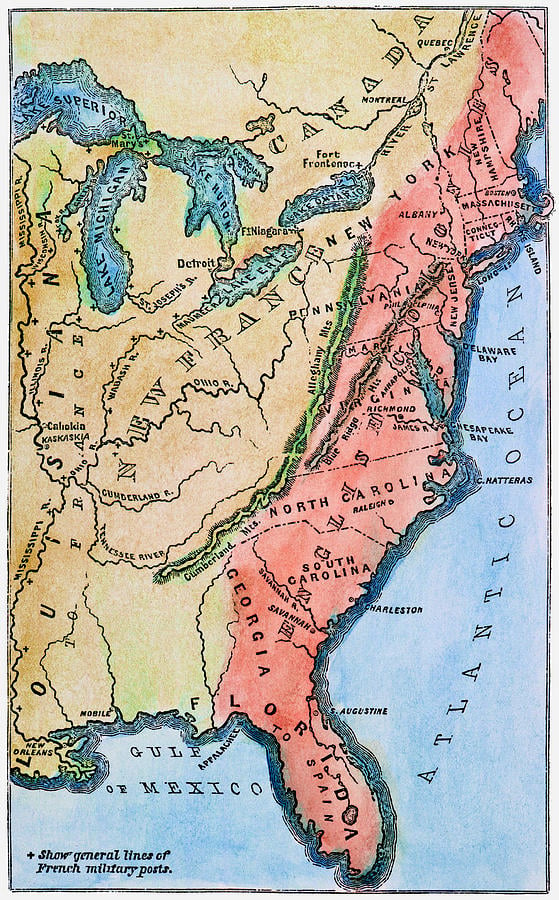
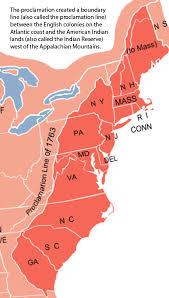
What was the result of the proclamation of 1763?
It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Proclamation forbade all settlements west of a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains, which was delineated as an Indian Reserve.
What happened to Native Americans after the Revolutionary War?
Native Americans, who had helped the French during the War, were still fighting over land even though the War was over. One large battle called Pontiac's Rebellion went on even after the Europeans called a ceasefire. >Even after Britain issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763, Daniel Boone continued to settle areas west of the Appalachian Mountains.
What caused tension between the colonists and the Native Americans?
Many colonists disregarded the proclamation line and settled west, which created tension between them and the Native Americans.
What were British colonists forbidden to do in colonies?
British colonials were forbidden to settle on native lands, and colonial officials were forbidden to grant ground or lands without royal approval. Organized land companies asked for land grants, but were denied by King George III.
See more
Why were the colonists angry?
The colonists were angry because they had to pay taxes to England but they did not get to have a representative in the English Parliament.
What was the final offer of peace made by the colonies?
On July 8, 1775, the colonies made a final offer of peace to Britain, agreeing to be loyal to the British government if it addressed their grievances (repealed the Coercive Acts, ended the taxation without representation policies). It was rejected by Parliament, which in December 1775 passed the American Prohibitory Act forbidding all further trade with the colonies.
Why were military courts established in the colonies?
Military courts, in which defendants are not entitled to a trial by jury of peers. These were established in the colonies to try colonial smugglers because colonial juries often sympathized with smugglers and would not convict them.
Who established the 13 colonies?
established the 13 American colonies as independent states, free from rule by Great Britain. Thomas Jefferson wrote the
Where was the first battle of the Revolution?
The first battle of the Revolution in which British general Thomas Gage went after the stockpiled weapons of the colonists in Concord, Massachusetts.
Why did the British want to prevent American colonists from settling in the mountains?
The British believed that if Americans moved west over the mountains, it would be too challenging to regulate trade and taxes, and that their resources would be spread too thin.
What did the colonists rebel against?
As a result, colonists rebelled against this law just like they did with the mercantile laws. They took scores of wagons westward toward the Ohio Valley. They believed that if they acted together, it would be nearly impossible for the British to enforce their new law. You are a British lawmaker.
What was the battle between the colonists and the British over the Royal Proclamation of 1763?
The fight between the colonists and the British over enforcement of the Royal Proclamation of 1763 was one of many political battles between the British and their subjects in America. The colonists did not feel the law respected their needs for growth, so they ignored the Proclamation and headed forth into the west.
Why was the Royal Proclamation of 1763 not helpful?
For those living in the colonies, creating a boundary was not helpful because it did not address some of their biggest problems with the War. Colonial blood had been shed to fight the French and Indians, and many felt they had the right to go settle on the land that was won. In addition, the Royal Proclamation of 1763 did not account for American colonists who had already settled in the West.
What was the boundary of the thirteen colonies?
The solution seemed simple. They issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which declared the boundaries of the thirteen colonies as the Appalachian Mountains. Any travel or settlement beyond the mountains would be illegal.
What was the name of the land that the British gained after the French and Indian war?
The territory that was gained, the Ohio Valley, was between the Appalachian Mountains in the east and the Mississippi River in the west. It gave the British access to important trade routes, ...
Did the French give up their claim to land in the Ohio Valley?
Even though the French government had given up this territory to Britain, the French people who had settled there didn’t give up their claims to land or trade routes.
Why did the British oppose the Proclamation Line?
British colonists and land speculators objected to the proclamation boundary since the British government had already assigned land grants to them. Including the wealthy owners of the Ohio company who protested the line to the governor of Virginia, as they had plans for settling the land to grow business. Many settlements already existed beyond the proclamation line, some of which had been temporarily evacuated during Pontiac's War, and there were many already granted land claims yet to be settled. For example, George Washington and his Virginia soldiers had been granted lands past the boundary. Prominent American colonials joined with the land speculators in Britain to lobby the government to move the line further west.
Who issued the Proclamation of 1763?
t. e. The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain.
How did the Royal Proclamation affect the American Revolution?
Others have argued that colonial resentment of the proclamation contributed to the growing divide between the colonies and the mother country. Some historians argue that even though the boundary was pushed west in subsequent treaties, the British government refused to permit new colonial settlements for fear of instigating a war with Native Americans, which angered colonial land speculators. Others argue that the Royal Proclamation imposed a fiduciary duty of care on the Crown.
What was the role of the Royal Proclamation in the Treaty of Upper Canada?
Upper Canada created a platform for treaty making based on the Royal Proclamation.
What was the name of the British colony in 1763?
John River on the Labrador coast was reassigned to the Newfoundland Colony. The lands west of Quebec and west of a line running along the crest of the Allegheny Mountains became (British) Indian Territory, barred to settlement from colonies east of the line.
What were the first two treaties that were signed with the Native Americans?
The first two of these treaties were completed in 1768; the Treaty of Fort Stanwix adjusted the border with the Iroquois Confederacy in the Ohio Country and the Treaty of Hard Labour adjusted the border with the Cherokee in the Carolinas. The Treaty of Hard Labour was followed by the Treaty of Lochaber in 1770, adjusting the border between Virginia and the Cherokee. These agreements opened much of what is now Kentucky and West Virginia to British settlement. The land granted by the Virginian and North Carolinian government heavily favored the land companies, seeing as they had more wealthy backers than the poorer settlers who wanted to settle west to hopefully gain a fortune.
What was the French and Indian War?
Under the treaty, all French colonial territory west of the Mississippi River was ceded to Spain, while all French colonial territory east of the Mississippi River and south of Rupert's Land (save Saint Pierre and Miquelon, which France kept) was ceded to Great Britain. Both Spain and Britain received some French islands in the Caribbean, while France kept Haiti and Guadeloupe.
