
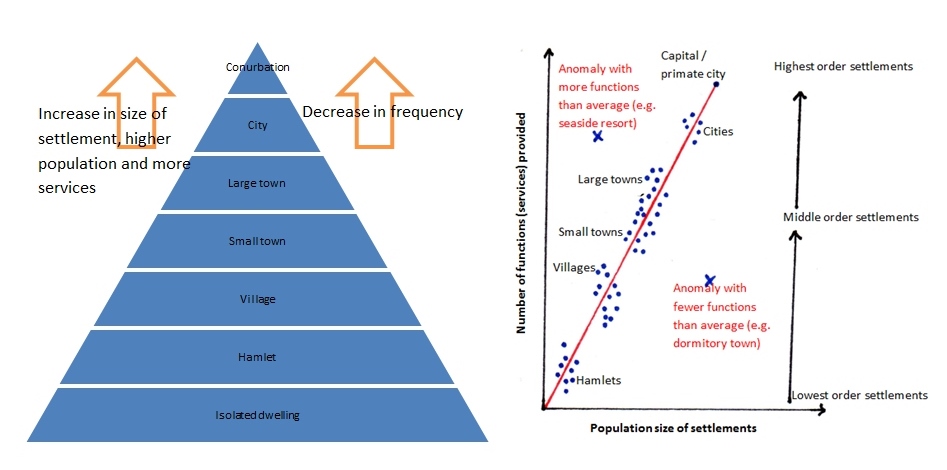
- Settlements can be described as being part of the urban hierarchy.
- Where they stand on the hierarchy depends on a number of factors, the main ones being population, the number of services a settlement has and its sphere of influence.
- This can be represented on a pyramid as shown above
- In a given area there will be many lower order urban centers e.g. ...
What is the settlement hierarchy in geography?
If we group and classify a number of settlements according to their size and shape, the result is settlement hierarchy. Settlements gradually evolve from rural to semi-urban and to urban. As you move up the hierarchy, the size of the settlement and the distance between similar-sized settlements increase.
What is urban hierarchy analysis?
The analysis of urban hierarchy mainly relates to the ranked order of cities based on different criteria, such as population size, economic power, retail sales, and the number of industrial workers. The hierarchy of urban settlements is arranging them vertically from top to bottom based on the size of the urban population.
How can we categorise settlements according to their size?
We can categorise settlements according to their size and shape. The result is a settlement hierarchy. A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services.
Why are urban hierarchies important?
Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are conventionally ranked at the national level; however, the ranking can be extended globally to include all cities. Urban hierarchies tell us about the general organization of cities and yield some important insights.
What is meant by urban hierarchy?
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area.
What is meant by hierarchy settlement?
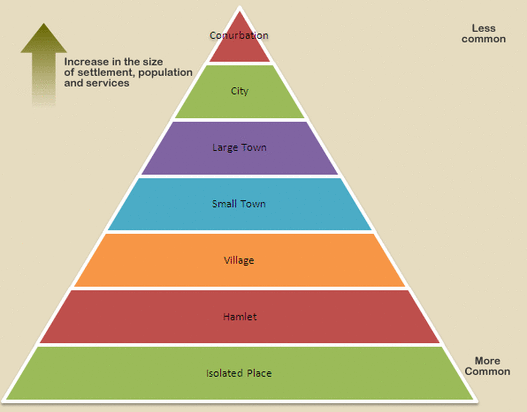
A settlement hierarchy is when settlements are put in an order and classified based on their size and/or the range of services that they provide for people. The higher up the hierarchy you go, there are fewer settlements but they increase in their size in terms of population and the number of services provided.
What is the order of settlement hierarchy?
A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services. As you move up the settlement hierarchy the size of the settlement increases, as does the population and the range of services available.
What are the 4 types of urban settlements?
Types of Urban SettlementsTown. A town is the closest term to a rural settlement. ... City. Cities are much larger in size and population than towns. ... Conurbation. Conurbation is applied to large areas of urban settlement that are combined. ... Megalopolis.
What is an example of a settlement hierarchy?
Example of a settlement hierarchy. In this example, a roadhouse is at the lowest level while the ecumenopolis is at the top with the greatest number of residents: This is only an example, and in other contexts, the population criteria for each category of settlement might be different.
What are the 5 types of settlements?
There are 5 types of settlement classified according to their pattern, these are, isolated, dispersed, nucleated, and linear.
What are high order settlements?
High-order centres – large settlements, e.g a city. The sphere of influence of this type of town will be larger. High-order functions and services = things and services that are specialised and required by fewer people, e.g e.g. jewelers, car dealers, banks, universities, legal services, hospitals and specialists.
What is hierarchy of rural settlement?
The hierarchy among rural settlements is characterised by their interdependence using gravity model and the central settlements are identified according to the forms of settlement clusters with their respective three spatial patterns (i.e., single-centre, dual-core and linear).
Which settlement is the smallest?
The generally accepted order of the hierarchy is:Isolated dwelling (>10 people)Hamlet (>100 people)Village (100-1,000 people)Small town (1,000-20,000 people)Large town (20,000-100,000 people)City (100,000-one million people)Large city or conurbation (<1,000,000 people)
What are the 3 types of urban areas?
Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs.
What are 2 main types of settlement?
Settlements can broadly be divided into two types – rural and urban.
What are the three types of settlement?
Settlement Types There are generally three types of settlements: compact, semi-compact, and dispersed. Each is based on its population density.
What is hierarchy of rural settlement?
The hierarchy among rural settlements is characterised by their interdependence using gravity model and the central settlements are identified according to the forms of settlement clusters with their respective three spatial patterns (i.e., single-centre, dual-core and linear).
What is a hierarchy in geography?
If we group and classify a number of settlements according to their size and shape, the result is settlement hierarchy. As you move up the hierarchy, the size of the settlement and the distance between similar sized settlements increases.
Should I take a lump sum or structured settlement?
You should take a lump sum settlement for all small settlements and most medium-sized settlements (less than $150,000 or so). But if you are settling a larger case, there are two good reasons for doing a structured settlement. First, the structure guarantees that you won't spend the money too fast.
What is meant by informal settlements?
Informal settlements are residential areas that do not comply with local authority requirements for conventional (formal) townships. They are, typically, unauthorised and are invariably located upon land that has not been proclaimed for residential use.
How does the urban hierarchy work?
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area. Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are conventionally ranked at the national level; however, the ranking can be extended globally to include all cities. Urban hierarchies tell us about the general organization of cities and yield some important insights. First, it tells us that within a system of cities, some cities will grow to be very large, but that number will be small relative to the universe of cities. Second, it refutes the expectation of an optimally sized city. Lastly, it establishes cities as belonging to an inter-related network where one city's growth affects others'.
How is the hierarchy related to the power law?
The hierarchy is usually related to the empirical regularity with which cities are distributed . The pattern has been formulated in a number of ways, but usually as a variation of the power law. Formally, it is a frequency distribution of rank data where the frequency is inversely proportional to rank such that cities with population larger than S are approximately proportional to S−a, where a is normally close to 1. There are no good explanations for the exponent consistently being close to 1. This is problematic because an exponent of 1 in the power law implies an infinite population. Paul Krugman proposes that, in the case of cities, the power law operates according to the percolation theory. This relaxes the condition on the exponent approaching the value of 1 and breaking down the model. Importantly, the application of a percolation model leads to one of the key insights regarding city sizes: geography and economic conditions give cities advantages that allow them to grow more than cities with a relative scarcity of these benefits.
What are some examples of primate cities?
Countries with a primate city, a city that dominates in population size and, usually, economically, have a deficit of intermediate size cities. Examples of primate cities include Paris in France, London in the United Kingdom, and Tokyo in Japan. The history of these countries play a large role in the persistence of their primate city. Particularly, the concentration of political power in one city early on has a large degree of path dependency.
How many metropolitan areas were there in 1991?
The urban hierarchy has been described in detail in the United States where the power law has held consistently for over a century. In 1991, there were 40 U.S. Metropolitan Areas with population above 1 million, 20 above 2 million, and 9 with more than 4 million.
What are the factors that influence the size of cities?
Henderson's model of urban system relies on three sets of factors that influence the size of cities: land inputs, labor, and capital. The model formally relates the benefits of economies of agglomeration and congestion cost. Cities benefit from economies of scale that attract firms and workers, making them larger. But, the limited supply of land means that the price of locating near the center of production increases as the population size increases. Eventually, the greater costs lead to diminishing returns to scale and cities tend towards an optimal equilibrium size, assuming they all share the same attributes. Henderson relaxed the assumption of identical cities to explore the implications of a diversified economy of traded goods. The extension of the model underlies the urban system literature and gives rise to the finding that cities will differ in size to account for the factor rewards associated with traded goods of varying degrees of return to scale and intensity of land use.
How many cities are in the Zipf distribution?
Shlomo Angel finds that the pattern holds remarkably well for a global sample of 3,646 cities. The predicted distribution based on Zipf's law and the actual distribution are virtually identical. The most common size ranges from 100,000 to 200,000 and constitutes about half of the entire sample. The distribution extends to the largest cities with population over 2.5 million.
What is the difference between a settlement hierarchy and a smaller settlement?
A settlement hierachy. As you move up the settlement hierarchy the size of the settlement increases, as does the population and the range of services available. Smaller settlements tend to provide only low order services such as a post office and newsagents. Whereas, larger settlements have more high order services such as leisure centres ...
How to categorize settlements?
We can categorise settlements according to their size and shape. The result is a settlement hierarchy. A settlement hierarchy is found by putting settlements in a region or country into a rank order either by population or type and range of services.
What is high order settlement?
This is the market area that a settlement services (the distance people will travel to use services). High order services usually have a high threshold. This means they need a higher number of people to use the service in order to remain profitable.
What are the characteristics of an urban settlement?
Definition of urban settlement varies from country to country, however, the following are the main characteristics: More than 75 % population are involved in secondary & tertiary sector. High population density. The urban settlement is notified by the government.
What are some examples of megalopolis?
Megalopolis: Population more than 1 crore or 10 million, Tokyo & New Delhi are the examples. Conurbation: Population between 50 lakh to 1 crore or 5 million to 10 million. The Metropolis: Population between 10 lakh to 50 lakh or 1 million to 5 million. The city: Population between 5 lakh to 10 lakh or 0.5 million to 1 million.
Who should notify the town area committee?
The area should have a municipality, corporation, canton board or urban area should have notified by the town area committee.
What is settlement hierarchy?
e. A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England.
How does a settlement affect its hierarchy?
A settlement's population size, its geographic area, its status and the availability of services can all affect this hierarchy. Position in a settlement hierarchy can also depend on the sphere of influence. This is how far people will travel to use the services in the settlement: if people travel further the town becomes more important and ranks higher in the settlement hierarchy.
What is the German planning system?
The German planning system is based on the Central Place Theory developed by Walter Christaller in the 1930s and first applied in the Nazi Era, especially in Poland. Every settlement is categorized by function: highly central cities Oberzentrum [ de] (e.g. Hamburg, with speciality clinics for tropical diseases), middle central cities Mittelzentrum [ de] (for periodic functions e.g. Homburg (Saar) with major schools (starting at 5th grade)) and basic central towns Grundzentrum [ de] /Unterzentrum (e.g. Illingen with basic doctors and Supermarket). The number of inhabitants is less important: thus a city such as Kaiserslautern (100,000 people) can be a highly specialized city, because it is a centre for the surrounding rural area.
What is the name of the city with a population of over one billion?
Eperopolis - incorporated gigacities in excess of one billion population, in which the entire continental region is an unbroken continuum of human settlements.
What is a Regiopolis?
Regiopolis or City - a large city with a large population and many services. The population is less than one million but over 300,000 people.
How many people are in a hamlet?
Hamlet or Band - a hamlet has a tiny population (fewer than 100), with only a few buildings. A social band are the simplest level of foraging societies with generally a maximum size of 30 to 50 people; consisting of a small kin group, no larger than an extended family or clan.
How many people are in a conurbation?
Conurbation or Global city - an extremely large city consists of a group of metropolises, containing between three and ten million residents.
Overview
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area. Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are conventionally ranked at the national level; however, the ranking can be extended globally to include all cities. Urban hierarchies tell us about the general organization of cities and yield some important insights. First, it tells us that within a …
Theoretical distribution
The hierarchy is usually related to the empirical regularity with which cities are distributed. The pattern has been formulated in a number of ways, but usually as a variation of the power law. Formally, it is a frequency distribution of rank data where the frequency is inversely proportional to rank such that cities with population larger than S are approximately proportional to S , where a is normally close to 1. There are no good explanations for the exponent consistently being close t…
Empirical evidence
The urban hierarchy has been described in detail in the United States where the power law has held consistently for over a century. In 1991, there were 40 U.S. Metropolitan Areas with population above 1 million, 20 above 2 million, and 9 with more than 4 million.
Recent advances in data collection have allowed researchers to test the theoretical distribution against global data. Shlomo Angel finds that the pattern holds remarkably well for a global sampl…
Explanation
While the frequency distribution of urban hierarchies is empirically simple, the set of factors that create it are complex and no individual explanation can account for the distribution. The unequal distribution of city sizes and lack of convergence on one equilibrium size are relatively well understood. Henderson's model of urban system relies on three sets of factors that influence the size of cities: land inputs, labor, and capital. The model formally relates the benefits of economie…
Alternative hierarchy
While the pattern of urban hierarchy tends to conform to the power law, it is not universal. Especially at the country level, significant deviations from the theoretical distribution are observed. Countries with a primate city, a city that dominates in population size and, usually, economically, have a deficit of intermediate size cities. Examples of primate cities include Paris in France, London in the United Kingdom, and Tokyo in Japan. The history of these countries play a large role in th…