
Area in the West Bank outside East Jerusalem
| Name | Hebrew | Population (2019) [7] | Est. [7] | Council |
| Adora | אדורה | 462 | 1984 | Har Hebron |
| Alei Zahav | עלי זהב | 3,399 | 1982 | Shomron |
| Alfei Menashe | אלפי מנשה | 7,952 | 1983 | Shomron |
| Alon Shvut | אלון שבות | 3,098 | 1970 | Gush Etzion |
Full Answer
What is it like to live on an Israeli settlement?
Settlements also have schools, playgrounds, libraries and swimming pools making life quite comfortable and high quality. For many Israelis this is attractive as a housing shortage within Israel proper has seen prices climb to new heights. In Modin Illit, one can buy a 4 room apartment for 1,050,000 Shekels.
Why are there Israeli settlements built in Palestine?
When the guns fell silent in 1967, the Israeli state began building colonies, or settlements, for its Jewish Israeli citizens on Palestinian land it had just occupied. Settlements have become the hallmark of the Israeli colonial project in Palestine.
Are there any Palestinian settlements in Israel?
on MYTH: There are no Palestinian settlements. An international furor erupted when Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said that if he won the election he would assert Israeli sovereignty over parts of Area C where the Oslo Accords already grants Israel full administrative control.
Does Israel have rights to settlements in the West Bank?
Settlements on “state land” often expand into surrounding, privately owned, Palestinian land. As an occupying power, Israel does not own the West Bank and is not permitted under international law to seize land in this manner. Based on the law in the West Bank, a state is only allowed to expropriate private land for public Palestinian needs.

What does settlement mean in Israel?
Israeli settlement, any of the communities of Israeli Jews built after 1967 in the territories occupied by Israel after the Six-Day War—the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. Most, but not all, were authorized and supported by the Israeli government.
Why are there Israeli settlements in Palestine?
After the military assaults of 1948-'50, Zionist armed forces, subsequently transformed into the Israeli army, constructed Jewish settlements over the ruins of Palestinian towns and villages throughout the 78 percent of historic Palestine they controlled.
How many settlements does Israel have?
Today they total around 400,000 and live in about 130 separate settlements (this doesn't include East Jerusalem, which we'll address in a moment). They have grown under every Israeli government over the past half-century despite consistent international opposition.
What is a settlement in Palestine?
Settlements are communities of Jews that have been moving to the West Bank since it came under Israeli occupation in 1967. Some of the settlers move there for religious reasons, some because they want to claim the West Bank territory as Israeli land, and some because the housing there tends to be cheap and subsidized.
Is Israel occupying Palestine land?
BACKGROUND: Palestinian territory – encompassing the Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East Jerusalem – has been illegally occupied by Israel since 1967.
Why is Israel entitled to the land?
Jewish religious belief defines the land as where Jewish religious law prevailed and excludes territory where it was not applied. It holds that the area is a God-given inheritance of the Jewish people based on the Torah, particularly the books of Genesis and Exodus, as well as on the later Prophets.
Are there Israeli settlements in Gaza?
According to the report of the Security Council Commission established under resolution 446 (1979): "Between 1967 and May 1979, Israel has established altogether 133 settlements in the occupied territories, consisting of 79 in the West Bank, 29 in the Golan Heights, 7 in the Gaza Strip and 18 in the Sinai.
What was Israel before 1948?
The region was ruled under the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948, when the Jewish State of Israel was proclaimed in part of the ancient land of Israel. This was made possible by the Zionist movement and its promotion of mass Jewish immigration.
Why is Israel settling the West Bank?
Israel has cited several reasons for retaining the West Bank within its ambit: a claim based on the notion of historic rights to this as a homeland as affirmed in the Balfour Declaration of 1917; security grounds, both internal and external; and the deep symbolic value for Jews of the area occupied.
When did Israel take Palestine?
Since the occupation first began in June 1967, Israel's ruthless policies of land confiscation, illegal settlement and dispossession, coupled with rampant discrimination, have inflicted immense suffering on Palestinians, depriving them of their basic rights.
What happened to Israeli settlements in Gaza?
The Israeli disengagement from Gaza (Hebrew: תוכנית ההתנתקות, Tokhnit HaHitnatkut) was the unilateral dismantling in 2005 of the 21 Israeli settlements in the Gaza Strip and the evacuation of Israeli settlers and army from inside the Gaza Strip.
Are there Israeli settlements in Gaza?
According to the report of the Security Council Commission established under resolution 446 (1979): "Between 1967 and May 1979, Israel has established altogether 133 settlements in the occupied territories, consisting of 79 in the West Bank, 29 in the Golan Heights, 7 in the Gaza Strip and 18 in the Sinai.
How many Israelis live in Palestinian lands?
Roughly 10 percent of Israel's 6.8 million Jewish population lives in these occupied Palestinian territories. Despite being outside of Israel proper, these settlers are granted Israeli citizenship and receive government subsidies that significantly lower their cost of living.
Where are the Israeli settlements?
Israeli settlements currently exist in the Palestinian territory of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and in the Syrian territory of the Golan Heights. East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights have been annexed by Israel, so residents are treated equivalently to the rest of Israel under Israeli law.
What are the settlements in East Jerusalem?
East Jerusalem settlements (2006) Golan Heights settlements (1992) Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Jewish ethnicity, built in violation of international law on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Israeli settlements currently exist in ...
How many settlements were there in the Gaza Strip?
Before Israel's unilateral disengagement plan in which the Israeli settlements were evacuated, there were 21 settlements in the Gaza Strip under the administration of the Hof Aza Regional Council. The land was allocated in such a way that each Israeli settler disposed of 400 times the land available to the Palestinian refugees, and 20 times the volume of water allowed to the peasant farmers of the Strip.
What was the Allon Plan?
It implied Israeli annexation of major parts of the Israeli-occupied territories, especially East Jerusalem, Gush Etzion and the Jordan Valley. The settlement policy of the government of Yitzhak Rabin was also derived from the Allon Plan.
How was Kiryat Arba established?
According to a secret document dating to 1970, obtained by Haaretz, the settlement of Kiryat Arba was established by confiscating land by military order and falsely representing the project as being strictly for military use while in reality, Kiryat Arba was planned for settler use.
What territories did Israel control?
It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and from Syria it captured most of the Golan Heights, which since 1981 has been administered under the Golan Heights Law .
How does settlement affect the economy?
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the security of the Israeli citizens living there.
Where are the Israeli settlements?
This is a list of Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights. Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement ...
When did Israel start building settlements in the Golan Heights?
Golan Heights. Construction of Israeli settlements began in the portion of the Golan Heights held by Israel in 1967, which was under military administration until Israel passed the Golan Heights Law extending Israeli law and administration throughout the territory in 1981.
What happened to East Jerusalem?
Following the capture and occupation of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem in 1967, the Israeli government effectively annexed the formerly Jordanian occupied territory and extended the Jerusalem municipality borders by adding 70,500 dunams of land with the aim of establishing Jewish settlements and cementing the status of a united city under Israeli control. The Jerusalem Master Plan 1968 called for increasing the Israeli population of Arab East Jerusalem, encircling the city with Israeli settlements and excluding large Palestinian neighborhoods from the expanded municipality. Jerusalem was effectively annexed by Israel in 1980, an act that was internationally condemned and ruled "null and void" by the United Nations Security Council in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478. The international community continues to regard East Jerusalem as occupied territory and Israel's settlements there illegal under international law.
Is the Israeli settlement illegal?
The international community considers Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories illegal under international law, violating the Fourth Geneva Convention 's prohibition on the transfer of a civilian population to or from occupied territory, though Israel disputes this.
Did Israel have settlements in the Sinai Peninsula?
Israel had previously established settlements in both the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula, however the Gaza settlements were dismantled in the Israeli disengagement from Gaza in 2005 and the Sinai settlements were evacuated with the Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty and the return of the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. This list does not include West Bank ...
Does Israel have a right to the Golan?
Israel maintains it has a right to retain the Golan, citing the text of UN Resolution 242, which calls for "safe and recognised boundaries free from threats or acts of force". However, the international community rejects Israeli claims to title to the territory and regards it as sovereign Syrian territory.
Is East Jerusalem annexed?
Israel in effect annexed East Jerusalem with the Jerusalem Law and considers settlements in the expanded boundaries of East Jerusalem to be neighborhoods of Jerusalem and not settlements. The United Nations Security Council ruled that act "null and void" in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, and the international community considers East Jerusalem to continue to be held under Israeli occupation .
What is settlement in Israel?
The term "settlements" may conjure up images of small encampments or temporary housing, and many have started that way. But they now include large subdivisions, even sizable cities, with manicured lawns and streets full of middle-class villas often set on arid hilltops. Israel is constantly building new homes and offers financial incentives for Israelis to live in the West Bank.
What are some interesting facts about Israeli settlements?
7 Things To Know About Israeli Settlements : Parallels West Bank settlements have expanded under every Israeli government over the past half-century. Nearly 10 percent of Israel's Jewish population now lives on land captured in the 1967 Six-Day War.
Where is the capital of Israel?
A Palestinian man walks near a construction site for new Israeli housing in the East Jerusalem neighborhood of Har Homa in September. The Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as a capital of a future state and object to Israeli building in the eastern part of the city and throughout the West Bank. Israel claims all of Jerusalem as its capital.
How many Israelis live in East Jerusalem?
Around 200,000 Israelis now live in East Jerusalem. Combined with the roughly 400,000 settlers in the West Bank, about 600,000 Israelis now live beyond the country's 1967 borders. That's nearly 10 percent of Israel's 6.3 million Jewish citizens.
What was the impact of the evacuation of the settlements?
The evacuation of the settlements was deeply divisive within Israel, and Israel's security forces had to drag some settlers from their homes kicking and screaming. The episode demonstrated that Israel could remove settlers, but it also showed how much friction it creates inside Israel.
Why did the Jewish people live in the West Bank?
The settlers and their supporters cite the Jewish Bible, thousands of years of Jewish history, and Israel's need for "strategic depth" as reasons for living in the West Bank.
When did Israel remove the settlers from the Gaza Strip?
Yes, on a few occasions, most notably in 2005, when it removed all 8,000 settlers from the Gaza Strip. Israel decided these small, isolated settlements were too difficult to defend in a territory where the Jewish residents accounted for less than 1 percent of the population.
How many Israeli settlements are there in the West Bank?
There are 126 Israeli settlements in the West Bank (excluding East Jerusalem), according to the September 2016 report from the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Geographically, these settlements are all across the West Bank. The West Bank is broken down into Areas A, B, and C, according to the Oslo Accords, ...
What are settlements?
Settlements are Israeli cities, towns and villages in the West Bank and the Golan Heights. (We will deal with East Jerusalem a bit later.) They tend to be gated communities with armed guards at the entrances. Why are they settlements and not simply Israeli residential areas? Because Israel is widely considered to be an occupying force in the territories. It is land that Palestinians, along with the international community, view as territory for a future Palestinian state.
Why are the West Bank and East Jerusalem considered occupied territory?
Israel began its occupation of the West Bank and East Jerusalem in 1967 during the Six-Day War. Seeing a military buildup in the surrounding Arab countries, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, after which Jordan, in turn, attacked Israel. Israel annexed East Jerusalem shortly thereafter, unifying the city under Israel’s authority. But Israel has never annexed the West Bank, part of which remains under military law.
Who are the settlers?
This is a very broad question, and requires a fair amount of generalization.
Why are the settlements controversial?
The settlements are built on land the Palestinians and the international community, along with some in the Israeli community, see as a future Palestinian state. Some of the settlements – especially the blocs – may be a part of Israel in a two-state solution through land swaps between Israelis and Palestinians. One concern, expressed by the European Union, and in the past by the US State Department, is that settlement expansion may make a contiguous, whole Palestinian state in the West Bank impossible.
What is the legal status of settlements?
The settlements are illegal under international law. The Fourth Geneva Convention, which concerns civilian populations during a time of war, states in Article 49 that, “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
What about East Jerusalem? And what is East Jerusalem anyway?
From 1948 to 1967, Jerusalem was divided by the Green Line, which is the cease-fire line of 1948 between Israel and Jordan. Although the city is now under Israeli governance, the distinction remains.
Where are the settlements in Israel?
Most of the settlements are in the West Bank, an area that Israel controls but never has formally annexed.
Why are there settlements in the West Bank?
Opponents see the settlements as part of an intentional Israeli strategy to take over the West Bank permanently. To them, the settlements' presence throughout the area gives the Israeli military a justification for being there as well, and makes it impossible for the Palestinians to ever really have an independent nation. They see the settlements rising in the hills around Palestinian cities — and the security buffers of empty land around them —as evidence that their chance for independence is fading. Additionally, they see the hundreds of checkpoints and roadblocks that the Israelis have created to thwart terror attacks on the settlements as restricting Palestinians' freedom of movement [source: BBC News ].
What Is a Settlement?
Cranes hover at a construction site in the Israeli settlement of Ramot, built in a suburb of mostly Arab East Jerusalem. AHMAD GHARABLI/AFP/Getty Images
What does the settlements represent?
To the Israeli government and supporters of the movement, including many people in the U.S., the settlements represent Israelis returning to live in places that once were part of ancient Israel, and where Jews lived in the centuries that followed. But to the Palestinians and much of the rest of the world — including 14 nations belonging to the U.N. Security Council who voted in December 2016 to condemn the settlements — they violate international law and are a major obstacle to the long-elusive vision of a two-state Israeli-Palestinian solution.
How many Israelis live in East Jerusalem?
Add to that another 200,000 Israelis who live in East Jerusalem and about 20,000 in the Golan Heights — areas also seized in the 1967 war that Israel eventually annexed — and you've got roughly 600,000 Israelis or 10 percent of Israel's 6.3 million Jewish citizens living outside Israel's pre-war borders [sources: Myre and Kaplow, BBC News ].
What was the Israeli government's goal after the 1967 war?
In 1968, they drove from Jerusalem to the West Bank city of Hebron, where Jews had been driven away by Arab armies in 1929; checked into a hotel and didn't leave. As the group's leader, Rabbi Moshe Levinger, told an interviewer years later, the objective was to reclaim land that was part of biblical Israel: "Jews are entitled to have it," he said.
What is the holiest site in Judaism?
This shot of Jerusalem shows the Wailing Wall in the foreground, the holiest site in Judaism, with the gold Dome of the Rock in the background, the third most-sacred site in Islam. Daniel Zelazo/Getty Images
Where are the settlements in Israel?
What are these settlements? They are Jewish communities built in Gaza, the West Bank and parts of East Jerusalem — areas captured by Israel during the 1967 war with neighboring Egypt, Jordan and Syria.
What is the U.N. resolution condemning Israel for building Jewish settlements on disputed land?
A controversial U.N. Security Council resolution condemning Israel for building Jewish settlements on disputed land has ripped open old wounds. Secretary of State John Kerry warned in his last major Mideast speech Wednesday that Israel was abandoning its chance for a two-state solution if it did not stop its settlement practices in ...
What is the two state solution?
The two-state solution envisions a Palestinian state made up of Gaza, the West Bank and East Jerusalem existing alongside an Israeli one. It has been the government of Israel's stated policy, but Palestinians accuse the government of negotiating it in bad faith because it has allowed settlements to grow.
What do Palestinians say about Israel?
Every time a settlement is built, Palestinians say, a little more is taken away from a future Palestinian state. The possibility of peace seems to grow less and less likely, and Palestinians accuse Israel of confiscating lands and taking away resources from the areas that Palestinians want for their statehood.
Why did Israel build a separation barrier?
Israelis say the barrier is to keep them safe. Palestinians say it amounts to nothing but a land grab and that the Israelis are taking water and other resources from Palestinian land.
What are the security measures in the settlements?
The settlements have a lot of security measures including Jewish-only roads and restrictions that split up Palestinian territory, often making it difficult for people to get to work, visit family or even go to the hospital when they are sick.
When did Israel withdraw from Gaza?
In 2005, Israel withdrew from Gaza and later placed a blockade on the Hamas-ruled territory. Israel has since fought two wars there. The West Bank and East Jerusalem are still in Israeli hands, although they are nominally governed by the Palestinian Authority based in Ramallah.
When did the Israeli government freeze settlements?
Following the first National Unity government of 1984, the Israeli cabinet announced a freeze on all new settlement activity. But, despite this and similar announcements by subsequent governments, settlement activity continued unabated, even under the pro-peace administrations of Yitzhak Rabin and Ehud Barak. At the most, there were periods in which no new settlements were constructed, but the expansion and consolidation of existing communities to allow for "natural growth" never ceased. Under the Ariel Sharon administration after February 2001, militant settlers constructed new settlement outposts on their own initiative. These were deemed illegal by the government as a means to differentiate them from the so-called "legal" settlements and were forcibly removed in an attempt to appease international criticism of settlement activity.
Why were civilian settlements necessary?
civilian settlements contributed to the defensive posture of the country and that it was necessary to ensure defensible borders between Israel and Jordan. The Allon Plan also proposed the establishment of additional settlements around Jerusalem and in close proximity to the Green Line border as a means of ensuring future territorial changes in favor of Israel. The rest of the West Bank region was deemed unsuitable for settlement because of the dense concentration of Palestinian population, unlike the Jordan valley, which was sparsely populated. Allon envisaged a situation in which the rest of the West Bank would eventually be part of an autonomous area under Jordanian administration and linked to the Kingdom of Jordan by means of a territorial corridor running from Ramallah via Jericho (the only major Palestinian population center in the Jordan Valley) to the border crossings on the Jordan River.
What is the issue of settlements?
The issue of settlements has been a major point for discussion in all negotiations aimed at bringing an end to the conflict. Most observers agree that any future peace agreement between Israel and the Palestinians based on territorial compromise will necessitate the evacuation and removal of most, if not all, of these settlements. The inconclusive territorial negotiations that accompanied the Oslo Accords either ignored the settlement issue altogether or attempted to redraw the borders in such a way as to include as many settlements on the Israeli side of the border — whether in exchange for territory elsewhere or as out-and-out annexation. The building of a unilaterally imposed security wall begun in 2002 in effect implemented this policy on the ground.
What was the West Bank settlement plan?
Known as the Allon Plan, after its initiator Deputy Prime Minister Yigal Allon, the settlement blueprint was a minimalist one aimed at constructing a line of agricultural settlements along the new eastern border in the Jordan valley. This was part of a concept that assumed that
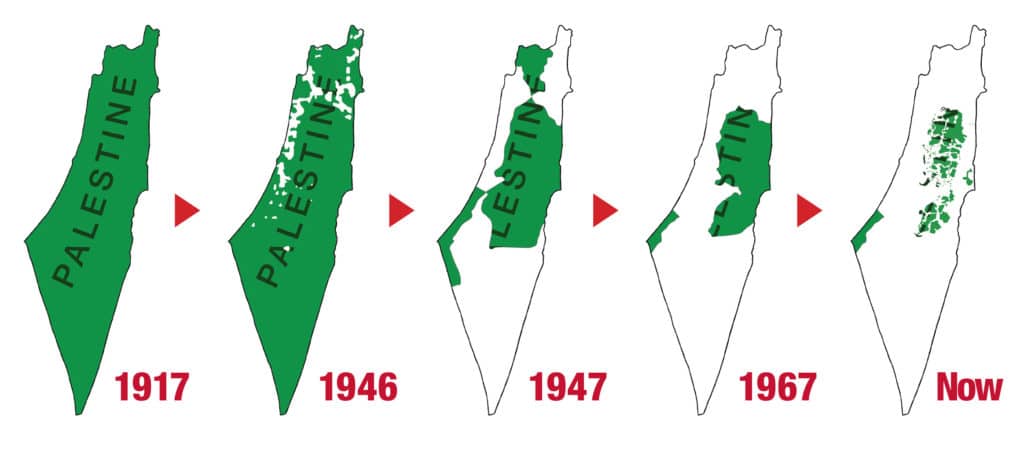
Overview
Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, overwhelmingly of Jewish ethnicity, built on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli settlements to be illegal under international law, though Israel disputes this.
Israeli settlements currently exist in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), …
Housing costs and state subventions
Settlement has an economic dimension, much of it driven by the significantly lower costs of housing for Israeli citizens living in Israeli settlements compared to the cost of housing and living in Israel proper. Government spending per citizen in the settlements is double that spent per Israeli citizen in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, while government spending for settlers in isolated Israeli settlements is three times the Israeli national average. Most of the spending goes to the securit…
Number of settlements and inhabitants
As of 2022, there are 140 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem. In addition, there are over 100 Israeli illegal outposts in the West Bank. In total, over 450,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank excluding East Jerusalem, with an additional 220,000 Jewish settlers residing in East Jerusalem.
Additionally, over 20,000 Israeli citizens live in settlements in the Golan Heights.
Character: rural and urban
Settlements range in character from farming communities and frontier villages to urban suburbs and neighborhoods. The four largest settlements, Modi'in Illit, Ma'ale Adumim, Beitar Illit and Ariel, have achieved city status. Ariel has 18,000 residents, while the rest have around 37,000 to 55,500 each.
History
Following the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel occupied a number of territories. It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt, it also captured the Sinai Peninsula a…
Geography and municipal status
Some settlements are self-contained cities with a stable population in the tens of thousands, infrastructure, and all other features of permanence. Examples are Beitar Illit (a city of close to 45,000 residents), Ma'ale Adumim, Modi'in Illit, and Ariel (almost 20,000 residents). Some are towns with a local council status with populations of 2,000–20,0000, such as Alfei Menashe, Eli, Elkana, Efrat and Kirya…
Types of settlement
• Cities/towns: Ariel, Betar Illit, Modi'in Illit and Ma'ale Adumim.
• Urban suburbs, such as Har Gilo.
• Block settlements, such as Gush Etzion and settlements in the Nablus area.
• Frontier villages, such as those along the Jordan River.
Resettlement of former Jewish communities
Some settlements were established on sites where Jewish communities had existed during the British Mandate of Palestine or even since the First Aliyah or ancient times.
• Golan Heights – Bnei Yehuda, founded in 1890, abandoned because of Arab attacks in 1920, rebuilt near the original site in 1972.
• Jerusalem – Jewish presence alongside other peoples since biblical times, various surrounding communities and neighborhoods, including Kfar Shiloah, als…