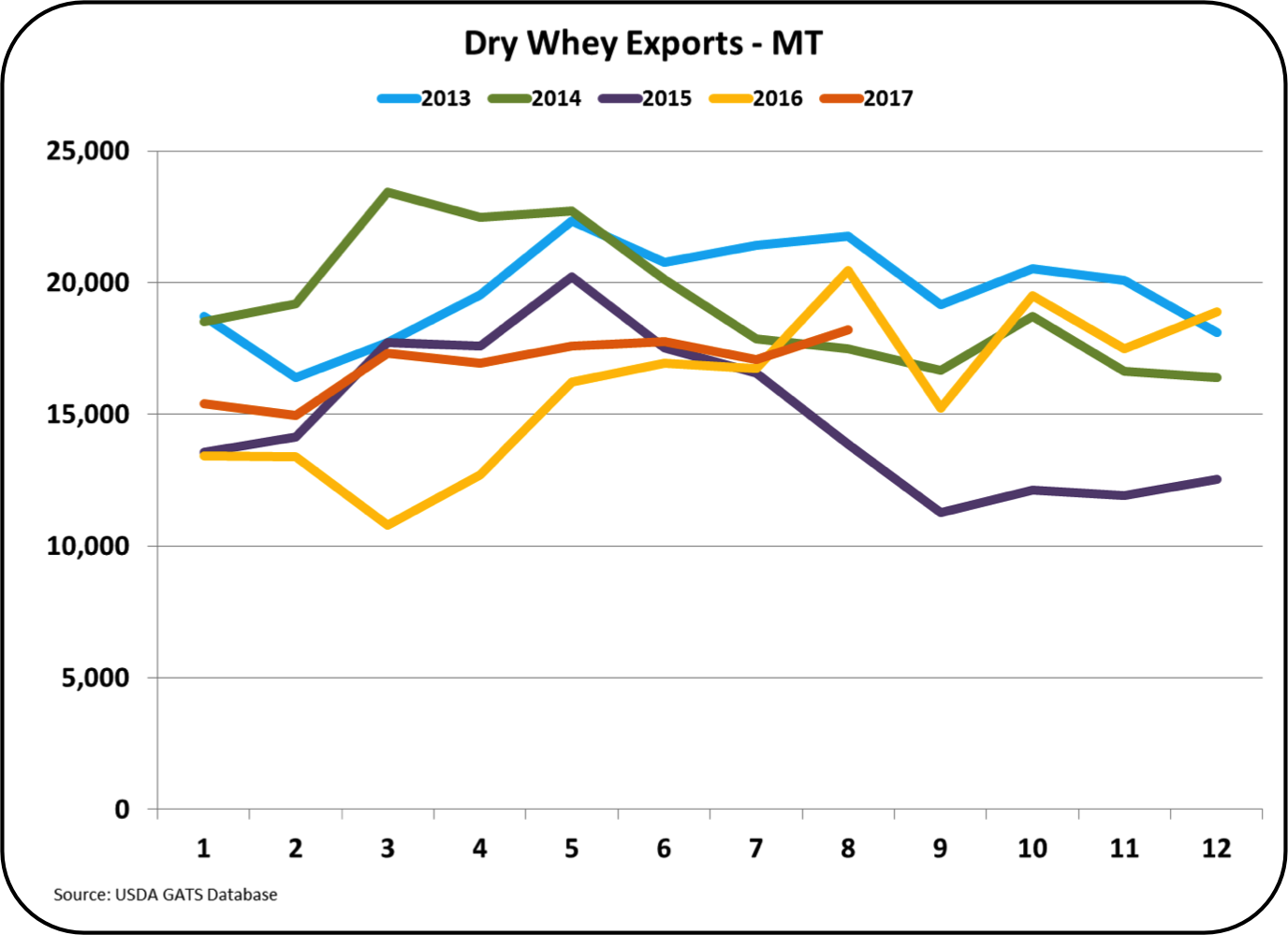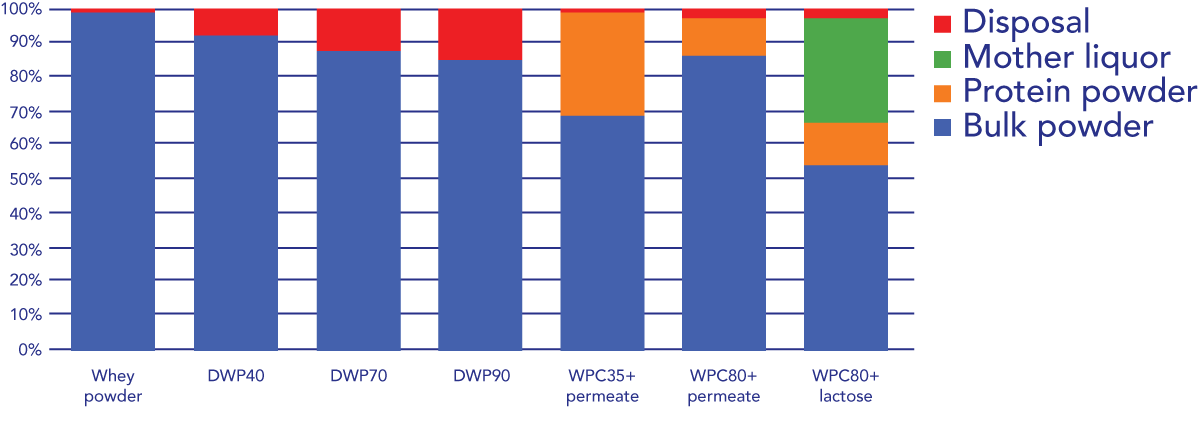
What is the difference between fluid whey and dry whey?
The whey is pasteurized and no preservatives have been added. Except for moisture, all the constituents of fluid whey are retained in the same relative proportion in dry whey. This product has a titratable acidity not over 0.16% on a reconstituted basis. Dry Sweet Whey shall not have a greater than 0.16% titratable acidity on a reconstituted basis.
What is the titratable acidity of dry sweet whey protein?
This product has a titratable acidity not over 0.16% on a reconstituted basis. Dry Sweet Whey shall not have a greater than 0.16% titratable acidity on a reconstituted basis. Dry Acid Whey shall have greater than 0.35% titratable acidity on a reconstituted basis.
What happens to whey before it is dried?
Before being dried, the whey concentrate is usually treated as mentioned above to form small lactose crystals, as this results in a non-hygroscopic product which does not go lumpy when it absorbs moisture. Acid whey from cottage cheese and casein production is difficult to dry due to its high lactic acid content.
What is spray dried whey?
Spray drying of whey, is at present, the most widely used method of drying. Before being dried, the whey concentrate is usually treated as mentioned above to form small lactose crystals, as this results in a non-hygroscopic product which does not go lumpy when it absorbs moisture.

How is dry whey made?
Dried whey product is the residue obtained when a portion of the lactose has been removed, while dried whey contains a minimum of 65% lactose. The protein content of whey products is relatively low (13%–17%), yet these products are classified as protein supplements.
What is dry whey?
Dry Whey is the product resulting from drying fresh whey which has been pasteurized and to which nothing has been added as a preservative. It shall conform to the applicable provisions of 21 CFR 184.1979. It contains all constituents, except moisture, in the same relative proportions as in the whey.
How is whey separated from milk?
After the milk has the bacteria, cooks add either powdered rennet or acidic bacteria (such as lactic acid bacteria). The culture converts the milk's lactose into lactic acid, while the rennet acts as a coagulate to set the cheese. The curds (solidified milk protein) separate from the whey during this process.
How is whey processed?
Whey is derived from the cheesemaking process. Once the milk passes quality tests, enzymes are added to separate the curd from the liquid whey. The liquid whey is then pasteurized and the protein is concentrated and isolated. The two main methods to achieve this are membrane filtration and ion exchange technology.
Does dried whey contain lactose?
Whey concentrate: This contains up to 85% protein and a small amount of lactose.
How much whey do you get from a gallon of milk?
To get your hands on some fresh whey, try making cheese at home. In general, a pound of soft cheese such as mozzarella or goat cheese, made from a gallon of fresh milk, yields 9 pounds of whey.
How protein is separated from whey?
This is typically done using Ultrafiltration (UF), Reverse osmosis (RO) or diafiltration. Whey protein concentrate (WPC) is usually processed by ultrafiltration. In whey processing, whey protein is separated by UF as a retentate and lactose as the permeate. Then, both products are concentrated by evaporation.
How do you turn whey powder into liquid?
0:395:06Homemade Whey Protein Powder - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt up to 180 degrees and then add five tablespoons of lemon juice mix. And then put a lid on top andMoreIt up to 180 degrees and then add five tablespoons of lemon juice mix. And then put a lid on top and let it sit for about 20 minutes off the heat. Then get a pot strainer.
Can whey be fermented?
Whey contains appreciable amount of lactose which can be fermented by lactic acid bacteria. This lactose component makes the whey fit for the preparation of fermented beverages. Sweet whey is generally utilized for fermentation purpose.
Why is whey not vegetarian?
“Vegetarian” can mean a variety of things to different people who try to limit animal foods in their diets. However, whey protein is made from milk, which is an animal product, and not from meat, generally making it appropriate for vegetarian consumption.
Is whey powder the same as whey protein?
Whey powder (or sweet whey) is a by-product of cheese production, which is directly dried into powder without separation, where the main components are whey protein and lactose.
What is the difference between whey powder and milk powder?
Nutrition Basics Whey powder contains more protein than skim milk powder -- 16 grams per serving, compared to 8 grams -- and it's also lower in carbohydrates, boasting 8 grams of total carbs as opposed to skim milk powder's 12 grams. Both types of powder are low in fat, containing less than 1/2 gram of fat per serving.
Is dried whey gluten free?
Yes, whey is gluten-free because the whey protein itself does not have gluten in it. You may see whey listed as “whey concentrate,” “whey isolate” or “whey hydrolysate” on the package. All of these forms of whey protein are gluten-free and are safe for people with celiac disease.
What animals eat whey?
Our feed grade whey permeate – also called dairy product solids or dry whey solids – is an ideal choice for baby pigs. It can also be used in cattle, poultry and aquaculture feed.
What country is whey from?
Whey Production#28 Countries5‑years CAGR1#1 Germany+0.6 %2#2 Netherlands+4.2 %3#3 Poland+8.7 %4#4 Turkey+56.6 %24 more rows
Can dogs have whey protein?
It's best to stick to an unflavored whey product when it comes to your dog. And of course, don't get carried away and continue to maintain a balanced diet. Caution: Creatine is another type of weight-training supplement but it is not recommended for dogs.
SUMMARY
The Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) of the Department of Agriculture (USDA) is soliciting comments on its proposal to change the United States Standards for Dry Whey.
ADDRESSES
Written comments may be submitted to Duane R. Spomer, Chief, Dairy Standardization Branch, Dairy Programs, Agricultural Marketing Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Room 2746, South Building, Stop 0230, P.O. Box 96456, Washington, DC 20090-6456; faxed to (202) 720-2643; or e-mailed to [email protected].
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Section 203 (c) of the Agricultural Marketing Act of 1946, as amended, directs and authorizes the Secretary of Agriculture “to develop and improve standards of quality, condition, quantity, grade, and packaging and to recommend and demonstrate such standards in order to encourage uniformity and consistency in commercial practices * * *”.
Why is whey processed?
Whey must be processed as soon as possible after it is drawn from the cheese curd as its temperature and composition promote the growth of bacteria that lead to protein degradation and lactic acid formation.
What is whey protein isolate?
Whey protein isolate (WPI) containing > 92 % protein in dry matter is growing rapidly in applications such as body-building supplements – where the fat and other non-protein constituents are undesirable as well as in egg white replacements for whipped products such as meringues or as a valuable ingredient in foods and acidic fruit beverages.#N#Advances in microfiltration have drastically improved the quality and economics of product available, moving from a traditionally hot ceramic filter process to a cold organic spiral wound process in recent years.#N#Treatment of the whey retentate from a UF plant at around 35 % protein in DM can reduce the fat content of a whey protein powder from over 7% to less than 0.4 %. Microfiltration also concentrates fat globule membranes and most of the bacteria in the MF retentate, which is collected and processed separately; in some cases, this retentate is dried on the same dryer as the WPI, resulting in a high fat WPC powder. The defatted MF permeate is routed to a second UF plant for concentration; this stage also includes diafiltration.#N#As Figure 15.4 shows, the pre-treated whey is pumped to a UF plant (2) where it is concentrated to about 35 % protein in DM. The retentate is pumped to the MF plant (3), while the permeate goes to a collecting tank after RO concentration and cooling.#N#The retentate from MF treatment, which contains most of the fat and bacteria, is collected separately, and the defatted permeate is forwarded to further ultrafiltration with diafiltration (4). The resulting WPI retentate is then further concentrated using high concentration NF (35-38 % DM) and spray-dried to reduce the moisture content to a maximum of 4 % before bagging.
How much whey protein is in an evaporator?
Up to 95 % of the whey is collected as permeate and protein concentrations as high as 80-85 % (calculated on the dry matter content) can be obtained in the dried product. Typically, the evaporator is not used for protein concentrations above 60 % dry matter so as to minimize heat damage to the proteins.
How much whey protein is in a 100 kg retentate?
Example: 100 kg of whey yields approximately 17 kg of retentate and 83 kg of permeate at close to six-fold (5.88) concentration.
How to increase whey concentration?
The first step in whey concentration typically involves increasing the dry matter from around 6 % to 18 – 25 % using RO (reverse osmosis) or a combination of RO-NF (nanofiltration). Then whey can either be transported to another site for further processing ( e.g. evaporation and drying) or dried directly on site.#N#With dry matter above 25-30 %, it is more economical to use mechanical vapour recompression (MVR) evaporation to concentrate whey. Utilizing MVR in this second step to whey concentration can increase dry matter from as low as 20 % to 45 – 65 %.#N#After evaporation, the concentrate is flash cooled rapidly to 30 – 40 °C thus initiating nucleation of lactose crystals before being further cooled and stirred in specially-designed crystallization tanks. The product is held in the crystallizers for 4 – 8 hours to obtain a uniform distribution of small lactose crystals, which will give a non-hygroscopic product when spray-dried.#N#Concentrated whey is a supersaturated lactose solution and, under certain temperature and concentration conditions, the lactose can sometimes crystallize spontaneously before the whey leaves the evaporator. At concentrations above a dry matter content of 65 %, the product can become so viscous that it no longer flows. For more information on RO and Evaporators see Chapter 6, Sections 6.4 and 6.5.
What is the main constituent of whey protein?
Lactose is the main constituent of whey. There are two basic methods of recovery, depending on the raw material:
How long can whey be stored?
For short-time storage (< 8 hours), chilling to < 5 °C is usually sufficient to reduce bacterial activity. Longer periods of storage and utilization of the whey in high-quality infant formula and sports nutrition applications require pasteurization of the whey directly after the removal of fat and fines; generally, this approach is recommended in order to cater to the increasingly strict demands on product quality.