all territory relinquished by Great Britain on May 15, 1948 (including the territory that anti-Israel people call the “West Bank”) it was recognized as the State of Israel by the General Assembly and Security Council by May1949 .
Why do Israelis want to settle in the West Bank?
Israeli civilians moved into the West Bank after Israel took control of it from Jordan in the 1967 war. Every Israeli government since then, whether hawkish, dovish or mixed, has supported Jewish settlements there. The reasons lie in history, politics and security concerns. Some Israelis consider settlements bulwarks against potential attacks of the kind that occurred in 1948, when Arab countries assaulted Israel after rejecting a UN plan partitioning the British-ruled Holy Land. (That plan would have made the West Bank part of a new Arab state, alongside a Jewish one.) Critics of Israeli settlements argue they are illegal under the Fourth Geneva Convention, which prohibits an occupying power from transferring its civilians into territories it occupies. Israel says the clause isn’t applicable to the West Bank because Jordan, which held the territory for 19 years before Israel, was never recognized as the sovereign power there, and the area was captured in a defensive war. Some settlers think modern-day Jews have a right to the West Bank because it was the heart of biblical Israel. Others simply like the relatively inexpensive housing. Government subsidies, including favorable mortgages and discounts on purchases of property declared state land, amount to about $700 per settler per year. The presence of settlements makes everyday life difficult for Palestinians. Barriers, fences and buffer zones meant to secure settlers restrict the freedom, movement and commerce of Palestinians. Both populations are frequently attacked by militants from the other side. When Palestinians are accused, 95% of cases are prosecuted and Israeli military law applies. When Israelis are suspected, that figure drops to 9%, and Israeli civil law applies.
Why do some settlers think modern day Jews have a right to the West Bank?
Some settlers think modern-day Jews have a right to the West Bank because it was the heart of biblical Israel. Others simply like the relatively inexpensive housing. Government subsidies, including favorable mortgages and discounts on purchases of property declared state land, amount to about $700 per settler per year.
What is the annexation of Jerusalem?
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced the annexation move after U.S. President Donald Trump effectively endorsed it in his proposed resolution of the Israel-Palestinian conflict. The U.S., Israel’s most important ally, had earlier said it would no longer consider settlements as inconsistent with international law. About 130 government-approved settlements and 100 unofficial ones are home to around 400,000 Israelis in the West Bank, where an estimated 2.6 million Palestinians live. An additional 200,000 Israelis reside in 12 neighborhoods in east Jerusalem, which the Palestinians hope to make their future capital. Israel annexed east Jerusalem decades ago, in a move not recognized outside of Israel. The U.S. under Trump became the only major power to recognize Jerusalem as Israel’s capital while adding that the city’s borders should be negotiated . About 20,000 settlers live on the Golan Heights, a strategic plateau Israel captured from Syria in the 1967 Arab-Israeli war. Israel continues to face censure for its settlements from the European Union, its biggest trading partner. The EU in 2015 instructed members to ensure imports produced in settlements are labeled as such, giving a boost to advocates of a boycott of such products.
Why would a future Palestinian state lack territorial contiguity?
Because the settlements are sprinkled throughout the West Bank, a future Palestinian state would lack territorial contiguity, which could impede the development of infrastructure and the movement of people and goods. Other Israelis say the access issue can be solved with tunnels and bridges.
How fast has the Jewish population grown in the West Bank?
The population of Jewish settlers in the West Bank has grown four times faster than Israel’s itself since 1995. Settlers regard themselves as inhabiting land that is rightfully theirs. A different view is held by the International Court of Justice, a branch of the United Nations, which Israel regards as biased against it.
Which country recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel?
The U.S. under Trump became the only major power to recognize Jerusalem as Israel’s capital while adding that the city’s borders should be negotiated . About 20,000 settlers live on the Golan Heights, a strategic plateau Israel captured from Syria in the 1967 Arab-Israeli war.
Can the Palestinians be compensated for land annexed in the West Bank?
Other Israelis say the access issue can be solved with tunnels and bridges. They argue that the Palestinians can be compensated for land annexed in the West Bank with other territory in Israel, mainly in the Negev desert, as Trump’s plan suggests.
What are the Israeli perspectives on the two state solution?
Israeli Perspectives on the Two-State Solution. “Israeli recognition of Palestinian statehood will tangibly advance the two-state vision and will eliminate the dangerous one-state vision that extremists on the right and the left are advancing, among us and among the Palestinians. We have to be honest with ourselves.
Why do Jews have the right to live in the West Bank?
While there are other moral and historic arguments why Israel and Jews have the right to live in the West Bank, the only REAL purpose of ‘settlements’ is to prevent the emergence of any ‘Palestinian state.’ No other rationalization or justification is needed.”
What is the apartheid issue?
The so-called apartheid issue is a canard. Israeli Arabs lived under martial law between the end of the War of Independence in 1949 and 1966, and no one spoke of apartheid. Israel’s most pressing problem in the near future may be Arab refugees trying to get in.”
What is the two state solution?
This will be a critical year for achieving the two-State solution, bringing an end to the occupation that started in 1967, and securing an independent, viable and sovereign State of Palestine living in peace and security with the State of Israel where each recognizes the other’s legitimate rights.
When was the 2 state solution archived?
This site was archived on Aug. 3, 2021. The two-state solution is no longer the most popular solution among the jurisdictions involved. A reconsideration of the topic on this site is possible in the future.
Is the Palestinian leadership committed to a peaceful settlement?
The Palestinian leadership remains committed to a peaceful, negotiated settlement to our conflict with Israel based on the two-state solution.”
Is there room for many Jews in Judea and Samaria?
In Judea and Samaria there is ample room for many Jews, many Palestinians and peaceful coexistence… After 20 years of failed attempts to reach a two-state solution, isn’t it time we admit our failures and move on? The time has come to invest in new, innovative paths to peace that unite people through acts of mutual respect.”
