
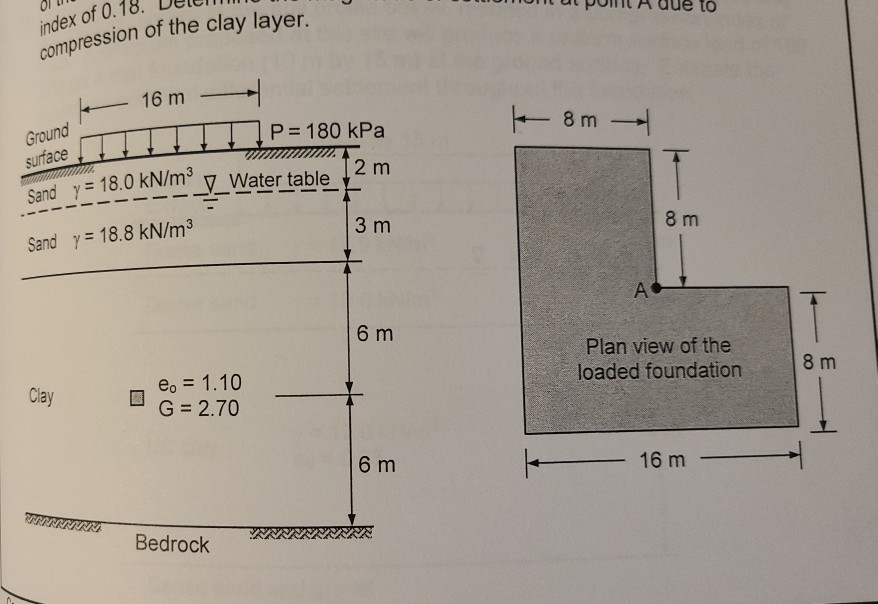
p’Cp’F = pressure after the footing is placed p’o + ΔpExample #3: Find the settlement due to consolidation of a 9 ft x 9 ft column foundation with a load of 2000 lbs. The foundation is placed 3 ft below the top surface, and the clay layer is 25ft thick. There is a sand layer underneath the clay layer. The density of the clay layer is 115 lbs/cf, the compression index of the clay layer is.32, the recompression index is.035. The preconsolidation pressure is 1615 lbs/sf and the initial void ratio of the clay is.80. Assume that the pressure is distributed at a 2:1 ratio and the clay is normally consolidated.2000 lbs
Full Answer
What are the compression index parameters needed for an settlement analysis?
Settlement analyses for embankments over soft soils require the compression index parameters that can be obtained from standard one-dimensional oedometer tests of the fine-grained soils.
What is the compression index used to find?
The compression index is used to find the settlement in the normally consolidated clay. The total stress applied is larger than the stress in the field, to which the soil sample has been undergone in the past. This kind of clayey soil is said to be normally consolidated clay.
How do you calculate the settlement of a material?
The settlement (ρ) may be calculated by means of the compression index by use of the followingρ expression= layer thickness x strain = thickness x ∆e + ei (9.14) Cc log 10((σ' +
How do you calculate secondary compression index in soil?
The modified secondary compression indices, Cɛα = Cα / (1 + e0 ), for the soft soils have been calculated using the Cα values derived from the laboratory testing and are tabulated in Table 25.16. Table 25.16. Modified secondary compression index of peat, organic soil, and clay from oedometer tests
How do you calculate compression index?
The Compression Index (Cc) is equal to the slope of the graph of pressure versus void ratio (log scale) [7]. Compression Index (Cc) for clay is in the range 0.258 to 0.968, while for laterite soil was in the range 0.101 to 0.940. Value of Compression Index (Cc) is different between each type of soil.
How do you calculate the compression index of a consolidation test?
3:294:41compression index - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis gap is Delta e then C C equal to change in void ratio. That is Delta e divided. By log of baseMoreThis gap is Delta e then C C equal to change in void ratio. That is Delta e divided. By log of base 10 final stress delta Z Sigma naught plus Delta Sigma bar whole divided by Sigma naught bar.
What is a compression index?
The compression index (Cc) is the slope of the linear portion of the pressure–void ratio curve on a semi-log plot, with pressure on the log scale (IS: 8009 – Part 1, 1976). This is a dimensionless parameter.
How do you calculate compression index and recompression index?
The compressibility parameters such as compression index and recompression index are usually obtained by using the graphical analysis of compression curve in void ratio—effective stress (e − log σ) plots in Fig.
What is the compression index for the normally consolidated soil?
constantExplanation: The compression index for normally consolidated soil is constant. To achieve normal consolidation, the total load applied on the sample is greater than that which is experienced in the field layer of soil from which the sample is collected.
How is consolidation settlement calculated?
5:489:18Consolidation Settlement Equations - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTimes the log of our final stress which is Sigma prime Z naught plus Delta Sigma minus the log ofMoreTimes the log of our final stress which is Sigma prime Z naught plus Delta Sigma minus the log of the initial vertical effective stress. That's the change in void ratio.
How do you calculate compression index from liquid limit?
Compressibility: The average specific gravity of organic soil Correlations of compressibility properties: particles could be calculated from: Compression index-liquid limit: The plot of found − 0.2848 compression index (C c ) versus the liquid limit of the Gs = 5.2636 × (OC) organic soils (Fig.
How do you calculate secondary compression index?
The magnitude of secondary compression is expressed by the secondary compression index, Cα = Δe/Δlog t, in which e = void ratio and t = time.
What is the difference between compression and compaction?
Compression is a process of compressing, or increase in density or lessening in the bulk volume of granules or powder. While Compaction is the process of alteration of powders into a coherent specimen or compacting powder or granules.
What is CC in consolidation?
Settlement is estimated from compression index cc, which is obtained from void ratio e versus vertical effective stress σ' in the semi-logarithmic plane. Coefficient of consolidation cv is used to predict the time required for a given amount of compression to take place i.e., rate of settlement.
How do you calculate Preconsolidation pressure?
Draw the bisector line between the previous horizontal and tangent lines, and draw the NCL; The vertical stress corresponding to the point of intersection between the bisector line and the NCL represents the preconsolidation pressure, .
What is swelling index of soil?
DEFINITION • Free Swell Index is the increase in volume of a soil, without any external constraints, on submergence in water.
How do you calculate secondary compression index?
The magnitude of secondary compression is expressed by the secondary compression index, Cα = Δe/Δlog t, in which e = void ratio and t = time.
What is CC in consolidation?
Settlement is estimated from compression index cc, which is obtained from void ratio e versus vertical effective stress σ' in the semi-logarithmic plane. Coefficient of consolidation cv is used to predict the time required for a given amount of compression to take place i.e., rate of settlement.
What is CV in consolidation?
cv is the coefficient of consolidation and is a measure of the rate at which the consolidation process proceeds. In many consolidation problems in which the total stress σ remains constant throughout.
How do you calculate the void ratio in a consolidation test?
Void ratio. The Coefficient of consolidation at each pressures increment is calculated by using the following equations : Cv = 0.197 d2/t50 (Log fitting method) Cv = 0.848 d2/t90 (Square fitting method)
Compression Index
It describes the variation of the void ratio e as a function of the change of effective stress σef plotted in the logarithmic scale:
Engineering Manuals
Download manuals with theory and practical explanations of the program use.
What is compression index?
The compression index is used to find the settlement in the normally consolidated clay. The total stress applied is larger than the stress in the field, to which the soil sample has been undergone in the past. This kind of clayey soil is said to be normally consolidated clay.
Why can't preconsolidation stress be determined?
The preconsolidation stress value cannot be determined exactly because it is through geological process. The expression for computing the settlement is given below. Here, the term H is height of the soil, e 0 is initial void ratio, increasing vertical stress and overburden stress.
What is the slope of a virginal curve?
The slope taken from virgin compression curve is termed as compression index . This is denoted by the symbol C c . The image representation of the virginal compression curve and slope for compression index are shown in the below image.
How to measure soil compressibility?
The compressibility of a soil is often measured in a laboratory device known as an oedometer or consolidometer. Fig. 9.9 shows a cross sectional outline of an oedometer in which the cylindrical soil sample is confined inside a ring in order to prevent lateral strain. Porous stones are placed on both sides of the soil to permit escape of water. The vertical load is applied to the soil in one of a variety of ways such as by application of weights to a hanger, by means of weights applied through a lever system to the top of the soil or by means of air pressure applied to a piston. The amount of vertical compression experienced by the soil as a result of the application of load is measured by means of a dial gauge or a displacement transducer. The conventional testing technique, which is described in most books on soil testing, consists of applying successive increments of load and observing the deflection after each increment until the movement ceases. In a saturated sample of soil the application of the vertical load results in the development of a pore pressure (equal to the vertical stress applied) within the soil. This pore pressure gradually dissipates as water is expelled from the soil through the porous stones. Movement of the soil continues until the pore pressure has fully dissipated. Typical time-deflection plots for a clay soil are illustrated in Fig. 9.10. This figure shows soil deflection continuing until approx. 24 hr. Valuable information relating to prediction of rate of settlement of structures may be extracted from data such as that shown in Fig. 9.10 and this matter will be explored in Chapter 10.
What is the symbol for confined compressibility?
The confined (one dimensional) compressibility is also referred to as the coefficient of volume compressibility or the coefficient of volume decrease and the symbol mv is widely used to indicate the value of this compressibility.
Which part of the e-log splot is curved?
The upper part of the e –log s’plot is as shown below somewhat curved with a flat slope, followed by a linear relationship having a steeper slope.
Who suggested a simple graphic construction to determine the preconsolidation pressure s’?
Casagrande (1936) suggested a simple graphic construction to determine the preconsolidation pressure s’
What is total pressure?
The total pressure includes effective overburden pressure and net additional pressure due to the structure.
What is the OCR of NC soils?
oFrom the definition of NC soils, they always have OCR=1.
Is a surcharge reasonable simplification?
reasonable simplification if the surcharge is of large lateral extent water squeezed out
Consolidation
When the construction of the foundation is done (application of additional load), pore water pressure in the saturated clay increases as the hydraulic conductivity of the clay is very small. Some time is required for excess pore water pressed to dissipate and increase the stress to be transferred to the soil skeleton.
Terminology
Consolidation of the compressible soils occurs in two stages defined previously.
Primary Consolidation
The definition of primary consolidation is discussed above under the terminology.
Secondary Consolidation
Secondary consolidation settlement occurs after the completion of dissipation of the excess pore water pressure developed immediately after the application of load.
Worked Example: Primary Consolidation Settlement Calculation in Normally Consolidated Clay
Consolidation of soil (normally consolidated) can be evaluated from the following equation as discussed in this article.
